HDLBits(12)2.22
1|03 电路
1|13.1 组合逻辑
3.1.2 数据选择器/多路复用器(Multiplexers)(MUX)
- Mux2to1(2-to-1 multiplexers)
创建位宽为 1 的 2 对 1 数据选择器。当 sel=0 时,选择 a。当 sel=1 时,选择 b
- Mux2to1v(2-to-1 bus multiplexers)
创建位宽为 100 的 2 对 1 数据选择器。当 sel=0 时,选择 a。当 sel=1 时,选择 b
- Mux9to1(9-to-1 multiplexers)
创建位宽为 16 的 9 对 1 数据选择器。当 sel=0 时,选择 a。当 sel=1 时,选择 b,以此类推,对于未使用的情况(sel = 9 to 15)输出位为1
- Mux256to1(256-to-1 multiplexers)
创建位宽为 1 的 256 对 1 的数据选择器,将 256 个输入全部打包成一个 256 位的输入向量。sel=0 应该选择in[0], sel=1 选择[1]中的位, sel=2 选择[2]中的位,以此类推
- Mux256to1v(256-to-1 4-bit multiplexers)
创建位宽为 4 的 256 对 1 的数据选择器,将 256 个 4 位输入全部打包成一个 1024 位的输入向量。sel=0 应该选择 [3:0] 中的位, sel=1 选择 [7:4] 中的位, sel=2 选择 [11:8] 中的位,以此类推
3.1.3 运算电路(Arithmetic Circuits)
- Hadd(Half adder)
创建一个半加法器。半加器将两位相加(没有进位)得到加和和进位
- Fadd(Full adder)
创建一个全加器,全加器将三位相加(包括进位)并产生加和和进位
- Adder3(3-bit binary adder)
创建 3 个实例来创建一个 3 位二进制波纹进位加法器。加法器将两个 3 位数字和一个进位相加产生一个 3 位加和和进位。为了鼓励实例化全加器,还要输出纹波进位加法器中每个全加器的进位。cout[2] 是最后一个全加器的最终进位,也是通常看到的进位。
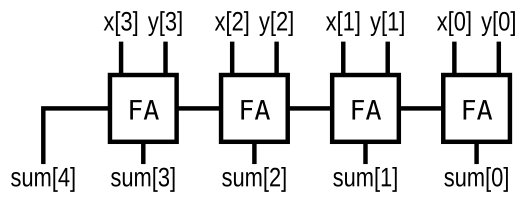
- Adder
实现下图电路,其中FA为加法器
- signed addition overflow
假设有两个 8 位的补码,a[7:0] 和 b[7:0]。这些数字相加产生 s[7:0]。还要计算是否发生了(有符号的)溢出。
* 当两个正数相加产生负结果或两个负数相加产生正结果时,会发生有符号溢出。有几种检测溢出的方法:可以通过比较输入和输出数的符号来计算,或者从位 n 和 n-1 的进位推导出。
- 100-bit binary adder
创建一个100 位二进制加法器。加法器将两个 100 位数字和一个进位相加,产生一个 100 位加和和进位。
- 4-digit BCD adder
实例化四个 bcd_fadd 副本以创建一个4位BCD(binary-coded decimal 二进制编码的十进制)波纹进位加法器。加法器应将两个4位BCD数字(打包成16位向量)和一个进位相加,以产生一个4位加和和进位
*会产生Warning:
Truncating values occur when the right side of an assignment is wider than the left side and the upper bits are cut off. This can indicate a bug if there is a truncation you didn't expect, so check these carefully. The most common case where this isn't a bug is when you're using literals without a width (32 bits is implied), e.g., using assign a[1:0] = 1; instead of assign a[1:0] = 2'd1;
暂不知原因
__EOF__

本文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/LhTian/p/17144470.html
关于博主:评论和私信会在第一时间回复。或者直接私信我。
版权声明:本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 BY-NC-SA 许可协议。转载请注明出处!
声援博主:如果您觉得文章对您有帮助,可以点击文章右下角【推荐】一下。您的鼓励是博主的最大动力!



【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 开源Multi-agent AI智能体框架aevatar.ai,欢迎大家贡献代码
· Manus重磅发布:全球首款通用AI代理技术深度解析与实战指南
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!
· 没有Manus邀请码?试试免邀请码的MGX或者开源的OpenManus吧
· 园子的第一款AI主题卫衣上架——"HELLO! HOW CAN I ASSIST YOU TODAY