数据库(表的使用)
表关系(外键)
使用原因:1. 表不清晰、2.字段重复的写,浪费资源、3.兼容性差解决方法:使用外键,外键:其实就是通过字段可以查询到另外一张表的数据。
表关系
如何判断表关系:换位思考法。
表关系有:一对多、一对一、多对多、没有关系
一对多
以图书表和出版社表为例
先站在图书表的角度:一本书只能有一个出版社出版
站在出版社的角度:一个出版社可以出版多本图书
那么表关系就是:一对多
一对多的表关系外键字建在多的那一方
在SQL 层面建立一对多的关系
多表的创建,先创建表的基本字段,再添加外键字段
1.先创建出版表在创建图书表,因为图书表中有一个外键字段,和出版表的id相关联
# 1.创建出版表 create table publish(id int primary key auto_increment, title varchar(128));
# 2.创建图书表 create table book(id int primary key auto_increment, title varchar(128), price decimal(8,2), publish_id int, foreign key(publish_id) references publish(id) # 意思是:book表中的publish_id 和 publish表中的id是外键关系);
2. 往表中录入数据,先往出版社表中录入,在往book表中录入数据
不然会报错,如下图所示:
![]()
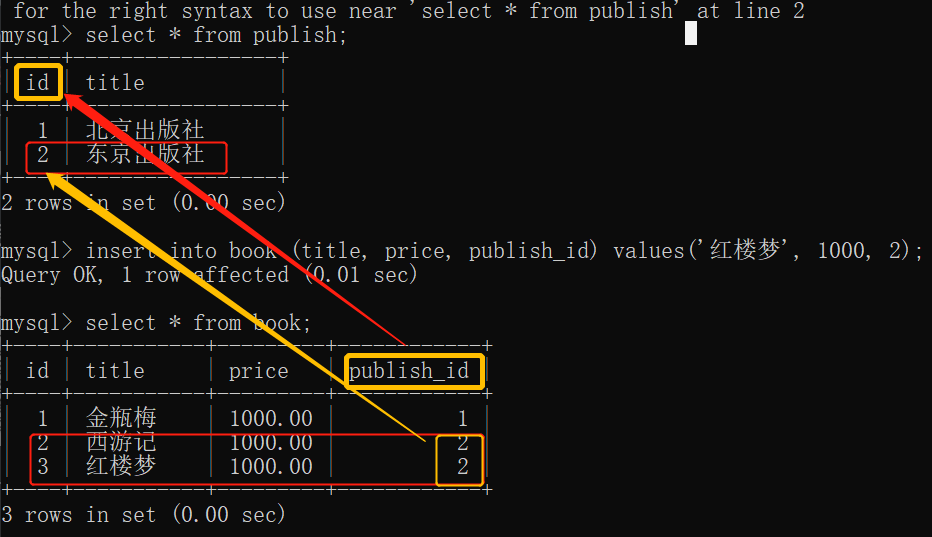
往publish表中录入数据
insert into publish (title) values ('北京出版社'); insert into publish (title) values ('东京出版社');
往book表中录入数据
insert into book (title, price, publish_id) values('水浒传', 1000, 1); insert into book (title, price, publish_id) values('西游记', 1000, 2);
insert into book (title, price, publish_id) values('红楼梦', 1000, 2);
外键约束
1. 在创建表的时候,应先创建被关联表(就是没有外键字段的表)
2. 在录入数据的时候,应先录入被关联表(没有外键字段的表)
3.在录入数据的时候,应录入被关联表中已经存在的值
4. 如果对被关联表中的数据进行修改或删除的时候,也需要把关联表中的数据也跟着修改或删除
改良版:
