刷题01
NC105 二分查找-I
请实现无重复数字的升序数组的二分查找
给定一个 元素升序的、无重复数字的整型数组 nums 和一个目标值 target ,写一个函数搜索 nums 中的 target,如果目标值存在返回下标(下标从 0 开始),否则返回 -1
数据范围:0≤len(nums)≤2×1050 \le len(nums) \le 2\times10^50≤len(nums)≤2×105 , 数组中任意值满足 ∣val∣≤109|val| \le 10^9∣val∣≤109
进阶:时间复杂度 O(logn)O(\log n)O(logn) ,空间复杂度 O(1)O(1)O(1)
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
/**
* 代码中的类名、方法名、参数名已经指定,请勿修改,直接返回方法规定的值即可
*
*
* @param nums int整型一维数组
* @param target int整型
* @return int整型
*/
public int search (int[] nums, int target) {
// write code here
int left=0;
int right=nums.length;
int mid;
while(left<right)
{
mid=left+((right-left)>>1);
if(nums[mid]>target)
{
right=mid;
}
else if(nums[mid]<target)
{
left=mid+1;
}
else{
return mid;
}
}
return -1;
}
}
NC105 二分查找-II
请实现有重复数字的升序数组的二分查找
给定一个 元素有序的(升序)长度为n的整型数组 nums 和一个目标值 target ,写一个函数搜索 nums 中的第一个出现的target,如果目标值存在返回下标,否则返回 -1
数据范围:0≤n≤100000 0 \le n \le 100000\ 0≤n≤100000
进阶:时间复杂度O(logn) O(logn)\ O(logn) ,空间复杂度O(n) O(n)\ O(n)
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
/**
