程序与进程
概念:
进程:程序在计算机上的一次执行过程,执行中的程序。
进程是一个抽象概念,其本质是:
程序在地址空间中按照代码逻辑控制流执行
资源分配最小单位
进程和程序的区别:
进程是动态的,有声明周期的,一个进程只能对应一个程序。
程序是静态的,是一系列指令的集合,可以对应多个进程。
从程序到进程
- 内核将程序读入内存,为程序镜像分配内存空间。
- 内核为该进程分配进程标志符PID。
- 内核为该进程保存PID及相应的进程状态信息。
进程的状态:
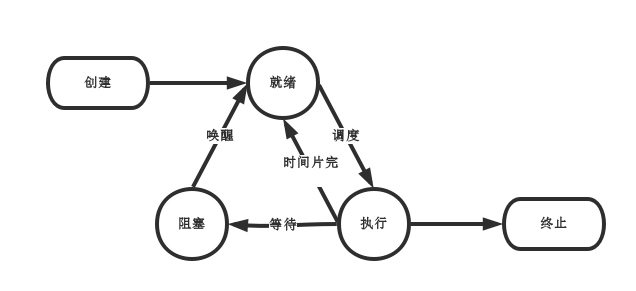
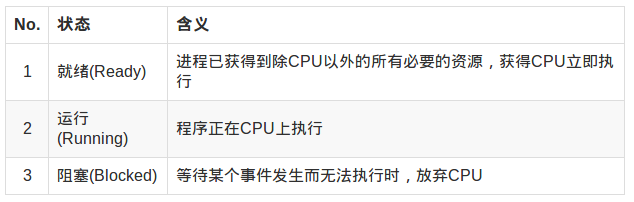
Linux中查看进程的命令:ps / pstree / top
ps命令
查看某进程
通过进程PID查看:ps -p 进程PID
通过命令行查看:ps -C 命令行
top命令
各列表示说明:
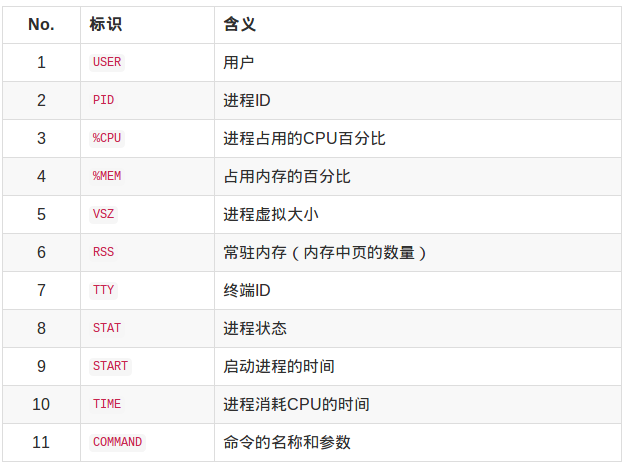
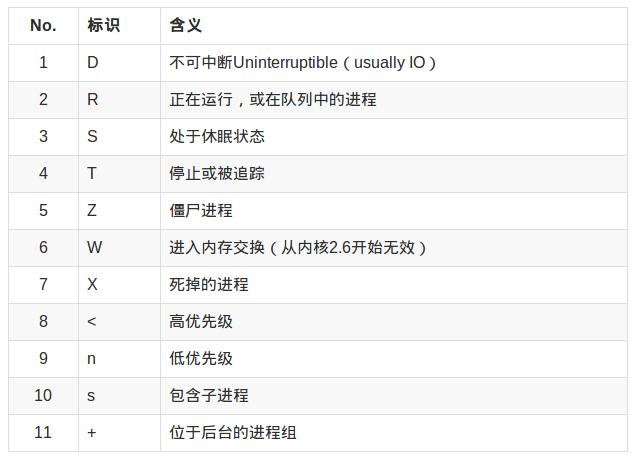
进程状态标识:
pstree命令
以树状图的方式展现进程之间的派生关系
安装: yum install psmisc
Linux下进程的相关操作
杀死进程:kill 进程标识符PID
获取进程PID:
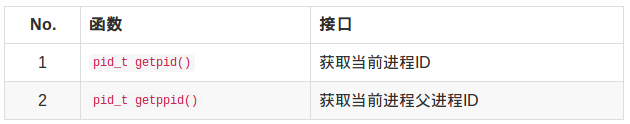
【示例】
1 #include <unistd.h> 2 #include <iostream> 3 using namespace std; 4 5 int main() 6 { 7 cout << "PID: " << getpid()<< "\t" << "PPID: " << getppid() << endl; 8 return 0; 9 }
创建进程
1、分叉函数 pid_t fork()
返回值:失败,返回-1
子进程逻辑控制流 返回0
父进程逻辑控制流 返回子进程的PID
特点:调用一次返回两次,相同但是独立的地址控件,并发执行,共享文件
【示例】
1 #include <unistd.h> 2 #include <iostream> 3 using namespace std; 4 5 //相同但是独立的地址控件&&并发执行 6 int i = 100; 7 int main() 8 { 9 int j = 100; 10 11 pid_t pid = fork();//创建进程 12 fork(); 13 if(pid == 0) 14 { 15 int k; 16 for(k = 0; k < 10000; k++) 17 { 18 cout << "this is child:" << ++i << "\t" << ++j << endl; 19 } 20 } 21 else 22 { 23 int k; 24 for(k = 0; k < 10000; k++) 25 { 26 cout << "this is father:" << --i << "\t" << --j << endl; 27 } 28 } 29 return 0; 30 }
1 #include <unistd.h> 2 #include <stdio.h> 3 #include <iostream> 4 using namespace std; 5 //共享文件 6 7 int i = 100; 8 int main() 9 { 10 int j = 100; 11 FILE * fd = fopen("./test", "w+"); 12 pid_t pid = fork(); 13 14 if(pid == 0) 15 { 16 int k; 17 for(k = 0; k < 10000; k++) 18 fprintf(fd, "this is child i: %d \t j: %d\n", ++i, ++j); 19 } 20 else 21 { 22 int k; 23 for(k = 0; k < 10000; k++) 24 fprintf(fd, "this is father i: %d \t j: %d\n", --i, --j); 25 } 26 27 return 0; 28 }
2 执行函数 exec()
分类:

exec函数组名字规律:
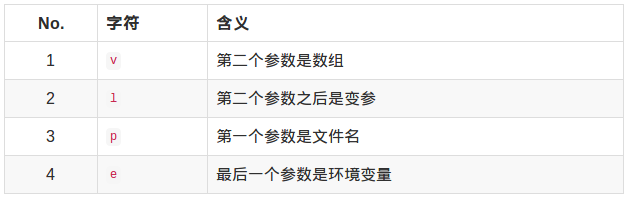
返回值:
成功:无返回值 失败:返回-1
