day 15
知识补充
1.关于压缩题,理解tar和gz
http://yuchaoit.cn/all_nginx.tgz
[root@yuanlai-0224 test_tar]# # 看到此tgz,就得记住,它是2个打包+压缩步骤,tar + gz
[root@yuanlai-0224 test_tar]#
[root@yuanlai-0224 test_tar]#
[root@yuanlai-0224 test_tar]# # 万能解压命令 tar -zxvf
[root@yuanlai-0224 test_tar]#
[root@yuanlai-0224 test_tar]# tar -zxvf all_nginx.tgz
# 第二条命令,分别进行先解压缩gz后缀,再拆包tar归档操作,最终得到,原本的零散文件
gzip -d all_nginx.tgz
tar -xvf all_nginx.tar
http://yuchaoit.cn/all_nginx.tar
tar -xf all_nginx.tar
http://yuchaoit.cn/all_nginx.tar.gz
tar -zxvf all_nginx.tar.gz
http://yuchaoit.cn/nginx-logo.png.gz
[root@yuanlai-0224 test_tar]# gzip -d nginx-logo.png.gz
[root@yuanlai-0224 test_tar]# ll
总用量 4
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 368 10月 19 07:55 nginx-logo.png
[root@yuanlai-0224 test_tar]#
[root@yuanlai-0224 test_tar]#
[root@yuanlai-0224 test_tar]# file nginx-logo.png
nginx-logo.png: PNG image data, 121 x 32, 1-bit colormap, non-interlaced
文件操作,测试数据
[root@yuanlai-0224 test_tar]# cat t1.txt
20
26
13
18
28
7
14
30
8
15
3
18
10
25
25
7
30
28
28
23
0
4
30
14
32
3
9
20
31
5
生成20个随机数
for i in {1..30};do echo $(expr $RANDOM / 1000 ) ;done> t1.txt
2.读取文件内容且倒叙排序,从小到大,从大到小,
# sort是对文本排序的,默认是以第一位字符进行大小比较
[root@yuanlai-0224 test_tar]# cat t1.txt | sort -n -r
3.读取文件内容,排序,再统计重复行的次数
[root@yuanlai-0224 test_tar]# cat t1.txt | sort -n | uniq -c
1 0
2 3
1 4
1 5
2 7
1 8
1 9
1 10
1 13
2 14
1 15
2 18
2 20
1 23
2 25
1 26
3 28
3 30
1 31
1 32
4.统计文件一共有多少行
cat t1.txt |wc -l
统计文件字符数
cat t1.txt |wc -m
统计文件字节数
cat t1.txt |wc -c
5.如何查看文件的详细信息。
file t1.txt
6.给启动django的命令做一个简单的别名(alias)
alias stdj='python3 manage.py runserver 0.0.0.0:8000'
取消别名
unalias stdj
永久好使,并且别影响到被人,怎么永久添加
写入到自己的用户环境变量文件中
~/.bash_profile
7.进程查找、进程杀死
linux 可以进程找出所有进程信息的组合命令
1. ps -ef | grep '你要找的进程名' # 找到的结果,去看它的pid进程号,然后kill干掉即可
2. kill 进程pid
8.linux解析dns的命令,解析,就是将域名,解析到ip的一个操作
1. linux能正确进行互联网dns解析的文件是什么
/etc/resolov.conf ,在这里头写入域名服务器地址
(114.114.114.114 223.5.5.5 115.115.115.115 223.6.6.6 119.29.29.29)
192.168.0.170 yjy.top # 只想在自己本地,测一测这个域名,(/etc/hosts)
如果yjy想让全班同学,咱们这个局域网内(比如在公司的集团,局域网内,也能够实现某域名的解析)
2. 如何查看域名,对应的ip是多少?