# 先创建出版表(被关联表) create table publish( id int primary key auto_increment, title varchar(128) );
# 创建图书表(关联表) create table book( id int primary key auto_increment, title varchar(128), price decimal(8, 2), publish_id int, foreign key(publish_id) references publish(id) # 意思是:book表中的publish_id和publish表中的id是外键关系 on update cascade # 级联更新 on delete cascade # 级联删除 );
因为创建了外键关系和级联更新、级联删除,所以两张表之间有了强制的约束关系,增强了表与表之间的强耦合度。
但在以后的实际项目中,大多数不建立这种强耦合关系,使用的是建立逻辑意义上的关系。
多对多的表关系
以图书表和作者表为例:
站在图书表的角度:一本书可以有多个作者
站在作者表的角度:一个作者可以写多本书
得出结论:此时表关系就是多对多
多对多的外键字段需要建立第三张表来存储
"""在SQL层面建立多对多的关系"""
先创建图书表:
create table book( id int primary key auto_increment, title varchar(128), price decimal(8, 2) );
再创建作者表
create table author( id int primary key auto_increment, name varchar(32) );
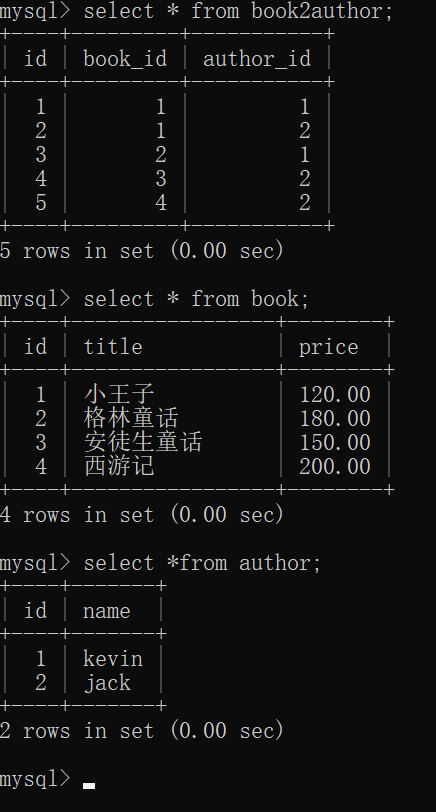
建立第三张表来保存两张表的关系
create table book2author(id int primary key auto_increment,
book_id int,author_id int,
foreign key(book_id) references book(id)
on update cascade
on delete casdate,
foreign kry(author_id) references author(id)
on update casdate
on delete casdate);
一对一的表关系
以作者表和作者详情表为例
站在作者表的角度:一个作者不能对应多个作者的详情
站在作者详情表的角度:一个作者详情信息不能对应多个作者
得出结论:表关系是一对一
一对一的外键字段可以建在任何一张表中,但是推荐建在查询频率较高的表中
在SQL层面建立一对一关系
# 创建作者表 create table author( id int primary key auto_increment, name varchar(32), author_detail_id int unique, foreign key (author_detail_id) references author_detail(id) );
# 创建作者详情表 create table author_detail( id int primary key auto_increment, addr varchar(32), height decimal(5,2) );
数据准备
