流程控制的基本语法和应用
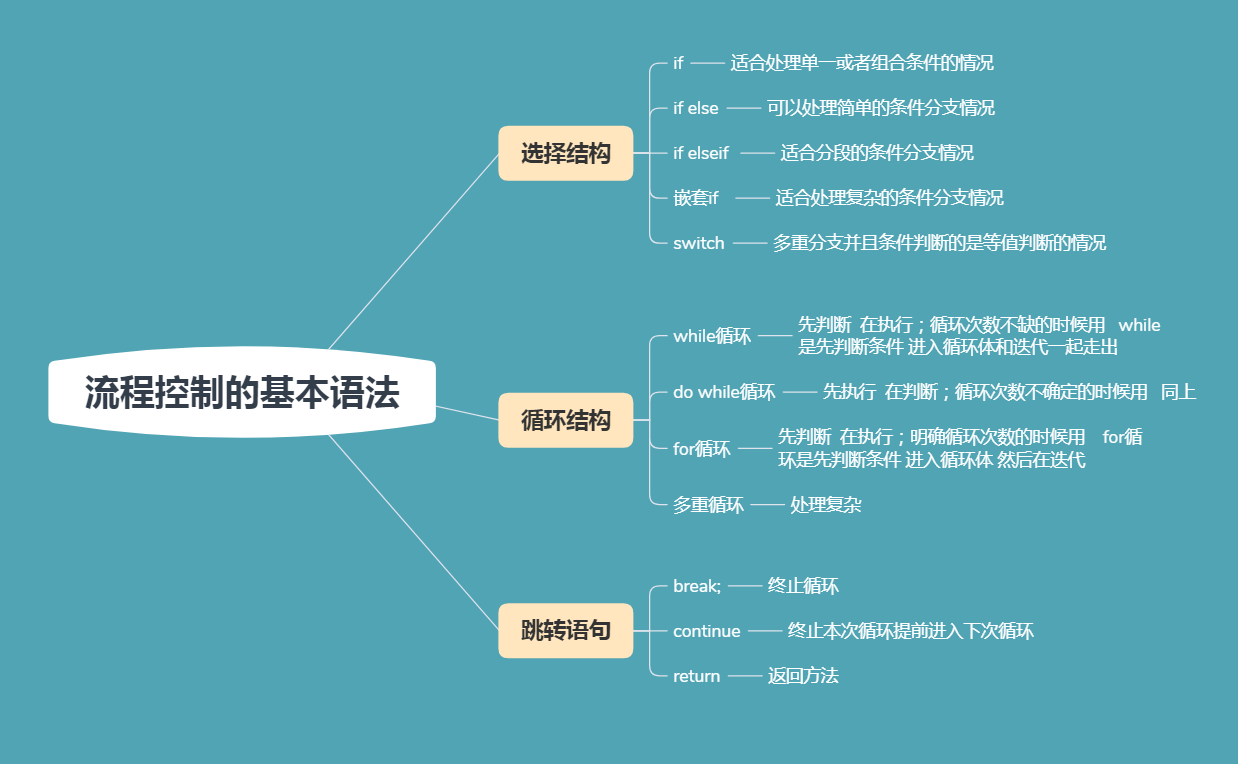
一.选择结构的基本语法
掌握if分支结构:基本if,if-else,多重if,嵌套if,
掌握switch分支结构
1.if结构
public class Demo3 { public static void main(){ int a=90; int b=95; if(a>80&&b>90){ System.out.println("奖励一部华为手机"); } } }
2.if-else
public class Demo3 { public static void main(){ int a=90; int b=95; if(a>80||b==100){ System.out.println("奖励一部华为手机"); }else{ System.out.println("你没有任何奖励"); } } }
3.多重if
public class Demo3 { public static void main(){ int a=90; int b=95; if(a>90&&b>95){ System.out.println("奖励一部华为手机"); }else if(a>85){ System.out.println("奖励一直钢笔"); } } }
4.嵌套if
public class Demo3 { public static void main() { Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); int a = 90; int b = 95; String sex = "男"; if (a > 90 && b > 95) { if (sex.equals("男")) { System.out.println("奖励一部华为手机 "); } } else { System.out.println("你没有任何奖励"); } } }
5.switch分支结构
package test; //导入Scanner包 import java.util.*; public class Demo3 { public static void main() { //创建Scanner类 Scanner input=new Scanner(System.in); //输出语句 System.out.println("请输入日期:"); //创建控制台接收的变量 int num=input.nextInt(); switch(num){ case 1: System.out.println("星期一"); break; case 2: System.out.println("星期二"); break; case 3: System.out.println("星期三"); break; case 4: System.out.println("星期四"); break; case 5: System.out.println("星期五"); break; case 6: System.out.println("星期六"); break; case 7: System.out.println("星期日"); break; default: System.out.println("输入错误"); } } }
二.循环结构的基本语法whie,do while,for循环
1.while循环结构
package test; import java.util.*; public class Demo3 { public static void main(String[] args){ Scanner input=new Scanner(System.in); int i=0; while(i<=100){ System.out.println("123"); i++; }
注意:
(1)while的循环条件是一个布尔表达式,它的值为布尔型 true或false
(2)大括号中的语句统称为循环操作,又称循环体
(3)循环体中千万不要忘记写迭代(i++) 否则会造成死循环
2.do while循环
package test; import java.util.*; public class Demo5 { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner input=new Scanner(System.in); double score; do{ System.out.println("请输入你的考试成绩:"); score=input.nextDouble(); if(score<90){ System.out.println("还要继续修学"); } }while(score<90); System.out.println("毕业"); } }
注意:
(1) do while语句是先执行一遍循环体 在进行判断
(2)do while是以分好结尾的,分号非常重要,不能省略
(3)不要忘记“i++”
for循环
package test; import java.util.*; public class Demo5 { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner input=new Scanner(System.in); for(int i=1;i<=100;i++){ System.out.println("输出第"+i+"数字"); } } }
注意:
(1)
(2)
(3)



