linux文件系统初探--Day2(3)
大致搞清楚mount过程在内核中是怎样一个过程之后,今天来看看day2的super.c中都干了啥。
samplefs_fill_super
samplefs_fill_super在挂载时作为samplefs_mount->mount_nodev中的回调函数被调用,接下来看一下 mount_nodev:
mount_nodev
struct dentry *mount_nodev(struct file_system_type *fs_type,
int flags, void *data,
int (*fill_super)(struct super_block *, void *, int))
{
int error;
struct super_block *s = sget(fs_type, NULL, set_anon_super, flags, NULL);
if (IS_ERR(s))
return ERR_CAST(s);
error = fill_super(s, data, flags & SB_SILENT ? 1 : 0);
if (error) {
deactivate_locked_super(s);
return ERR_PTR(error);
}
s->s_flags |= SB_ACTIVE;
return dget(s->s_root);
}
可见mount_nodev的逻辑如下:
- 根据fs_type创建一个super_block;
- 调用fill_super填充这个super_block;
- 返回super_block的root dentry。
所以fill_super的功能顾名思义,就是fill mount_nodev 创建的super_block:
static int samplefs_fill_super(struct super_block *sb, void *data, int silent)
{
struct inode *inode;
struct samplefs_sb_info *sfs_sb;
/* 设置超级块中的部分成员 */
sb->s_maxbytes = MAX_LFS_FILESIZE; /* NB: may be too large for mem */
sb->s_blocksize = PAGE_CACHE_SIZE;
sb->s_blocksize_bits = PAGE_CACHE_SHIFT;
sb->s_magic = SAMPLEFS_MAGIC;
sb->s_op = &samplefs_super_ops;
sb->s_time_gran = 1; /* 1 nanosecond time granularity */
/* Eventually replace iget with:
inode = samplefs_get_inode(sb, S_IFDIR | 0755, 0); */
// 这里原来是iget,新内核中,iget被iget_locked代替
// 根据super_block和inode ino找到相应的inode,如果找不到就新建一个。
// 这个inode是特定文件系统的root inode
inode = iget_locked(sb, SAMPLEFS_ROOT_I);
if (!inode)
return -ENOMEM;
unlock_new_inode(inode);
// 将内存中的super_block的s_fs_info设为samplefs_sb_info
sb->s_fs_info = kzalloc(sizeof(struct samplefs_sb_info), GFP_KERNEL);
sfs_sb = SFS_SB(sb);
