[数据结构]双向链表及双向循环链表(C语言)
双向链表
双向链表概念
双向链表也叫双链表,其每个数据结点中都有两个指针,分别指向直接后继和直接前驱。在单向链表中若要找到某个节点的前驱节点,需要先遍历到这个节点,然后再遍历一次找到其前驱节点,这无疑是十分低效的。而双向链表可以做到正向反向遍历,由此相比单向链表可以更高效地找到某个节点的前驱节点。
双向链表的创建
双向链表的节点构成
双向链表的单个节点含有两个指针域,一个值域。
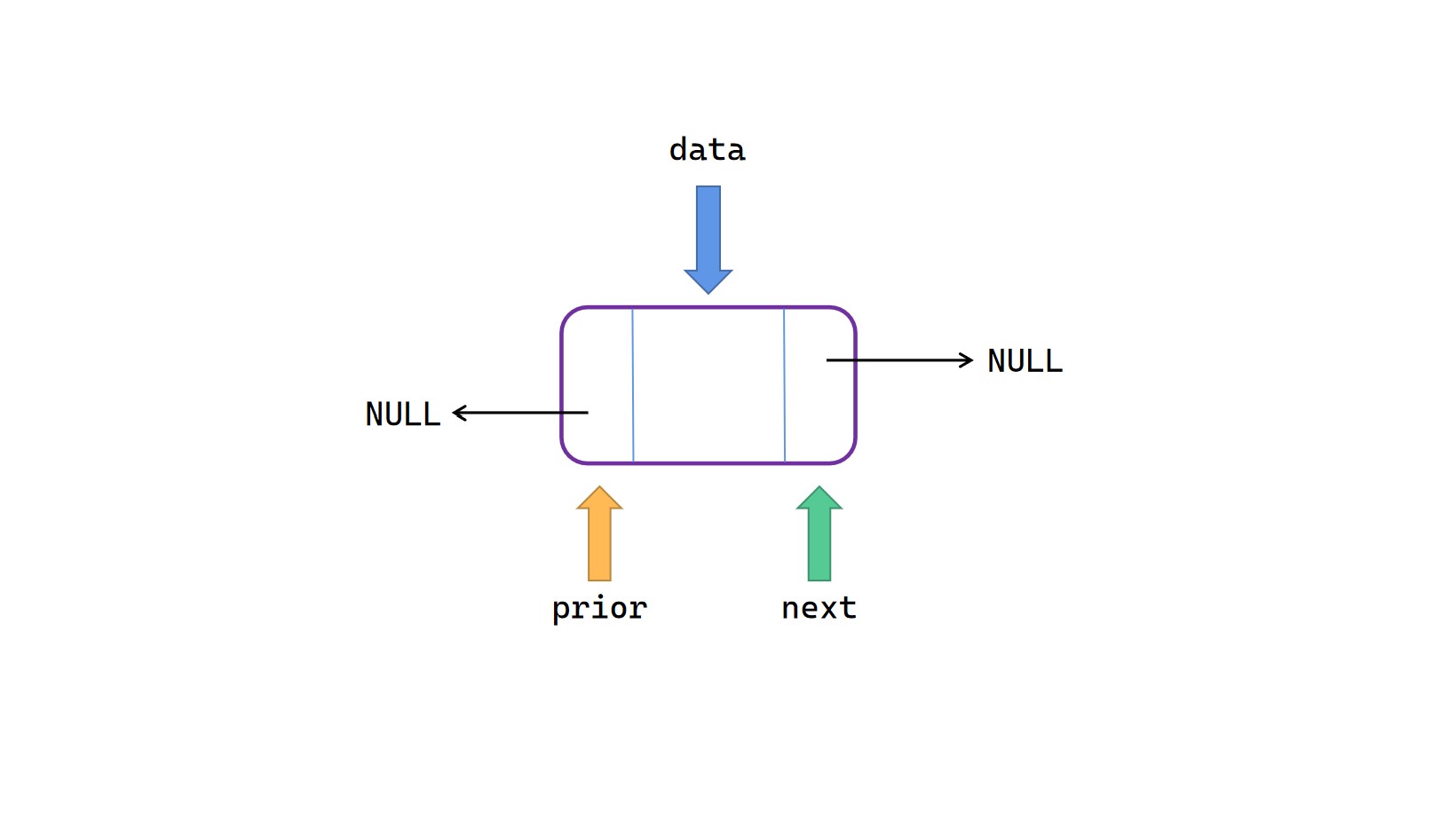
结构体
typedef int Elemtype;
typedef struct Node {
Elemtype data;
struct Node *prior; //前驱指针
struct Node *next; //后驱指针
} Duplist;
双向链表的初始化创建
双向链表基本上就是在单向链表的基础上多了一个前驱指针,用类似的方式建立每个节点与前驱之间关系就可以了🤪。
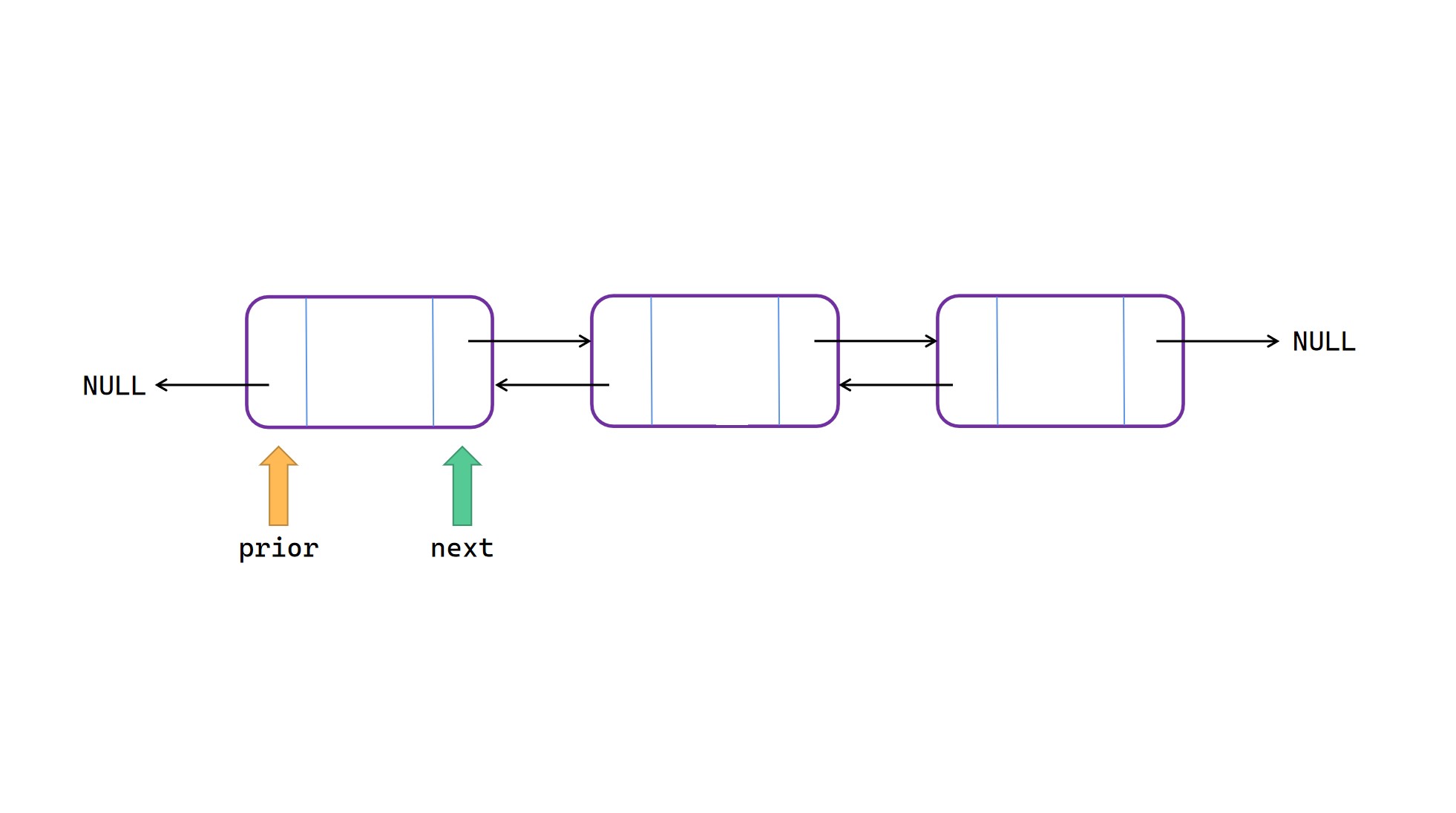
创建初始双向链表一般都是在链表尾部插入新节点:
(1)将 end 的 next 指向新节点 node;
(2)将 node 的 prior 指向 end。
双向链表图
双向链表创建代码
//创建初始化双向链表(头节点有数据,便于表头插入)
Duplist* Create_DuplexLinklist(Duplist *head, int n) {
head = (Duplist*)malloc(sizeof(Duplist));
head->next = NULL;
head->prior = NULL;
Duplist *end = head;
printf("创建双向链表输入 %d 个数据: ", n);
scanf("%d", &head->data);
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
Duplist *node = (Duplist *)malloc(sizeof(Duplist));
node->prior = NULL;
node->next = NULL;
scanf("%d", &node->data);
end->next = node; //end的next指向新节点node
node->prior = end; //新节点node的前驱prior指向之前的end
end = node; //end指向最后的node节点
}
return head;
}
双向链表的插入操作
双向链表的插入分为三种,分别为表头插入,表中插入和表尾插入。
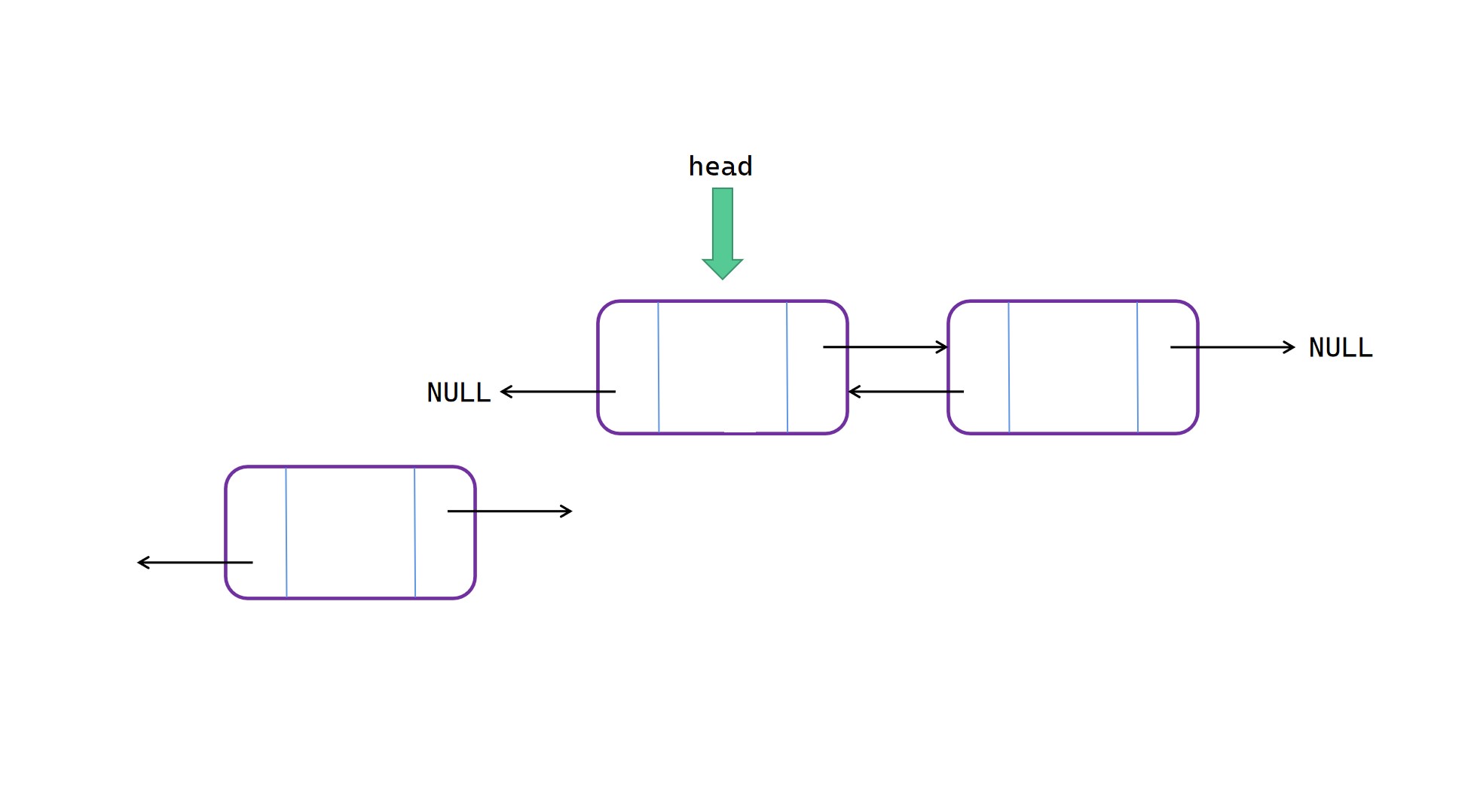
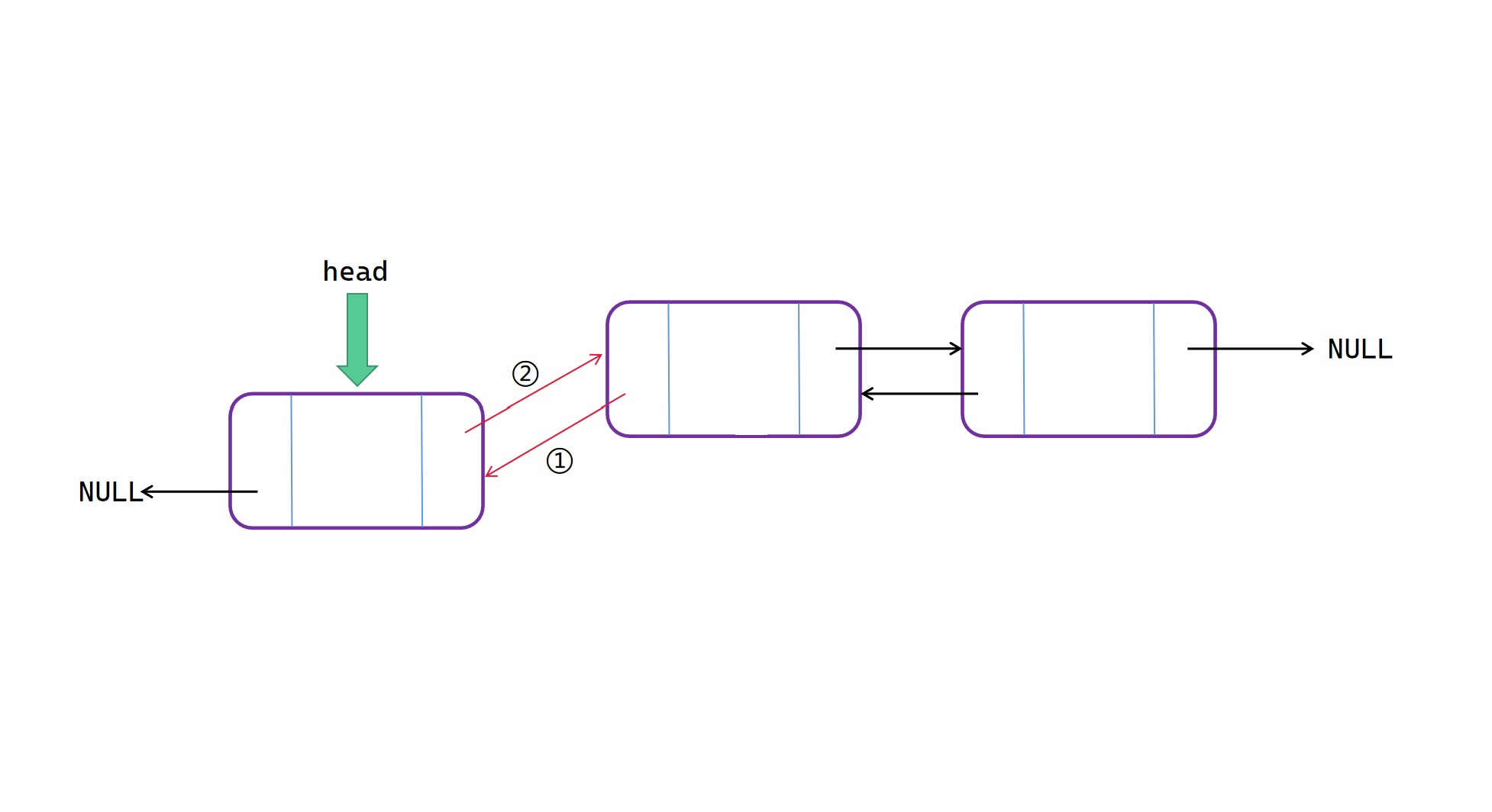
表头插入
表头插入操作(这里顺序无所谓):
(1)将 head 的 prior 指向新节点 node;