ping 会自动帮你去做域名查找
ping baidu.com
(ping 在你本机,去测一测,你和对方的机器,是否通信,ping命令会不断的发送数据包,给对方服务器,对方如果存活,会给你响应)
3. linux也提供了更专业化的,域名查找,解析的命令
- dig
dig @223.5.5.5 你的域名
- nslookup (name server look up 名称服务器查找,简称,域名查找 )
如何用,提供了交互式(等待你输入,然后等待给结果),非交互式(命令下去,直接出结果)的2个操作
# 交互式,直接输入该命令
[root@yuanlai-0224 test_tar]# nslookup
> www.yuchaoit.cn
Server: 114.114.114.114
Address: 114.114.114.114#53
Non-authoritative answer:
Name: www.yuchaoit.cn
Address: 123.206.16.61
# 非交互式
[root@yuanlai-0224 test_tar]# nslookup apecome.com
Server: 114.114.114.114
Address: 114.114.114.114#53
Non-authoritative answer:
Name: apecome.com
Address: 123.57.242.10
9.scp远程传输
windows 和linux如何传递呀
lrzsz一个
xftp一个
你的windows,你的虚机,(互相传文件,有什么限制吗?,比如穿不过去,网络不通等限制)
有,如何理解
lrzsz,不支持直接传输零散文件,需要打包为单个文件,即可传输
linux打开了防火墙,禁止文件传输
正常情况下
win,linux之间互传,没什么影响
你的linux虚拟机,和你同桌的linux虚拟机,传文件,有什么影响吗?
有
1. 同桌不给你密码
2. 你和同桌不在一个网段 (每个人都是NAT网段,都是自己的私有局域网)(改为桥接,在同一个网段下即可)
你的linux虚拟机(自己本地的局域网),和你的阿里云(互联网中的公网),有什么限制吗?
1.虚拟机,能找到 阿里云
你的虚拟机(192.168.0.xx)
↓
宿主机windows
↓
交换机,路由器(有绑定的中国移动的公网宽带ip)
↓
阿里云(购买阿里云时候,人家绑定了一个固定的公网ip,全世界都可以访问到的)
2. 阿里云找不到你的虚拟机
阿里云(购买阿里云时候,人家绑定了一个固定的公网ip,全世界都可以访问到的)
×
你们家,你的学校的路由器的公网ip(这里就没有)
×
你的虚拟机
先玩简单的,两个linux机器之间,传递文件
systemctl restart network # 重启network,读取网卡配置文件再生效吧!
准备虚拟机1 192.168.0.240
虚拟机2 192.168.0.158
# scp的语法(安装的,远程传输,基于ssh协议认证的传输,机器1,要传文件给机器2,需要进行ssh的账户密码认证
# 好比ssh去登录其他人的机器
# scp的语法
1. 我登录了192.168.0.240 这个机器A,把机器A的/etc/passwd文件,发给机器B 192.168.0.158,放到/opt下
语法
scp 源数据的机器 远程机器
# 把当前登录的机器的 /etc/passwd文件发给别人
scp /etc/passwd root@192.168.0.158:/opt
# 把自己的 /var/log/整个目录,全发过去到 /tmp/
scp -r /var/log/ root@192.168.0.158:/tmp/
# 以登录的机器是 192.168.0.240这台
# 需求是, 把远程的数据 拿过来
把192.168.0.158上的/etc/passwd 拿到自己的 /opt目录下
scp 你想要的数据机器 放到那
scp root@192.168.0.158:/etc/passwd /opt/
# 递归的远程 拿别人的文件夹数据
scp -r root@192.168.0.158:/var/log /opt/
# 课件,准备好2个linux机器(安装2个虚机,和同桌互传,改为 桥接模式)
10.粉碎文件
# rm命令,删除文件,其实还是可以恢复的,现在的文件系统,都是日志型系统(你的操作,其实被系统监控,录制,做了个备份)
# rm删除数据后,磁盘其实还未立即彻底删除,根据磁盘恢复数据手段,还是可以把数据拿回来的
shred 文件名
这个命令之所以叫粉碎文件,是随机写入一堆二进制数据,导致原文件无法使用
随机写入二进制数据到文件中,比较危险,不推荐使用
[root@yuanlai-0224 test_tar]# shred gushi.txt
服务管理
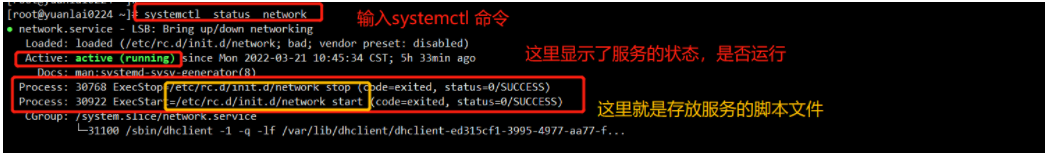
回顾systemctl
你的机器机器会有默认的软件(服务),比如 network 管理网络的软件, sshd提供远程连接的服务。
