AIM Tech Round 3 (Div. 1) D. Incorrect Flow
At the entrance examination for the magistracy of the MSU Cyber-Mechanics Department Sasha got the question about Ford-Fulkerson algorithm. He knew the topic perfectly as he worked with it many times on programming competition. As the task for the question he was given a network with partially build flow that he had to use in order to demonstrate the workflow of the algorithm. He quickly finished to write the text and took a look at the problem only to understand that the given network is incorrect!
Suppose you are given a directed graph G(V, E) with two special nodes s and t called source and sink. We denote as n the number of nodes in the graph, i.e. n = |V| and m stands for the number of directed edges in the graph, i.e. m = |E|. For the purpose of this problem we always consider node 1 to be the source and node n to be the sink. In addition, for each edge of the graph e we define the capacity function c(e) and flow function f(e). Function f(e) represents the correct flow if the following conditions are satisfied:
- For each edge
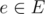 the flow is non-negative and does not exceed capacity c(e), i.e. 0 ≤ f(e) ≤ c(e).
the flow is non-negative and does not exceed capacity c(e), i.e. 0 ≤ f(e) ≤ c(e). - For each node
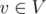 , that is not source or sink (v ≠ s and v ≠ t) the sum of flows of all edges going in v is equal to the sum of the flows among all edges going out from v. In other words, there is no flow stuck in v.
, that is not source or sink (v ≠ s and v ≠ t) the sum of flows of all edges going in v is equal to the sum of the flows among all edges going out from v. In other words, there is no flow stuck in v.
It was clear that as the exam was prepared last night and there are plenty of mistakes in the tasks. Sasha asked one of the professors to fix the network or give the correct task, but the reply was that the magistrate student should be able to fix the network himself. As the professor doesn't want the task to become easier, he asks Sasha to fix the network in a such way that the total number of changes is minimum possible. Sasha is not allowed to remove edges, add new ones or reverse the direction of existing edges. The only thing he is able to do is to change capacity function c(e) and flow function f(e). Moreover, all the values should remain non-negative integers. There is no requirement on the flow to be maximum in any sense.
Find the minimum possible total change of the functions f(e) and c(e) that Sasha has to make in order to make the flow correct. The total change is defined as the sum of absolute differences, i.e. if new functions are f * (e) and c * (e), then the total change is 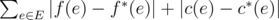 .
.
The first line of the input contains two integers n and m (2 ≤ n ≤ 100, 0 ≤ m ≤ 100) — the number of nodes and edges in the graph respectively. Each of the following m lines contains the description of the edges, consisting of four integers ui, vi, ci and fi (1 ≤ ui, vi ≤ n, ui ≠ vi, 0 ≤ ci, fi ≤ 1 000 000) — index of the node the edges starts from, the index of the node the edge goes to, current capacity and flow value.
Node number 1 is the source, and node number n is the sink. It's guaranteed that no edge goes to the source, and no edges starts in the sink.
Given graph contains no self-loops but may contain multiple edges.
Print one integer — the minimum total sum of changes that Sasha has to do in order to get the correct flow description.
2 1
1 2 2 1
0
2 1
1 2 1 2
1
3 3
1 2 1 1
2 3 2 2
1 3 3 3
1
4 2
2 3 1 1
3 2 1 1
0
In the first sample, the flow is initially correct. Note, that the flow is not maximum, but this is not required.
In the second sample, the flow value of the only edge is greater than its capacity. There are two ways to fix this: either increase the capacity up to 2 or reduce the flow down to 1.
In the third sample, there is only 1 unit of flow coming to vertex 2, but there are 2 units going out of it. One of the possible solutions is to reduce the value of the flow on the second edge by 1.
In the fourth sample, there is isolated circulation of flow, but this description is correct by definition.