(2)将 node 的 next 指向 head;
(3)将 head 指向新节点 node。
表头插入图解
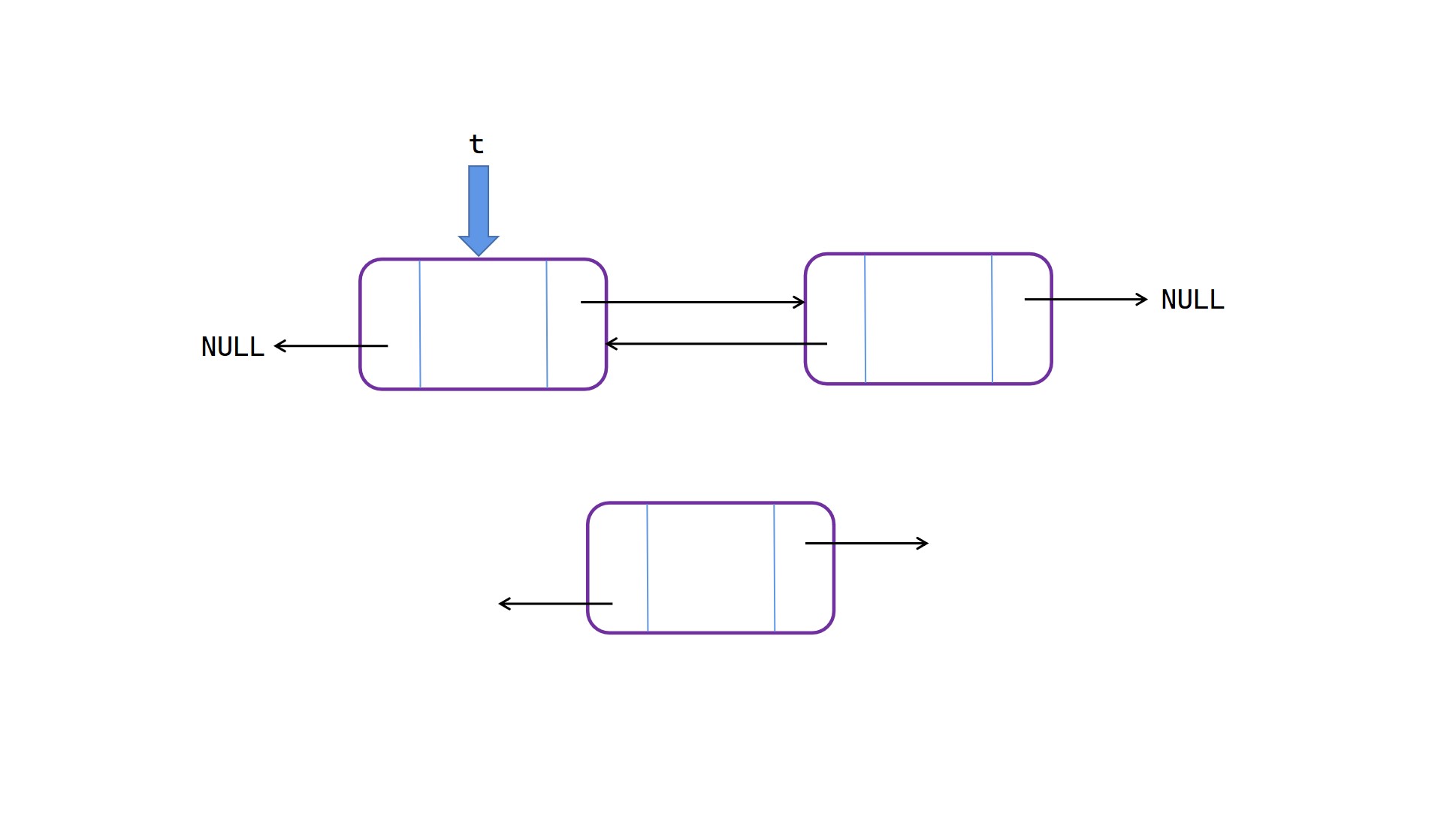
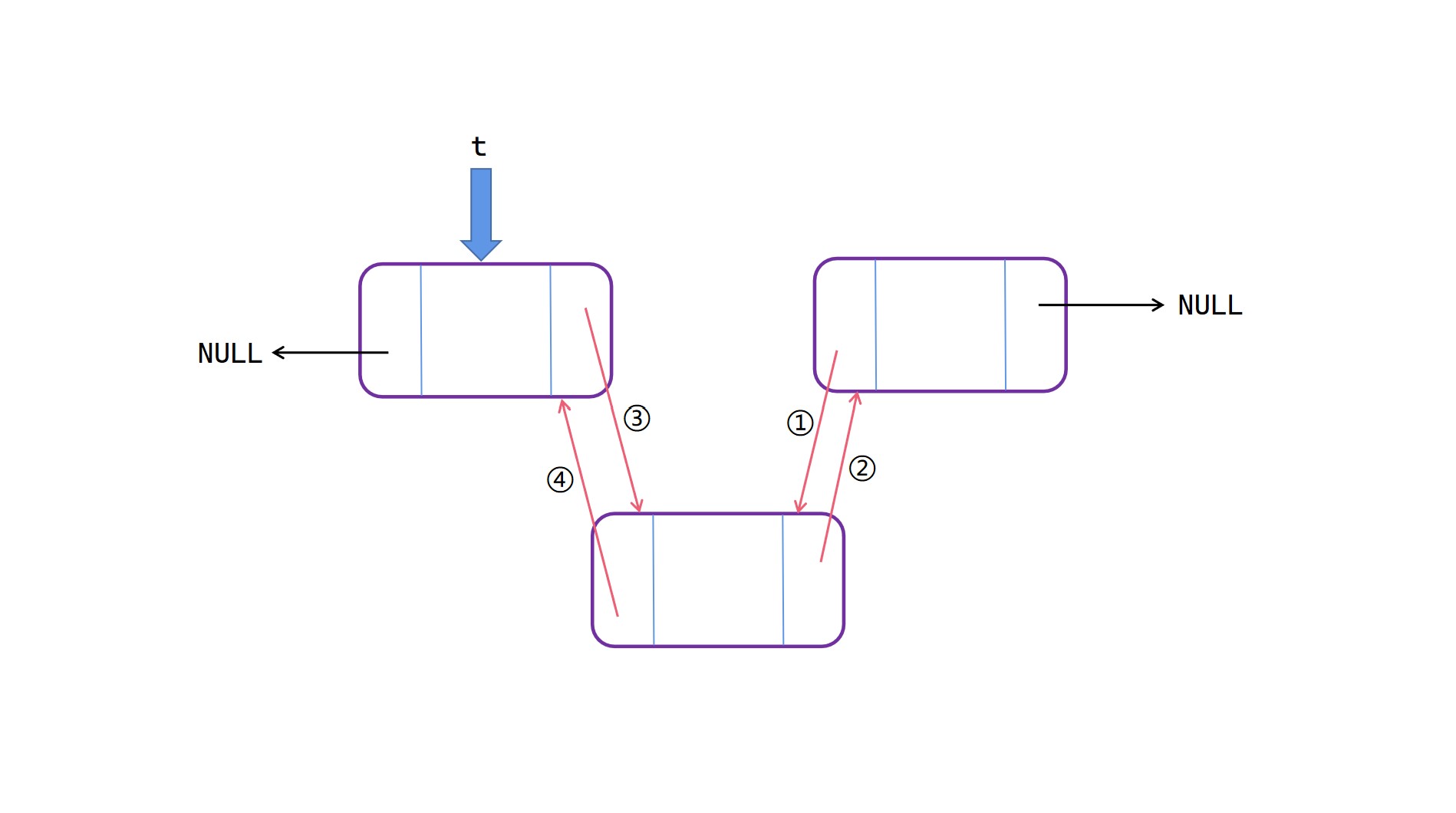
表中插入
表中插入操作(这里的顺序不能轻易改变,画图有助于理解):
找到插入位置处pos之前的节点 t;
(1)将 t 的 next 的 prior 指向新节点 node;
(2)将 node 的 next 指向 t 的 next;
(3)将 t 的 next 指向新节点 node;
(4)将 node 的 prior 指向 t。
表中插入图解
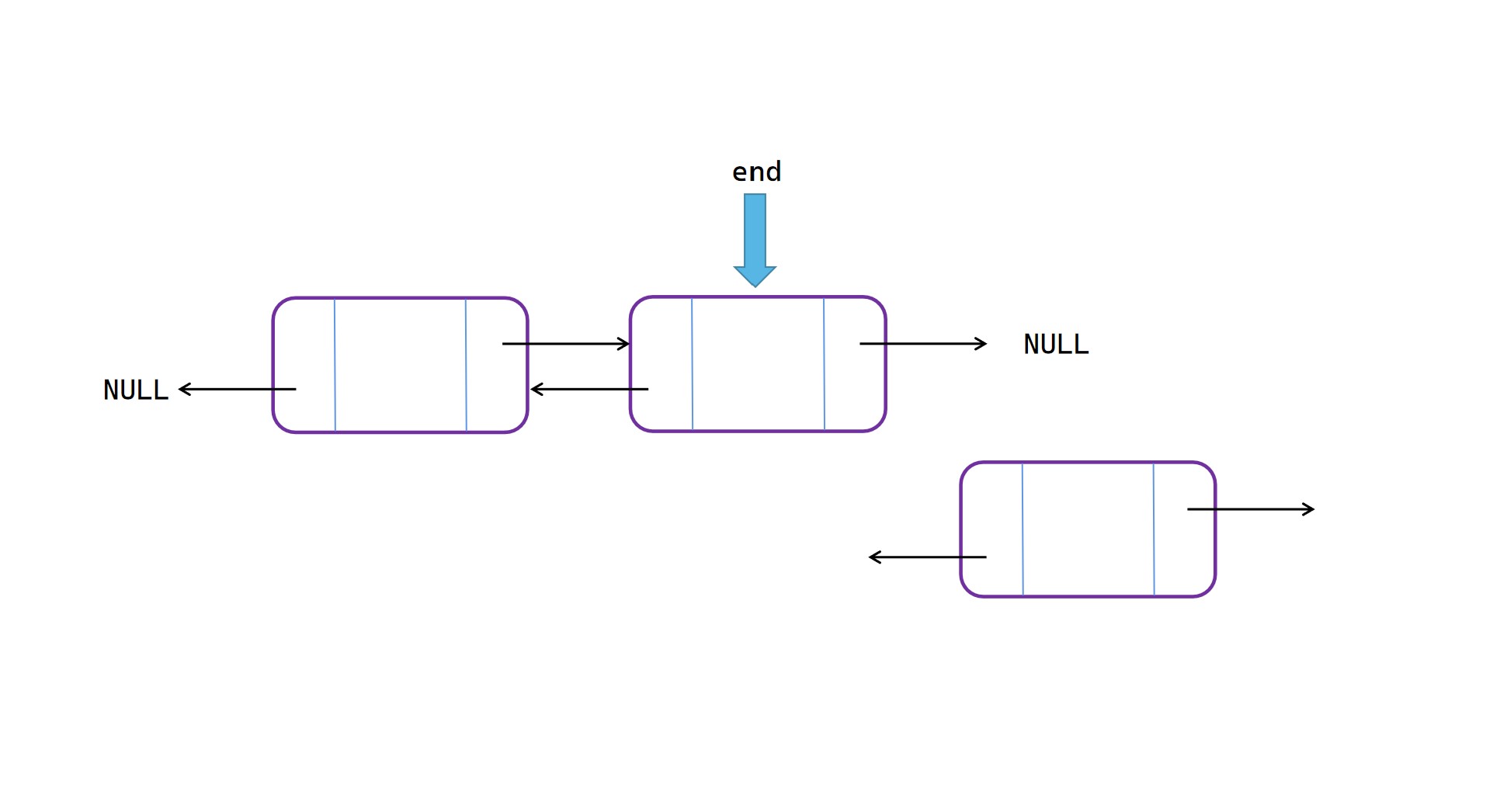
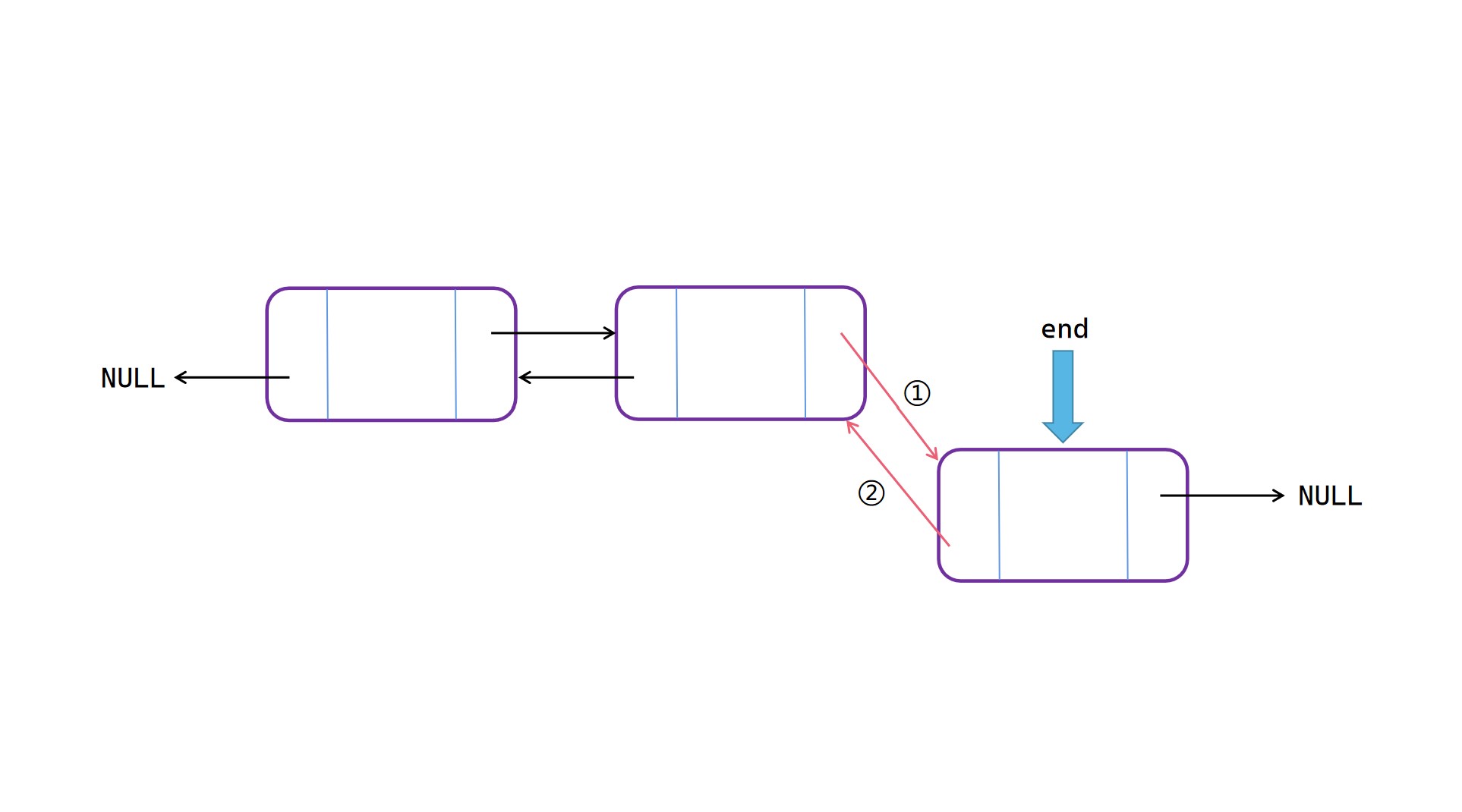
表尾插入
表尾插入操作:
(1)将 end 的 next 指向新节点 node;
(2)将 node 的 prior 指向 end;
(3)将 end 指向新节点 node。
表尾插入图解
双向链表插入操作代码
//插入新节点(包含三种情况 头插 尾插 和 指定位置插入)
Duplist *Insert_DuplexLinklist(Duplist *head, int pos, int data) {
Duplist *node = (Duplist *)malloc(sizeof(Duplist));
node->data = data;
node->prior = NULL;
node->next = NULL;
//pos表示要插入的位置(head为1)
if (pos == 1) { //插在链表头的情况
node->next = head; //新节点node的next指向之前的头head
head->prior = node; //之前的head的前驱prior指向了node
head = node; //head重新指向了插在表头的新节点
} else {
Duplist *t = head; //t为遍历指针
for (int i = 1; i < pos - 1; i++) //t指向要插入位置的前一个节点
t = t->next;
if (t->next == NULL) { //插在链表尾的情况
t->next = node; //t指向表尾,t的next指向新节点node
node->prior = t; //新节点node的前驱prior指向t
} else {
//插在表中的情况
t->next->prior = node; //t的下一个节点(要代替位置的节点)的前驱指向新node
node->next = t->next; //新node的next指向了之前t的下一个节点
t->next = node; //t的next重新指向新node
node->prior = t; //node前驱prior指向了t
}
}
return head;
}
双向链表的删除操作