如何管理这些服务
启动 (start)
停止 (stop)
重启 (restart)
重新加载 (reload)
开机自启(持久化) (enable)
禁止开机自启 (disable)
查询是否持久化(是否开机自启) (is-enabled)
centos 7 用这个命令,同时对服务进行启停管理,以及开机自启
systemctl start/stop/restart/reload/enable/disable/is-enabaled 服务名
这个命令属于是对centos 6提供的两个命令,做了一个整合
1.service
Linux的命令,大多数都是去机器上找到某个文件,然后读取文件配置,加载功能
service 旧的命令,是默认去 /etc/init.d/ 目录下寻找(服务管理脚本文件)
然后根据你的指令 service start /stop network (/etc/init.d/network)
service 服务名 启停服务
然后会去读取 /etc/init.d 目录下的脚本
我们在用 centos 6 的时候,自己按爪那个了某软件,比如nginx 网站,但是某又不方便的启停管理脚本
自己去写nginx启停脚本,放到 /etc/init.d/nginx
然后使用 service nginx start
2.chkconfig
在centos 7 中 systemctl 就是把上面的两个命令整合到一起。
关于systemctl命令其实是找到脚本
无论敲的是 service 还是 systemctl start stop restart
其实都是去找到这个脚本文件(/etc/init.d/),然后去传入你的参数,再去start stop
service 启动网络服务
service network start
命令启动网络服务
/etc/init.d/network start
用脚本文件启动网络服务

用 service 或者 用脚本管理服务,其实就等于 systemctl start network
通过上面可以看到 service 其实是去读取脚本 /etc/init.d/ 目录下的脚本文件
而在 centos7 中的脚本目录就不一样了
系统默认的所有服务,管理脚本的存放目录,以及你自己安装了某软件,也可以放入到这个目录下,就可以通过systemctl
start/stop 来实现管理
比如,安装了 nginx 软件,查看启动命令以及脚本在哪
yum install nginx -y #安装 nginx
yum安装的程序,会自动生成nginx管理脚本,自动的在systemctl 管理脚本目录下
nginx这个服务名其实是一个缩写,完整的服务名叫 nginx.service
[root@yuanlai0224 ~]# systemctl status nginx
● nginx.service - The nginx HTTP and reverse proxy server
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/nginx.service; disabled; vendor preset: disabled)
Active: inactive (dead)
[root@yuanlai0224 ~]#
查看 nginx 的运行状态,他会给出一个 nginx 的存放目录就是
/usr/lib/systemd/system/ 也就是systemctl 统一管理脚本的目录
比如 sshd 这个服务它的脚本就可以在这个目录中搜到
[root@yuanlai0224 ~]# ll /usr/lib/systemd/system/sshd*
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 313 Apr 11 2018 /usr/lib/systemd/system/sshd-keygen.service
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 373 Apr 11 2018 /usr/lib/systemd/system/sshd.service
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 260 Apr 11 2018 /usr/lib/systemd/system/sshd@.service
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 181 Apr 11 2018 /usr/lib/systemd/system/sshd.socket
[root@yuanlai0224 ~]#
理解systemctl 管理脚本的流程
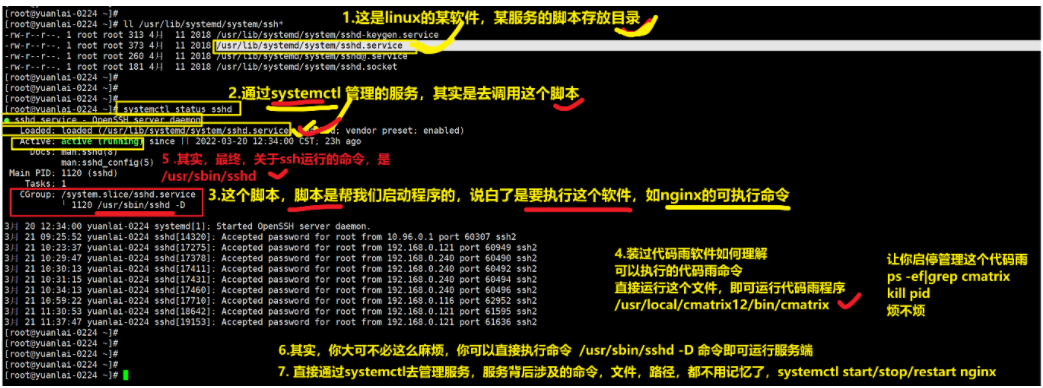
实践操作来演示上面所说:
直接运行指令
