结对项目
Github项目地址:https://github.com/HanKiSei/TheLuOfHope
简介:拿到作业先不急,找好队友最要紧;动手之前先放松,等着队友立大功;吃喝玩乐八九天,全靠队友活神仙;握着鼠标手一抖,项目pull全都有。
结对项目成员:卢楚钦 3118005012 潘毅成 3118005018
PSP:
| PSP | Personal Software Process Stages | 预估耗时(分钟) | 实际耗时(分钟) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Planning | 计划 | ||
| · Estimate | 估计这个任务需要多少时间 | 20*60 | 24*60 |
| Development | 开发 | ||
| Analysis | 需求分析 (包括学习新技术) | 150 | 150 |
| ·Design Spec | 生成设计文档 | 45 | 60 |
| ·Design Review | 设计复审 (和同事审核设计文档) | 60 | 90 |
| · Coding Standard | 代码规范 (为目前的开发制定合适的规范) | 60 | 60 |
| ·Design | 具体设计 | 120 | 120 |
| ·Coding | 具体编码 | 480 | 700 |
| ·Code Review | 代码复审 | 150 | 180 |
| ·Test | 测试(自我测试,修改代码,提交修改) | 240 | 300 |
| Reporting | 报告 | ||
| ·Test Report | 测试报告 | 60 | 60 |
| ·Size Measurement | 计算工作量 | 30 | 30 |
| ·Postmortem & Process Improvement Plan | 事后总结, 并提出过程改进计划 | ||
| 合计 |
题目:
- 实现一个自动生成小学四则运算题目的命令行程序(也可以用图像界面,具有相似功能)。
说明:
- 自然数:0, 1, 2, …。
- 真分数:1/2, 1/3, 2/3, 1/4, 1’1/2, …。
- 运算符:+, −, ×, ÷。
- 括号:(, )。
- 等号:=。
- 分隔符:空格(用于四则运算符和等号前后)。
- 算术表达式:
需求:
- 控制生成题目的个数
- 控制题目中数值(自然数、真分数和真分数分母)的范围
- 生成的题目中计算过程不能产生负数,也就是说算术表达式中如果存在形如e1− e2的子表达式,那么e1≥ e2。
- 生成的题目中如果存在形如e1÷ e2的子表达式,那么其结果应是真分数。
- 每道题目中出现的运算符个数不超过3个。
- 程序一次运行生成的题目不能重复,即任何两道题目不能通过有限次交换+和×左右的算术表达式变换为同一道题目。例如,23 + 45 = 和45 + 23 = 是重复的题目,6 × 8 = 和8 × 6 = 也是重复的题目。3+(2+1)和1+2+3这两个题目是重复的,由于+是左结合的,1+2+3等价于(1+2)+3,也就是3+(1+2),也就是3+(2+1)。但是1+2+3和3+2+1是不重复的两道题,因为1+2+3等价于(1+2)+3,而3+2+1等价于(3+2)+1,它们之间不能通过有限次交换变成同一个题目。
生成的题目存入执行程序的当前目录下的Exercises.txt文件,格式如下:
- 四则运算题目1
- 四则运算题目2
……
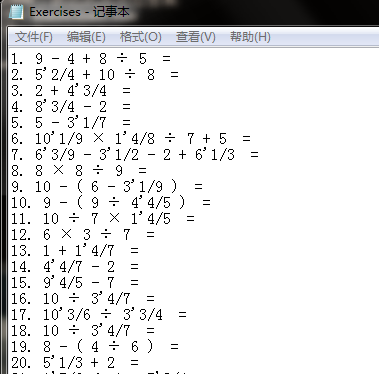
其中真分数在输入输出时采用如下格式,真分数五分之三表示为3/5,真分数二又八分之三表示为2’3/8。
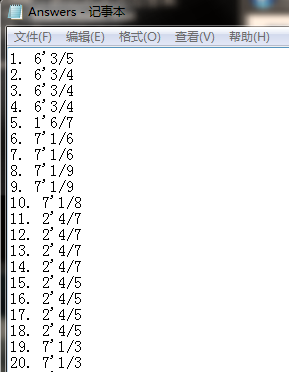
7.在生成题目的同时,计算出所有题目的答案,并存入执行程序的当前目录下的Answers.txt文件,格式如下:
- 答案1
- 答案2
特别的,真分数的运算如下例所示:1/6 + 1/8 = 7/24。
- 程序应能支持一万道题目的生成。
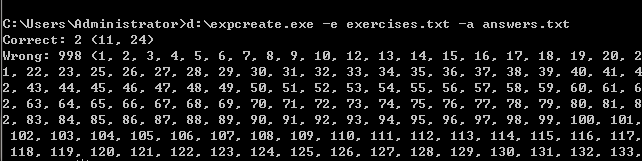
- 程序支持对给定的题目文件和答案文件,判定答案中的对错并进行数量统计,输入参数如下:
Myapp.exe -e <exercisefile>.txt -a <answerfile>.txt
统计结果输出到文件Grade.txt,格式如下:
Correct: 5 (1, 3, 5, 7, 9)
Wrong: 5 (2, 4, 6, 8, 10)
其中“:”后面的数字5表示对/错的题目的数量,括号内的是对/错题目的编号。为简单起见,假设输入的题目都是按照顺序编号的符合规范的题目。
遇到的困难及解决方法
困难描述
- 关于随机生成的带括号的位置,经过了大量的推演后选择了懒人方法。为了解决在计算过程中不能出现负数的问题,在走投无路的情况下,也是使用了懒人方法
- 不明白如何根据作业需求,对形如x'y/z的真分数进行计算
- 本人对编程语言的了解不够,缺乏面向对象的思想,有很多简便的功能都不会使用,绕了一些大圈子
- 关于对表达式进行查重,使用了set,使用起来有点麻烦
- 在进行乘法运算的时候,有可能出现操作数过大导致int型溢出的问题,所以把range限制为20以内
关键代码or设计说明
用于封装操作数的Number类
enum Type {
// 枚举实例
NaturalNumber, TrueFraction;
}
public class Number {
/**
* 数的类型:<br/>
* 1.自然数<br/>
* 2.真分数
*/
public Type type;
/** [整数,分子,分母] */
public int[] value = new int[3];
/** 整数部分 */
public static final byte INTEGRAL_NUMBER_PART = 0;
/** 分子部分 */
public static final byte NUMERATOR_PART = 1;
/** 分母部分 */
public static final byte DENOMINATOR_PART = 2;
@Override
public String toString() {
if (value[NUMERATOR_PART] == 0) {
// 分子为0
return String.valueOf(value[INTEGRAL_NUMBER_PART]);
} else if (value[INTEGRAL_NUMBER_PART] == 0) {
// 整数部分为0
return String.valueOf(value[NUMERATOR_PART]) + "/" + String.valueOf(value[DENOMINATOR_PART]);
} else {
// 都不为0
return String.valueOf(value[INTEGRAL_NUMBER_PART]) + "'" + String.valueOf(value[NUMERATOR_PART]) + "/" + String.valueOf(value[DENOMINATOR_PART]);
