centos7系统管理和运维实战
centos7系统管理和运维实战

centos7安装配置
yum install -y net-tools >/etc/hostname echo "sqlserver01" >/etc/hostname systemctl stop firewalld systemctl disable firewalld yum install -y iptables-services systemctl start iptables systemctl enable iptables
firewalld
优点:不需要像iptables重启服务,比iptables人性化
图形工具firewall-config
命令行工具firewall-cmd
zone
网卡
规则
firewall-cmd --reload命令的作用:清除内存中的规则,并且从规则文件加载规则 #永久保存防火墙规则 如果想让临时规则变成永久规则,可以使用下面命令,内存中的规则写到文件 [root@server ~]# firewall-cmd --runtime-to-permanent 如何确定规则是永久的呢? 如果使用firewall-cmd --reload命令之后规则还会存在,就是永久的规则 如果想做永久规则,只需要在规则后加上--permanent 虽然加上--permanent规则,会让规则永久生效,但是并不会立刻生效,需要firewall-cmd --reload [root@server ~]# firewall-cmd --add-service=ftp --permanent success 为了避免防火墙规则firewall-cmd --reload,reload,建议敲两次 [root@server ~]# firewall-cmd --add-service=ftp --permanent #写到规则文件 [root@server ~]# firewall-cmd --add-service=ftp #写入内存
[root@server ~]# firewall-cmd --add-port=7888/tcp --permanent
[root@server ~]# firewall-cmd --add-port=7888/tcp 规则文件位置 ll /etc/firewalld/zones/ total 8 -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 339 Apr 16 11:51 public.xml -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 315 Jan 23 2018 public.xml.old 显示所有公共区域(public)的规则 firewall-cmd --zone=public --list-all
centos和RHEL也有很多不同之处 P2
RHEL中包含了红帽自行开发的闭源软件,如红帽集群套件,这些软件并未开放源代码,因此也就未包含在centos发行版中
centos发行版通常会修改RHEL中存在的bug,并提供了一个yum源以便用户可以随时更新操作系统
centos7的最新改进 P3
centos7使用的内核是3.10.0:对swap内存空间进行压缩,提高IO性能,优化KVM虚拟化,默认使用XFS文件系统,使用firewalld防火墙,Linux容器,systemd代替sysvinit使存在依赖的服务之间更好地并行化
P20
root密码:密码通常用四分之三原则来设置,即密码要包含密码的4种字符,大写字母,小写字母,数字,字符中的3种
安装ifconfig、netstat、route命令,并关闭防火墙
yum install -y net-tools service firewalld stop Redirecting to /bin/systemctl stop firewalld.service
traceroute命令 P50
每行记录对应一跳,每跳表示一个网关,每行有3个时间,单位是ms,星号表示ICMP信息没有返回
traceroute一次同时发送3个UDP包来探测,最多经过30个路由器,也就是最多30跳,经过30跳还未到达目标主机traceroute就会停止
3个UDP数据包,每经过一跳,会返回3个数据包的跳步数,路由器IP或名字,数据包周转时间
3 120.197.23.49 6.945 ms 183.233.19.205 7.164 ms 120.197.23.49 6.750 ms
3跳 第一个数据包经过的路由器ip 时间 第二个数据包经过的路由器ip 时间 第三个数据包经过的路由器ip 时间
直到收到ICMPPORT_UNREACHABLE消息或到达最大跳步数30跳
traceroute -n www.baidu.com (Linux下 -n表示只显示ip不显示域名)
tracert -d www.csdn.net (Windows下 -d表示只显示ip不显示域名)
http://network.51cto.com/art/201505/476087_all.htm
traceroute to www.baidu.com (183.232.231.173), 30 hops max, 60 byte packets
1 * * *
2 183.233.92.217 7.809 ms 183.233.19.205 7.247 ms 120.197.23.73 7.124 ms
3 120.197.23.49 6.945 ms 183.233.19.205 7.164 ms 120.197.23.49 6.750 ms
4 * 120.196.240.97 6.993 ms *
5 * 183.235.226.166 6.682 ms 211.136.208.82 9.998 ms
6 211.139.158.66 10.092 ms 183.235.225.194 6.594 ms 6.776 ms
7 120.198.207.125 6.295 ms * 120.196.241.174 8.864 ms
8 * * *
9 * * *
10 * * *
11 * * *
12 * * *
13 * * *
14 * * *
15 * * *
16 * * *
17 * * *
18 * * *
19 * * *
20 * * *
21 * * *
22 * * *
23 * * *
24 * * *
25 * * *
26 * * *
27 * * *
28 * * *
29 * * *
30 * * *
上面显示访问百度不通,数据包到达某一个节点时没有返回,可以将此结果提交IDC运营商,以便解决问题
配置网卡地址 一定要设置DNS P54
vi /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eno16777736