[root@yuanlai0224 ~]# /usr/sbin/nginx
[root@yuanlai0224 ~]#
执行上述命令可以看到页面的
要关闭nginx这个进程,要先找到这个服务的进程给他杀掉
[root@yuanlai0224 ~]# ps -ef | grep nginx
root 51512 1 0 17:15 ? 00:00:00 nginx: master process /usr/sbin/nginx
nginx 51513 51512 0 17:15 ? 00:00:00 nginx: worker process
root 51640 49953 0 17:17 pts/1 00:00:00 grep --color=auto nginx
[root@yuanlai0224 ~]#
[root@yuanlai0224 ~]# kill 51512 #结束nginx 的进程号
但是下次要运行 nginx 还要把这个流程走一遍,而且还要重新去查看进程 id 这个过程很麻烦
#我们再次执行 nginx 查看它的进程号,这个进程号是不断发生变化的,因此应证了上边所说的来回操作会很麻烦
[root@yuanlai0224 ~]# /usr/sbin/nginx
[root@yuanlai0224 ~]# ps -ef | grep nginx
root 51764 1 0 17:20 ? 00:00:00 nginx: master process /usr/sbin/nginx
nginx 51765 51764 0 17:20 ? 00:00:00 nginx: worker process
root 51770 49953 0 17:20 pts/1 00:00:00 grep --color=auto nginx
[root@yuanlai0224 ~]#
以服务器管理模式运行 systemctl
简单的两条命令就完事
[root@yuanlai0224 ~]# systemctl start nginx #开启 nginx 服务
[root@yuanlai0224 ~]#
[root@yuanlai0224 ~]# systemctl stop nginx #关闭 nginx 服务
[root@yuanlai0224 ~]#
[root@yuanlai0224 ~]# systemctl restart nginx #重新启动 nginx 服务
ntp时间服务部署
全世界的服务器,时间统一标准,可以以这个为准 cn.ntp.org.cn
timedatectl
可以修改Linux的日期,时间
timedatectl 整合了下边的两个命令
date 改时间日期(软件时间,你的系统运行了,程序计算的时间)
hwclock 改硬件时间(计算的主板上,有一个BISO系统,以及纽扣电池,提供电量)
在 centos 6 时代修改系统的时间,时区,需要用到的
date 修改时间,日期
修改时区 修改时区,cp /usr/share/zoneinfo/Asia/Shanghai /etc/localtime #亚洲上海的时区
#查看系统中有哪些失去文件
ls /usr/share/zoneinfo
ll /usr/share/zoneinfo/Asia/Shanghai
修改硬件时间 --- hwclock 命令
查看当前时间
下边的两条命令都可查看当前时间
[root@yuanlai0224 ~]# timedatectl
Local time: Mon 2022-03-21 17:32:09 CST
Universal time: Mon 2022-03-21 09:32:09 UTC
RTC time: Mon 2022-03-21 09:32:09
Time zone: Asia/Shanghai (CST, +0800)
NTP enabled: no
NTP synchronized: yes
RTC in local TZ: no
DST active: n/a
[root@yuanlai0224 ~]#
[root@yuanlai0224 ~]# timedatectl status
Local time: Mon 2022-03-21 17:32:39 CST
Universal time: Mon 2022-03-21 09:32:39 UTC
RTC time: Mon 2022-03-21 09:32:39
Time zone: Asia/Shanghai (CST, +0800)
NTP enabled: no
NTP synchronized: yes
RTC in local TZ: no
DST active: n/a
[root@yuanlai0224 ~]#
修改时间,时区
#查看下 timedatectl 的参数以及用法
[root@yuanlai0224 ~]# timedatectl --help
timedatectl [OPTIONS...] COMMAND ...
