MyBatis-Plus Generator自定义模板
相信大家在开发过程中,应该都用过Mybatis-Plus的Generator,但是可能没有自定义过模板并使用。
每个项目都应该有一个从Controller层到Mapper层的通用模板,来去掉哪些简单的重复开发工作。
至于如何自定义模板并开发,大家可以先看看这篇博文,以及其附带的三篇博文,相信您一定有收获。
Ⅰ、奋斗青年LOVE
Ⅱ、Github链接
Ⅲ、呵呵彡
如果您看完的话,应该也能手动制作一个自己风格的开发模板。
MyBatis-Plus的默认模板引擎是Velocity,但是这个引擎似乎多年没有人维护了,所以推荐使用FreeMarker。
官网的例子:
public class CodeGenerator { /** * <p> * 读取控制台内容 * </p> */ public static String scanner(String tip) { Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); StringBuilder help = new StringBuilder(); help.append("请输入" + tip + ":"); System.out.println(help.toString()); if (scanner.hasNext()) { String ipt = scanner.next(); if (StringUtils.isNotBlank(ipt)) { return ipt; } } throw new MybatisPlusException("请输入正确的" + tip + "!"); } public static void main(String[] args) { // 代码生成器 AutoGenerator mpg = new AutoGenerator(); // 全局配置 GlobalConfig gc = new GlobalConfig(); String projectPath = System.getProperty("user.dir"); gc.setOutputDir(projectPath + "/src/main/java"); // 文件输出位置,不要把文件输出位置写在那个System.getProperty方法那里,会输出null,看清楚哈!!! gc.setAuthor("jobob"); gc.setOpen(false); // 是否打开文件位置 // gc.setSwagger2(true); 实体属性 Swagger2 注解 mpg.setGlobalConfig(gc); // 数据源配置 DataSourceConfig dsc = new DataSourceConfig(); dsc.setUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/ant?useUnicode=true&useSSL=false&characterEncoding=utf8"); // dsc.setSchemaName("public"); dsc.setDriverName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); dsc.setUsername("root"); dsc.setPassword("密码"); mpg.setDataSource(dsc); // 包配置 PackageConfig pc = new PackageConfig(); pc.setModuleName(scanner("模块名")); pc.setParent("com.baomidou.ant"); // pc.getParent方法会输出 包名+模块名 mpg.setPackageInfo(pc); // 自定义配置 InjectionConfig cfg = new InjectionConfig() { @Override public void initMap() { // to do nothing } }; // 如果模板引擎是 freemarker String templatePath = "/templates/mapper.xml.ftl"; // 如果模板引擎是 velocity // String templatePath = "/templates/mapper.xml.vm"; // 自定义输出配置 List<FileOutConfig> focList = new ArrayList<>(); // 自定义配置会被优先输出 focList.add(new FileOutConfig(templatePath) { @Override public String outputFile(TableInfo tableInfo) { // 自定义输出文件名 , 如果你 Entity 设置了前后缀、此处注意 xml 的名称会跟着发生变化!! return projectPath + "/src/main/resources/mapper/" + pc.getModuleName() + "/" + tableInfo.getEntityName() + "Mapper" + StringPool.DOT_XML; } }); /* cfg.setFileCreate(new IFileCreate() { @Override public boolean isCreate(ConfigBuilder configBuilder, FileType fileType, String filePath) { // 判断自定义文件夹是否需要创建 checkDir("调用默认方法创建的目录,自定义目录用"); if (fileType == FileType.MAPPER) { // 已经生成 mapper 文件判断存在,不想重新生成返回 false return !new File(filePath).exists(); } // 允许生成模板文件 return true; } }); */ cfg.setFileOutConfigList(focList); mpg.setCfg(cfg); // 配置模板 TemplateConfig templateConfig = new TemplateConfig(); // 配置自定义输出模板 //指定自定义模板路径,注意不要带上.ftl/.vm, 