双向链表删除节点也可以分成三种,表头删除、表中删除和表尾删除。
表头删除
表头删除操作:
(1)head 后移;
(2)此时的 head 的 prior 置NULL。
操作比较简单就省略图解了😪
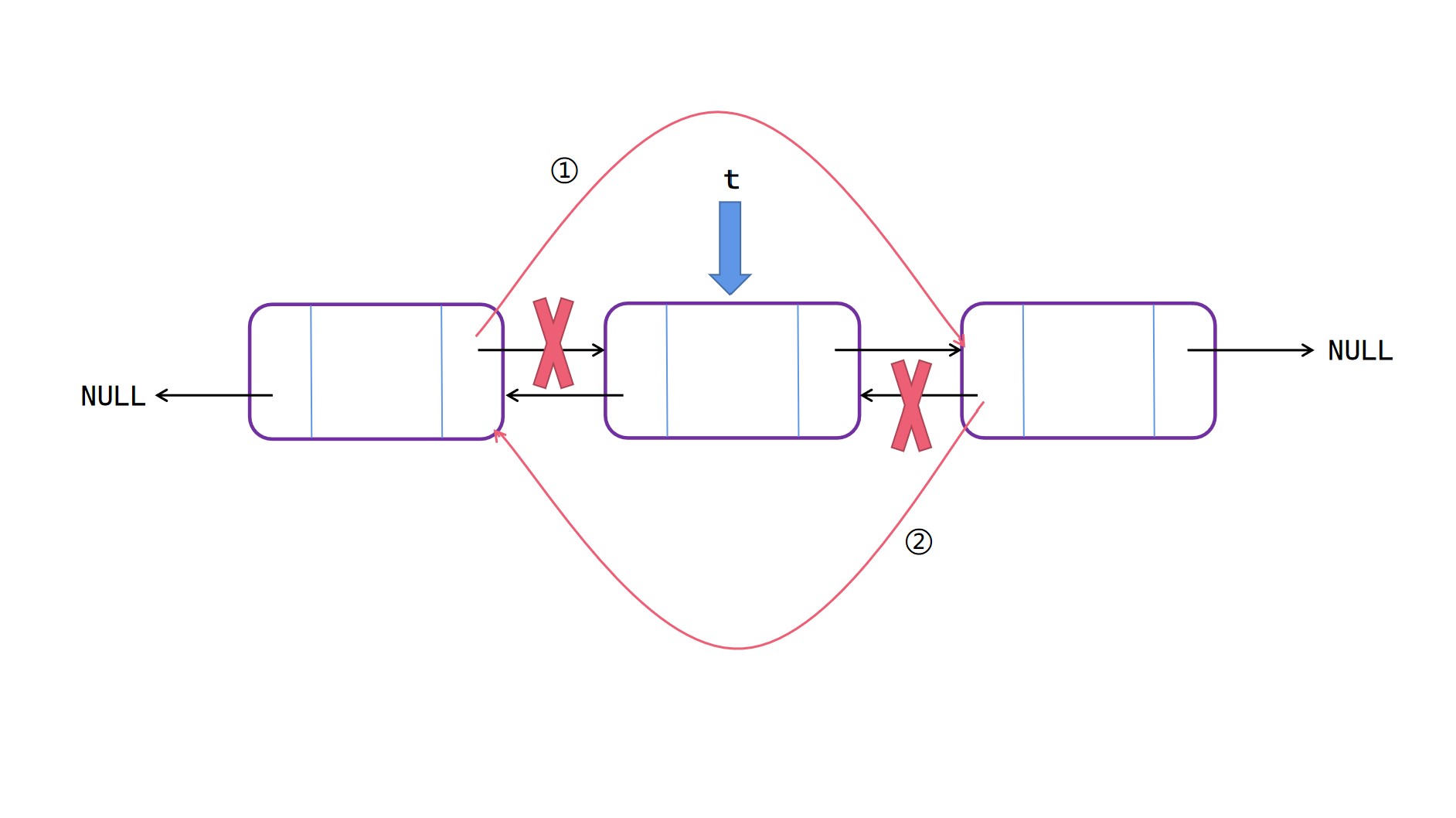
表中删除
表中删除操作:
(1)t 的 prior 的 next 指向 t 的 next;
(2)t 的 next 的 prior 指向 t 的 prior。
表中删除图解
表尾删除
表尾删除操作
如果 t 指向表尾
(1)直接将此时 t 的 prior 的 next 置 NULL。
操作比较简单就省略图解了😪
双向链表删除操作代码
//删除指定位置节点
Duplist* Delete_DuplexLinklist(Duplist *head, int pos) {
Duplist *t = head;
for (int i = 1; i < pos; i++)
t = t->next; //找到要删除的节点
if (t != NULL) {
if (t->prior == NULL) { //如果是头节点
head = t->next; //head往后移
free(t);
head->prior = NULL;
return head;
} else if (t->next == NULL) { //如果是尾节点
t->prior->next = NULL; //表尾的前一个节点的next置NULL
free(t);
return head;
} else { //删除表中节点的情况
t->prior->next = t->next; //要删除节点的前一个节点的next跨越直接指向下下个节点
t->next->prior = t->prior;//要删除节点的后一个节点的prior跨越指向上上个节点
free(t);
return head;
}
} else
printf("节点不存在\n");
return head;
}
双向链表测试代码(附带其他操作)
源代码
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
typedef int Elemtype;
typedef struct Node {
Elemtype data;
struct Node *prior; //前驱指针
struct Node *next; //后驱指针
} Duplist;
//创建初始化双向链表(头节点有数据,便于表头插入,要与单向链表区分)
Duplist *Create_DuplexLinklist(Duplist *head, int n) {
head = (Duplist*)malloc(sizeof(Duplist));
head->next = NULL;
head->prior = NULL;
Duplist *end = head; //用于在尾部插入新节点
printf("创建双向链表输入 %d 个数据: ", n);