Query or change system time and date settings.
-h --help Show this help message
--version Show package version
--no-pager Do not pipe output into a pager
--no-ask-password Do not prompt for password
-H --host=[USER@]HOST Operate on remote host
-M --machine=CONTAINER Operate on local container
--adjust-system-clock Adjust system clock when changing local RTC mode
Commands:
status Show current time settings #查看当前状态
set-time TIME Set system time #设置当前的时间
set-timezone ZONE Set system time zone #设置当前的时区
list-timezones Show known time zones #查看系统支持哪些时区
set-local-rtc BOOL Control whether RTC is in local time
set-ntp BOOL Control whether NTP is enabled
[root@yuanlai0224 ~]#
#修改时间
[root@yuanlai0224 ~]# timedatectl set-time '2018-9-1 12:00'
[root@yuanlai0224 ~]# timedatectl
Local time: Sat 2018-09-01 12:00:04 CST
Universal time: Sat 2018-09-01 04:00:04 UTC
RTC time: Sat 2018-09-01 04:00:04
Time zone: Asia/Shanghai (CST, +0800)
NTP enabled: no
NTP synchronized: no
RTC in local TZ: no
DST active: n/a
[root@yuanlai0224 ~]#
#查看系统中有多少个时区
[root@yuanlai0224 ~]# timedatectl list-timezones | wc -l
425
[root@yuanlai0224 ~]#
#找出关于上海的时区
[root@yuanlai0224 ~]# timedatectl list-timezones | grep -i 'shanghai'
Asia/Shanghai
[root@yuanlai0224 ~]#
#先把他的时区修改为其他
[root@yuanlai0224 ~]# timedatectl set-timezone Africa/Tunis
[root@yuanlai0224 ~]# timedatectl
Local time: Sat 2018-09-01 05:07:13 CET
Universal time: Sat 2018-09-01 04:07:13 UTC
RTC time: Sat 2018-09-01 04:07:13
Time zone: Africa/Tunis (CET, +0100)
NTP enabled: no
NTP synchronized: no
RTC in local TZ: no
DST active: n/a
[root@yuanlai0224 ~]#
#修改时间为上海的时间
[root@yuanlai0224 ~]# timedatectl set-timezone Asia/Shanghai
[root@yuanlai0224 ~]# timedatectl
Local time: Sat 2018-09-01 12:08:20 CST
Universal time: Sat 2018-09-01 04:08:20 UTC
RTC time: Sat 2018-09-01 04:08:20
Time zone: Asia/Shanghai (CST, +0800)
NTP enabled: no
NTP synchronized: no
RTC in local TZ: no
DST active: n/a
[root@yuanlai0224 ~]#
ntp时间同步
强制性更新整个系统的时间 ntpdate 它是不友好的强制同步时间
搭建ntp服务,自动的,有好的更新,校准系统时间
强制性的ntpdate 命令
1.找到时间服务器地址,强制更新即可
[root@yuanlai0224 ~]# ntpdate -u ntp.aliyun.com
21 Mar 17:48:16 ntpdate[53257]: step time server 203.107.6.88 offset 112080992.401459 sec
[root@yuanlai0224 ~]#
#来确认一下时间是否更新
[root@yuanlai0224 ~]# timedatectl
Local time: Mon 2022-03-21 17:48:38 CST
Universal time: Mon 2022-03-21 09:48:38 UTC
RTC time: Sat 2018-09-01 04:12:06
Time zone: Asia/Shanghai (CST, +0800)
NTP enabled: no
NTP synchronized: no
RTC in local TZ: no
DST active: n/a