与网络流斗智斗勇
题目的大概意思是给出一个有源汇网络,里面有一些边已经给出了流量,你可以用1的代价增加或者减少某条边1的流量,或者增加某条边1的容量,最小化使这个网络合法的代价
我一开始还以为可以线性规划水过去,直到发现虽然最优解里一定不会降低c,但是我们并不知道f是增大还是减小,所以没法表示收益函数
这个东西怎么乍一看和有下界网络流的网络流这么像,也是要把一个不满足流量守恒的网络转化为正常的网络,那就套用有下界网络流的方法来做
首先如果一条边的流量超过了它的流量,那一开始就把他的容量增加到它的流量,这部分代价是肯定要花的
新建一个超级源和一个超级汇
然后如果流进一个点的流量比流出的多c,从超级源向它连一条容量为c的边(和有上下界网络流的构图一样)
如果流进一个点的流量比流出的少c,从它向超级汇连一条容量为c的边
然后从原来的汇点向源点连一条INF的边
还不知道原图的边怎么处理,但是如果这个图流满了最大流,那么原图肯定流量守恒了
然后我们考虑原图中的边的处理
对于一条原图中的边,我们可以:
1、还没流满的,花费1的代价,顺着原来的方向流1流量、
2、已经流满的,花费2的代价,顺着原来的方向流1流量
3、还有流量的,花费1的代价,逆着原来的方向流1流量
注意对于我们之前因为f>c提高过容量的边,逆着流前f-c的流量费用是0,因为这部分代价之前已经付出过了
然后从超级源向超级汇跑费用流即可


1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <cstdlib> 3 #include <cstdio> 4 #include <algorithm> 5 #include <string> 6 #include <cstring> 7 #include <cmath> 8 #include <map> 9 #include <stack> 10 #include <set> 11 #include <vector> 12 #include <queue> 13 #include <time.h> 14 #define eps 1e-7 15 #define INF 0x3f3f3f3f 16 #define MOD 1000000007 17 #define rep0(j,n) for(int j=0;j<n;++j) 18 #define rep1(j,n) for(int j=1;j<=n;++j) 19 #define pb push_back 20 #define set0(n) memset(n,0,sizeof(n)) 21 #define ll long long 22 #define ull unsigned long long 23 #define iter(i,v) for(edge *i=head[v];i;i=i->nxt) 24 #define max(a,b) (a>b?a:b) 25 #define min(a,b) (a<b?a:b) 26 #define print_runtime printf("Running time:%.3lfs\n",double(clock())/1000.0) 27 #define TO(j) printf(#j": %d\n",j); 28 //#define OJ 29 using namespace std; 30 const int MAXINT = 100010; 31 const int MAXNODE = 300; 32 const int MAXEDGE = 2000; 33 char BUF, *buf; 34 int read() { 35 char c = getchar(); int f = 1, x = 0; 36 while (!isdigit(c)) {if (c == '-') f = -1; c = getchar();} 37 while (isdigit(c)) {x = x * 10 + c - '0'; c = getchar();} 38 return f * x; 39 } 40 char get_ch() { 41 char c = getchar(); 42 while (!isalpha(c)) c = getchar(); 43 return c; 44 } 45 //------------------- Head Files ----------------------// 46 47 int ans,n, m,cnt,dis[MAXNODE],q[MAXNODE*MAXNODE],SS=MAXNODE-2,TT=MAXNODE-1,out[MAXNODE],in[MAXNODE],d,inq[MAXNODE]; 48 struct edge { 49 int u, v, c, cost; 50 edge *nxt; 51 edge() {} 52 edge(int _u, int _v, int _c, int _cost, edge * _nxt): u(_u), v(_v), c(_c), cost(_cost), nxt(_nxt) {} 53 } mp[MAXEDGE], *head[MAXNODE],*from[MAXNODE]; 54 void addedge(int u, int v, int c, int cost) { 55 mp[cnt] = edge(u, v, c, cost, head[u]); 56 head[u] = &mp[cnt++]; 57 mp[cnt] = edge(v, u, 0, -cost, head[v]); 58 head[v] = &mp[cnt++]; 59 } 60 int spfa(int ss,int tt){ 61 memset(dis,INF,sizeof(dis)); 62 int *h=q,*t=q; 63 dis[ss]=0; 64 *t++=ss; 65 while(h!=t){ 66 int p =*h++; 67 inq[p]=0; 68 iter(i,p){ 69 if(i->c&&dis[i->v]>dis[p]+i->cost){ 70 dis[i->v]=dis[p]+i->cost; 71 from[i->v]=i; 72 if(!inq[i->v]){ 73 *t++=i->v; 74 inq[i->v]=1; 75 } 76 } 77 } 78 } 79 return dis[tt]!=INF; 80 } 81 edge *rev(edge *e){ 82 return &mp[(e-mp)^1]; 83 } 84 int extend(int ss,int tt){ 85 int cost = dis[tt],f=INF; 86 int p=tt; 87 while(p!=ss){ 88 f=min(from[p]->c,f); 89 p=from[p]->u; 90 } 91 p=tt; 92 while(p!=ss){ 93 from[p]->c-=f; 94 rev(from[p])->c+=f; 95 p=from[p]->u; 96 } 97 return cost*f; 98 } 99 int costflow(int ss,int tt){ 100 int ans=0; 101 while(spfa(ss,tt)){ 102 ans+=extend(ss,tt); 103 } 104 return ans; 105 } 106 void get_input(); 107 void work(); 108 int main() { 109 get_input(); 110 work(); 111 return 0; 112 } 113 void work() { 114 printf("%d\n",ans+costflow(SS,TT)); 115 } 116 void get_input() { 117 n = read(); m = read(); 118 rep0(i,m){ 119 int u=read(),v=read(),c=read(),f=read(); 120 in[v]+=f; 121 out[u]+=f; 122 if(f>c){ 123 ans+=f-c; 124 addedge(u,v,INF,2); 125 addedge(v,u,f-c,0); 126 addedge(v,u,c,1); 127 }else{ 128 addedge(u,v,c-f,1); 129 addedge(u,v,INF,2); 130 addedge(v,u,f,1); 131 } 132 } 133 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) { 134 if(in[i]>out[i]) addedge(SS,i,in[i]-out[i],0); 135 if(in[i]<out[i]) addedge(i,TT,out[i]-in[i],0); 136 } 137 addedge(n,1,INF,0); 138 }