}
}
/**
* 求最大公约数
*
* @param n1
* @param n2
* @return
*/
public static final int gcd(int n1, int n2) {
int gcd = 0;
if (n1 < n2) {// 交换n1、n2的值
n1 = n1 + n2;
n2 = n1 - n2;
n1 = n1 - n2;
}
if (n1 % n2 == 0) {
gcd = n2;
}
while (n1 % n2 > 0) {
n1 = n1 % n2;
if (n1 < n2) {
n1 = n1 + n2;
n2 = n1 - n2;
n1 = n1 - n2;
}
if (n1 % n2 == 0) {
gcd = n2;
}
}
return gcd;
}
/**
*
* @param range 控制生成范围
*/
public Number(int range) {
Random r = new Random();
value[INTEGRAL_NUMBER_PART] = r.nextInt(range) + 1;
value[NUMERATOR_PART] = r.nextInt(range) + 1;
value[DENOMINATOR_PART] = 1 + r.nextInt(range - 1);
// 分母小于等于分子,视为自然数
if (value[DENOMINATOR_PART] <= value[NUMERATOR_PART]) {
type = Type.NaturalNumber;
// 分子,分母分别设置为0和1
value[NUMERATOR_PART] = 0;
value[DENOMINATOR_PART] = 1;
} else {
type = Type.TrueFraction;
}
}
private Number(int numerator, int denominator) throws Exception {
if (numerator < 0) {
throw new Exception("分子小于0");
}
if (denominator <= 0) {
throw new Exception("分母小于等于0");
}
if (numerator != 0) {
int greatestCommonDivisor = gcd(numerator, denominator);
numerator /= greatestCommonDivisor;
denominator /= greatestCommonDivisor;
}
value[INTEGRAL_NUMBER_PART] = numerator / denominator;
value[NUMERATOR_PART] = numerator % denominator;
value[DENOMINATOR_PART] = denominator;
// 分子等于0
if (value[NUMERATOR_PART] == 0) {
// 分母设置为1
value[DENOMINATOR_PART] = 1;
type = Type.NaturalNumber;
} else {
type = Type.TrueFraction;
}
}
/**
* 加法: this + b
*
* @param b
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
public Number plus(Number b) throws Exception {
Number result = new Number(this.value[NUMERATOR_PART] * b.value[DENOMINATOR_PART] + this.value[DENOMINATOR_PART] * b.value[NUMERATOR_PART],
this.value[DENOMINATOR_PART] * b.value[DENOMINATOR_PART]);
result.value[INTEGRAL_NUMBER_PART] += this.value[INTEGRAL_NUMBER_PART] + b.value[INTEGRAL_NUMBER_PART];
return result;
}
/**
* 减法: this-b
*
* @param b
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
public Number subtract(Number b) throws Exception {
int condition = (this.value[INTEGRAL_NUMBER_PART] * this.value[DENOMINATOR_PART] + this.value[NUMERATOR_PART]) * b.value[DENOMINATOR_PART]
- (b.value[INTEGRAL_NUMBER_PART] * b.value[DENOMINATOR_PART] + b.value[NUMERATOR_PART]) * this.value[DENOMINATOR_PART];
if (condition <= 0) {
return null;
}
Number result = new Number(
// n1整数乘分母加小数的和,再乘n2分母 - n2整数乘分母加小数的和,再乘n1分母
condition, this.value[DENOMINATOR_PART] * b.value[DENOMINATOR_PART]);
return result;
}
/**
* 乘法: this*b
*
* @param b
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
public Number multiply(Number b) throws Exception {
Number result = new Number(
(this.value[INTEGRAL_NUMBER_PART] * this.value[DENOMINATOR_PART] + this.value[NUMERATOR_PART]) * (b.value[INTEGRAL_NUMBER_PART] * b.value[DENOMINATOR_PART] + b.value[NUMERATOR_PART]),
this.value[DENOMINATOR_PART] * b.value[DENOMINATOR_PART]);
return result;
}
/**
* 除法: this/b
*
* @param b
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
public Number divide(Number b) throws Exception {