* 代码中的类名、方法名、参数名已经指定,请勿修改,直接返回方法规定的值即可
*
* 如果目标值存在返回下标,否则返回 -1
* @param nums int整型一维数组
* @param target int整型
* @return int整型
*/
public int search (int[] nums, int target) {
// write code here
int left=0;
int right=nums.length;
int mid=-1;
while(left<right)
{
mid=(left+right)>>1;
if(nums[mid]>target)
{
right=mid;
}
else if(nums[mid]<target)
{
left=mid+1;
}
else
{
while(mid>0&&nums[mid-1]==nums[mid])
{
mid--;
}
return mid;
}
}
return -1;
}
}
移除元素
给你一个数组 nums 和一个值 val,你需要 原地 移除所有数值等于 val 的元素,并返回移除后数组的新长度。
不要使用额外的数组空间,你必须仅使用 O(1) 额外空间并 原地 修改输入数组。
元素的顺序可以改变。你不需要考虑数组中超出新长度后面的元素。
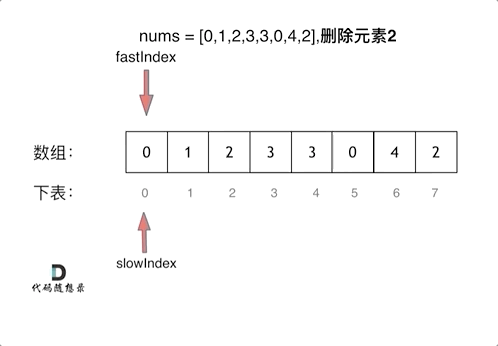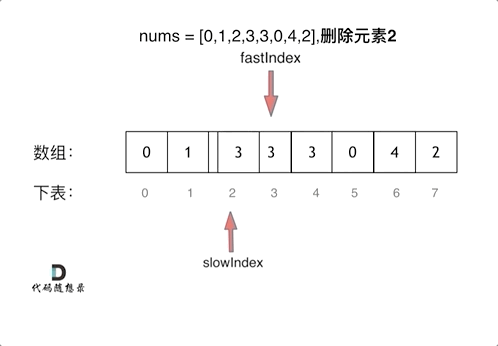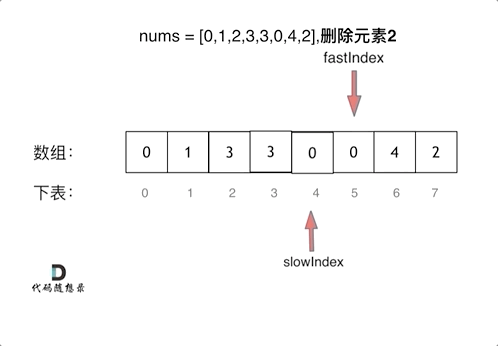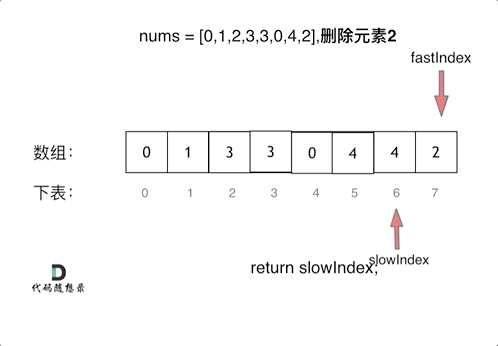
class Solution {
public int removeElement(int[] nums, int val) {
int slow;
int fast=0;
for(slow=0;fast<nums.length;fast++){
if(nums[fast]!=val){
nums[slow]=nums[fast];
slow++;
}
}
return slow;
}
}
有序数据的平方
class Solution {
public int[] sortedSquares(int[] nums) {
for(int i=0;i<nums.length;i++)
{
nums[i]=nums[i]*nums[i];