[root@yuanlai0224 ~]#
搭建ntpd服务
所有的Linux软件用法都一样
安装
改配置
启动
使用
以后就是继续该配置,重新加载,重启
继续使用
1.安装 ntp 软件
yum install ntp -y
2.查看ntp软件信息
[root@yuanlai0224 ~]# ls /usr/lib/systemd/system/ | grep ntp
ntpdate.service
ntpd.service
[root@yuanlai0224 ~]#
3.找到ntp软件的配置文件
[root@yuanlai0224 ~]# rpm -ql ntp |grep conf
/etc/ntp.conf
/etc/sysconfig/ntpd
/usr/share/man/man5/ntp.conf.5.gz
[root@yuanlai0224 ~]#
4.修改ntp配置文件
[root@yuanlai0224 ~]# vim /etc/ntp.conf
11 # 添加ntp的运行日志
12 logfile /var/log/my_ntp.log
13
14 # 记录程序的运行进程号的,可以用于写脚本,读取这个文件,就找到了程序的进程id
15 pidfile /var/run/ntpd.pid
36 server ntp.aliyun.com prefer
37 server cn.pool.ntp.org iburst
5.修改机器的时间为错误的
[root@yuanlai0224 ~]# timedatectl set-time '2012-12-12 12:12'
[root@yuanlai0224 ~]# timedatectl
Local time: Wed 2012-12-12 12:12:06 CST
Universal time: Wed 2012-12-12 04:12:06 UTC
RTC time: Wed 2012-12-12 04:12:06
Time zone: Asia/Shanghai (CST, +0800)
NTP enabled: no
NTP synchronized: no
RTC in local TZ: no
DST active: n/a
[root@yuanlai0224 ~]#
6.启动ntpd服务,等待时间是否同步
关于ntpd的服务脚本文件/usr/lib/systemd/system/ntpd.service
[root@yuanlai0224 ~]# systemctl start ntpd
[root@yuanlai0224 ~]# systemctl status ntpd
● ntpd.service - Network Time Service
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/ntpd.service; disabled; vendor preset: disabled)
Active: active (running) since Sun 2022-03-20 14:25:54 CST; 9 years 3 months left
Process: 11370 ExecStart=/usr/sbin/ntpd -u ntp:ntp $OPTIONS (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Main PID: 11371 (ntpd)
CGroup: /system.slice/ntpd.service
└─11371 /usr/sbin/ntpd -u ntp:ntp -g
Mar 21 16:39:53 yuanlai0224 ntpd[11371]: new interface(s) found: waking up resolver
Mar 21 16:39:54 yuanlai0224 ntpd[11371]: 0.0.0.0 0638 08 no_sys_peer
Mar 21 17:56:27 yuanlai0224 ntpd[11371]: Deleting interface #15 ens33, 192.168.0.162#123, in...ecs
Mar 21 17:56:27 yuanlai0224 ntpd[11371]: 202.118.1.130 interface 192.168.0.162 -> (none)
Mar 21 17:56:27 yuanlai0224 ntpd[11371]: 185.209.85.222 interface 192.168.0.162 -> (none)
Mar 21 17:56:27 yuanlai0224 ntpd[11371]: 162.159.200.123 interface 192.168.0.162 -> (none)
Mar 21 17:56:27 yuanlai0224 ntpd[11371]: 193.182.111.12 interface 192.168.0.162 -> (none)
Mar 21 17:56:29 yuanlai0224 ntpd[11371]: Listen normally on 17 ens33 192.168.0.162 UDP 123
Mar 21 17:56:29 yuanlai0224 ntpd[11371]: new interface(s) found: waking up resolver
Mar 21 17:56:30 yuanlai0224 ntpd[11371]: 0.0.0.0 0648 08 no_sys_peer
Hint: Some lines were ellipsized, use -l to show in full.