特点:一次调用,失败返回-1, 成功则执行新的进程(PID不变, 地址空间内容变化)。
【示例】
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 #include <unistd.h> 4 #include <iostream> 5 using namespace std; 6 7 extern char ** environ; 8 int main(int argc, char** argv) 9 { 10 cout << argv[0] << " PID:" << getpid() << endl; 11 //execlp("ls", "ls", "-l", 0); 12 13 char * args[] = {"ls", "-l", 0}; 14 execve("/bin/ls", args, environ); 15 //cout << argv[0] << " PID:" << getpid() << endl; 16 return 0; 17 }
本质:覆盖程序
3、系统函数 int system(shell字符串)
返回值:
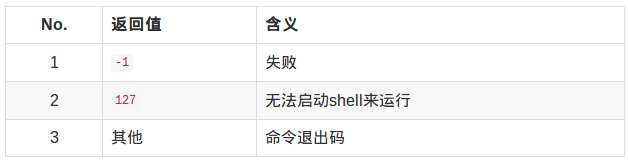
特点:一次调用,一次返回
【示例】
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 #include <unistd.h> 4 #include <iostream> 5 using namespace std; 6 7 int main() 8 { 9 cout << "PID: " << getpid() << endl; 10 system("sleep 3&"); 11 cout << "PID: " << getpid() << endl; 12 return 0; 13 }
结束进程:
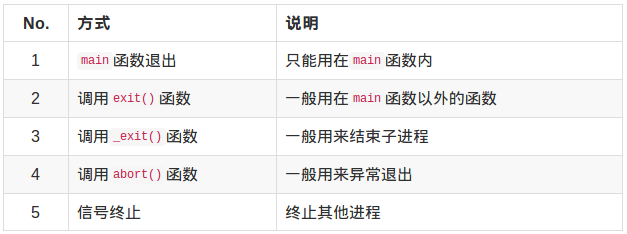
【示例】
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 #include <unistd.h> 4 #include <iostream> 5 using namespace std; 6 7 int main() 8 { 9 cout << "PID : " << getpid() << " PPID : " << getppid() << endl; 10 exit(EXIT_FAILURE); 11 //abort(); 12 return 0; 13 }
停止进程
休眠:
int sleep(unsigned int secs)
参数
secs指定休眠的秒数,-1表示永久休眠
返回值
未休眠的秒数
特性
如果没有信号中断,休眠指定秒数返回0,否则马上返回未休眠的秒数。
【示例】
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <unistd.h> 3 #include <time.h> 4 #include <strings.h> 5 #include <iostream> 6 using namespace std; 7 8 int main() 9 { 10 int i = 0; 11 for(;;) 12 { 13 time_t t; 14 time(&t); 15 16 struct tm * ptm = gmtime(&t); 17 char buf[BUFSIZ]; 18 19 bzero(buf, BUFSIZ); 20 21 strftime(buf, BUFSIZ, "%P %T", ptm); 22 cout << buf << endl; 23 24 fflush(stdout); 25 sleep(1); 26 } 27 28 return 0; 29 }
暂停:
int pause()
返回值
总是-1
特性
如果程序没有处理信号,直接中断,执行默认信号处理,程序后续代码不再执行。
如果程序存在信号处理,执行信号处理后,执行后续代码。
等待信号
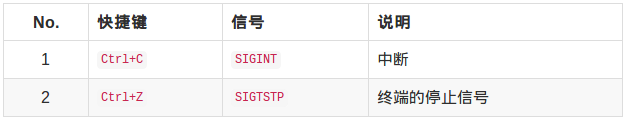
【示例】