会根据使用的模板引擎自动识别 // templateConfig.setEntity("templates/entity2.java"); // templateConfig.setService(); // templateConfig.setController(); templateConfig.setXml(null); mpg.setTemplate(templateConfig); // 策略配置 StrategyConfig strategy = new StrategyConfig(); strategy.setNaming(NamingStrategy.underline_to_camel); strategy.setColumnNaming(NamingStrategy.underline_to_camel); strategy.setSuperEntityClass("你自己的父类实体,没有就不用设置!"); strategy.setEntityLombokModel(true); strategy.setRestControllerStyle(true); // 公共父类 strategy.setSuperControllerClass("你自己的父类控制器,没有就不用设置!"); // 写于父类中的公共字段 strategy.setSuperEntityColumns("id"); strategy.setInclude(scanner("表名,多个英文逗号分割").split(",")); strategy.setControllerMappingHyphenStyle(true); strategy.setTablePrefix(pc.getModuleName() + "_"); mpg.setStrategy(strategy); mpg.setTemplateEngine(new FreemarkerTemplateEngine()); mpg.execute(); } }
上面的例子,全局配置,数据源配置,包配置,主要看的应该是自定义配置和策略配置。
// 自定义配置 InjectionConfig cfg = new InjectionConfig() { @Override public void initMap() { // to do nothing } };
比如这个,就是给自定义模板提供参数用的,官方示例:
InjectionConfig injectionConfig = new InjectionConfig() { //自定义属性注入:abc //在.ftl(或者是.vm)模板中,通过${cfg.abc}获取属性 @Override public void initMap() { Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>(); map.put("abc", this.getConfig().getGlobalConfig().getAuthor() + "-mp"); this.setMap(map); } };
我们先看下官方的一个controller模板:
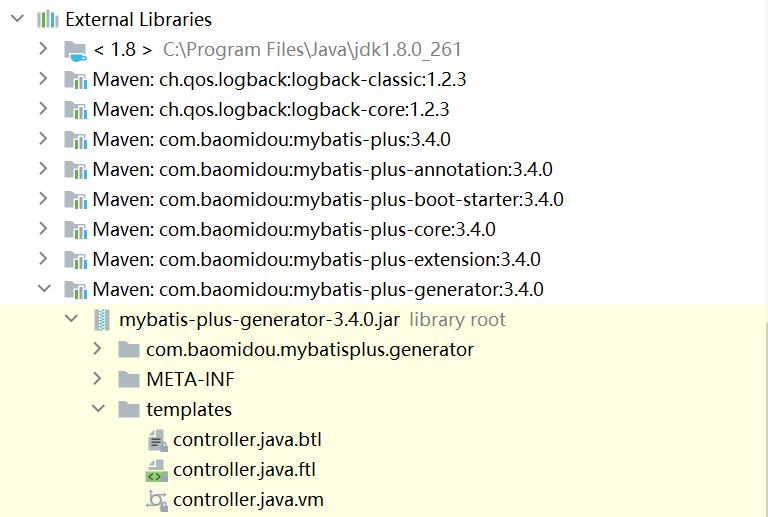
这个是模板的位置,我们就以controller.java.ftl为例:
package ${package.Controller}; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; <#if restControllerStyle> import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; <#else> import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; </#if> <#if superControllerClassPackage??> import ${superControllerClassPackage}; </#if> /** * <p> * ${table.comment!} 前端控制器 * </p> * * @author ${author} * @since ${date} */ <#if restControllerStyle> @RestController <#else> @Controller </#if> @RequestMapping("<#if package.ModuleName?? && package.ModuleName != "">/${package.ModuleName}</#if>/<#if controllerMappingHyphenStyle??>${controllerMappingHyphen}<#else>${table.entityPath}</#if>") <#if kotlin> class ${table.controllerName}<#if superControllerClass??> : ${superControllerClass}()</#if> <#else> <#if superControllerClass??> public class ${table.controllerName} extends ${superControllerClass} { <#else> public class ${table.controllerName} { </#if> } </#if>
这个FreeMarker模板上面是不是有很多参数呢,你肯定会疑惑他们从哪儿来的,官网给其实给出了介绍:

我们可以Debug官方的CodeGenerator,在AbstractTemplateEngine的getObjectMap方法的末尾打上断点,
然后再看看objectMap的值有哪些可用。
