With the HTML DOM, JavaScript can access all the elements of an HTML document.
The HTML DOM (Document Object Model)
When a web page is loaded, the browser creates a Document Object Model of the page.
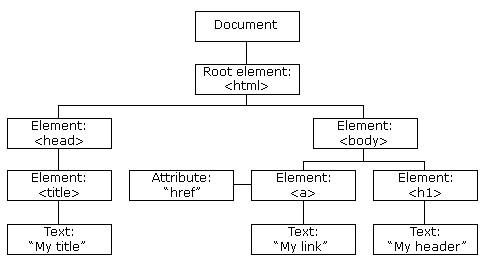
The HTML DOM model is constructed as a tree of Objects
The HTML DOM Tree
With a programmable object model, JavaScript gets all the power it needs to create dynamic HTML:
- JavaScript can change all the HTML elements in the page
- JavaScript can change all the HTML attributes in the page
- JavaScript can change all the CSS styles in the page
- JavaScript can react to all the events in the page
Finding HTML Elements
Often, with JavaScript, you want to manipulate HTML elements.
To do so, you have to find the elements first. There are a couple of ways to do this:
- Finding HTML elements by id
- Finding HTML elements by tag name
- Finding HTML elements by class name
Finding HTML Elements by Id
The easiest way to find HTML elements in the DOM, is by using the element id.
This example finds the element with id="intro":
Example
var x=document.getElementById("intro");
If the element is found, the method will return the element as an object (in x).
If the element is not found, x will contain null.
Finding HTML Elements by Tag Name
This example finds the element with id="main", and then finds all <p> elements inside "main":
Example
var x=document.getElementById("main"); var y=x.getElementsByTagName("p");
Notice: Finding elements by class name does not work in Internet Explorer 5,6,7, and 8.