[root@yuanlai0224 ~]#
7.查看 ntp 是否和上游服务器同步
[root@yuanlai0224 ~]# ntpstat
synchronised to NTP server (202.118.1.130) at stratum 2
time correct to within 482 ms
polling server every 1024 s
8.查看时间同步的状态
[root@yuanlai0224 ~]# ntpq -p
remote refid st t when poll reach delay offset jitter
==============================================================================
+time.cloudflare 10.28.12.207 3 u 123 1024 7 281.850 -24.579 1105815
+stratum2-1.ntp. 62.231.6.98 2 u 124 1024 7 136.137 -14.645 1105815
ntp1.flashdance 192.36.143.151 2 u 59 1024 5 287.856 19.093 1308418
*202.118.1.130 .PTP. 1 u 4632 1024 3 15.125 1.451 15.223
[root@yuanlai0224 ~]#
9.这台机器就是一个时间服务器了可以作为上游机使用了
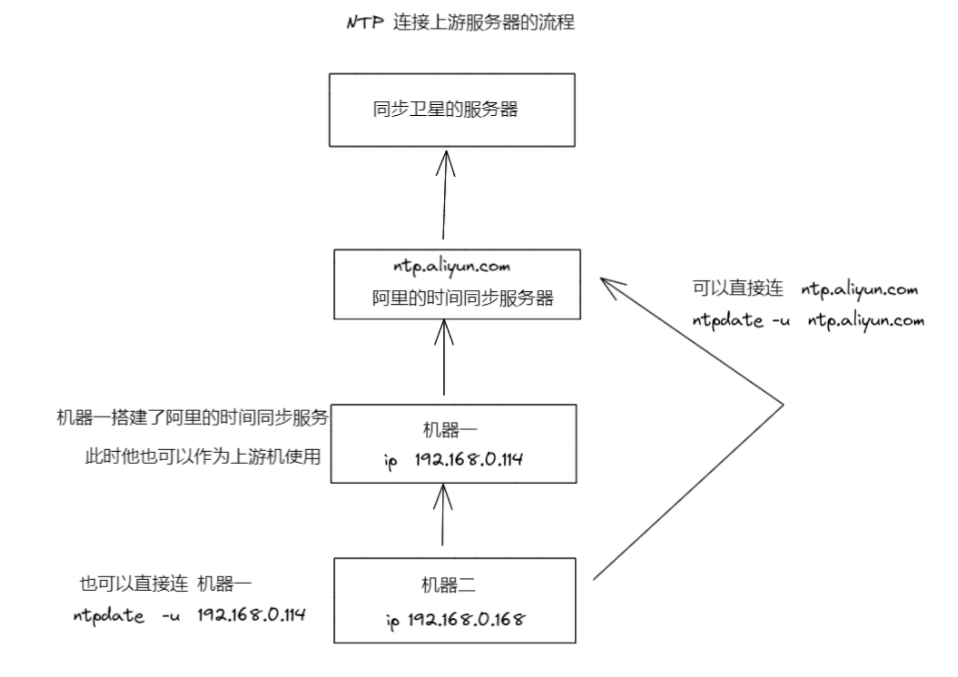
date命令和hwclock命令
hwclock 可以将硬件和软件时间做同步
-s hctosys 从硬件时钟设置系统时间
-w systohc 从当前系统时间设置硬件时间



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号