Cho J., Mall U., Bala K. and Hariharan B. PiCIE: unsupervised semantic segmentation using invariance and equivariance in clustering. In IEEE Conference on Computer Vsion and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2021.
概
利用聚类和 invariance to photometric transformations and equivariance to geometric transformations 来无监督地语义分割.
符号说明
- xi∈RCHW,i=1,2,⋯,n, unlabeled images;
- fθ:RCHW→RDHW, 将图片 x 映射为后续所用的特征;
- yi[p], 为 xi[p] 所对应的(预测)标签;
- μk∈RD,k=1,2,⋯,K, 为 K 个聚类中心;
- P, photometric 变换, 满足 x,P(x) 的语义分割是一致的;
- G, geometric 变换, 满足 G(x) 的语义分割为 G(y);
流程
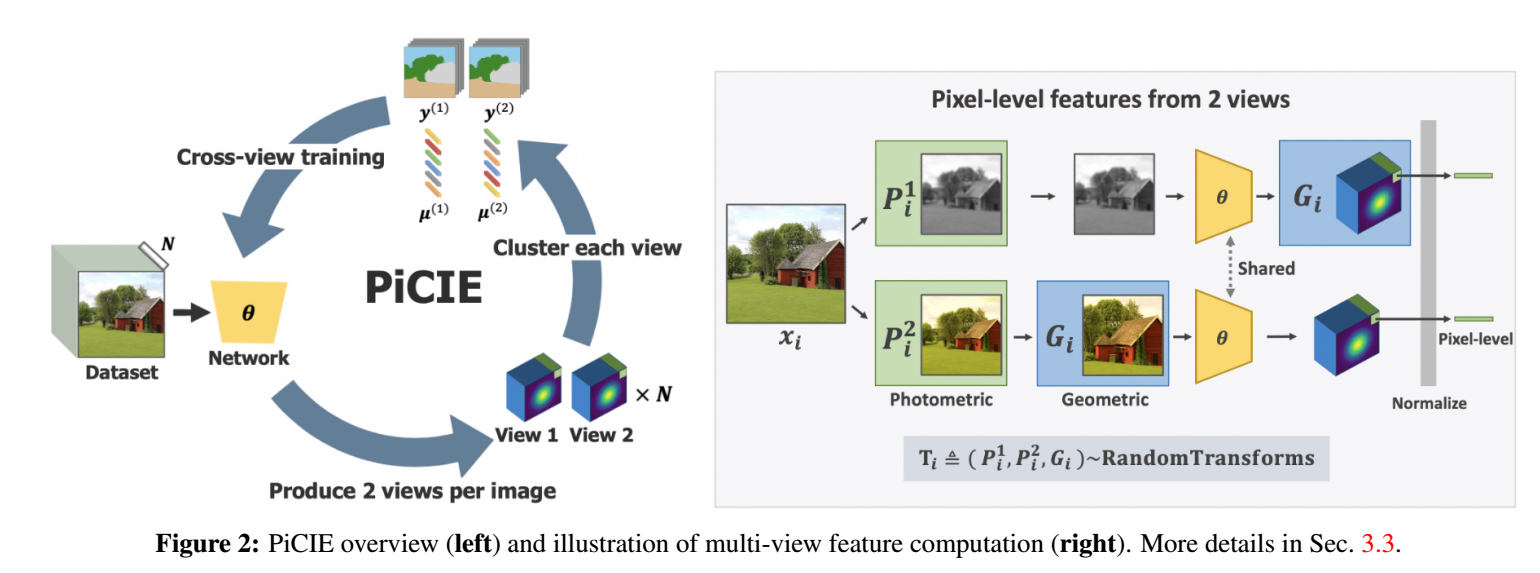
-
采样样本 x, photometric 变换 P(1),P(2), geometric 变换 G;
-
得到特征:
z(1)←G(fθ(P(1)(x))),z(2)←fθ(G(P(1)(x)));
-
通过 K-means 计算类别中心, 并为 zi[p] 指定标签:
μ(1),y(1)←KMeans({z(1)i[p]:i∈[n],p∈[HW]}),μ(2),y(2)←KMeans({z(2)i[p]:i∈[n],p∈[HW]});
-
我们希望特征 z[p] 靠近所指定的类别, 即需要关于 θ 最小化如下损失:
Lwithin=∑i,pLclust(z(1)i[p],y(1)i[p],μ(1))+Lclust(z(2)i[p],y(2)i[p],μ(2)),
其中
Lclust(zi[p],yi[p],μ):=−logexp(−d(zi[p],μip))∑kexp(−d(zi[p],μk)),
以及 d(⋅,⋅) 为 cosine similarity;
-
但是注意到, 即便 z 中的各个元素都靠近了各自的聚类中心, 我们没法保证聚类是按照 '语义' 来分割的, 为此, 我们引入 Invariance 和 Equivariance:
Lcross=∑i,pLclust(z(1)i[p],y(2)i[p],μ(2))+Lclust(z(2)i[p],y(1)i[p],μ(1)),
即采用了 photometric 和 geometric 变换后的特征保持语义分割上的一致.
代码
[official]





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· Manus重磅发布:全球首款通用AI代理技术深度解析与实战指南
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!
· 没有Manus邀请码?试试免邀请码的MGX或者开源的OpenManus吧
· 园子的第一款AI主题卫衣上架——"HELLO! HOW CAN I ASSIST YOU TODAY
· 【自荐】一款简洁、开源的在线白板工具 Drawnix