git使用的常见命令
Git的使用
1.下载git:https://www.cnblogs.com/ximiaomiao/p/7140456.html
Git常用命令及使用方法
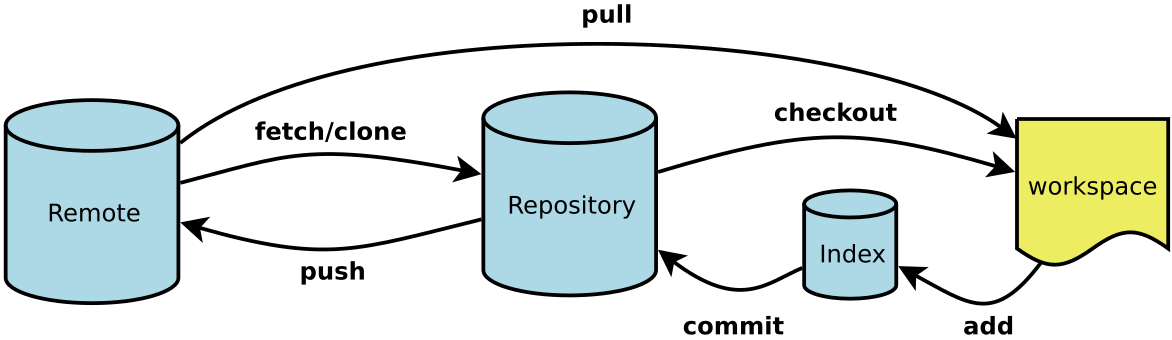
- Workspace:工作区
- Index / Stage:暂存区
- Repository:仓库区(或本地仓库)
- Remote:远程仓库
项目常见命令
# 在当前目录新建一个Git代码库 $ git init # 设置提交代码时的用户信息 $ git config [--global] user.name "[name]" $ git config [--global] user.email "[email address]" # 下载一个项目和它的整个代码历史 $ git clone [url] # 增加一个新的远程仓库,并命名 $ git remote add [shortname] [url] # 指把两段不相干的 分支进行强行合并 git pull origin master --allow-unrelated-histories # 新建一个分支,但依然停留在当前分支 $ git branch [branch-name] # 列出所有本地分支和远程分支 $ git branch -a # 切换到指定分支,并更新工作区 $ git checkout [branch-name] #添加当前目录的所有文件到暂存区 $ git add . # 提交暂存区到仓库区 $ git commit -m [message] # 合并指定分支到当前分支 $ git merge [branch] # 上传本地指定分支到远程仓库 $ git push [remote] [branch]
项目常见命令:版本回退
Git配置
1 # 显示当前的Git配置 2 $ git config --list 3 4 # 编辑Git配置文件 5 $ git config -e [--global] 6 7 # 设置提交代码时的用户信息 8 $ git config [--global] user.name "[name]" 9 $ git config [--global] user.email "[email address]"
添加文件到暂存区
1 # 添加指定文件到暂存区 2 $ git add [file1] [file2] ... 3 4 # 添加指定目录到暂存区,包括子目录 5 $ git add [dir] 6 7 # 添加当前目录的所有文件到暂存区 8 $ git add . 9 10 # 添加每个变化前,都会要求确认 11 # 对于同一个文件的多处变化,可以实现分次提交 12 $ git add -p 13 14 # 删除工作区文件,并且将这次删除放入暂存区 15 $ git rm [file1] [file2] ... 16 17 # 停止追踪指定文件,但该文件会保留在工作区 18 $ git rm --cached [file] 19 20 # 改名文件,并且将这个改名放入暂存区 21 $ git mv [file-original] [file-renamed]
添加文件到仓库区
1 # 提交暂存区到仓库区 2 $ git commit -m [message] 3 4 # 提交暂存区的指定文件到仓库区 5 $ git commit [file1] [file2] ... -m [message] 6 7 # 提交工作区自上次commit之后的变化,直接到仓库区 8 $ git commit -a 9 10 # 提交时显示所有diff信息 11 $ git commit -v 12 13 # 使用一次新的commit,替代上一次提交 14 # 如果代码没有任何新变化,则用来改写上一次commit的提交信息 15 $ git commit --amend -m [message] 16 17 # 重做上一次commit,并包括指定文件的新变化 18 $ git commit --amend [file1] [file2] ...