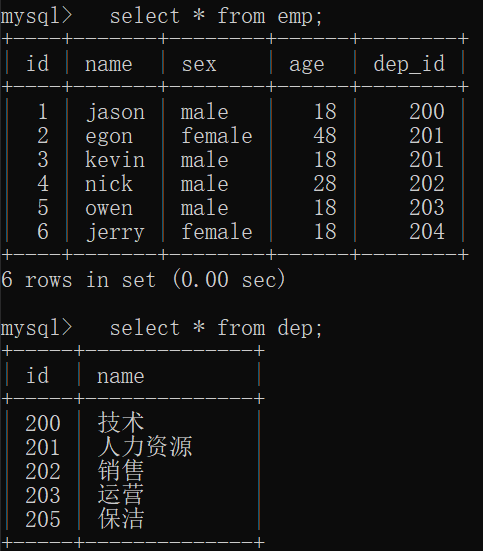
create table dep( id int primary key auto_increment, name varchar(20) );
create table emp( id int primary key auto_increment, name varchar(20), sex enum('male','female') not null default 'male', age int, dep_id int );
#插入数据 insert into dep values (200,'技术'), (201,'人力资源'), (202,'销售'), (203,'运营'), (205,'保洁'); insert into emp(name,sex,age,dep_id) values('jason','male',18,200),
('egon','female',48,201),
('kevin','male',18,201),
('nick','male',28,202),
('owen','male',18,203),
('jerry','female',18,204);
多表查询(核心)
多表:就是多张表连在一起使用
查询思路:
1. 子查询:
一条SQL语句的执行结果当成另外一条SQL语句的执行条件,即分步操作
问题:查看姓名为jason的部门名称:
1. 先查询部门id
select dep_id from emp where name='jason';
2. 拿着部门id作为条件,在去部门表中查询部门名称
select * from dep where id=200;
3. 把上述两条SQL语句合并为一条SQL语句
select * from dep where id= (select dep_id from emp where name='jason');
结果:
![]()
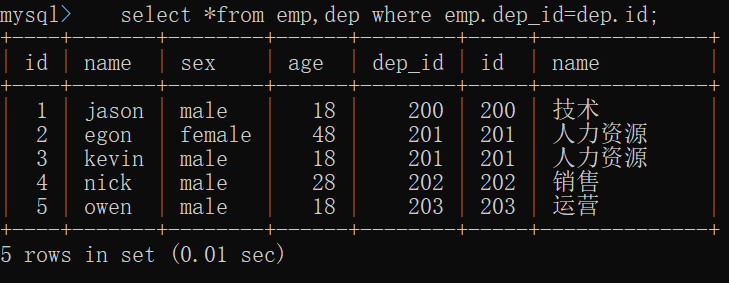
2. 连表查询
把多张实际存在的表按照表关系连成一张虚拟表(不是实际存在的表,而是临时在内存中存的)
select *from emp,dep where emp.dep_id=dep.id;
结果:
专业的连表语法:
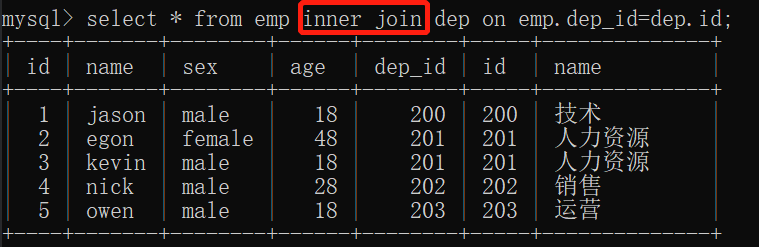
1.inner join: 内连接,数据只取两张表中共有的数据
select * from emp inner join dep on emp.dep_id=dep.id;
结果:
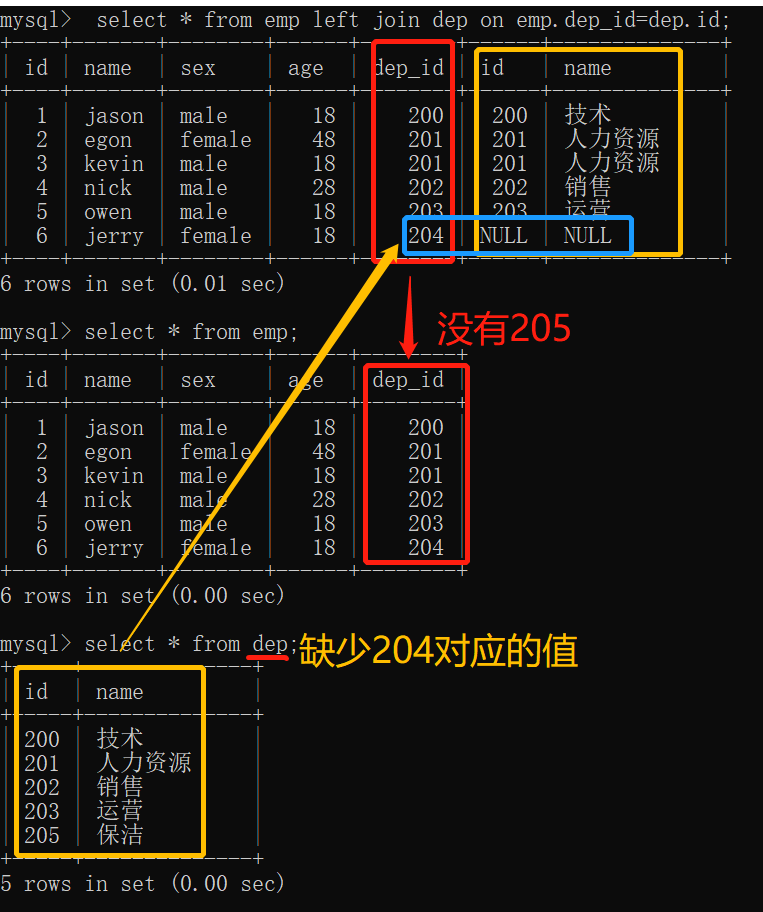
2.left join:左连接,数据以左表为准,展示左表所有的数据,右表没有的数据使用NULL填充
