SpringBoot 启动流程分析(寻找扩展点)
1、SpringBoot maven 依赖版本
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <groupId>org.example</groupId> <artifactId>SpringBootStudy</artifactId> <version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version> <properties> <maven.compiler.source>8</maven.compiler.source> <maven.compiler.target>8</maven.compiler.target> <project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding> </properties> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> <version>2.7.14</version> </dependency> </dependencies> </project>
2、启动代码
package com.springboot.study; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; @SpringBootApplication public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication springApplication = new SpringApplication(Main.class); springApplication.run(args); } }
3、启动流程分析
1、获取Spring工厂实例
private <T> Collection<T> getSpringFactoriesInstances(Class<T> type, Class<?>[] parameterTypes, Object... args) { ClassLoader classLoader = getClassLoader(); // Use names and ensure unique to protect against duplicates Set<String> names = new LinkedHashSet<>(SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(type, classLoader)); List<T> instances = createSpringFactoriesInstances(type, parameterTypes, classLoader, args, names); AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(instances); return instances; }
public static List<String> loadFactoryNames(Class<?> factoryType, @Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) { ClassLoader classLoaderToUse = classLoader; if (classLoaderToUse == null) { classLoaderToUse = SpringFactoriesLoader.class.getClassLoader(); } String factoryTypeName = factoryType.getName(); return loadSpringFactories(classLoaderToUse).getOrDefault(factoryTypeName, Collections.emptyList()); }
private static Map<String, List<String>> loadSpringFactories(ClassLoader classLoader) { Map<String, List<String>> result = cache.get(classLoader); if (result != null) { return result; } result = new HashMap<>(); try { Enumeration<URL> urls = classLoader.getResources(FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION); while (urls.hasMoreElements()) { URL url = urls.nextElement(); UrlResource resource = new UrlResource(url); Properties properties = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource); for (Map.Entry<?, ?> entry : properties.entrySet()) { String factoryTypeName = ((String) entry.getKey()).trim(); String[] factoryImplementationNames = StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray((String) entry.getValue()); for (String factoryImplementationName : factoryImplementationNames) { result.computeIfAbsent(factoryTypeName, key -> new ArrayList<>()) .add(factoryImplementationName.trim()); } } } // Replace all lists with unmodifiable lists containing unique elements result.replaceAll((factoryType, implementations) -> implementations.stream().distinct() .collect(Collectors.collectingAndThen(Collectors.toList(), Collections::unmodifiableList))); cache.put(classLoader, result); } catch (IOException ex) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unable to load factories from location [" + FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION + "]", ex); } return result; }
这个地方会扫描项目中 resource 目录下的 META-INF/spring.factories 文件,默认如果不添加其他依赖,会扫描到如下项目:
- spring-boot-2.7.14.jar
- spring-boot-autoconfigure-2.7.14.jar
- spring-beans-5.3.29.jar
最终会扫描到如下对象:

2、run 方法分析
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) { long startTime = System.nanoTime(); DefaultBootstrapContext bootstrapContext = createBootstrapContext(); ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null; configureHeadlessProperty(); SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args); listeners.starting(bootstrapContext, this.mainApplicationClass); try { ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args); ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners, bootstrapContext, applicationArguments); configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment); Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment); context = createApplicationContext(); context.setApplicationStartup(this.applicationStartup); prepareContext(bootstrapContext, context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner); refreshContext(context); afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments); Duration timeTakenToStartup = Duration.ofNanos(System.nanoTime() - startTime); if (this.logStartupInfo) { new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass).logStarted(getApplicationLog(), timeTakenToStartup); } listeners.started(context, timeTakenToStartup); callRunners(context, applicationArguments); } catch (Throwable ex) { handleRunFailure(context, ex, listeners); throw new IllegalStateException(ex); } try { Duration timeTakenToReady = Duration.ofNanos(System.nanoTime() - startTime); listeners.ready(context, timeTakenToReady); } catch (Throwable ex) { handleRunFailure(context, ex, null); throw new IllegalStateException(ex); } return context; }
1、首先是 createBootstrapContext 方法,该方法会调用第一个扩展点:BootstrapRegistryInitializer->initializer,但是项目中没有该接口的实现类。
2、其次就是 listeners.starting 方法, 该方法中会调用第二个扩展点 SpringApplicationRunListener->starting,这个 SpringApplicationRunListener 项目中只存在一个实现类:EventPublishingRunListener,它会触发所有的 ApplicationListener 监听 ApplicationStartingEvent 的事件,后文就不特别声明这个实现类了。
2.1、配置属性(prepareEnvironment->configureEnvironment)
