CS106L C++ 笔记
CS106L
reference & const(引用与常量)
- 如果不使用引用,C++会默认对声明的对象进行拷贝
-
std::vector<int> vec{1, 2, 3}; const std::vector<int>& c_ref = vec; std::vector<int> copy = c_ref; copy.push_back(4); // vec = {1, 2, 3} // copy = {1, 2, 3, 4} - 使用auto显式指定const 和 引用
-
std::vector<int> vec{1, 2, 3}; const std::vector<int> c_vec{7, 8}; std::vector<int>& ref = vec; const std::vector<int>& c_ref = vec; auto copy = c_ref; // a non-const copy const auto copy = c_ref; // a const copy auto& a_ref = ref; // a non-const reference const auto& c_aref = ref; // a const reference 记住, 当我们对变量进行赋值时,C++默认的会进行copy,我们需要使用引用代替- 对于一个函数,我们可以将返回类型设置为引用,但是要注意的事Dangling reference, 即如果返回的是临时变量则会出现报错,如下:vec只是在front里调用临时的变量,front执行完以后就会销毁
-
int& front(const std::string& file) { std::vector<int> vec = readFile(file); return vec[0]; } int main() { front("text.txt") = 4; // undefined behavior return 0; }
-
什么时候需要使用引用or const引用- 如果我们工作的变量占用很小的内存空间(int, double) ,我们不需要使用引用也可以很快的拷贝变量
- 如果我们需要给变量起别名来修改变量值,那么我们可以使用引用
- 如果我们不需要修改变量,但是它看起来是个大变量(vector),我们可以使用const引用
C++ Streams流
-
Output Streams
- std::ostream, 仅接收 << 操作符, 将数据转换为字符串并将其发送到流
- ofstream是对文件操作的流
-
#include <iostream> #include <string> #include <fstream> //No using namespace std;!!!! using std::cout; using std::endl; using std::string; //function to write num to any ostream int main() { // Write an int to the user's console. int myNum = 42; cout << "The answer is: " << myNum << endl; // Write an int to a file. std::ofstream out_stream("out.txt"); out_stream << "The answer is: " << myNum << endl; // Write method to take any ostream return 0; }
-
Input Streams
- 仅接收>>操作符, 从流中接收string转化为data
- istream work的流程:
)
>>读取到下一个空白字符且不超过该空白字符- getline读取到下一个分隔符(默认情况\n)
不要将getline和>>混用- iostream 是一个istream or ostream
-
流的内部工作
- 缓冲(存储在流内部数据序列称为缓冲区):
- 在临时缓冲区累积所有字符, 当缓冲区满了,将所有缓冲区内容写入输出。
- 通过std::flush 刷新缓冲区
- Istreams使用buffer存储我们尚未使用的数据
- Ostreams使用缓冲区来存储我们尚未输出的数据
- state bit(状态位)
- Good bit : 是否准备好read/write
- Faile bit: 之前的操作失败,之后的操作冻结
- EOF bit:前一个操作达到了文件末尾(EOF是文件末尾结束符)
- Bad bit:外部的完整性错误
- Chaining(连续的链式<< << or >> >>)
-
std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& out, const std::string& s); std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& out, const std::string& s); std::cout << "hello" <=> operator<<(std::cout, "hello") std::cin << input; <=> operator>>(std::cout, input)
-
- 缓冲(存储在流内部数据序列称为缓冲区):
containers容器
- Suqence Containers(序列容器, vector, deque, list)
- std中vector的实现
- vector是由固定长度的数组组成,这个数组在必要时可以自动重定义大小
- std中list: 给定一个指向该位置的迭代器,std::list在序列中的任何位置提供快速插入,但是不能通过索引获得元素
- std中vector的实现
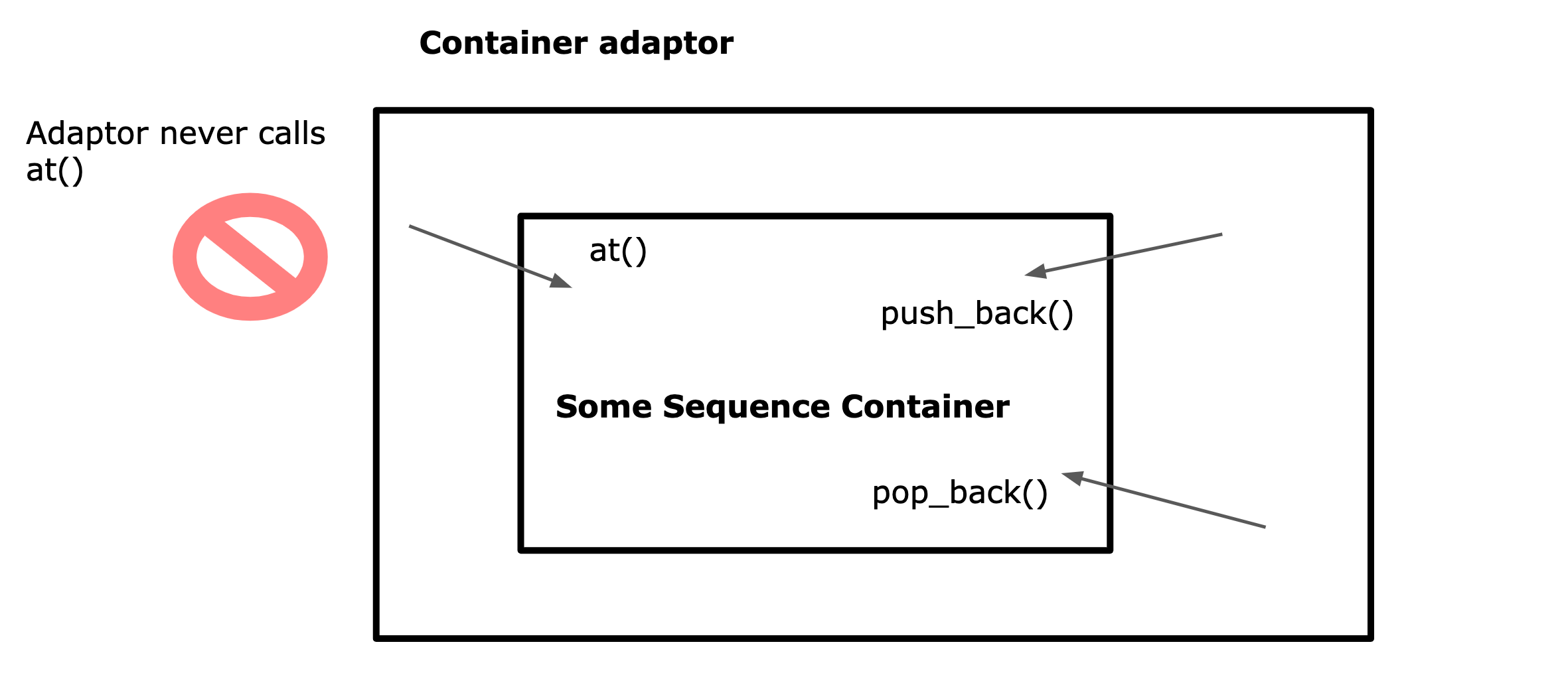
- Container Adaptors



【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· Manus的开源复刻OpenManus初探
· AI 智能体引爆开源社区「GitHub 热点速览」
· 三行代码完成国际化适配,妙~啊~
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?