scanf("%d", &head->data);
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
Duplist *node = (Duplist *)malloc(sizeof(Duplist));
node->prior = NULL;
node->next = NULL;
scanf("%d", &node->data);
end->next = node; //之前的end的next指向新节点node
node->prior = end; //新节点node的前驱prior指向之前的end
end = node; //end永远指向最后的node节点
}
return head;
}
//插入新节点(包含三种情况 头插 尾插 和 指定位置插入)
Duplist *Insert_DuplexLinklist(Duplist *head, int pos, int data) {
Duplist *node = (Duplist *)malloc(sizeof(Duplist));
node->data = data;
node->prior = NULL;
node->next = NULL;
//pos表示要插入的位置(head为1)
if (pos == 1) { //插在链表头的情况
node->next = head; //新节点node的next指向之前的头head
head->prior = node; //之前的head的前驱prior指向了node
head = node; //head重新指向了插在表头的新节点
} else {
Duplist *t = head; //t为遍历指针
for (int i = 1; i < pos - 1; i++) //t指向要插入位置的前一个节点
t = t->next;
if (t->next == NULL) { //插在链表尾的情况
t->next = node; //t指向表尾,t的next指向新节点node
node->prior = t; //新节点node的前驱prior指向t
} else {
//插在表中的情况
t->next->prior = node; //t的下一个节点(要代替位置的节点)的前驱指向新node
node->next = t->next; //新node的next指向了之前t的下一个节点
t->next = node; //t的next重新指向新node
node->prior = t; //node前驱prior指向了t
}
}
return head;
}
//删除指定位置节点
Duplist* Delete_DuplexLinklist(Duplist *head, int pos) {
Duplist *t = head;
for (int i = 1; i < pos; i++)
t = t->next; //找到要删除的节点
if (t != NULL) {
if (t->prior == NULL) { //如果是头节点