}
Arrays.sort(nums);
return nums;
}
}
长度最小的子数组
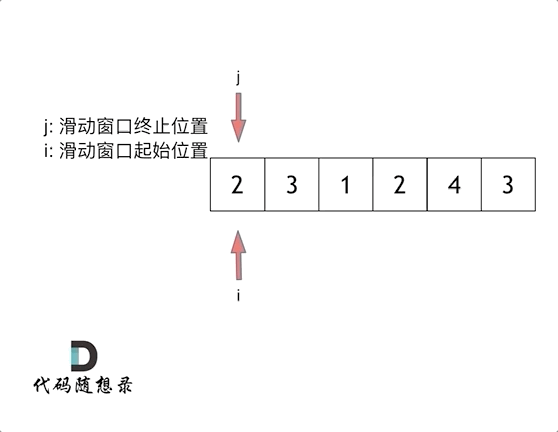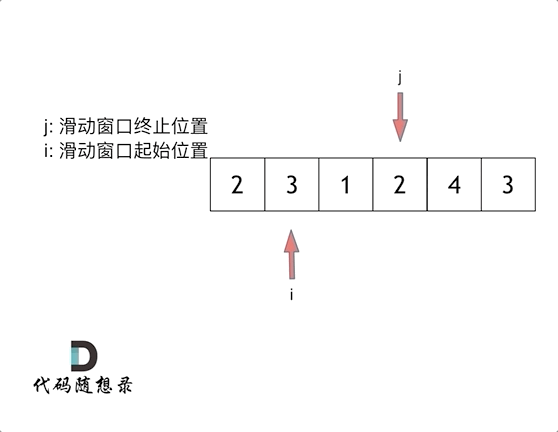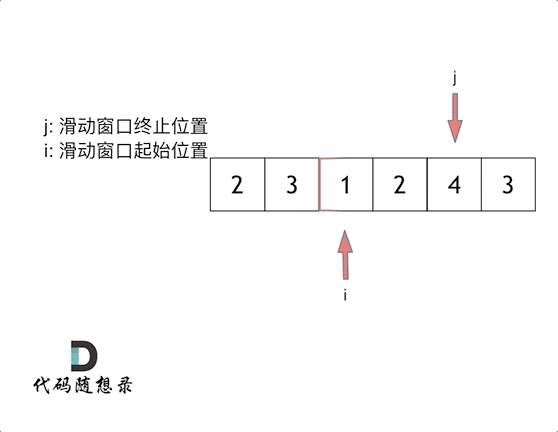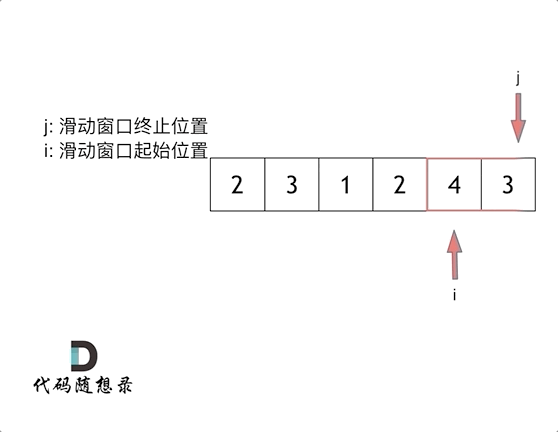
给定一个含有 n 个正整数的数组和一个正整数 target 。
找出该数组中满足其和 ≥ target 的长度最小的 连续子数组 [numsl, numsl+1, ..., numsr-1, numsr] ,并返回其长度。如果不存在符合条件的子数组,返回 0 。
class Solution {
public int minSubArrayLen(int target, int[] nums) {
int left=0;
int right=0;
int sum=0;
int result=Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for(right=0;right<nums.length;right++)
{
sum=sum+nums[right];
while(sum>=target)
{
result=Math.min(result,right-left+1);
sum=sum-nums[left++];
}
}
return result==Integer.MAX_VALUE?0:result;
}
}
螺旋矩阵II
给你一个正整数 n ,生成一个包含 1 到 n2 所有元素,且元素按顺时针顺序螺旋排列的 n x n 正方形矩阵 matrix 。
class Solution {
public int[][] generateMatrix(int n) {
int[][] result=new int[n][n];
int sum=1;
int j=0;
while(sum<=n*n)
{
for(int i=j;i<n-j;i++)
{
result[j][i]=sum++;
}
for(int i=j+1;i<n-j;i++)
{
result[i][n-j-1]=sum++;
}
for(int i=n-j-2;i>=j;i--)
{