select * from emp left join dep on emp.dep_id=dep.id;
结果:
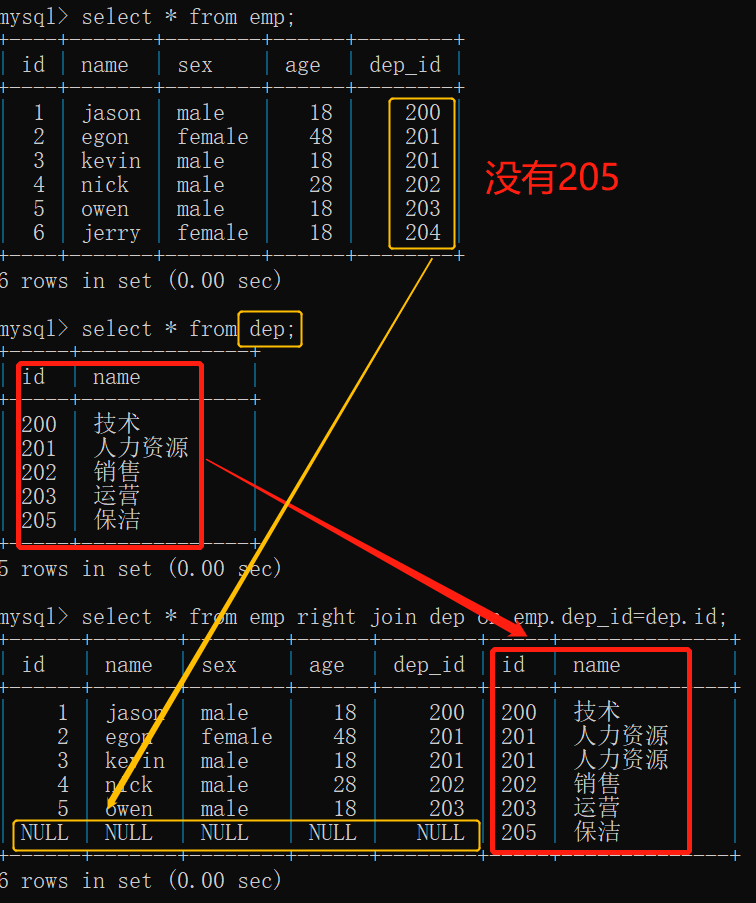
3.right join:右连接,数据以右表为准,展示右表所有的数据,左表没有的数据使用NULL填充
select * from emp right join dep on emp.dep_id=dep.id;
结果:
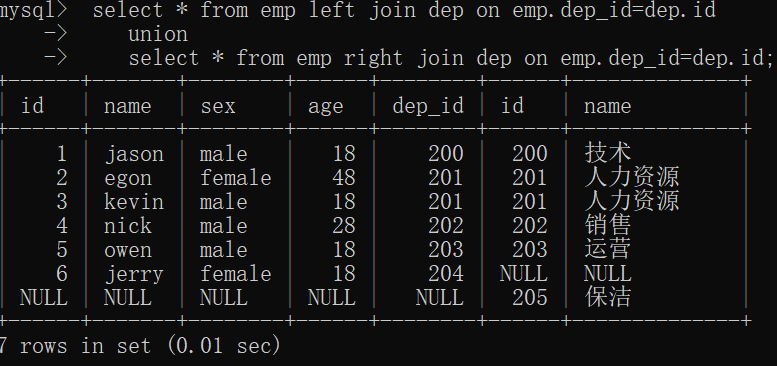
4.union: 连接多条SQL语句执行的结果
select * from emp left join dep on emp.dep_id=dep.id union select * from emp right join dep on emp.dep_id=dep.id;
结果:
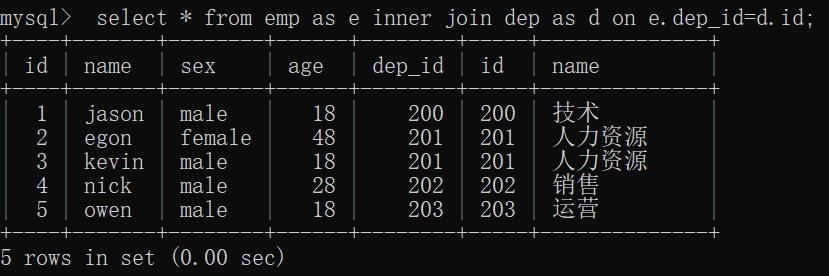
5. 还可以给表名起别名
select * from emp as e inner join dep as d on e.dep_id=d.id;
结果:
Navicat客户化工具
它不是免费的,是收费的
1. 破解2. 免费试用14天
去官网下载:https://www.navicat.com.cn/download/navicat-premium
写注释:
create table t1 ( id int primary key auto_increment comment '主键id', );
补充:
SQL语句的注释
1.-- 注释
2.# 注释
Python操作MySQL,对于Python这门语言来说,就是客户端。你使用Python操作mysql的时候,也要保证MySQL的服务端正常启动。
操作MySQL需要借助于第三方模块:1. pymysql 、2 mysqlclient(非常好用,一般情况下很难安装成功)、3. mysqldb(Django中使用)
操作:
1. 先连接MySQL的服务端
import pymysql # 1. 连接MySQL的服务端 conn = pymysql.connect( host='127.0.0.1', port=3306, user='root', passwd='root', db='db8', charset='utf8', autocommit=True )
2. 获取游标
cursor = conn.cursor(cursor=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor)
3. 执行SQL语句
# sql = 'select *from emp;' sql = "insert into emp (name, sex, age, dep_id, gender) values('aa', 'male', 10, 1, 0)"
4.开始执行