protected void configurePropertySources(ConfigurableEnvironment environment, String[] args) { MutablePropertySources sources = environment.getPropertySources(); if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(this.defaultProperties)) { DefaultPropertiesPropertySource.addOrMerge(this.defaultProperties, sources); } if (this.addCommandLineProperties && args.length > 0) { String name = CommandLinePropertySource.COMMAND_LINE_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME; if (sources.contains(name)) { PropertySource<?> source = sources.get(name); CompositePropertySource composite = new CompositePropertySource(name); composite .addPropertySource(new SimpleCommandLinePropertySource("springApplicationCommandLineArgs", args)); composite.addPropertySource(source); sources.replace(name, composite); } else { sources.addFirst(new SimpleCommandLinePropertySource(args)); } } }
3、然后就是 prepareEnvironment 方法,该方法会调用第三个扩展点:SpringApplicationRunListener->environmentPrepared,它会触发所有的 ApplicationListener 监听 ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent 的事件。
2.2、配置 Banner
private Banner getBanner(Environment environment) { Banners banners = new Banners(); banners.addIfNotNull(getImageBanner(environment)); banners.addIfNotNull(getTextBanner(environment)); if (banners.hasAtLeastOneBanner()) { return banners; } if (this.fallbackBanner != null) { return this.fallbackBanner; } return DEFAULT_BANNER; }
4、第四个扩展点在 prepareContext->applyInitializers 方法里,ApplicationContextInitializer->initialize。
5、第五个扩展点在 prepareContext->listeners.contextPrepared 方法里,SpringApplicationRunListeners->contextPrepared,它会触发所有的 ApplicationListener 监听 ApplicationContextInitializedEvent 的事件。
6、第六个扩展点在 prepareContext->bootstrapContext.close 方法里,它会触发所有的 ApplicationListener 监听 BootstrapContextClosedEvent 的事件。
2.3、加载 Source(prepareContext)
public Set<Object> getAllSources() { Set<Object> allSources = new LinkedHashSet<>(); if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(this.primarySources)) { allSources.addAll(this.primarySources); } if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(this.sources)) { allSources.addAll(this.sources); } return Collections.unmodifiableSet(allSources); }
private void load(Object source) { Assert.notNull(source, "Source must not be null"); if (source instanceof Class<?>) { load((Class<?>) source); return; } if (source instanceof Resource) { load((Resource) source); return; } if (source instanceof Package) { load((Package) source); return; } if (source instanceof CharSequence) { load((CharSequence) source); return; } throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid source type " + source.getClass()); }
这个地方会从 SpringApplication 中的 primarySources、sources 加载源,然后注册为 Bean。
7、第七个扩展点在 prepareContext->listeners.contextLoaded 方法里,SpringApplicationRunListeners->contextLoaded,会触发 ApplicationListener 监听 ApplicationPreparedEvent 的事件。
2.4、ServletWebServerApplicationContext->refresh
@Override public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException { synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) { StartupStep contextRefresh = this.applicationStartup.start("spring.context.refresh"); // Prepare this context for refreshing. prepareRefresh(); // Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory. ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory(); // Prepare the bean factory for use in this context. prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory); try { // Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses. postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory); StartupStep beanPostProcess = this.applicationStartup.start("spring.context.beans.post-process"); // Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context. invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory); // Register bean processors that intercept bean creation. registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory); beanPostProcess.end(); // Initialize message source for this context. initMessageSource(); // Initialize event multicaster for this context. initApplicationEventMulticaster(); // Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses. onRefresh(); // Check for listener beans and register them. registerListeners(); // Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons. finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory); // Last step: publish corresponding event. finishRefresh(); } catch (BeansException ex) { if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) { logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " + "cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex); } // Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources. destroyBeans(); // Reset 'active' flag. cancelRefresh(ex); // Propagate exception to caller. throw ex; } finally { // Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we // might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore... resetCommonCaches(); contextRefresh.end(); } } }
这里我们直接看到 invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors 方法,不过这个方法蛮长的,就先看一部分:
for (BeanFactoryPostProcessor postProcessor : beanFactoryPostProcessors) { if (postProcessor instanceof BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor) { BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor registryProcessor = (BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor) postProcessor; registryProcessor.postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(registry); registryProcessors.add(registryProcessor); } else { regularPostProcessors.add(postProcessor); } }
这个地方可以猜到这个 postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry 也是一个扩展点,但是这个 beanFactoryPostProcessors 的值是从哪里来的呢?
