Java暑期学习第二十二天日报
一、今日学习内容:
今天学习了8.1.1在Java中如何进行异常处理的内容和8.2用log4j记录异常日志信息的内容。
二、遇到的问题:
关于Java中的异常处理应用不够熟练,不了解具体应该应用到什么地方。对于此个问题,上网查找资料进行深入了解。
三、明日计划:
明天计划学习8.3的综合实例和8.5的课后习题。
今天学习的具体内容:
1.在Java中如何进行异常处理:
| try...catch...finally | 该语句用来捕获被命名为异常类的异常,并调用方法处理它。其中finally无论有无异常都会执行。 |
| 通过throws抛出异常 | 声明抛弃异常是在一个方法声明中的throws子句中指明的。[修饰符] 返回类型 方法名(参数1,参数2,....) throws 异常列表{} |
| 通过throw抛出异常 | 用于手动抛出异常对象,但可以抛出的异常对象必须是Throwable或其他子类的实例。 |
| 自定义异常 | 建立自己的异常类型,只要建立Exception的一个子类就可以,子类不需要实际执行什么 |
(1)try...catch异常处理代码块的基本形式如下:
try //监视
{
可能发生异常的代码块;
}
catch(异常类型 异常对象名) //捕获并处理异常
{
异常处理代码块;
}
finally{ //最终执行
}
(2)实例:
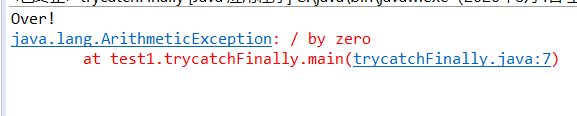
public class trycatchFinally { public static void main(String[] args) { try { int x=5; int y=x/0; System.out.println(y); } catch(Exception e ) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { System.out.println("Over!"); } } }
测试截图:
(3)finally带return语句返回的结果:
下面代码中的finally是最后执行的,故返回的值是10
public class trycatchFinally { public static void main(String[] args) { trycatchFinally t=new trycatchFinally(); int m=t.get(); System.out.println("m="+m); } public int get() { int x=0; try { x=5; return x; } catch(Exception e ) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally { x=10; return x; } } }

(3)finally中没有return x时
当finally中没有return x时尽管令x=10了,但结果是5,这不是因为finally中的语句没有执行,而是因为返回的是try中的x。
public class trycatchFinally { public static void main(String[] args) { trycatchFinally t=new trycatchFinally(); int m=t.get(); System.out.println("m="+m); } public int get() { int x=0; try { x=5; return x; } catch(Exception e ) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { x=10; } return x; } }

(4)catch语句可以有多个,如果用户要捕获Exception,需要将Exception放在最后,因为如果要捕获多个异常,异常的范围要按照从小到大的顺序叠放。
(5)throws子句方法的基本形式
[修饰符] 返回类型 方法名(参数1,参数2,....) throws 异常列表{}
public class ThrowsDemo { public static void main(String [] args) throws Exception{ int x=5; int y=x/0; System.out.println(y); } }
测试截图:

(6)throws子句中同时可以声明多个异常
该方法不对这些异常进行处理,而是声明抛弃它们。
public class ThrowsDemo { public static void main(String [] args) throws IllegalArgumentException{ int x=5; int y=x/0; System.out.println(y); } }
(7)通过throw抛出异常
形式:throw 异常名;
throw关键字主要用于try块中,用来说明已经发生的异常情况,throw后面跟的异常对象用于说明发出的异常类型。
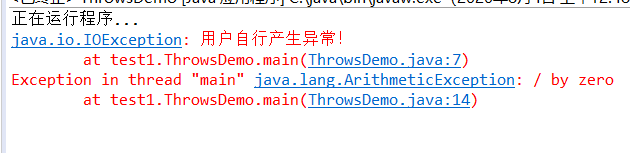
import java.io.IOException; public class ThrowsDemo { public static void main(String [] args){ try { System.out.println("正在运行程序..."); throw new IOException("用户自行产生异常!"); } catch(IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } int x=5; int y=x/0; System.out.println(y); } }
测试截图:
(8)自定义异常
基本形式:
class 自定义异常 extends 父异常类名
{
类体;
}
实例:
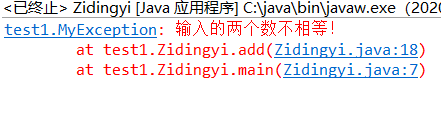
public class Zidingyi { public static void main(String []args) { Zidingyi z=new Zidingyi(); try { z.add(2,3); } catch(MyException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } private void add(int a,int b) throws MyException{ if(a==b) throw new MyException("输入的两个数相等!"); else throw new MyException("输入的两个数不相等!"); } } class MyException extends Exception{ public MyException(String mag) { super(mag); } public MyException() { super(); } public MyException(String message,Throwable cause) { super(message,cause); } public MyException(Throwable cause) { super(cause); } }
测试截图:
2.用log4j记录异常日志信息
(1)如何使用
需要先下载log4j的jar包,log4i组成三大组件为:
| Logger | 决定什么日志信息应该被输出,什么日志信息应该被忽略。 |
| Appender | 指定日志信息应该输出到什么地方,这些地方可以是控制台、网络设备和文件。 |
| Layout | 指定日志信息的输出格式。 |

