[数据结构] 二叉树的层次遍历
二叉树的层次遍历
层次遍历的思路
二叉树的层次遍历本质上用的是广度优先搜索算法,我们通常使用队列来实现这一过程。
层次遍历的基本步骤
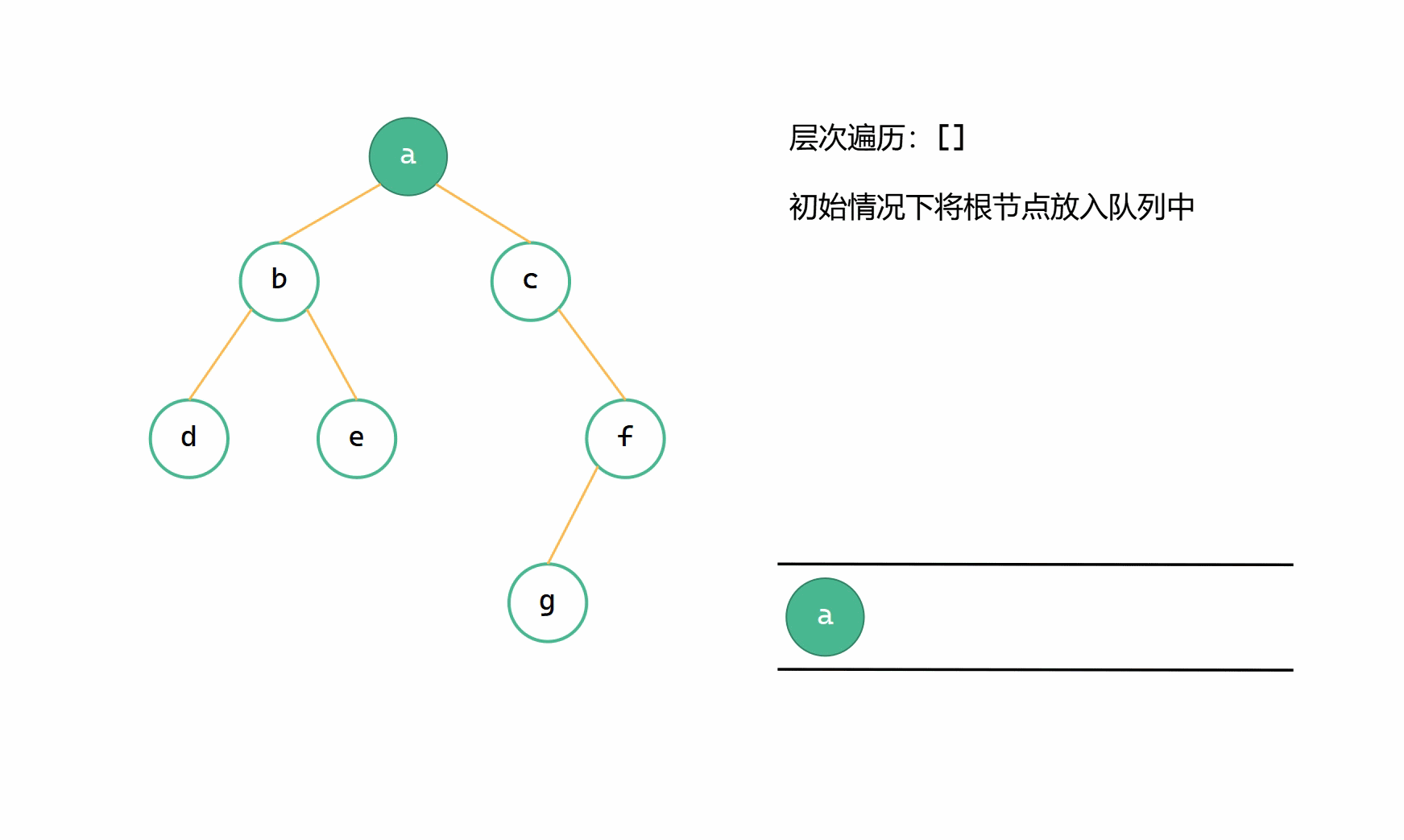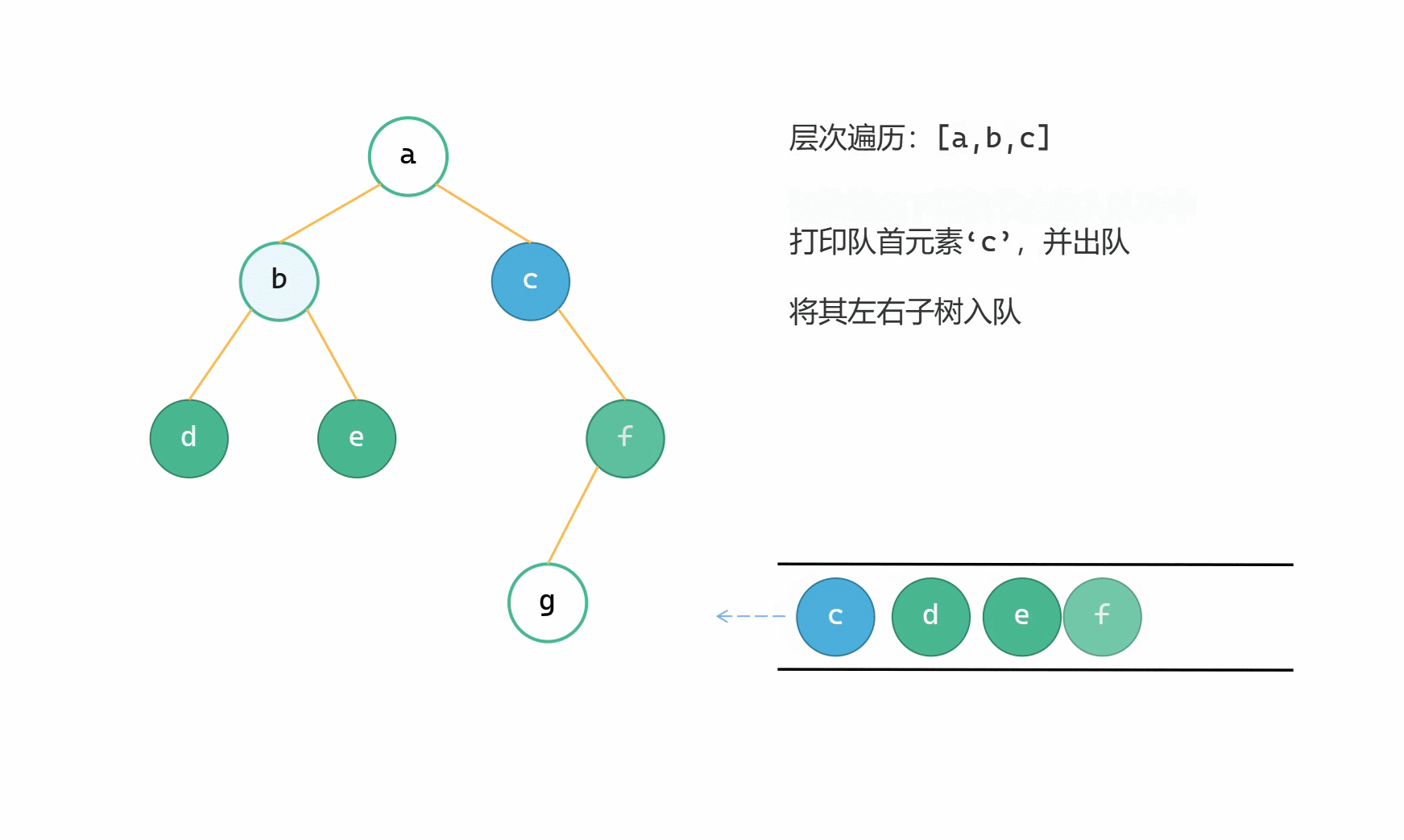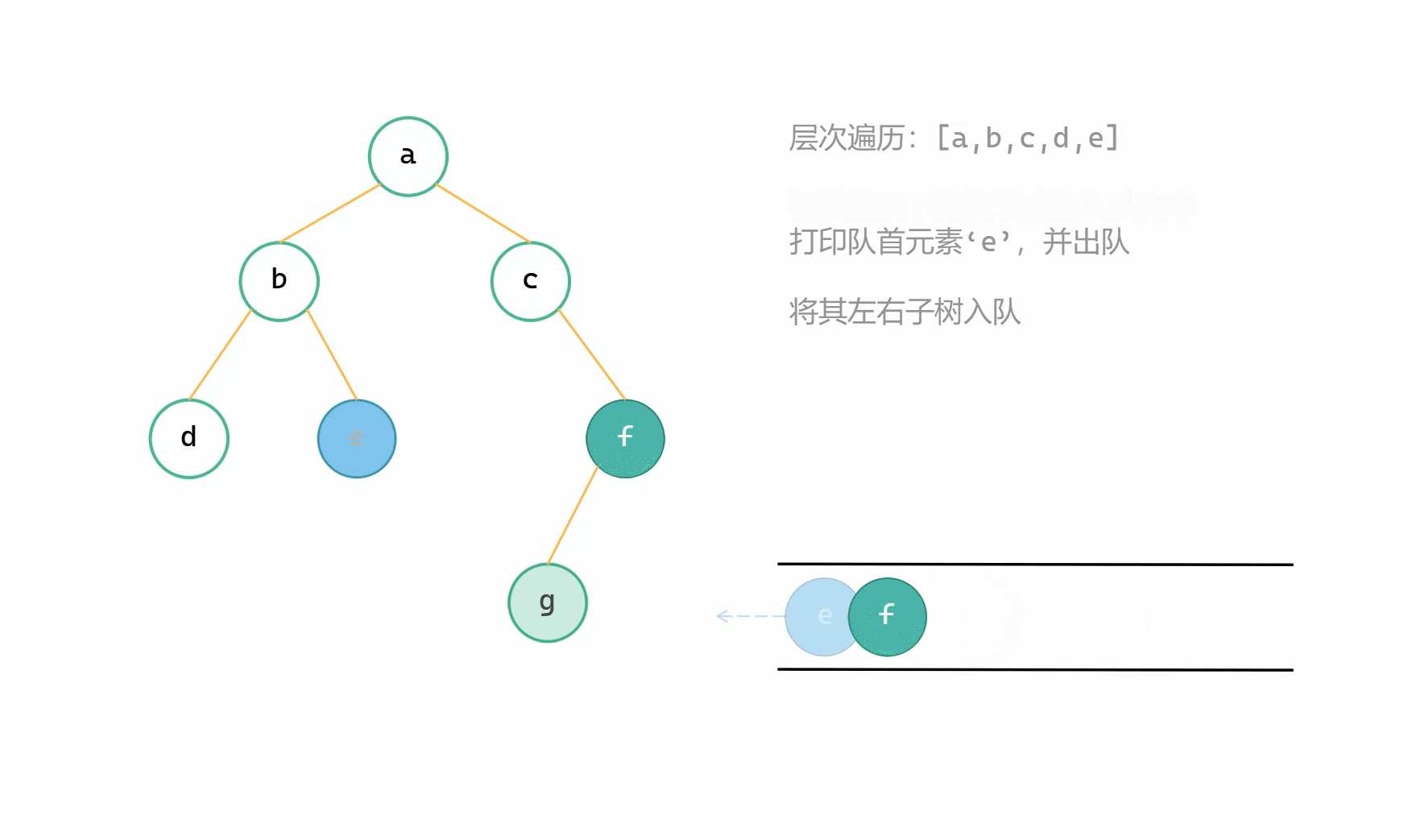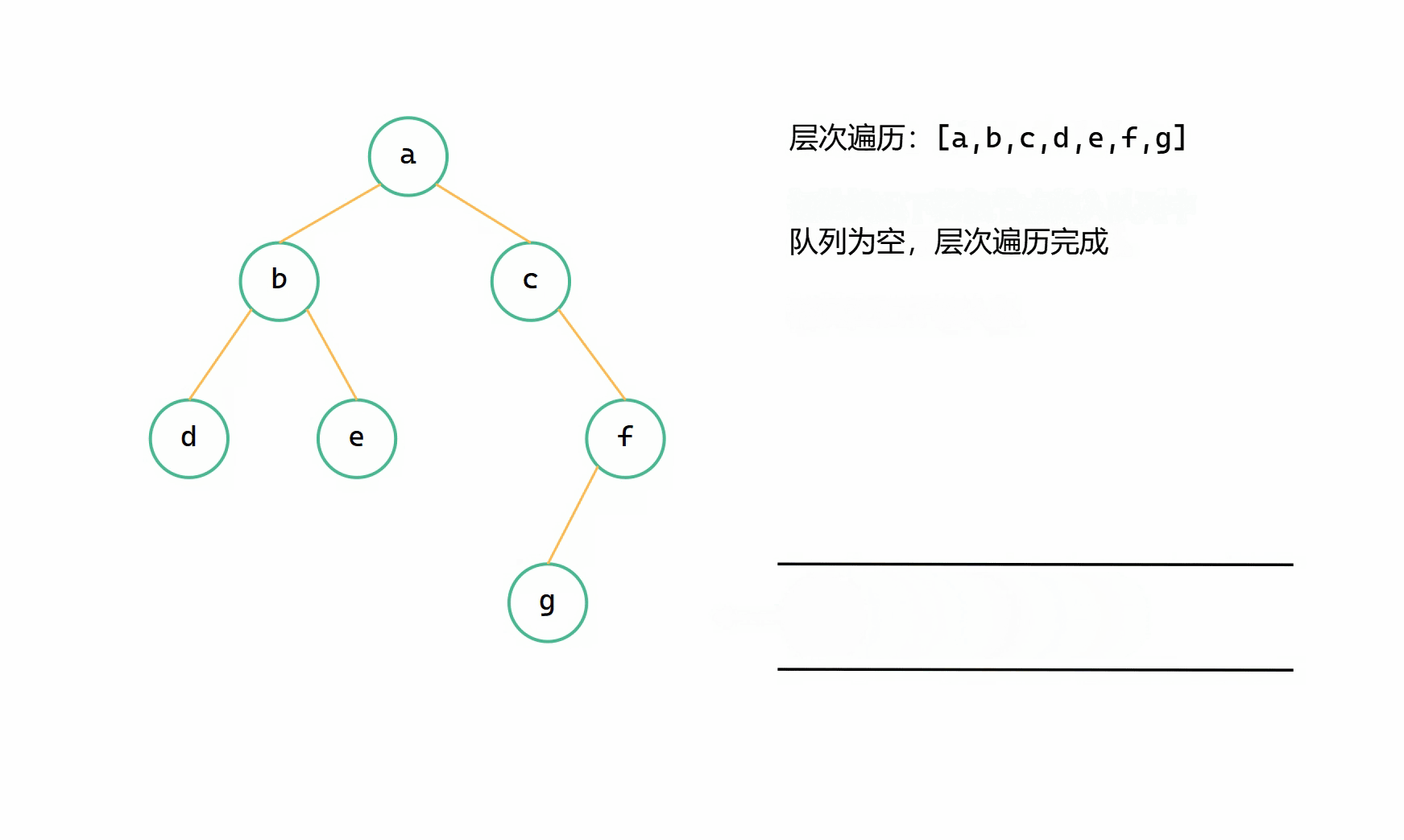
(1)先将二叉树的根节点放入队列中;
(2)取队首节点值,队首节点出队,将节点的左右子树根节点入队;
(3)重复步骤(2),直到队列为空。
层次遍历图解
自建队列层次遍历
typedef struct SqQueue{
BinaryTree data[MAXSIZE];
int front;
int rear;
}SqQueue;
SqQueue Q; //设为全局变量
//队列初始化
void Create_SqQueue(){
Q.front = Q.rear = 0;
}
//判断队列是否为空
bool IsEmpty(){
return Q.front == Q.rear;
}
//返回队列当前大小
int QueueSize(){
return Q.rear - Q.front;
}
//入队 利用队列 层次输入
void Push(BinaryTree T){
Q.data[++Q.rear] = T;
}
//出队并取队首 利用队列 层次输出
BinaryTree Pop(){
return Q.data[++Q.front];
}
//层次遍历二叉树 利用自己写的队列