head = t->next; //head往后移
free(t);
head->prior = NULL;
return head;
} else if (t->next == NULL) { //如果是尾节点
t->prior->next = NULL; //表尾的前一个节点的next置NULL
free(t);
return head;
} else { //删除表中节点的情况
t->prior->next = t->next; //要删除节点的前一个节点的next跨越直接指向下下个节点
t->next->prior = t->prior;//要删除节点的后一个节点的prior跨越指向上上个节点
free(t);
return head;
}
} else
printf("节点不存在\n");
return head;
}
//读取单个数据
void Read_DuplexLinklist(Duplist *head, int pos) {
Duplist *t = head;
for (int i = 1; i < pos; i++)
t = t->next;
if (t != NULL)
printf("第 %d 个位置的数据为 %d", pos, t->data);
else
puts("节点不存在");
}
//改变指定位置数据
Duplist* Change_DuplexLinklist(Duplist *head, int pos, int data){
Duplist *t = head;
for(int i = 1; i < pos; i++)
t = t->next;
if(t != NULL)
t->data = data;
else
puts("节点不存在");
return head;
}
//查找数据返回下标
int Find_DuplexLinklist(Duplist *head, int n) {
Duplist *t = head;
int pos = 1;
while (t != NULL) {
if (t->data == n) {
printf("该数据的位置为 %d", pos);
}
t = t->next;
pos++;
}
return -1;
}
//遍历打印双向链表
void Show_DuplexLinklist(Duplist *head) {
Duplist *t = head;
while (t != NULL) {
printf("%d ", t->data);
t = t->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
//反向打印双向链表
void Reverse_DuplexLinklist(Duplist *head){
Duplist *t = head;
while (t->next != NULL) //指向最后一个节点
t = t->next;
while (t != NULL)
{
printf("%d ",t->data);