分支
# 列出所有本地分支 $ git branch # 列出所有远程分支 $ git branch -r # 列出所有本地分支和远程分支 $ git branch -a # 新建一个分支,但依然停留在当前分支 $ git branch [branch-name] # 以远程分支为基础新建一个分支,并切换到该分支 $ git checkout -b [branch] origin/[remote-branch] # 新建一个分支,指向指定commit $ git branch [branch] [commit] # 新建一个分支,与指定的远程分支建立追踪关系 $ git branch --track [branch] [remote-branch] # 切换到指定分支,并更新工作区 $ git checkout [branch-name] # 切换到上一个分支 $ git checkout - # 建立追踪关系,在现有分支与指定的远程分支之间 $ git branch --set-upstream [branch] [remote-branch] # 合并指定分支到当前分支 $ git merge [branch] # 选择一个commit,合并进当前分支 $ git cherry-pick [commit] # 删除分支 $ git branch -d [branch-name] # 删除远程分支 $ git push origin --delete [branch-name] $ git branch -dr [remote/branch]
标签
1 # 列出所有tag 2 $ git tag 3 4 # 新建一个tag在当前commit 5 $ git tag [tag] 6 7 # 新建一个tag在指定commit 8 $ git tag [tag] [commit] 9 10 # 删除本地tag 11 $ git tag -d [tag] 12 13 # 删除远程tag 14 $ git push origin :refs/tags/[tagName] 15 16 # 查看tag信息 17 $ git show [tag] 18 19 # 提交指定tag 20 $ git push [remote] [tag] 21 22 # 提交所有tag 23 $ git push [remote] --tags 24 25 # 新建一个分支,指向某个tag 26 $ git checkout -b [branch] [tag]
远程同步
1 # 下载远程仓库的所有变动 2 $ git fetch [remote] 3 4 # 显示所有远程仓库 5 $ git remote -v 6 7 # 显示某个远程仓库的信息 8 $ git remote show [remote] 9 10 # 增加一个新的远程仓库,并命名 11 $ git remote add [shortname] [url] 12 13 # 取回远程仓库的变化,并与本地分支合并 14 $ git pull [remote] [branch] 15 16 # 上传本地指定分支到远程仓库 17 $ git push [remote] [branch] 18 19 # 强行推送当前分支到远程仓库,即使有冲突 20 $ git push [remote] --force 21 22 # 推送所有分支到远程仓库 23 $ git push [remote] --all
PS: git pull origin master --allow-unrelated-histories 指把两段不相干的 分支进行强行合并
撤销
1 # 恢复暂存区的指定文件到工作区 2 $ git checkout [file] 3 4 # 恢复某个commit的指定文件到暂存区和工作区 5 $ git checkout [commit] [file] 6 7 # 恢复暂存区的所有文件到工作区 8 $ git checkout . 9 10 # 重置暂存区的指定文件,与上一次commit保持一致,但工作区不变 11 $ git reset [file] 12 13 # 重置暂存区与工作区,与上一次commit保持一致 14 $ git reset --hard 15 16 # 重置当前分支的指针为指定commit,同时重置暂存区,但工作区不变 17 $ git reset [commit] 18 19 # 重置当前分支的HEAD为指定commit,同时重置暂存区和工作区,与指定commit一致 20 $ git reset --hard [commit] 21 22 # 重置当前HEAD为指定commit,但保持暂存区和工作区不变 23 $ git reset --keep [commit] 24 25 # 新建一个commit,用来撤销指定commit 26 # 后者的所有变化都将被前者抵消,并且应用到当前分支 27 $ git revert [commit] 28 29 # 暂时将未提交的变化移除,稍后再移入 30 $ git stash 31 $ git stash pop
.gitignore
1.Django项目中常用的不需要提交的清单设置
.idea/ __pycache__/ *.pyc *.log *.pot db.sqlite3 media
2.使用Git管理代码的过程中,可以修改.gitignore文件中的标示的方法来忽略开发者想忽略掉的文件或目录,如果没有.gitignore文件,可以自己手工创建。在.gitignore文件中的每一行保存一个匹配的规则例如:
1 # 此为注释 – 将被 Git 忽略 2 3 *.a # 忽略所有 .a 结尾的文件 4 !lib.a # 但 lib.a 除外 5 /TODO # 仅仅忽略项目根目录下的 TODO 文件,不包括 subdir/TODO 6 build/ # 忽略 build/ 目录下的所有文件 7 doc/*.txt # 会忽略 doc/notes.txt 但不包括 doc/server/arch.txt
3.Git使用时.gitignore设置的文件无法生效的的问题,执行以下命令。
1 git rm -r --cached . 2 git add . 3 git commit -m 'update .gitignore'
Git分支管理策略
主分支Master
首先,代码库应该有一个、且仅有一个主分支。所有提供给用户使用的正式版本,都在这个主分支上发布。
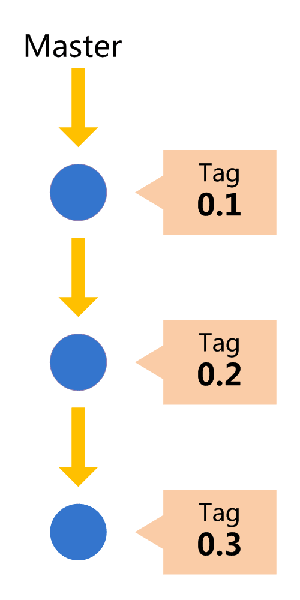
Git主分支的名字,默认叫做Master。它是自动建立的,版本库初始化以后,默认就是在主分支在进行开发。
开发分支Develop
主分支只用来分布重大版本,日常开发应该在另一条分支上完成。我们把开发用的分支,叫做Develop。
这个分支可以用来生成代码的最新隔夜版本(nightly)。如果想正式对外发布,就在Master分支上,对Develop分支进行"合并"(merge)。
Git创建Develop分支的命令
1 git checkout -b develop master
将Develop分支发布到Master分支的命令
1 # 切换到Master分支 2 git checkout master 3 4 # 对Develop分支进行合并 5 git merge --no-ff develop
这里稍微解释一下,上一条命令的--no-ff参数是什么意思。默认情况下,Git执行"快进式合并"(fast-farward merge),会直接将Master分支指向Develop分支。
使用--no-ff参数后,会执行正常合并,在Master分支上生成一个新节点。为了保证版本演进的清晰,我们希望采用这种做法。关于合并的更多解释,请参考Benjamin Sandofsky的《Understanding the Git Workflow》。
原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/web_csdn_share/article/details/79243308