result[n-j-1][i]=sum++;
}
for(int i=n-j-2;i>j;i--)
{
result[i][j]=sum++;
}
j++;
}
return result;
}
}
移除链表元素
双指针
class Solution {
public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) {
ListNode DummyHead=new ListNode(0);
DummyHead.next=head;
ListNode pre=DummyHead;
while(pre.next!=null)
{
if(pre.next.val==val)
{
pre.next=pre.next.next;
}
else
{
pre=pre.next;
}
}
return DummyHead.next;
}
}
反转链表
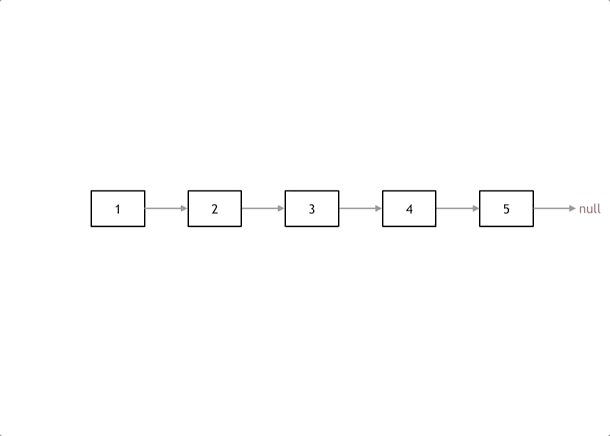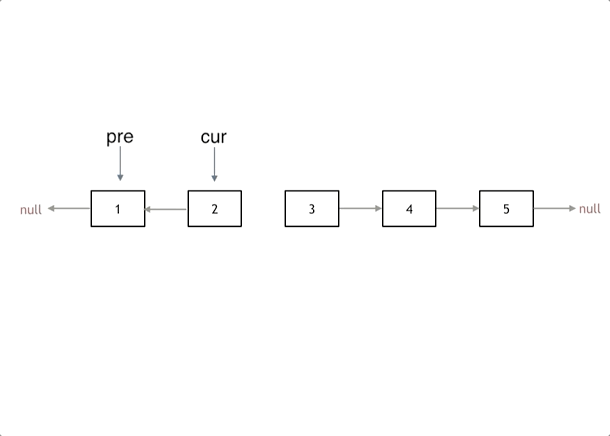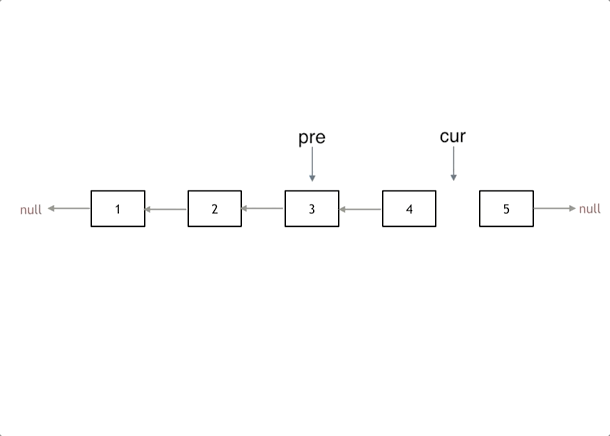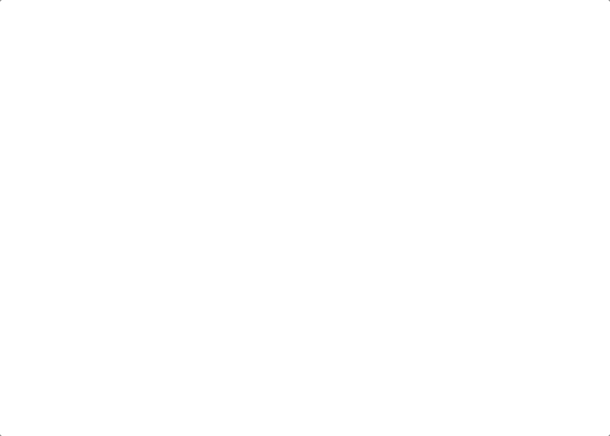
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode cur=head;
ListNode temp=null;
ListNode pre=null;
while(cur!=null)
{
temp=cur.next;
cur.next=pre;
pre=cur;
cur=temp;
}
return pre;
}
}
##两两交换链表中节点
```java
class Solution {
public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {
if(head==null||head.next==null) return head;
ListNode next=head.next;
ListNode temp=swapPairs(next.next);
next.next=head;
head.next=temp;
return next;
}
}
删除链表中倒数第n个节点
class Solution {