t = t->prior;
}
printf("\n");
}
int main() {
Duplist *mylist = NULL;
mylist = Create_DuplexLinklist(mylist, 10);
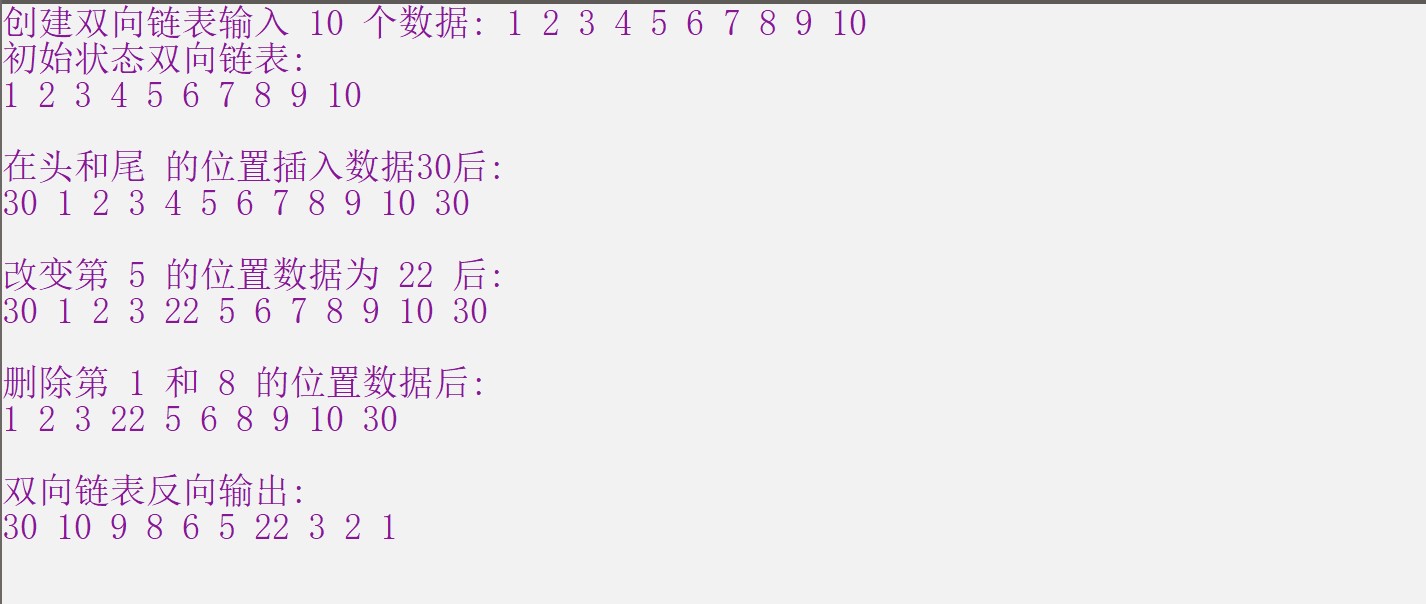
puts("初始状态双向链表:");
Show_DuplexLinklist(mylist);
printf("\n");
mylist = Insert_DuplexLinklist(mylist, 11, 30);
mylist = Insert_DuplexLinklist(mylist, 1, 30);
puts("在头和尾 的位置插入数据30后:");
Show_DuplexLinklist(mylist);
printf("\n");
mylist = Change_DuplexLinklist(mylist,5,22);
puts("改变第 5 的位置数据为 22 后:");
Show_DuplexLinklist(mylist);
printf("\n");
mylist = Delete_DuplexLinklist(mylist, 8);
mylist = Delete_DuplexLinklist(mylist, 1);
puts("删除第 1 和 8 的位置数据后:");
Show_DuplexLinklist(mylist);
printf("\n");
puts("双向链表反向输出:");
Reverse_DuplexLinklist(mylist);
printf("\n");
return 0;
}
测试结果
双向循环链表以及判断对称
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
typedef int Elemtype;
typedef struct Node{
Elemtype data;
struct Node *prior;
struct Node *next;
} DupLooplist;
//创建初始双向循环链表 (头节点带数据)
DupLooplist* Create_DupLooplist(DupLooplist *head, int n){
head = (DupLooplist *)malloc(sizeof(DupLooplist));
head->next = head;
head->prior = head;
DupLooplist *end = head;
printf("创建初始双向循环链表输入 %d 个数据: \n", n);
scanf("%d", &head->data);
for(int i = 1; i < n; i++){
DupLooplist *node = (DupLooplist *)malloc(sizeof(DupLooplist));
node->next = NULL;
node->prior = NULL;