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <signal.h> 3 #include <unistd.h> 4 #include <iostream> 5 using namespace std; 6 7 void test(int sig) 8 { 9 cout << "revc a signal" << sig << endl; 10 } 11 int main() 12 { 13 signal(SIGINT, test); 14 cout << "before pause" << endl; 15 pause(); 16 cout << "after pause" << endl; 17 18 return 0; 19 }
等待:
1 pid_t wait(int* status):等价pid_t waitpid(-1,stauts,0) 2 pid_t waitpid(pid_t pid,int * status,int options)
参数:

返回值:
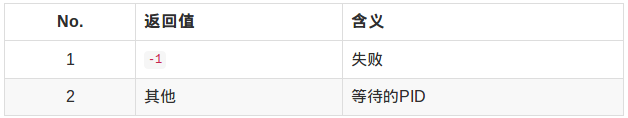
正常结束: WIFEXITED(status)

WTERMSIG(status)取得子进程因信号而中止的信号代码
一般会先用 WIFSIGNALED 来判断后才使用此宏
异常结束: WIFSIGNALED(status)
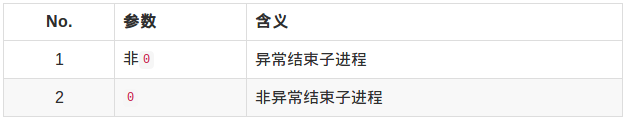
WTERMSIG(status)取得子进程因信号而中止的信号代码
一般会先用 WIFSIGNALED 来判断后才使用此宏
暂停: WIFSTOPPED(status)
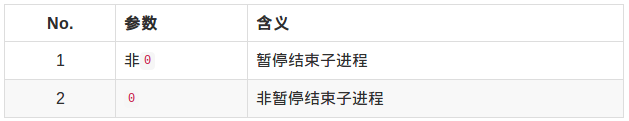
WSTOPSIG(status)取得引发子进程暂停的信号代码
一般会先用 WIFSTOPPED 来判断后才使用此宏。
【示例】父进程等待子进程退出
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 #include <unistd.h> 4 #include <wait.h> 5 #include <iostream> 6 using namespace std; 7 8 int main() 9 { 10 cout << "PID : " << getpid() << "PPID : " << getppid() << endl; 11 pid_t pid = fork(); 12 if(pid == 0) 13 { 14 sleep(2); 15 cout << "this is child" << endl; 16 cout << "res: " << pid << "PID : " << getpid() << "PPID : " << getppid() << endl; 17 } 18 else 19 { 20 cout << "this is father" << endl; 21 cout << "res: " << pid << "PID : " << getpid() << "PPID : " << getppid() << endl; 22 cout << "pid : " << waitpid(pid, NULL, 0) << "exit" << endl; 23 } 24 25 return 0; 26 }
更加安全的方式:
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 #include <unistd.h> 4 #include <wait.h> 5 #include <iostream> 6 using namespace std; 7 8 void handler(int sig) 9 { 10 int status; 11 pid_t cpid = wait(&status); 12 13 if(WIFEXITED(status)) 14 { 15 cout << "child exit by " << WEXITSTATUS(status) << endl; 16 } 17 if(WIFSIGNALED(status)) 18 { 19 cout << "child exit by signal" << WTERMSIG(status) << endl; 20 } 21 cout << "child " << cpid << " exit" << endl; 22 } 23 int main() 24 { 25 signal(SIGINT, handler); 26 cout << "PID : " << getpid() << "PPID : " << getppid() << endl; 