if (!sfs_sb) {
iput(inode);
return -ENOMEM;
}
// 根据root inode创建root dentry
sb->s_root = d_make_root(inode);
if (!sb->s_root) {
iput(inode);
kfree(sfs_sb);
return -ENOMEM;
}
// 设置 negative language support,这是samplefs_sb_info自带的成员。
/* below not needed for many fs - but an example of per fs sb data */
sfs_sb->local_nls = load_nls_default();
// samplefs 挂载时的多个选项,这部分在接下来详细讨论。
samplefs_parse_mount_options(data, sfs_sb);
/* FS-FILLIN your filesystem specific mount logic/checks here */
return 0;
}
samplefs_parse_mount_options
这个函数主要是解析mount命令的options,options由mount系统调用(用户态)传给ksys_mount,在ksys_mount中将参数从用户态转换为内核态。解析得到的数据都存放在samplefs_sb_info中。
static void
samplefs_parse_mount_options(char *options, struct samplefs_sb_info *sfs_sb)
{
char *value;
char *data;
int size;
if (!options)
return;
while ((data = strsep(&options, ",")) != NULL) {
if (!*data)
continue;
if ((value = strchr(data, '=')) != NULL)
*value++ = '\0';
// 这里strnicmp改为strncasecmp,一样的功能。
if (strncasecmp(data, "rsize", 5) == 0) {
if (value && *value) {
size = simple_strtoul(value, &value, 0);
if (size > 0)
sfs_sb->rsize = size;
}
} else if (strncasecmp(data, "wsize", 5) == 0) {
if (value && *value) {
size = simple_strtoul(value, &value, 0);
if (size > 0)
sfs_sb->wsize = size;
}
} /* else unknown mount option */
}
}
samplefs_put_super负责将super_block的私有信息(s_fs_info)从内存移除,我们看代码也确实是做了这样的操作。
现在,我们的samplefs可以执行mount过程了。
小结
其实day2的代码还是容易搞懂的,day2最难弄清楚的其实是mount的具体过程。
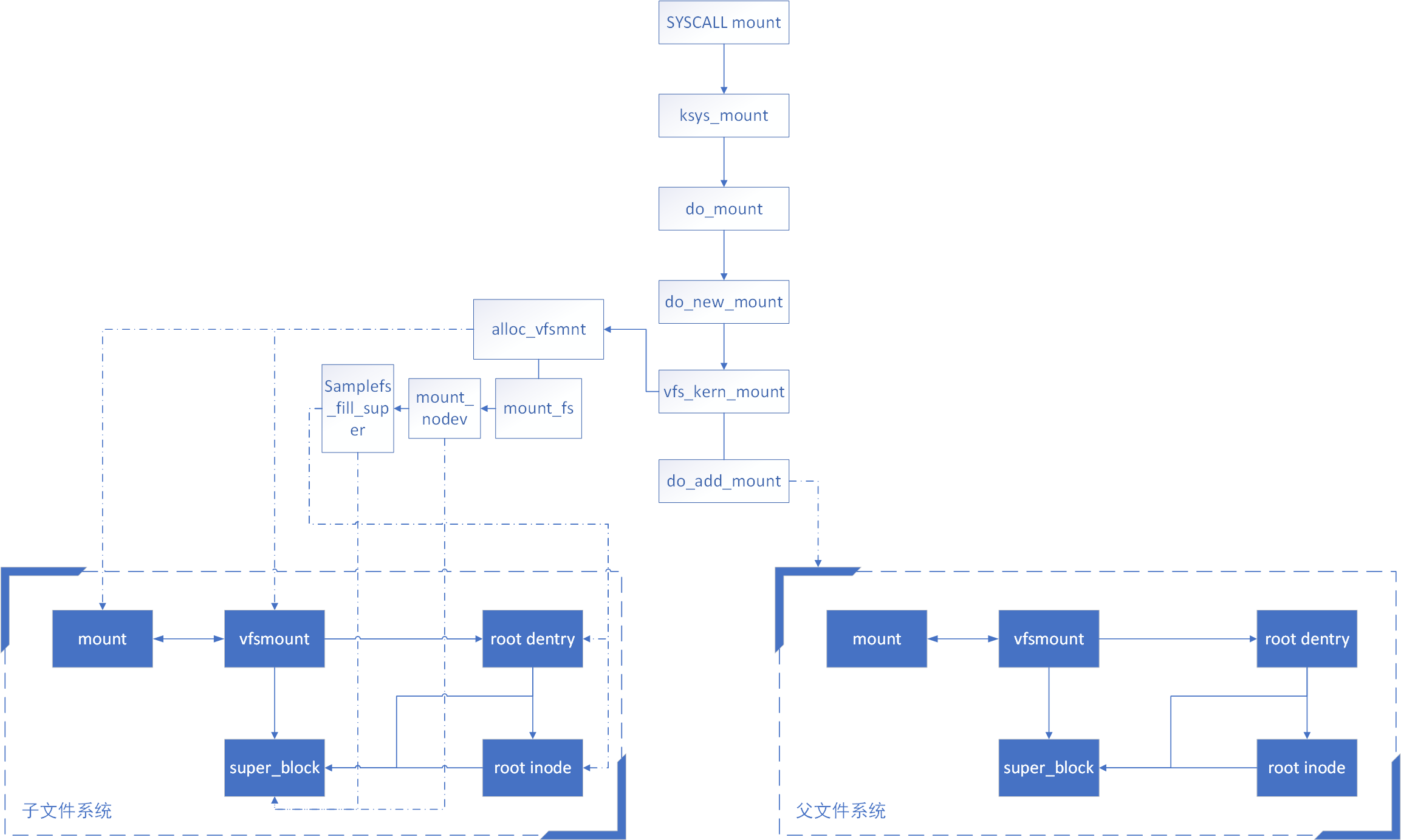
上图部分借鉴了这里
vfs_kern_mount负责完成mount过程中文件系统各种结构(mount、vfsmount、super_block、inode以及dentry)的创建与填写,do_add_mount负责将文件系统以及其root_dentry指向正确的父文件系统中dentry的位置。


