wordcount
Github项目地址:https://github.com/454469625/SoftwareEngineering
题目描述
Word Count
1. 实现一个简单而完整的软件工具(源程序特征统计程序)。
2. 进行单元测试、回归测试、效能测试,在实现上述程序的过程中使用相关的工具。
3. 进行个人软件过程(PSP)的实践,逐步记录自己在每个软件工程环节花费的时间。
WC 项目要求
wc.exe 是一个常见的工具,它能统计文本文件的字符数、单词数和行数。这个项目要求写一个命令行程序,模仿已有wc.exe 的功能,并加以扩充,给出某程序设计语言源文件的字符数、单词数和行数。
实现一个统计程序,它能正确统计程序文件中的字符数、单词数、行数,以及还具备其他扩展功能,并能够快速地处理多个文件。
具体功能要求:
程序处理用户需求的模式为:
wc.exe [parameter] [file_name]
基本功能列表:
wc.exe -c file.c //返回文件 file.c 的字符数
wc.exe -w file.c //返回文件 file.c 的词的数目
wc.exe -l file.c //返回文件 file.c 的行数
扩展功能:
-s 递归处理目录下符合条件的文件。(引用他人博客并自己加以理解,未能自己实现)
-a 返回更复杂的数据(代码行 / 空行 / 注释行)。(引用他人博客并加以理解,非自己实现)
支持各种文件的通配符(*,?)(同引用他人博客,未能自己实现)
高级功能:
-x 参数。这个参数单独使用。如果命令行有这个参数,则程序会显示图形界面,用户可以通过界面选取单个文件,程序就会显示文件的字符数、行数等全部统计信息。(未完成)
需求举例:
wc.exe -s -a *.c
返回当前目录及子目录中所有*.c 文件的代码行数、空行数、注释行数。
解题思路:
1.学习java的文件IO以及与String相关的java类的使用
2.学习正则表达式,使用正则表达式来匹配空格,注释符号等
3.学习java文件转为exe的方法
主要代码:
1.main函数
package cn.lu.wordcount; import cn.lu.wordcount.CountUtils; import java.io.*; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Scanner; public class Main{ private static boolean isCountchar = false; private static boolean isCountword = false; private static boolean isCountline = false; private static boolean isRecursion = false; private static boolean isCountdiffline = false; //利用arraylist存储符合条件的文件的绝对路径 private static ArrayList<String> fileList = new ArrayList<String>(); private static Scanner scanner; public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException,ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException{ /*此处在exe中测试出错,因此改用另一种方法,用scanner //此处args似乎越界了也许我应该给它分配一个空间? //args = new String[2]; //运行报错了但是测试可以通过 //默认最后一个参数为路径名 String path = args[args.length-1]; CountUtils countUtils = new CountUtils(); //判断需要执行的功能 for(int i=0; i<args.length-1; i++){ if(args[i].equals("-c")){ isCountchar = true; } if(args[i].equals("-w")){ isCountword = true; } if(args[i].equals("-l")){ isCountline = true; } if(args[i].equals("-s")){ isRecursion = true; } if(args[i].equals("-a")){ isCountdiffline = true; } } */ //方法二,用scanner获取输入 //switch匹配字符串好像只在1.7版本以上才可以 CountUtils countUtils = new CountUtils(); String opera = null; String path = null; scanner = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("请输入你要执行的操作:"); opera = scanner.nextLine(); System.out.println("请输入你要操作的文件绝对路径:"); path = scanner.nextLine(); switch (opera) { case "-c": isCountchar = true; break; case "-w": isCountword = true; break; case "-l": isCountline = true; break; case "-s": isRecursion = true; break; case "-a": isCountdiffline = true; break; default: System.out.println("操作不存在."); } //获取目录名 //split 里面的参数是正则表达式,在Java里面用字符串表示正则表达式时, //反斜杠是转义符,表示一个反斜杠时,要在前面加一个斜杠,即 \\ 表示一个斜杠。 //所以此处split中的\\\\表示\\用于分割文件路径 //此处的一系列操作是为了获取所给文件路径的目录,即将路径最后的文件名删去 String paths[] = path.split("\\\\"); StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); for(int i=0; i<paths.length-1; i++){ if(i==paths.length-2){ sb.append(paths[i]); }else{ sb.append(paths[i] + "\\"); } } String dirName = sb.toString(); //File(String pathname)通过给定路径名字符串转换为抽象路径名来创建一个新File实例 File file = new File(dirName); if (!file.isDirectory()){ System.out.println("路径错误!"); } String fileName = paths[paths.length - 1]; //对文件名通配符处理 //replaceAll() 方法使用给定的参数 replacement 替换字符串所有匹配给定的正则表达式的子字符串。 //在 Java中,\\ 表示:我要插入一个正则表达式的反斜线,所以其后的字符具有特殊的意义 fileName = fileName.replaceAll("\\*","\\.+").replaceAll("\\?","\\."); //若IS_RECURSION,则使用递归获取文件名(包括子目录),否则只获取当前目录下符合条件的文件名 if (isRecursion){ countUtils.getRecursionFiles(dirName, fileName); }else{ countUtils.getFiles(dirName,fileName); } fileList = countUtils.fileList; //遍历fileList,对每一个文件使用选择的功能 for (String fList : fileList) { System.out.println("文件路径为:"+fList); if (isCountchar){ countUtils.countChar(fList); } if (isCountword){ countUtils.countWord(fList); } if (isCountline){ countUtils.countLine(fList); } if (isCountdiffline){ countUtils.countDiffline(fList); } } } }
2.工具类
package cn.lu.wordcount; import java.io.*; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.regex.Matcher; import java.util.regex.Pattern; /** * 部分引用:https://www.cnblogs.com/yw0219/p/8047938.html,https://www.cnblogs.com/happyOwen/p/9646411.html * */ public class CountUtils { //实现-c功能 利用BufferedReader整行读取统计字符数 public int countChar(String path){ File file = new File(path); BufferedReader br = null; String line; int charCount = 0; try { br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(file)); while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) { char[] chars = line.toCharArray(); for (int i = 0; i < chars.length; i++) { //Character 类用于对单个字符进行操作 //若不是空格,则字符数加1 if (!Character.isWhitespace(chars[i])) { charCount++; } } } System.out.println("the charCount is:" + charCount); br.close(); } catch (Exception e) { System.out.println(path+"文件名错误"); } return charCount; } //实现-w功能 //统计英文单词数 //先用Bufferedreader整行读取,然后添加到StringBuffer中, //将StringBuffer转化为字符串后,然后将非英文字符替换为空格,再根据空格分割 public int countWord(String path) { BufferedReader br = null; String line; String[] strings; StringBuffer sbf = new StringBuffer(); int wordCount = 0; String reg = "\\s+"; try { br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(path)); while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) { sbf.append(line); } //将不是英文字母的字符替换成空格 String s = sbf.toString().replaceAll("[^A-Za-z]", " "); strings = s.split(reg); wordCount = strings.length; System.out.println("the wordcount is;"+wordCount); br.close(); }catch (Exception e){ System.out.println(path+"文件名错误"); } return wordCount; } //-l 统计总行数 public int countLine(String path) { BufferedReader br = null; String line; int lineCount = 0; try { br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(path)); while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) { lineCount++; } System.out.println("the lineCount is:"+lineCount); br.close(); }catch (Exception e){ System.out.println(path+"文件名错误"); } return lineCount; } //-a 统计注释行、空行、代码行 public void countDiffline(String path) { int annotationLineCount = 0; int codeLineCount = 0; int spaceLineCount = 0; String line; BufferedReader br = null; //注释匹配器(匹配单行、多行、文档注释) Pattern annotationLinePattern = Pattern.compile("(//)|(/\\*)|(^\\s*\\*)|(^\\s*\\*+/)"); try { br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(path)); while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) { if (annotationLinePattern.matcher(line).find()) { //注释行 annotationLineCount++; } else if (line.matches("\\s*\\p{Graph}?