void Show_Level_Order(BinaryTree root){
BinaryTree t = NULL;
if(!root) return;
Push(root);
while(!IsEmpty()){
int n = QueueSize(); //取二叉树每层的节点个数
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
t = Pop();
printf("%c ", t->data);
if(t->leftchild) Push(t->leftchild); //探索左子树
if(t->rightchild) Push(t->rightchild); //探索右子树
}
printf("\n");
}
}
STL queue层次遍历
//利用STL标准库queue层次遍历
void Show_Level_OrderSTL(BinaryTree root){
BinaryTree t = NULL;
std::queue<BinaryTree> q;
if(!root) return;
q.push(root);
while(!q.empty()){
int n = q.size();
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
t = q.front();
q.pop();
printf("%c ", t->data);
if(t->leftchild) q.push(t->leftchild);
if(t->rightchild) q.push(t->rightchild);
}
printf("\n");
}
}
完整程序
代码
点击查看代码
//#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<queue>
#define MAXSIZE 1000
typedef char Elemtype;
typedef struct BiNode{
Elemtype data;
struct BiNode *leftchild; //左儿子
struct BiNode *rightchild; //右儿子
} Node, *BinaryTree; //BinaryTree结构体指针
typedef struct SqQueue{
BinaryTree data[MAXSIZE];
int front;
int rear;
}SqQueue;
SqQueue Q; //设为全局变量
//队列初始化
void Create_SqQueue(){
Q.front = Q.rear = 0;
}
//判断队列是否为空
bool IsEmpty(){
return Q.front == Q.rear;
}
//返回队列当前大小
int QueueSize(){
return Q.rear - Q.front;
}
//入队 利用队列 层次输入
void Push(BinaryTree T){
Q.data[++Q.rear] = T;
}
//出队并取队首 利用队列 层次输出
BinaryTree Pop(){
return Q.data[++Q.front];
}
//层次遍历二叉树 利用自己写的队列
void Show_Level_Order(BinaryTree root){
BinaryTree t = NULL;
