Array.Sort和快速排序
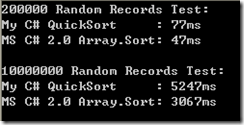
最近测试了一个自己写的快速排序,和System.Array.Sort做了个性能对比,发现System.Array.Sort比自己写的排序算法要快很多,拿20W和1000W随机数来测试效率相差40%左右,结果如下:
快速排序的主要思想就是:将待排序数组以某一个元素为阈值分为两个子列,一个子列包含所有比改阈值小的元素,另一个子列反之。这样只要将这两个子列排好序,整个数组也就排好序了。这里有一个关键的子过程就是划分的过程Partition,一般可以选择数组中任意的元素作为划分阈值,这里选择的是数组中最右端的元素。
Partition使用了二分查找类似的思想:使用两个索引器从数组的两端进行遍历,左边的索引器遇到比阈值大的元素停止,右边的索引器遇到比自己小的元素停止,然后交换这两个元素,依次循环。这样数组就划分为了比该阈值大和小(含等于)两个子列了。
自己写的快速排序:
/// <summary>/// Swap position/// </summary>/// <param name="v"></param>/// <param name="index1"></param>/// <param name="index2"></param>private void Swrap(int[] v, int index1, int index2)
{ int temp = v[index1];v[index1] = v[index2];
v[index2] = temp;
}
/// <summary>/// Split into left and right sub-table/// </summary>private int PivotIndex(int[] v, int first, int last)
{ if (last == first) { return last;}
if (last - first == 1) { return first;}
int mid = (first + last) / 2; int midVal = v[mid]; //Swap v[first] v[mid]Swrap(v, first, mid);
int scanA = first + 1; int scanB = last - 1; for (; ; ) { while (scanA <= scanB && v[scanA] < midVal) {scanA++;
}
while (scanB > first && midVal <= v[scanB]) {scanB--;
}
if (scanA >= scanB) { break;}
Swrap(v, scanA, scanB);
scanA++;
scanB--;
}
Swrap(v, first, scanB);
return scanB;}
public void Sort(int[] v, int first, int last)
{ if (last - first <= 1) { return;}
if (last - first == 2) { //Sub-table contains two elements if (v[first] > v[last - 1]) {Swrap(v, first, last - 1);
}
return;}
else { int pivotIndex = PivotIndex(v, first, last);Sort(v, first, pivotIndex);
Sort(v, pivotIndex + 1, last);
}
}
C++
测试程序:
static void Main ( string[] args )
{Test ( 200000 );
Test ( 10000000 );
Console.Read ();
}
static void Test ( int LEN )
{ Program p = new Program ();int[] v = new int[LEN];
System.Random rd = new Random ();for ( long i = 0; i < LEN; i++ )
{v[i] = rd.Next ();
}
int[] v2 = new int[LEN];
for ( long i = 0; i < LEN; i++ )
{v2[i] = v[i];
}
System.Diagnostics.Stopwatch sw = new System.Diagnostics.Stopwatch ();sw.Start ();
p.Sort ( v, 0, v.Length ); /* Test QuickSort */sw.Stop ();
long tim1 = sw.ElapsedMilliseconds;sw.Reset ();
sw.Start ();
System.Array.Sort<int> ( v2 ); /* Test Array.Sort */
sw.Stop ();
long tim2 = sw.ElapsedMilliseconds; //int m = 0; //foreach ( int i in v ) //{ // m++; // if (m < 100 ) // Console.Write ( i.ToString () + " " ); // else break; //} Console.WriteLine ( LEN + " Random Records Test:" + Environment.NewLine +"My C# QuickSort : " + tim1 + "ms" + Environment.NewLine + "MS C# 2.0 Array.Sort: " + tim2 + "ms");
Console.WriteLine ();
}
微软MSDN上对System.Array.Sort的说明:
“Array 中的每个元素均必须实现 IComparable 接口,才能与 array 中的其他所有元素进行比较。 如果排序不能成功地完成,则结果未定义。此方法使用 QuickSort 算法。此实现执行不稳定排序;亦即,如果两元素相等,则其顺序可能不被保留。相反,稳定排序保留相等元素的顺序。 一般情况下,此方法的运算复杂度为 O(n log n),其中 n 是 array 的 Length;最坏的情况下其运算复杂度为 O(n ^ 2)。”
结论:
System.Array.Sort其内部使用了大数据量时效率最高的快速排序算法。C#实现的快速排序没有C++的快这一点原因很明显。
System.Array.Sort效率是很高的,没有必要怀疑它,建议使用它。如排序自己的类:Array.Sort<Customer> ( customer, new CustomerComparer () ); //CustomerComparer 实现IComparer接口。代码示例:
using System.Collections.Generic;public class Customer
{private string firstName;
public string FirstName
{ get { return firstName; } set { firstName = value; }}
private string secondName;
public string SecondName
{ get { return secondName; } set { secondName = value; }}
public Customer ( string _firstName, string _secondName )
:this() {firstName = _firstName;
secondName = _secondName;
}
public Customer (){}}
public class CustomerComparer : IComparer<Customer>
{public int Compare ( Customer c1, Customer c2 )
{if ( c1 == null || c2 == null )
throw new ArgumentNullException ( "Both objects must not be null" );
return String.Compare ( c1.FirstName, c2.FirstName, true );
}
}
static void Main ( string[] args )
{Customer c1 = new Customer ( "c", "c" );
Customer c2 = new Customer ( "b", "b" );
Customer c3 = new Customer ( "a", "a" );
Customer[] cus = new Customer[] { c1, c2, c3 }; Array.Sort<Customer> ( cus, new CustomerComparer () );}







 }
} }
}