\\s*")) { //空行 spaceLineCount++; } else { codeLineCount++; } } System.out.println("the nullLineNum is:" + spaceLineCount); System.out.println("the annotationLineNum is:" + annotationLineCount); System.out.println("the codeLineNum is:" + codeLineCount); br.close(); } catch (Exception e) { System.out.println(path+"文件名错误"); } } //用ArrayList存储符合条件的文件的绝对路径 public ArrayList<String> fileList = new ArrayList<String>(); //递归获取符合条件的文件的绝对路径(在Main.java中已经对fileName进行通配符处理) public void getRecursionFiles(String dirName, String fileName) { File file = new File(dirName); if (file.isDirectory()) { File[] files = file.listFiles(); if (files!=null){ for (File f : files) { //当file1仍然是目录时,递归调用此函数 if (f.isDirectory()) { getRecursionFiles(dirName+"\\"+f.getName(),fileName); }else{ //处理后的fileName作为匹配规则,对遍历的文件进行匹配 //pattern 对象是一个正则表达式的编译表示。Pattern 类没有公共构造方法。 // 要创建一个 Pattern 对象,必须首先调用其公共静态编译方法, // 它返回一个 Pattern 对象。该方法接受一个正则表达式作为它的第一个参数。 Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile(fileName); //Matcher 对象是对输入字符串进行解释和匹配操作的引擎。Matcher 也没有公共构造方法。 // 需要调用 Pattern 对象的 matcher 方法来获得一个 Matcher 对象 Matcher m = pattern.matcher(f.getName()); if (m.matches()) { fileList.add(dirName+"\\"+f.getName()); } } } } } } //非递归获取符合条件的文件的绝对路径(在Main.java中已对fileName进行通配符处理) //仅获取当前目录下符合条件的文件,并将其绝对路径添加到ArrayList public void getFiles(String dirName, String fileName) { File file = new File(dirName); if (file.isDirectory()) { File[] files = file.listFiles(); if (files != null) { for (File f : files) { if (!f.isDirectory()) { Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile(fileName); Matcher m = pattern.matcher(f.getName()); if (m.matches()) { fileList.add(dirName+"\\"+f.getName()); } } } } } } }
测试结果
1.空文件

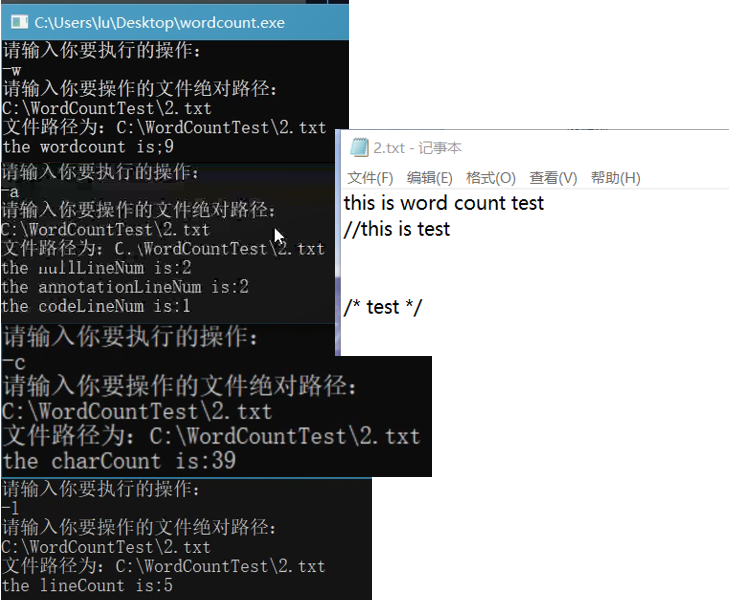
2.典型的文件
psp
|
PSP2.1 |
Personal Software Process Stages |
预估耗时(分钟) |
实际耗时(分钟) |
|
Planning |
计划 |
30 |
40 |
|
· Estimate |
· 估计这个任务需要多少时间 |
360 |
480 |
|
Development |
开发 |
120 |
150 |
|
· Analysis |
· 需求分析 (包括学习新技术) |
360 |
420 |
|
· Design Spec |
· 生成设计文档 |
10 |
10 |
|
· Design Review |
· 设计复审 (和同事审核设计文档) |
10 |
10 |
|
· Coding Standard |
· 代码规范 (为目前的开发制定合适的规范) |
10 |
30 |
|
· Design |
· 具体设计 |
40 |
75 |
|
· Coding |
· 具体编码 |
100 |
150 |
|
· Code Review |
· 代码复审 |
20 |
30 |
|
· Test |
· 测试(自我测试,修改代码,提交修改) |
30 |
60 |
|
Reporting |
报告 |
25 |
25 |
|
· Test Report |
· 测试报告 |
10 |
10 |
|
· Size Measurement |
· 计算工作量 |
5 |
5 |
|
· Postmortem & Process Improvement Plan |
· 事后总结, 并提出过程改进计划 |
15 |
30 |
|
合计 |
|
1055 |
1525
|
总结:由于实践次数少之又少,导致知识学了完全不会用,而且学的知识也有很大的漏洞,在实际设计的时候需要一直百度,即使自己明白怎么做,可是在开发的时候又有各种小问题,就连github的上传都要花半小时重新学习,希望以后自己能提高实践的次数,千里之行始于足下。