if(!root) return;
Push(root);
while(!IsEmpty()){
int n = QueueSize(); //取二叉树每层的节点个数
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
t = Pop();
printf("%c ", t->data);
if(t->leftchild) Push(t->leftchild); //探索左子树
if(t->rightchild) Push(t->rightchild); //探索右子树
}
printf("\n");
}
}
/*————————————————————————————————— 2 —————————————————————————————————————*/
//利用STL标准库queue层次遍历
void Show_Level_OrderSTL(BinaryTree root){
BinaryTree t = NULL;
std::queue<BinaryTree> q;
if(!root) return;
q.push(root);
while(!q.empty()){
int n = q.size();
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
t = q.front();
q.pop();
printf("%c ", t->data);
if(t->leftchild) q.push(t->leftchild);
if(t->rightchild) q.push(t->rightchild);
}
printf("\n");
}
}
//创建二叉树
BinaryTree Create_BinaryTree(){
Elemtype data;
BinaryTree T;
scanf("%c", &data); //输入节点数据
getchar();
if(data == '#') //输入#以停止创建子树
return NULL;
T = (BinaryTree)malloc(sizeof(Node));
T->data = data;
printf("输入 %c 的左儿子数据(#停止): ", data); //递归创建左子树
T->leftchild = Create_BinaryTree();
printf("输入 %c 的右儿子数据(#停止): ", data); //递归创建右子树
T->rightchild = Create_BinaryTree();
return T;
}
int main(){
BinaryTree T;
printf("输入二叉树根节点数据: ");
T = Create_BinaryTree();
Create_SqQueue();
printf("\n\n层次遍历二叉树结果: \n");
Show_Level_Order(T);
printf("\n");
Show_Level_OrderSTL(T);
}
运行结果

一切都是命运石之门的选择,本文章来源于博客园,作者:MarisaMagic,出处:https://www.cnblogs.com/MarisaMagic/p/17076912.html,未经允许严禁转载


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号