打断点这里是有三个值的:
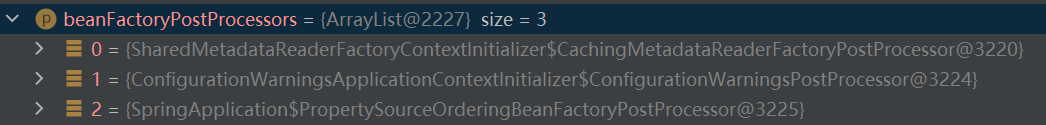
这里直接说答案,还记得这段代码吗:
context = createApplicationContext(); context.setApplicationStartup(this.applicationStartup); prepareContext(bootstrapContext, context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner);
这里获取了 context 之后,就调用了 prepareContext 方法,prepareContext 方法里曾提到过有第四、第五、第六、第七个扩展点。
举个例子,就拿第四个扩展点说:
ConfigurationWarningsApplicationContextInitializer 实现了 ApplicationContextInitializer 接口,然后添加了一个值:
@Override public void initialize(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) { context.addBeanFactoryPostProcessor(new ConfigurationWarningsPostProcessor(getChecks())); }
相同的还有 SharedMetadataReaderFactoryContextInitializer,至于第三个值则是直接在 prepareContext 方法里添加的。
8、第八个扩展点在 refresh->invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors 方法里,会调用 invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors。
紧接着,就是如下代码:
String[] postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false); for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) { if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) { currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class)); processedBeans.add(ppName); } }
我们看看这个 postProcessorNames 是怎么来的,追踪到 beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType 方法,进去可以看到 doGetBeanNamesForType 方法,总而言之,是从 beanDefinitionNames 和 manualSingletonNames 的值来的,那这些值又是怎么来的呢,仍然是如下一段代码:
context = createApplicationContext(); context.setApplicationStartup(this.applicationStartup); prepareContext(bootstrapContext, context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner);
在创建 context 的时候,实际上是调用 AnnotationConfigApplicationContext 的构造方法,里面会调用 registerAnnotationConfigProcessors 方法,这个方法会初始化 5 个 beanDefinitionName。
然后就是 prepareContext 方法里,在第四个扩展点会初始化两个 manualSingletonName,prepareContext 方法里的 registerSingleton 方法也添加了两个 manualSingletonName,并且后面的 load 方法也添加了一个 main 的 beanDefinitionName,在最后的第七个扩展点里又添加了 3 个 manualSingletonName,总之在执行 refreshContext 之前,context 的 beanFactory 里包含 6 个 beanDefinitionName 7 个 manualSingletonName,后面的就不分析了,毕竟能扩展的就在这里。
9、第九个扩展点也在 refresh->invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors 方法里,会调用 invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors。
不过有一点要注意的是,虽说第八个、第九个也算是扩展点,但其只有在第四到第七个扩展点里面配置了才能进行扩展。
2.5、refresh->onRefresh
@Override protected void onRefresh() { super.onRefresh(); try { createWebServer(); } catch (Throwable ex) { throw new ApplicationContextException("Unable to start web server", ex); } }
该方法会调用 createWebServer 创建一个 webserver。
2.6、refresh->finishBeanFactoryInitialization
protected void finishBeanFactoryInitialization(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) { // Initialize conversion service for this context. if (beanFactory.containsBean(CONVERSION_SERVICE_BEAN_NAME) && beanFactory.isTypeMatch(CONVERSION_SERVICE_BEAN_NAME, ConversionService.class)) { beanFactory.setConversionService( beanFactory.getBean(CONVERSION_SERVICE_BEAN_NAME, ConversionService.class)); } // Register a default embedded value resolver if no BeanFactoryPostProcessor // (such as a PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer bean) registered any before: // at this point, primarily for resolution in annotation attribute values. if (!beanFactory.hasEmbeddedValueResolver()) { beanFactory.addEmbeddedValueResolver(strVal -> getEnvironment().resolvePlaceholders(strVal)); } // Initialize LoadTimeWeaverAware beans early to allow for registering their transformers early. String[] weaverAwareNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(LoadTimeWeaverAware.class, false, false); for (String weaverAwareName : weaverAwareNames) { getBean(weaverAwareName); } // Stop using the temporary ClassLoader for type matching. beanFactory.setTempClassLoader(null); // Allow for caching all bean definition metadata, not expecting further changes. beanFactory.freezeConfiguration(); // Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons. beanFactory.preInstantiateSingletons(); }
这个方法会调用 beanFactory,实例化所有的 bean。
10、第十个扩展点在 refresh->finishRefresh 方法里,会调用 getLifecycleProcessor().onRefresh(),会调用 SmartLifecycle->start 方法。
11、第十一个扩展点也在 refresh->finishRefresh 方法里,会调用 publishEvent 然后触发 ApplicationListener 监听 ContextRefreshedEvent 的事件。
2.7、最后的三个扩展点-> run 方法
12、第十二个扩展点在 run 方法里,会调用 listeners.started 方法,SpringApplicationRunListener->started。
13、第十三个扩展点也在 run 方法里,会调用 callRunners 方法,ApplicationRunner 或 CommandLineRunner 的 run 方法。
14、第十四个扩展点也在 run 方法里,会调用 listeners.ready方法,SpringApplicationRunListener->ready。
3、结语
第一篇分析 SpringBoot 启动源码到这里就结束了,我们这次的目标是找到 SpringBoot 有哪些地方可以自己进行代码扩展的,其中不免有些遗漏的,欢迎各位补充。
目前看完还是有很多问题,比如 SpringBootApplication 注解的作用是什么、Bean 的实例化流程是什么、以及我们 Web 的 URL 请求是如何到方法上的...等等。
最后,这篇分析完的这些扩展点能干些什么呢?



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号