public Map<String, Object> getObjectMap(TableInfo tableInfo) { ConfigBuilder config = this.getConfigBuilder(); HashMap objectMap; if (config.getStrategyConfig().isControllerMappingHyphenStyle()) { objectMap = CollectionUtils.newHashMapWithExpectedSize(33); objectMap.put("controllerMappingHyphenStyle", config.getStrategyConfig().isControllerMappingHyphenStyle()); objectMap.put("controllerMappingHyphen", StringUtils.camelToHyphen(tableInfo.getEntityPath())); } else { objectMap = CollectionUtils.newHashMapWithExpectedSize(31); } objectMap.put("restControllerStyle", config.getStrategyConfig().isRestControllerStyle()); objectMap.put("config", config); objectMap.put("package", config.getPackageInfo()); GlobalConfig globalConfig = config.getGlobalConfig(); objectMap.put("author", globalConfig.getAuthor()); objectMap.put("idType", globalConfig.getIdType() == null ? null : globalConfig.getIdType().toString()); objectMap.put("logicDeleteFieldName", config.getStrategyConfig().getLogicDeleteFieldName()); objectMap.put("versionFieldName", config.getStrategyConfig().getVersionFieldName()); objectMap.put("activeRecord", globalConfig.isActiveRecord()); objectMap.put("kotlin", globalConfig.isKotlin()); objectMap.put("swagger2", globalConfig.isSwagger2()); objectMap.put("date", (new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd")).format(new Date())); objectMap.put("table", tableInfo); objectMap.put("enableCache", globalConfig.isEnableCache()); objectMap.put("baseResultMap", globalConfig.isBaseResultMap()); objectMap.put("baseColumnList", globalConfig.isBaseColumnList()); objectMap.put("entity", tableInfo.getEntityName()); objectMap.put("entitySerialVersionUID", config.getStrategyConfig().isEntitySerialVersionUID()); objectMap.put("entityColumnConstant", config.getStrategyConfig().isEntityColumnConstant()); objectMap.put("entityBuilderModel", config.getStrategyConfig().isEntityBuilderModel()); objectMap.put("chainModel", config.getStrategyConfig().isChainModel()); objectMap.put("entityLombokModel", config.getStrategyConfig().isEntityLombokModel()); objectMap.put("entityBooleanColumnRemoveIsPrefix", config.getStrategyConfig().isEntityBooleanColumnRemoveIsPrefix()); objectMap.put("superEntityClass", this.getSuperClassName(config.getSuperEntityClass())); objectMap.put("superMapperClassPackage", config.getSuperMapperClass()); objectMap.put("superMapperClass", this.getSuperClassName(config.getSuperMapperClass())); objectMap.put("superServiceClassPackage", config.getSuperServiceClass()); objectMap.put("superServiceClass", this.getSuperClassName(config.getSuperServiceClass())); objectMap.put("superServiceImplClassPackage", config.getSuperServiceImplClass()); objectMap.put("superServiceImplClass", this.getSuperClassName(config.getSuperServiceImplClass())); objectMap.put("superControllerClassPackage", this.verifyClassPacket(config.getSuperControllerClass())); objectMap.put("superControllerClass", this.getSuperClassName(config.getSuperControllerClass())); return (Map)(Objects.isNull(config.getInjectionConfig()) ? objectMap : config.getInjectionConfig().prepareObjectMap(objectMap));//这里上断点。 }