public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
if(head==null) return head;
ListNode dummyHead=new ListNode(0);
dummyHead.next=head;
ListNode slow=dummyHead;
ListNode fast=dummyHead;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
fast=fast.next;
}
while(fast.next!=null)
{
slow=slow.next;
fast=fast.next;
}
slow.next=slow.next.next;
return dummyHead.next;
}
}
链表相交
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
ListNode h1=headA;
ListNode h2=headB;
while(h1!=h2)
{
h1=h1==null?headB:h1.next;
h2=h2==null?headA:h2.next;
}
return h1;
}
//假设相交(相交点8->8):headA(1->2->3->8->8): 3+2;headB(7->6->8->8): 2+2。则 h1走3+2+2+2 = 9步(每一步访问:1->2->3->8->8->7->6->8->8); h2走2+2+2+3 = 9步(每一步访问:7->6->8->8->1->2->3->8->8)。 看最后两步。 不相交最终满足 h1 == h2 == null
}
环形链表Ⅱ
判断链表是否有环
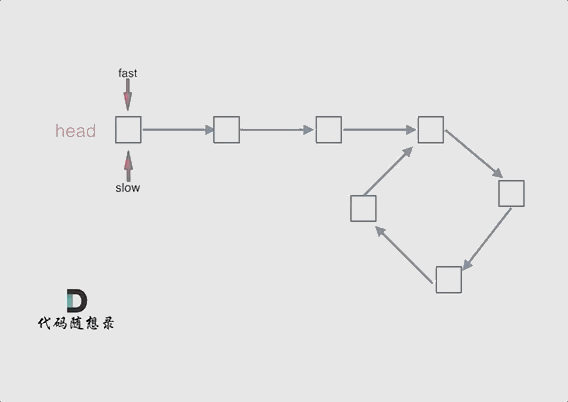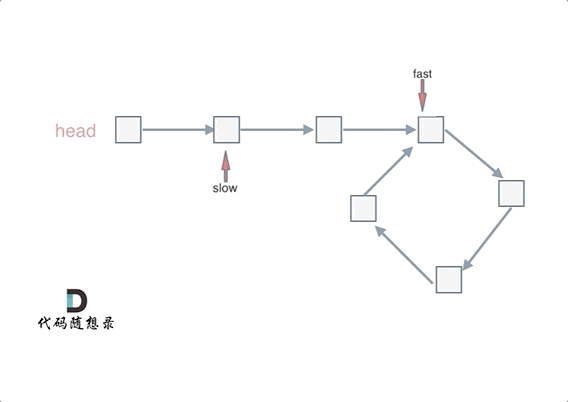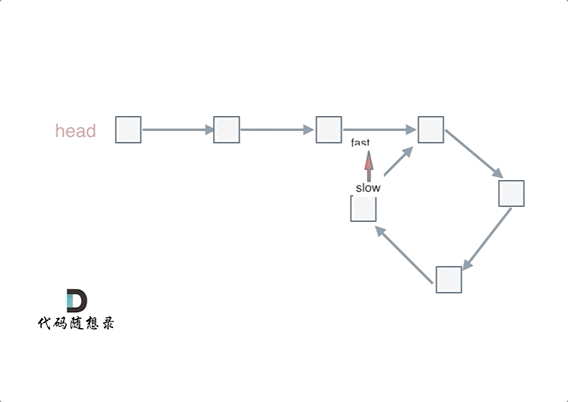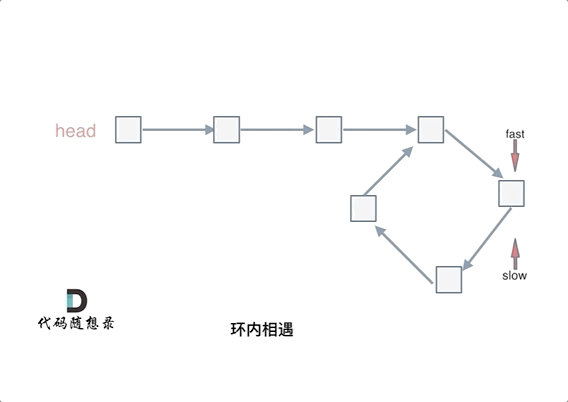
可以使用快慢指针法,分别定义 fast 和 slow 指针,从头结点出发,fast指针每次移动两个节点,slow指针每次移动一个节点,如果 fast 和 slow指针在途中相遇 ,说明这个链表有环。