Number result = new Number((this.value[INTEGRAL_NUMBER_PART] * this.value[DENOMINATOR_PART] + this.value[NUMERATOR_PART]) * b.value[DENOMINATOR_PART],
(b.value[INTEGRAL_NUMBER_PART] * b.value[DENOMINATOR_PART] + b.value[NUMERATOR_PART]) * this.value[DENOMINATOR_PART]);
return result;
}
}
生成表达式与计算
public class Expression {
private static final Random r = new Random();
private static final char[] operates = new char[] { '+', '-', '×', '÷' };
// 储存中缀表达式
private LinkedList<Object> infixExpList;
// 储存后缀表达式
private LinkedList<Object> suffixExpList;
// 操作数个数
private int count;
// 范围
private int range;
// 储存计算结果
private Number result;
// 是否计算过
private boolean isCalculated ;
/**
*
* @param count 操作数个数
* @param range 操作数范围,[1,range]
* @throws Exception
*/
public Expression(int count, int range) throws Exception {
this(count, range, r.nextBoolean());
}
/**
*
* @param count 操作数个数
* @param range 操作数范围
* @param containParentheses 是否包含括号
* @throws Exception
*/
public Expression(int count, int range, boolean containParentheses) throws Exception {
// Stack不推荐使用,一般用LinkedList作栈
if (count > 4) {
throw new Exception("操作数大于4");
}
this.infixExpList = new LinkedList<>();
this.count = count;
this.range = range;
this.isCalculated = false;
for (int i = 0 ; i < this.count ; i++) {
// 每个操作数前面push一个随机操作符
if (i != 0) {
infixExpList.push(operates[r.nextInt(operates.length)]);
}
infixExpList.push(new Number(this.range));
}
if (containParentheses && this.count > 2) {
int j = r.nextInt(2 * this.count - 4); // 左括号的位置应小于2*count-4
// 左括号的位置应该为偶数并且非零
if (j % 2 != 0 && j != 0) {
j++;
}
infixExpList.add(j, '(');
infixExpList.add(2 * this.count - r.nextInt(this.count - 1 - j / 2) * 2, ')');
}
// 括号不能括整个表达式
if(infixExpList.getFirst().equals('(') && infixExpList.getLast().equals(')')) {
infixExpList.removeLast();
infixExpList.removeFirst();
}
}
/**
* 中缀转后缀
*/
public void infixToSuffix() {
// 后缀表达式
suffixExpList = new LinkedList<>();
// 操作符栈
LinkedList<Character> s = new LinkedList<>();
int size = infixExpList.size();
for (int i = 0 ; i < size ; i++) {
Object e = infixExpList.get(i);
// 若e的类是Character,即字符
if (e.getClass() == Character.class) {
char tmp;
char ch = (Character) e;
switch (ch) {
case '(':
s.push(ch);
break;
case '+':
case '-':
while (!s.isEmpty()) {
tmp = s.pop();
if (tmp == '(') {
s.push('(');
break;
}
suffixExpList.push(tmp);
}
s.push(ch);
break;
case '×':
case '÷':
while (!s.isEmpty()) {
tmp = s.pop();
if (tmp == '+' || tmp == '-' || tmp == '(') {
s.push(tmp);
break;
} else {
suffixExpList.push(tmp);
}
}
s.push(ch);
break;
case ')':
while (!s.isEmpty()) {
tmp = s.pop();
if (tmp == '(') {
break;
} else {
suffixExpList.push(tmp);
}
}
break;
}// switch
} else {
suffixExpList.push(e);
} // if
} // for
while (!s.isEmpty()) {
suffixExpList.push(s.pop());
}
Collections.reverse(suffixExpList);
}
/**
* 计算后缀
*
* @throws Exception
*/
public void suffixToArithmetic() throws Exception {
// 操作数栈
LinkedList<Number> numberStack = new LinkedList<>();
int size = suffixExpList.size();
for (int i = 0 ; i < size ; i++) {
Object e = suffixExpList.get(i);
if (e.equals('+') || e.equals('-') || e.equals('×') || e.equals('÷')) {