scanf("%d", &node->data);
end->next = node;
node->prior = end;
end = node;
}
end->next = head;
head->prior = end;
return head;
}
//遍历打印双向循环链表
void Show_DupLooplist(DupLooplist *head){
DupLooplist *t = head;
while(true){
printf("%d ", t->data);
t = t->next;
if(t == head)
break;
}
printf("\n");
}
//反向遍历打印双向循环链表
void Reverse_DupLooplist(DupLooplist *head){
DupLooplist *t = head->prior;
DupLooplist *end = head->prior;
while(true){
printf("%d ", t->data);
t = t->prior;
if(t == end)
break;
}
printf("\n");
}
//插入数据
DupLooplist* Insert_DupLooplist(DupLooplist *head, int pos, Elemtype data){
DupLooplist *node = (DupLooplist *)malloc(sizeof(DupLooplist));
DupLooplist *end = head->prior;
node->data = data;
node->prior = NULL;
node->next = NULL;
if(pos == 1){ //插在表头 新节点作为表头
node->next = head;
head->prior = node;
node->prior = end;
end->next = node;
head = node;
}else{
DupLooplist *t = head;
for(int i = 1; i < pos - 1; i++) //找到要插入位置的前一个节点
t = t->next;
if(t->next == head){ //插在表尾 新节点作为表尾
end->next = node;
node->prior = end;
node->next = head;
head->prior = node;
end = node;
}else{ //插在表中
t->next->prior = node;
node->next = t->next;
t->next = node;
node->prior = t;
}
}
return head;
}
//删除双向循环链表指定位置元素
DupLooplist* Delete_DupLooplist(DupLooplist *head, int pos){
DupLooplist *t = head;
DupLooplist *p = t->prior;
