wait/notify的原理
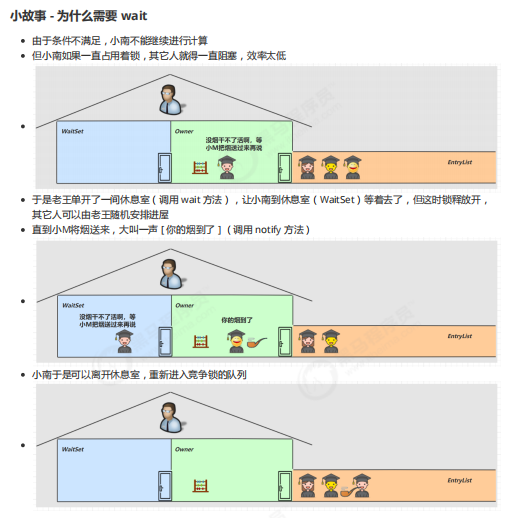
场景类比
wait/notify的原理
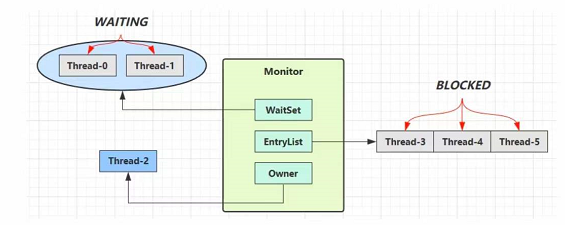
Owner线程发现条件不满足,调用wait方法,即可进入WaitSet变为WAITING
BLOCKED和WAITING的线程都处于阻塞状态,不占用CPU时间片
BLOCKED线程会在Owner线程释放锁时唤醒
WATING线程会在Owner线程调用notify和notifyAll时唤醒,但唤醒后并不意味着立刻获得锁,仍需进入EntryList重新竞争
wait/notify通讯demo
public class ThreadTest {
/**
* 共享对象 res
*/
class Res {
public String userName;
public char sex;
/**
* flag false 输入线程 输入值
* flag true 输出线程 输出值
*/
public boolean flag = false;
}
/**
* 第一次 输出xx,男
* 第二次 输出yy,女
* 第三次 输出xx,男
* 第四次 输出yy,女
*/
class InputThread extends Thread {
private Res res;
public InputThread(Res res) {
this.res = res;
}
@Override
public void run() {
int count = 0;
while (true) {
synchronized (res) {
if (res.flag) {
try {
res.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (count == 0) {
res.userName = "xx";
res.sex = '男';
} else {
res.userName = "yy";
res.sex = '女';
}
// 输出线程 输出值
res.flag = true;
// 唤醒输出线程
res.notify();
}
// 1%2 = 2%2 3%2 4%2=
count = (count + 1) % 2;
}
}
}
/**
* 输出的线程
*/
class OutPutThread extends Thread {
private Res res;
public OutPutThread(Res res) {
this.res = res;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
synchronized (res) {
if (!res.flag) {
// 如果 res.flag=false 则 输出的线程 主动释放锁 同时会阻塞该线程
try {
res.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println(res.userName + "," + res.sex);
// 输出完毕 交给我们的输入线程继续的输入
res.flag = false;
res.notify();;
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new ThreadTest().print();
}
public void print() {
// 全局对象
Res res = new Res();
// 输入线程
InputThread inputThread = new InputThread(res);
OutPutThread outPutThread = new OutPutThread(res);
inputThread.start();
outPutThread.start();
}
}
执行效果:
xx,男
yy,女
xx,男
yy,女
xx,男
yy,女
xx,男
yy,女
......