// char型
char ch = (Character) e;
Number y = numberStack.pop();
Number x = numberStack.pop();
// z = x (操作符) y
Number z = null;
switch (ch) {
case '+':
z = x.plus(y);
break;
case '-':
z = x.subtract(y);
if (z == null) {
result = null;
return;
}
break;
case '×':
z = x.multiply(y);
break;
case '÷':
z = x.divide(y);
break;
}
numberStack.push(z);
} else {
// Number类
numberStack.push((Number) e);
}
}
result = numberStack.pop();
}
public Number getResult() throws Exception {
if (isCalculated) {
// 如果计算过一次了
return result;
} else {
// 转后缀,同时suffixExpList变成非null
infixToSuffix();
// 计算
suffixToArithmetic();
// isCalculated为计算标记,记录是否计算过
isCalculated = true;
// 自然数、真分数、真分数分母 <range
if (result != null
&& (result.value[Number.INTEGRAL_NUMBER_PART] >= range || result.value[Number.DENOMINATOR_PART] >= range) ) {
result = null;
}
return result;
}
}
@Override
public String toString() {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for (Object instance : infixExpList) {
sb.append(instance.toString() + " ");
}
return sb.append(" = ").toString();
}
}
思路:
- 用随机数控制运算符的个数
- 对表达式随机插入括号,如果括号涵括了整条表达式,则此条表达式不合格舍去,并重新生成
- 中缀转后缀,后缀求结果,计算过程中,若出现负数,直接舍弃掉,再生成一条
Main函数与文件IO
public class Main {
private static final Random r = new Random();
private static final int OPERAND_MIN_COUNT = 2;
private static final int OPERAND_MAX_COUNT = 4;
private static final int PROBLEM_DEFAULT_COUNT = 100;
private static final String NUMBER_PATTERN = "^[1-9]{1}\\d*$";
private static final File EXERCISES_FILE = new File("./Exercises.txt");
private static final File ANSWERS_FILE = new File("./Answers.txt");
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
int range = 0, count = 0;
String exerciseFilename = null, answerFilename = null;
for (int i = 0 ; i < (args.length - 1) ; i++) {
String arg = args[i];
switch (arg) {
case "-r":
if (Pattern.matches(NUMBER_PATTERN, args[i + 1])) {
range = Integer.parseInt(args[i + 1]);
}
break;
case "-n":
if (Pattern.matches(NUMBER_PATTERN, args[i + 1])) {
count = Integer.parseInt(args[i + 1]);
}
break;
case "-e":
exerciseFilename = args[i + 1];
break;
case "-a":
answerFilename = args[i + 1];
break;
}
}
// 对答案
if (exerciseFilename != null || answerFilename != null) {
if (exerciseFilename == null) {
System.out.println("缺少-e参数,应提供形如" + EXERCISES_FILE.getName() + "的参数");
}
if (answerFilename == null) {
System.out.println("缺少-a参数应提供形如" + ANSWERS_FILE.getName() + "的参数");
}
checkAnswer(exerciseFilename, answerFilename);
return;
}
if (range == 0) {
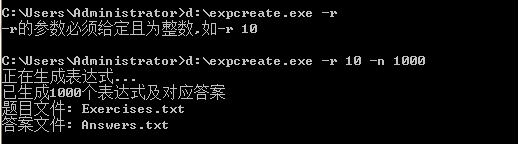
System.out.println("-r的参数必须给定且为整数,如-r 10");
return;
}
if (range > 20) {
System.out.println("-r的参数必须小于等于20,否则太为难小学生了");
return;
}
if (count == 0) {
count = PROBLEM_DEFAULT_COUNT;
}
System.out.println("正在生成表达式...");
HashMap<String, HashSet<Expression>> map = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0 ; i < count ;) {
Expression exp = new Expression(OPERAND_MIN_COUNT + r.nextInt(1 + OPERAND_MAX_COUNT - OPERAND_MIN_COUNT), range);
Number result = exp.getResult();
// 若计算出一个正确的result
if (result != null ) {
// 若对应result的位置为空
if(map.get(result.toString()) == null) {