为什么fast 走两个节点,slow走一个节点,有环的话,一定会在环内相遇呢,而不是永远的错开呢
首先第一点:fast指针一定先进入环中,如果fast指针和slow指针相遇的话,一定是在环中相遇,这是毋庸置疑的。
那么来看一下,为什么fast指针和slow指针一定会相遇呢?
可以画一个环,然后让 fast指针在任意一个节点开始追赶slow指针。
会发现最终都是这种情况, 如下图:
fast和slow各自再走一步, fast和slow就相遇了
这是因为fast是走两步,slow是走一步,其实相对于slow来说,fast是一个节点一个节点的靠近slow的,所以fast一定可以和slow重合。
动画如下:
如果有环,如何找到这个环的入口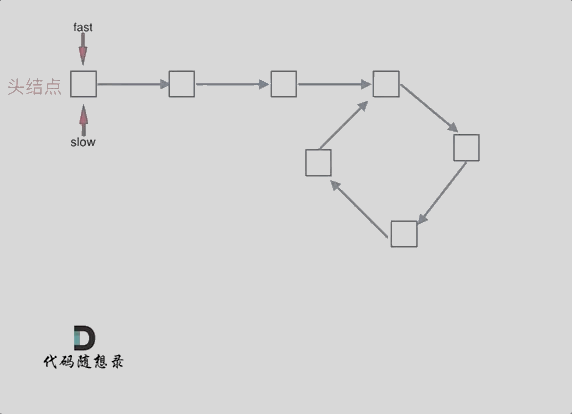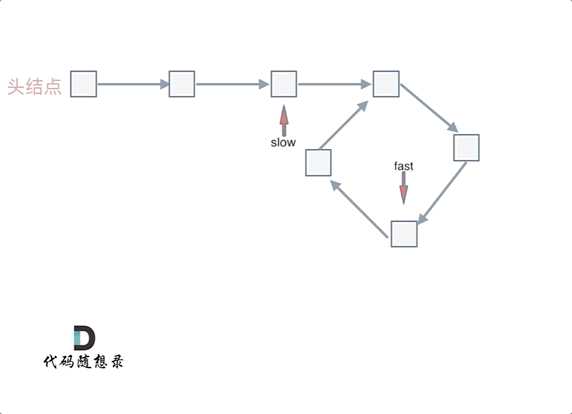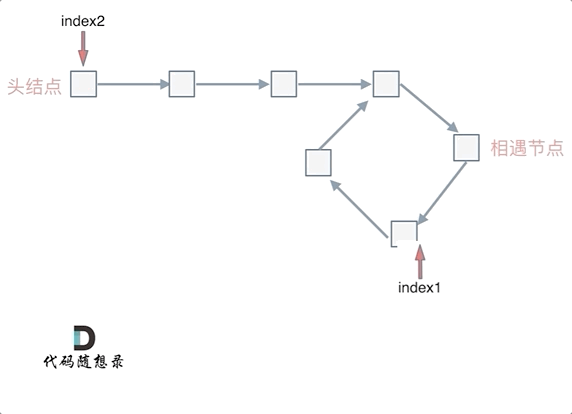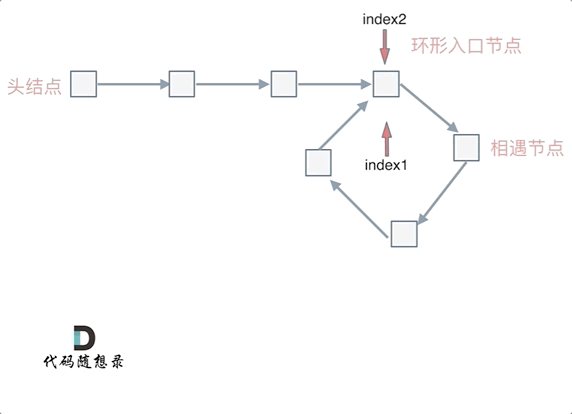
此时已经可以判断链表是否有环了,那么接下来要找这个环的入口了。
假设从头结点到环形入口节点 的节点数为x。 环形入口节点到 fast指针与slow指针相遇节点 节点数为y。 从相遇节点 再到环形入口节点节点数为 z。 如图所示:
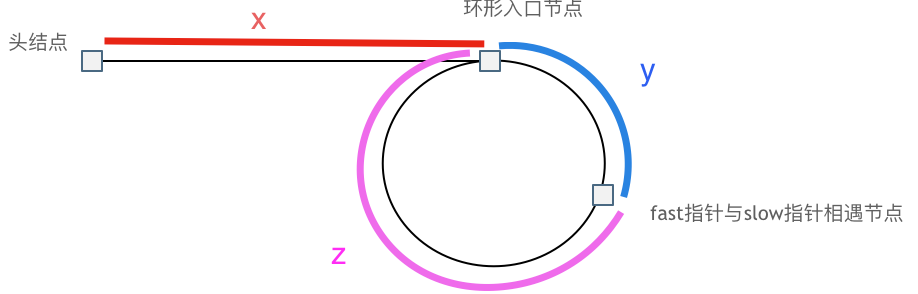
那么相遇时: slow指针走过的节点数为: x + y, fast指针走过的节点数:x + y + n (y + z),n为fast指针在环内走了n圈才遇到slow指针, (y+z)为 一圈内节点的个数A。
因为fast指针是一步走两个节点,slow指针一步走一个节点, 所以 fast指针走过的节点数 = slow指针走过的节点数 * 2:
(x + y) * 2 = x + y + n (y + z)
两边消掉一个(x+y): x + y = n (y + z)
因为要找环形的入口,那么要求的是x,因为x表示 头结点到 环形入口节点的的距离。
所以要求x ,将x单独放在左面:x = n (y + z) - y ,
再从n(y+z)中提出一个 (y+z)来,整理公式之后为如下公式:x = (n - 1) (y + z) + z 注意这里n一定是大于等于1的,因为 fast指针至少要多走一圈才能相遇slow指针。
这个公式说明什么呢?