那么加入这些参数不够用怎么办呢,上面提到了可以通过自定义模板参数,不知你们记得吗,那么如何引用呢?
我们首先定位到官方的自定义属性注入:
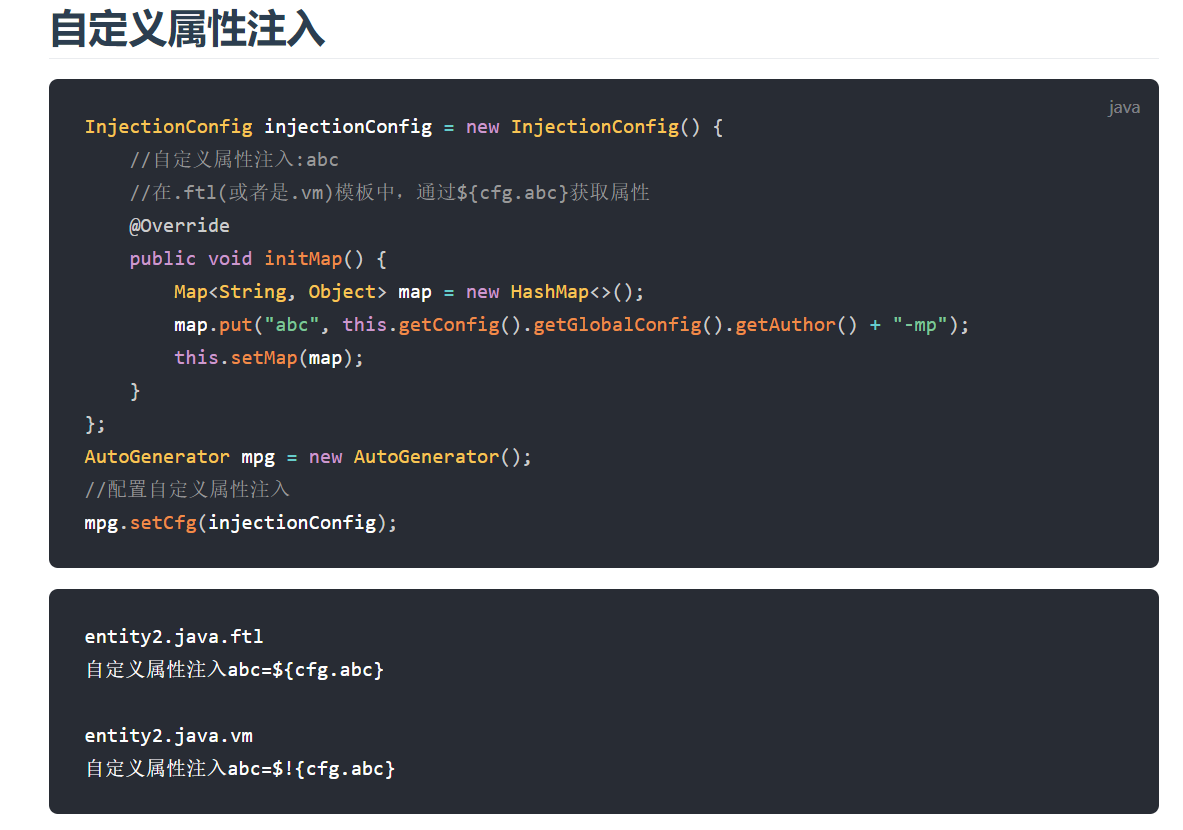
现在就不会出现了属性不够用的情况了,自定义的模板参数通过${cfg.param}来引用。
现在我们来看到官方这段代码:
// 如果模板引擎是 freemarker String templatePath = "/templates/mapper.xml.ftl"; // 如果模板引擎是 velocity // String templatePath = "/templates/mapper.xml.vm"; // 自定义输出配置 List<FileOutConfig> focList = new ArrayList<>(); // 自定义配置会被优先输出 focList.add(new FileOutConfig(templatePath) { @Override public String outputFile(TableInfo tableInfo) { // 自定义输出文件名 , 如果你 Entity 设置了前后缀、此处注意 xml 的名称会跟着发生变化!! return projectPath + "/src/main/resources/mapper/" + pc.getModuleName() + "/" + tableInfo.getEntityName() + "Mapper" + StringPool.DOT_XML; } });
templatePath是你自定义的模板的位置,return的是你用模板生成的文件的位置。
// 配置模板 TemplateConfig templateConfig = new TemplateConfig(); // 配置自定义输出模板 //指定自定义模板路径,注意不要带上.ftl/.vm, 会根据使用的模板引擎自动识别 // templateConfig.setEntity("templates/entity2.java"); // templateConfig.setService(); // templateConfig.setController(); templateConfig.setXml(null); mpg.setTemplate(templateConfig);
这个templateConfig是官方提供的Controller层到Mapper层的基本示例,如果你想自定义的话,就提供自定义模板的位置。
现在我想你已经知道如何自己开发一套模板了吧,我们现在来看看策略配置(上文提到的奋斗的青年的代码)。
// 策略配置 StrategyConfig strategy = new StrategyConfig(); // strategy.setCapitalMode(true);// 全局大写命名 ORACLE 注意 //strategy.setTablePrefix(new String[] { "tlog_", "tsys_" });// 此处可以修改为您的表前缀 strategy.setNaming(NamingStrategy.underline_to_camel);// 表名生成策略 strategy.setInclude(new String[] { "app_certificate" }); // 需要生成的表 // strategy.setExclude(new String[]{"test"}); // 排除生成的表 // 自定义实体父类 // strategy.setSuperEntityClass("com.baomidou.demo.TestEntity"); // 自定义实体,公共字段 // strategy.setSuperEntityColumns(new String[] { "test_id", "age" }); // 自定义 mapper 父类 // strategy.setSuperMapperClass("com.baomidou.demo.TestMapper"); // 自定义 service 父类 // strategy.setSuperServiceClass("com.baomidou.demo.TestService"); // 自定义 service 实现类父类 // strategy.setSuperServiceImplClass("com.baomidou.demo.TestServiceImpl"); // 自定义 controller 父类 // strategy.setSuperControllerClass("com.baomidou.demo.TestController"); // 【实体】是否生成字段常量(默认 false) // public static final String ID = "test_id"; strategy.setEntityColumnConstant(true); // 【实体】是否为构建者模型(默认 false) // public User setName(String name) {this.name = name; return this;} //strategy.setEntityBuilderModel(true); mpg.setStrategy(strategy);
可以仿照上面的例子,然后再结合官方文档,再比对生成的代码,我相信你一定更清楚了。
最后提示一下自己,看文档一定要细心奥。






【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· Linux系列:如何用 C#调用 C方法造成内存泄露
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(二):开始使用ML.NET
· 无需6万激活码!GitHub神秘组织3小时极速复刻Manus,手把手教你使用OpenManus搭建本
· C#/.NET/.NET Core优秀项目和框架2025年2月简报
· Manus爆火,是硬核还是营销?
· 终于写完轮子一部分:tcp代理 了,记录一下
· 【杭电多校比赛记录】2025“钉耙编程”中国大学生算法设计春季联赛(1)