TYPE=Ethernet BOOTPROTO=static NAME=eno16777736 DEVICE=eno16777736 NM_CONTROLLED=yes ONBOOT=yes IPADDR=192.168.0.128 NETMASK=255.255.255.0 GATEWAY=192.168.0.1 DNS1=114.114.114.114 DNS2=114.114.115.115
修改主机名 P55
vi /etc/hostname
cat /etc/hostname aaa
P56
使用service命令要注意,centos7使用的是systemd,因此开启和停止服务实际执行的时候会用systemd替代service命令脚本
在centos7中,系统有两个防火墙工具firewalld和iptables P56
两个工具调用底层的都是net-filter,所以这两个工具的功能都是一样的,只是firewall-cmd的命令简化了iptables的命令
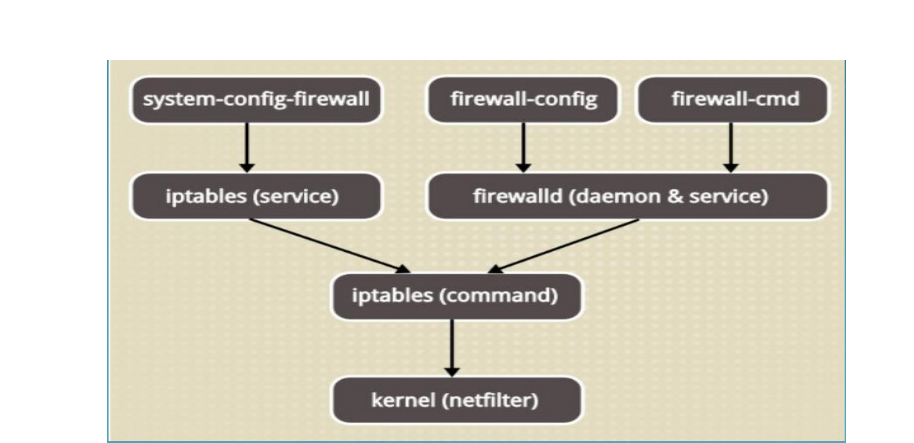
如果不适应可以将默认的firewalld停止,让系统将iptables作为默认防火墙 P58
#关闭并禁用firewalld
systemctl stop firewalld
systemctl disable firewalld
#启动并启用iptables
centos6 iptables是内核一部分 rpm -qf /sbin/iptables file /sbin/iptables is not owned by any package #centos7 iptables变为可选的安装包,需要安装 yum install -y iptables-services systemctl start iptables systemctl enable iptables
#如果使用了ipv6 还需要开启ip6tables
systemctl start ip6tables
systemctl enable ip6tables
iproute2
iproute2提供网络参数设置,路由设置,带宽控制,最新GRE隧道VPN
iproute2工具包中主要管理工具为ip命令
#安装 yum install -y iproute #查看版本号 ip -V
ip utility, iproute2-ss170501
ip命令可以替代ifconfig和route命令
ip --help
Usage: ip [ OPTIONS ] OBJECT { COMMAND | help }
ip [ -force ] -batch filename
where OBJECT := { link | address | addrlabel | route | rule | neigh | ntable |
tunnel | tuntap | maddress | mroute | mrule | monitor | xfrm |
netns | l2tp | fou | macsec | tcp_metrics | token | netconf | ila |
vrf }
OPTIONS := { -V[ersion] | -s[tatistics] | -d[etails] | -r[esolve] |
-h[uman-readable] | -iec |
-f[amily] { inet | inet6 | ipx | dnet | mpls | bridge | link } |
-4 | -6 | -I | -D | -B | -0 |
-l[oops] { maximum-addr-flush-attempts } | -br[ief] |
-o[neline] | -t[imestamp] | -ts[hort] | -b[atch] [filename] |
-rc[vbuf] [size] | -n[etns] name | -a[ll] | -c[olor]}
#显示所有的ip地址,同ipconfig -a
ip addr list
ip addr list 1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00 inet 127.0.0.1/8 scope host lo 2: eth0: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast state UP qlen 1000 link/ether 52:54:00:22:02:4a brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff inet 10.105.9.115/18 brd 10.105.63.255 scope global eth0
#显示路由信息ip route list可以显示网卡地址,route -n命令只会显示内网网段
ip route list
ip route list 10.105.0.0/18 dev eth0 proto kernel scope link src 10.105.9.115 169.254.0.0/16 dev eth0 scope link metric 1002 default via 10.105.0.1 dev eth0 10.105.9.115 :网卡地址 10.105.0.0/18:内网网段 dev eth0 :网卡名称 default via 10.105.0.1 dev eth0 :网关
路由表管理 P92
以下命令和概念centos6也有
默认情况下Linux只有一个路由表,如果系统中只有一个路由表,策略路由许多功能无法实现
数据包转发到哪个路由表由系统设定的规则决定,查看系统默认的规则使用命令ip rule list
[root@sqlserver01 ~]# ip rule list
0: from all lookup local
32766: from all lookup main
32767: from all lookup default
上面显示系统有三张路由表,local,main,default
#ip route list不加任何参数默认显示main路由表
[root@sqlserver01 ~]# ip route list table main
default via 10.11.10.1 dev eth0 proto static metric 100
10.11.10.0/24 dev eth0 proto kernel scope link src 10.11.10.33 metric 100
[root@sqlserver01 ~]# ip route list
default via 10.11.10.1 dev eth0 proto static metric 100