for(int i = 1; i < pos; i++) //找到要删除的节点 以及其前驱节点
{
t = t->next;
p = p->next;
}
if(t){
if(pos == 1){ //如果是头节点
p->next = t->next;
t->next->prior = p;
head = t->next;
free(t);
return head;
}
else{ //如果是中间节点
p->next = t->next;
t->next->prior = p;
free(t);
return head;
}
}
}
//判断双向循环链表是否对称 (以头尾之间为基准)
bool IsSymmetry(DupLooplist *head){
if(head->next == head && head->prior == head)
return false;
DupLooplist *front, *back;
front = head;
back = head->prior; //双指针
while(front != back && front->prior != back){ //奇数个或者偶数数个节点
if(front->data != back->data)
return false;
front = front->next;
back = back->prior;
}
return true;
}
int main(){
DupLooplist *mylist = NULL;
mylist = Create_DupLooplist(mylist, 10);
puts("\n打印初始状态双向循环链表: ");
Show_DupLooplist(mylist);
puts("\n反向遍历打印双向循环链表: ");
Reverse_DupLooplist(mylist);
printf("\n");
puts("判断双向循环链表是否对称: ");
if(IsSymmetry(mylist))
puts("此双向循环链表对称");
else
puts("此双向循环链表不是对称的");
printf("\n");
puts("在位置2插入新节点后: ");
mylist = Insert_DupLooplist(mylist, 2, 30);
Show_DupLooplist(mylist);
printf("\n");
puts("删除位置2的节点后: ");
mylist = Delete_DupLooplist(mylist, 2);
Show_DupLooplist(mylist);
printf("\n");
}
一切都是命运石之门的选择,本文章来源于博客园,作者:MarisaMagic,出处:https://www.cnblogs.com/MarisaMagic/p/17058633.html,未经允许严禁转载


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号