先拿n为1的情况来举例,意味着fast指针在环形里转了一圈之后,就遇到了 slow指针了。
当 n为1的时候,公式就化解为 x = z,
这就意味着,从头结点出发一个指针,从相遇节点 也出发一个指针,这两个指针每次只走一个节点, 那么当这两个指针相遇的时候就是 环形入口的节点。
也就是在相遇节点处,定义一个指针index1,在头结点处定一个指针index2。
让index1和index2同时移动,每次移动一个节点, 那么他们相遇的地方就是 环形入口的节点。
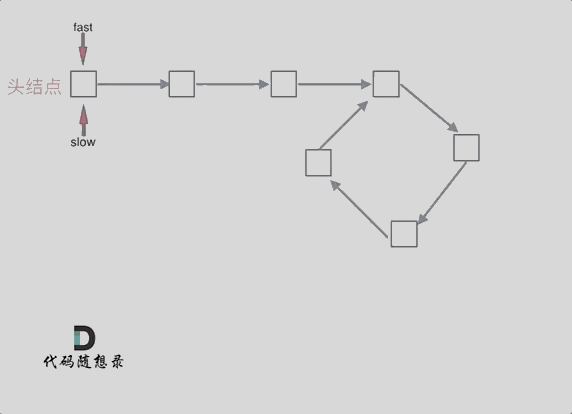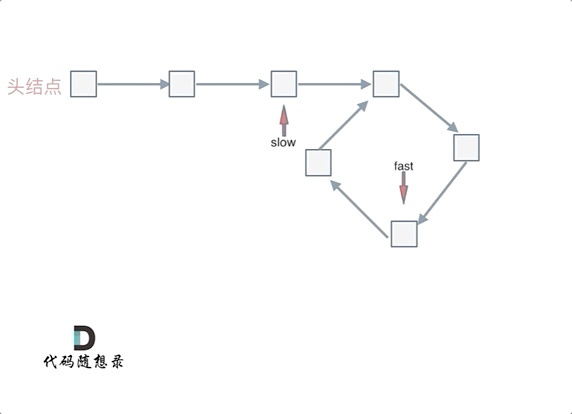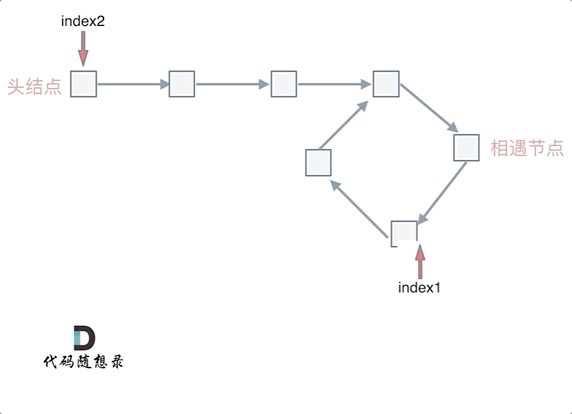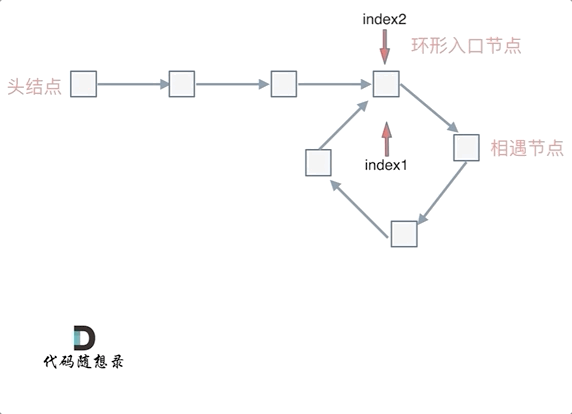
那么 n如果大于1是什么情况呢,就是fast指针在环形转n圈之后才遇到 slow指针。
其实这种情况和n为1的时候 效果是一样的,一样可以通过这个方法找到 环形的入口节点,只不过,index1 指针在环里 多转了(n-1)圈,然后再遇到index2,相遇点依然是环形的入口节点。
public class Solution {
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
ListNode fast=head;
ListNode slow=head;
while(fast!=null&&fast.next!=null)
{
slow=slow.next;
fast=fast.next.next;
if(slow==fast)
{
ListNode x=head;
ListNode y=fast;
while(x!=y)
{
x=x.next;
y=y.next;
}
return x;
}
}
return null;
}
}