10.11.10.0/24 dev eth0 proto kernel scope link src 10.11.10.33 metric 100
FTP文件共享基于TCP/IP协议 P107
21端口用户验证
20端口传数据
主动模式和被动模式都是用21端口做验证,只是传数据端口不一样
Systemd和systemctl
https://linux.cn/article-5926-1.html
重要:Systemctl接受服务(.service),挂载点(.mount),套接口(.socket)和设备(.device)作为单元。
7. 列出所有可用单元
# systemctl list-unit-files
9. 列出所有失败单元
# systemctl --failed
8. 列出所有运行中单元
# systemctl list-units
上面这组命令很少用
----------------------------------------
进入系统救援模式
32. 启动系统救援模式,机器会马上重启,所以要在电脑面前做
# systemctl rescue
33. 进入紧急模式
# systemctl emergency
----------------------------------------
控制系统运行等级
/etc/inittab 文件不再可用,但是init命令依然可用,可以切换运行等级
34. 列出当前使用的运行等级
# systemctl get-default
35. 设置多用户模式或图形模式为默认运行等级
# systemctl set-default runlevel3.target
# systemctl set-default runlevel5.target
36. 启动运行等级5,即图形模式
# systemctl isolate runlevel5.target
或
# systemctl isolate graphical.target
37. 启动运行等级3,即多用户模式(命令行)
# systemctl isolate runlevel3.target
或
# systemctl isolate multiuser.target
38. 重启、停止、挂起、休眠系统或使系统进入混合睡眠
# systemctl reboot
# systemctl halt
# systemctl suspend
# systemctl hibernate
# systemctl hybrid-sleep
----------------------------------------
使用Systemctl控制并管理服务
12. 列出所有服务(包括启用的和禁用的)
# systemctl list-unit-files --type=service
13. 查看所有已启动的服务 看打active running 表示已经启动
systemctl list-units --type=service |grep acpi
14. Linux中如何启动、重启、停止、重载服务以及检查服务(如 httpd.service)状态
注意:当我们使用systemctl的start,restart,stop和reload命令时,我们不会从终端获取到任何输出内容,只有status命令可以打印输出。
# systemctl start httpd.service
# systemctl restart httpd.service
# systemctl stop httpd.service
# systemctl reload httpd.service
# systemctl status httpd.service #对应systemctl list-units --type=service的ACTIVE 和SUB 字段
15. 如何激活服务并在启动时启用或禁用服务(即系统启动时自动启动服务)
# systemctl is-active httpd.service
# systemctl enable httpd.service --now #--now意思是立即启动start/stop该服务,不需要再执行systemctl start/stop
# systemctl disable httpd.service
16. 使用systemctl命令杀死服务
# systemctl kill httpd
# systemctl status httpd
17. 使用systemctl命令重置失败状态
# systemctl reset-failed mysql3307.service
用于在 CentOS 或其他使用 `systemd` 的 Linux 发行版中重置某个服务的“失败”状态。
1、清除失败状态:当 `mysql3307.service` 失败(例如启动失败或崩溃)时,`systemd` 会记录这个失败状态,
并且在使用 `systemctl status` 命令查看时会显示该服务的失败状态。这个状态会一直保留,直到手动清除。
2、重置服务失败计数:使用 `systemctl reset-failed` 命令可以重置这个失败计数,使 `mysql3307.service` 看起来像是从未失败过。
systemd下的常用命令有
主机名管理
hostnamectl
hostnamectl命令用于查看当前主机的信息。
显示当前主机的信息 #hostnamectl 设置主机名。 #hostnamectl set-hostname rhel7
时区管理
timedatectl
timedatectl命令用于查看当前时区设置。
显示所有可用的时区 #timedatectl list-timezones 设置当前时区 #timedatectl set-timezone America/New_York #timedatectl set-time YYYY-MM-DD #timedatectl set-time HH:MM:SS
服务管理
systemctl /service / 相当于centos6的chkconfig 服务自启管理
登录用户管理
loginctl
loginctl命令用于查看当前登录的用户。
列出当前session #loginctl list-sessions 列出当前登录用户 #loginctl list-users 列出显示指定用户的信息 #loginctl show-user (ruanyf) 用户 开启普通用户使用systemd管理自己服务的权限 #loginctl enable-linger
本地化设置管理
localctl
localectl命令用于查看本地化设置。
查看本地化设置 #localectl 设置本地化参数。 #localectl set-locale LANG=en_GB.utf8 #localectl set-keymap en_GB
f