27 pid_t pid = fork(); 28 if(pid == 0) 29 { 30 sleep(2); 31 cout << "this is child" << endl; 32 cout << "res: " << pid << "PID : " << getpid() << "PPID : " << getppid() << endl; 33 } 34 else 35 { 36 cout << "this is father" << endl; 37 cout << "res: " << pid << "PID : " << getpid() << "PPID : " << getppid() << endl; 38 cout << "leave : " << sleep(5)<< endl; 39 } 40 41 return 0; 42 }
如果不关心退出的情况:
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 #include <unistd.h> 4 #include <wait.h> 5 #include <iostream> 6 using namespace std; 7 8 void handler(int sig) 9 { 10 pid_t cpid = wait(NULL); 11 cout << "child " << cpid << " exit" << endl; 12 } 13 int main() 14 { 15 signal(SIGINT, handler); 16 cout << "PID : " << getpid() << "PPID : " << getppid() << endl; 17 pid_t pid = fork(); 18 if(pid == 0) 19 { 20 sleep(2); 21 cout << "this is child" << endl; 22 cout << "res: " << pid << "PID : " << getpid() << "PPID : " << getppid() << endl; 23 } 24 else 25 { 26 cout << "this is father" << endl; 27 cout << "res: " << pid << "PID : " << getpid() << "PPID : " << getppid() << endl; 28 //cout << "leave : " << sleep(5)<< endl; 29 } 30 31 return 0; 32 }
特殊进程
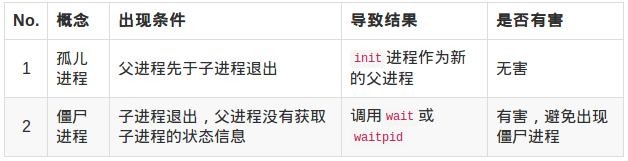
【示例】
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 #include <unistd.h> 4 #include <wait.h> 5 #include <iostream> 6 using namespace std; 7 8 void handler(int sig) 9 { 10 cout << "this is child exit" << sig << endl; 11 } 12 int main() 13 { 14 signal(SIGINT, handler); 15 cout << "PID : " << getpid() << "PPID : " << getppid() << endl; 16 pid_t pid = fork(); 17 if(pid == 0) 18 { 19 sleep(2); 20 cout << "this is child" << endl; 21 cout << "res: " << pid << "PID : " << getpid() << "PPID : " << getppid() << endl; 22 } 23 else 24 { 25 cout << "this is father" << endl; 26 cout << "res: " << pid << "PID : " << getpid() << "PPID : " << getppid() << endl; 27 for(;;); 28 } 29 30 return 0; 31 }

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号