map.put(result.toString(), new HashSet<>());
}
Set<Expression> expSet = map.get(result.toString());
// 若expSet没有这个exp
if(!expSet.contains(exp)) {
expSet.add(exp);
++i;
}
}
}
writeToLocal(map);
System.out.println("已生成" + count + "个表达式及对应答案");
System.out.println("题目文件: " + EXERCISES_FILE.getName());
System.out.println("答案文件: " + ANSWERS_FILE.getName());
}
private static void writeToLocal(HashMap<String, HashSet<Expression>> map) throws Exception {
deleteFile(EXERCISES_FILE, ANSWERS_FILE);
BufferedWriter ebos = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(EXERCISES_FILE));
BufferedWriter abos = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(ANSWERS_FILE));
int i = 1;
for (String result : map.keySet()) {
Set<Expression> expSet = map.get(result);
for(Expression exp : expSet) {
String exercise = "" + i + ". " + exp.toString();
String answer = "" + i + ". " + result.toString();
ebos.write(exercise);
abos.write(answer);
ebos.newLine();
abos.newLine();
i++;
}
}
// 答案文件写入完毕,设置只读
ANSWERS_FILE.setReadOnly();
ebos.close();
abos.close();
}
/**
*
* @param exerciseFilename 当前目录下的题目文件名(含后缀)
* @param answerFilename 当前目录下的答案文件名(含后缀)
* @throws FileNotFoundException
*/
private static void checkAnswer(String exerciseFilename, String answerFilename) throws Exception {
File exerciseFile = new File(exerciseFilename);
File answerFile = new File(answerFilename);
if (isExists(exerciseFile, answerFile)) {
BufferedReader ebr = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(exerciseFile));
BufferedReader abr = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(answerFile));
// correct正确的题目数,wrong错误的题目数
int correct = 0;
int wrong = 0;
List<String> correctNumberList = new ArrayList<>();
List<String> wrongNumberList = new ArrayList<>();
String exerciseLine;
String answerLine;
while ((exerciseLine = ebr.readLine()) != null && (answerLine = abr.readLine()) != null) {
String exerciseAnswer = exerciseLine.substring(1 + exerciseLine.indexOf('=')).trim();
String realAnswer = answerLine.substring(1 + answerLine.indexOf('.')).trim();
if (exerciseAnswer.equals(realAnswer)) {
++correct;
correctNumberList.add(exerciseLine.substring(0, exerciseLine.indexOf('.')));
} else {
++wrong;
wrongNumberList.add(answerLine.substring(0, answerLine.indexOf('.')));
}
}
System.out.println("Correct: " + correct + " (" + Arrays.toString(correctNumberList.toArray()).replaceAll("\\[|\\]", "") + ")");
System.out.println("Wrong: " + wrong + " (" + Arrays.toString(wrongNumberList.toArray()).replaceAll("\\[|\\]", "") + ")");
ebr.close();
abr.close();
}
}
private static void deleteFile(File... files) {
for (File file : files) {
if (file.exists()) {
file.delete();
}
}
}
private static boolean isExists(File... files) {
for (File file : files) {
if (!file.exists()) {
System.out.println(file.getAbsolutePath() + "不存在");
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
思路:
- 判断一个result相等的表达式中的所有操作数是否重复,若操作数都相同则舍弃该表达式,“完美”实现查重功能(懒人方法,接地气)
- 文件IO:老一套了,懂的都懂,不懂就学,形而上学,不行退学
程序测试截图:
1.生成1000条数值在10以内的表达式
2.-r参数大于20则会报错

3.在Exercises文件中几道表达式添加答案,其中11,24为正确答案,将Exercises与正确答案Answers对比


4.测试生成一万条表达式