affect_rows = cursor.execute(sql) # 影响的行数 print(affect_rows) # 6行
注意:'''增加,修改,删除的数据的时候,需要二次提交(conn.commit()), 只有查询的时候不需要二次提交'''
5. 拿到具体的数据
print(cursor.fetchall()) # 取完所有的数据 # print(cursor.fetchone()) #取出一条数据 # print(cursor.fetchmany(3)) 一次取出三条数据
多表查询练习题
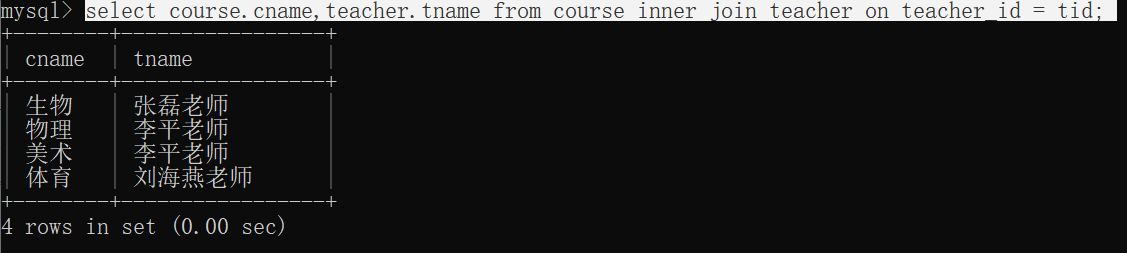
1、查询所有的课程的名称以及对应的任课老师姓名
select course.cname,teacher.tname from course inner join teacher on teacher_id = tid;
结果:
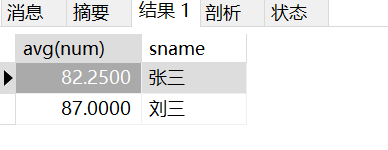
2、查询平均成绩大于八十分的同学的姓名和平均成绩
select avg(num),student.sname from student inner join score on student_id = student.sid group by student_id having avg(num) > 80;
结果:
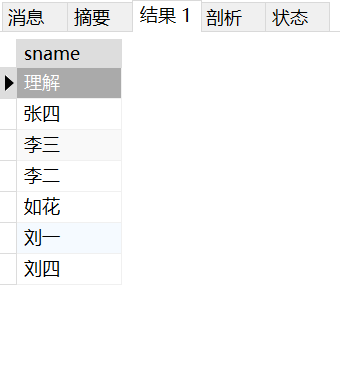
3、查询没有报李平老师课的学生姓名
SELECT student.sname from student INNER JOIN score on student.sid = score.sid WHERE score.course_id not in (SELECT course.cid from course INNER JOIN teacher on teacher_id = teacher.tid WHERE teacher.tname='李平老师');
结果:
4、查询挂科超过两门(包括两门)的学生姓名和班级
select sname,caption from student inner join class on class_id = class.cid where student.sid in (select student_id from score where num < 60 having COUNT(course_id)>=2);
结果:





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 25岁的心里话
· 闲置电脑爆改个人服务器(超详细) #公网映射 #Vmware虚拟网络编辑器
· 零经验选手,Compose 一天开发一款小游戏!
· 因为Apifox不支持离线,我果断选择了Apipost!
· 通过 API 将Deepseek响应流式内容输出到前端