使用ASP.NET WEB API构建基于REST风格的服务实战系列教程(一)——使用EF6构建数据库及模型
系列导航地址http://www.cnblogs.com/fzrain/p/3490137.html
使用Entity Framework Code First模式构建数据库对象
已经决定使用EF CodeFirst来创建数据库了,因此我们使用POCO类(“Plain Old CLR Objects)来定义我们的Model。我们通过写标准的.NET类来定义适合我们API的领域模型。那些POCO类就会为我们创建数据库。
我们的培训系统数据库比较简单,首先我们需要有学生”Students”,导师”Tutors”,除此之外我们还需要定义课程”Courses”以及科目”Subjects”。在我们的系统中,我们允许每个学生去报名参加不同的课程
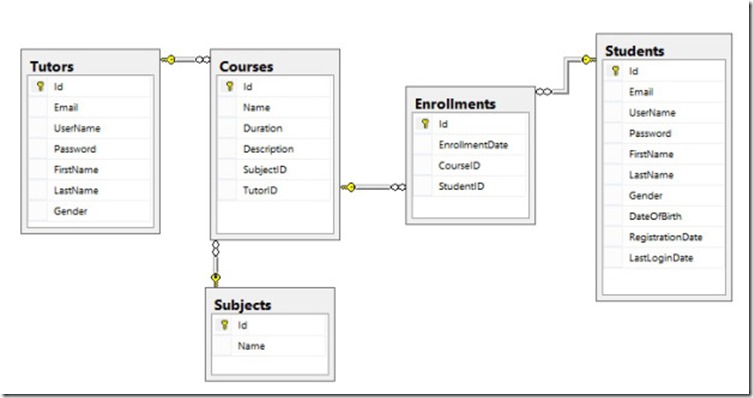
下图是我们数据库建立后的结果,我在这里列出来的目的是为了帮助大家更好的理解接下来创建的POCO类(图不是很清晰,凑合看吧):
第一步:创建一个空的类库项目
打开VS,创建一个空的类库项目
.NET Framewok版本的话我用的事4.5的,选4.0的也行
第二步:使用NuGet添加Entity Framework的引用
右击引用->管理NuGet程序包->右上角输入Entity Framework,选择安装。装好之后就应该是这么一个样子:
这里用的是Entity Framework6,因为这个版本支持了枚举类型,在这次的项目里也有涉及
第三步:创建Model
前面已经说了,到目前为止我们还没有数据库。因此我们需要写标准的.NET类来定义领域模型并帮我们生成数据库
新建一个Entities文件夹并创建5个类(“Student”,“Course”,“Subject”,“Tutor”,“Enrollment”),这几个简单的实体类将为我们创建数据库
public class Course { public Course() { Enrollments = new List<Enrollment>(); CourseTutor = new Tutor(); CourseSubject = new Subject(); } public int Id { get; set; } public string Name { get; set; } public Double Duration { get; set; } public string Description { get; set; } public Tutor CourseTutor { get; set; } public Subject CourseSubject { get; set; } public ICollection<Enrollment> Enrollments { get; set; } } public class Enrollment { public Enrollment() { Student = new Student(); Course = new Course(); } public int Id { get; set; } public DateTime EnrollmentDate { get; set; } public Student Student { get; set; } public Course Course { get; set; } } public class Student { public Student() { Enrollments = new List<Enrollment>(); } public int Id { get; set; } public string Email { get; set; } public string UserName { get; set; } public string Password { get; set; } public string FirstName { get; set; } public string LastName { get; set; } public Gender Gender { get; set; } public DateTime DateOfBirth { get; set; } public DateTime? RegistrationDate { get; set; } public DateTime? LastLoginDate { get; set; } public ICollection<Enrollment> Enrollments { get; set; } } public class Subject { public Subject() { Courses = new List<Course>(); } public int Id { get; set; } public string Name { get; set; } public ICollection<Course> Courses; } public class Tutor { public Tutor() { Courses = new List<Course>(); } public int Id { get; set; } public string Email { get; set; } public string UserName { get; set; } public string Password { get; set; } public string FirstName { get; set; } public string LastName { get; set; } public Gender Gender { get; set; } public ICollection<Course> Courses; }
不难发现,上面我们创建的Model并没有从任何基类继承,也没有打任何attributes。有哪些标准的话会使我们的数据访问拥有更好的延展性,这样的话我们就可以专心地去处理业务而不用过多地考虑数据的持久化。
Entity framework Code First默认使用一种叫“约定大于配置”的方式来为我们创建数据库(通过POCO类映射数据库的表,字段的数据类型,外键等)。在一些简单的应用程序中来说是非常好用的。但在我们的项目中将使用Fluent API配置我们自定义的数据库生成规则——“配置覆盖约定”
第四步:应用自定义映射规则
当我们决定使用配置来覆盖默认规则时,我们可以为每张表的字段配置数据类型,是否可空,表与表之间外键关系,主键以及标识列等等。
于是乎我们创建一个“Mappers”文件夹,新建5个继承自System.Data.Entity.ModelConfiguration.EntityTypeConfiguration<T>的类。分别命名为: “CourseMapper”, “EnrollmentMapper”, “StudentMapper”, “SubjectMapper”, and “TutorMapper”
class CourseMapper : EntityTypeConfiguration<Course> { public CourseMapper() { this.ToTable("Courses"); this.HasKey(c => c.Id); this.Property(c => c.Id).HasDatabaseGeneratedOption(DatabaseGeneratedOption.Identity); this.Property(c => c.Id).IsRequired(); this.Property(c => c.Name).IsRequired(); this.Property(c => c.Name).HasMaxLength(255); this.Property(c => c.Duration).IsRequired(); this.Property(c => c.Description).IsOptional(); this.Property(c => c.Description).HasMaxLength(1000); this.HasRequired(c => c.CourseSubject).WithMany().Map(s => s.MapKey("SubjectID")); this.HasRequired(c => c.CourseTutor).WithMany().Map(t => t.MapKey("TutorID")); } } class EnrollmentMapper : EntityTypeConfiguration<Enrollment> { public EnrollmentMapper() { this.ToTable("Enrollments"); this.HasKey(e => e.Id); this.Property(e => e.Id).HasDatabaseGeneratedOption(DatabaseGeneratedOption.Identity); this.Property(e => e.Id).IsRequired(); this.Property(e => e.EnrollmentDate).IsRequired(); this.Property(e => e.EnrollmentDate).HasColumnType("smalldatetime"); this.HasOptional(e => e.Student).WithMany(e => e.Enrollments).Map(s => s.MapKey("StudentID")).WillCascadeOnDelete(false); this.HasOptional(e => e.Course).WithMany(e => e.Enrollments).Map(c => c.MapKey("CourseID")).WillCascadeOnDelete(false); } } class StudentMapper : EntityTypeConfiguration<Student> { public StudentMapper() { this.ToTable("Students"); this.HasKey(s => s.Id); this.Property(s => s.Id).HasDatabaseGeneratedOption(DatabaseGeneratedOption.Identity); this.Property(s => s.Id).IsRequired(); this.Property(s => s.Email).IsRequired(); this.Property(s => s.Email).HasMaxLength(255); this.Property(s => s.Email).IsUnicode(false); this.Property(s => s.UserName).IsRequired(); this.Property(s => s.UserName).HasMaxLength(50); this.Property(s => s.UserName).IsUnicode(false); this.Property(s => s.Password).IsRequired(); this.Property(s => s.Password).HasMaxLength(255); this.Property(s => s.FirstName).IsRequired(); this.Property(s => s.FirstName).HasMaxLength(50); this.Property(s => s.LastName).IsRequired(); this.Property(s => s.LastName).HasMaxLength(50); this.Property(s => s.Gender).IsOptional(); this.Property(s => s.DateOfBirth).IsRequired(); this.Property(s => s.DateOfBirth).HasColumnType("smalldatetime"); this.Property(s => s.RegistrationDate).IsOptional(); this.Property(s => s.RegistrationDate).HasColumnType("smalldatetime"); this.Property(s => s.LastLoginDate).IsOptional(); this.Property(s => s.LastLoginDate).HasColumnType("smalldatetime"); } } class SubjectMapper : EntityTypeConfiguration<Subject> { public SubjectMapper() { this.ToTable("Subjects"); this.HasKey(s => s.Id); this.Property(s => s.Id).HasDatabaseGeneratedOption(DatabaseGeneratedOption.Identity); this.Property(s => s.Id).IsRequired(); this.Property(s => s.Name).IsRequired(); this.Property(s => s.Name).HasMaxLength(255); } } class TutorMapper : EntityTypeConfiguration<Tutor> { public TutorMapper() { this.ToTable("Tutors"); this.HasKey(s => s.Id); this.Property(s => s.Id).HasDatabaseGeneratedOption(DatabaseGeneratedOption.Identity); this.Property(s => s.Id).IsRequired(); this.Property(s => s.Email).IsRequired(); this.Property(s => s.Email).HasMaxLength(255); this.Property(s => s.Email).IsUnicode(false); this.Property(s => s.UserName).IsRequired(); this.Property(s => s.UserName).HasMaxLength(50); this.Property(s => s.UserName).IsUnicode(false); this.Property(s => s.Password).IsRequired(); this.Property(s => s.Password).HasMaxLength(255); this.Property(s => s.FirstName).IsRequired(); this.Property(s => s.FirstName).HasMaxLength(50); this.Property(s => s.LastName).IsRequired(); this.Property(s => s.LastName).HasMaxLength(50); this.Property(s => s.Gender).IsOptional(); } }
看看上面的代码,不难发现我们为每个POCO类属性(数据类型,是否为空,主键标识,外键关系)都做了配置。这些配置最终会影响我们数据库中表的创建。
关于具体Fluent API的配置方法,可以参考:http://www.cnblogs.com/hyl8218/archive/2011/10/10/2205240.html
第五步:创建Context类来实现数据持久化
现在我们要创建一个LearningContext类继承自System.Data.Entity.DbContext:
public class LearningContext : DbContext { public LearningContext() : base("eLearningConnection") { Configuration.ProxyCreationEnabled = false; Configuration.LazyLoadingEnabled = false; Database.SetInitializer(new MigrateDatabaseToLatestVersion<LearningContext, LearningContextMigrationConfiguration>()); } public DbSet<Course> Courses { get; set; } public DbSet<Enrollment> Enrollments { get; set; } public DbSet<Student> Students { get; set; } public DbSet<Subject> Subjects { get; set; } public DbSet<Tutor> Tutors { get; set; } protected override void OnModelCreating(DbModelBuilder modelBuilder) { modelBuilder.Configurations.Add(new StudentMapper()); modelBuilder.Configurations.Add(new SubjectMapper()); modelBuilder.Configurations.Add(new TutorMapper()); modelBuilder.Configurations.Add(new CourseMapper()); modelBuilder.Configurations.Add(new EnrollmentMapper()); base.OnModelCreating(modelBuilder); } }
这个LearningContext类主要有三大任务
1.把我们定义的POCO类作为DBSet的属性对外公开,这意味着每一个POCO类都将被转化为数据库中的表
2.重写OnModelCreating方法将我们为POCO类自定义的映射规则添加到DbModelBuilder配置中
3.在LearningContext的构造函数中我们做了2件事:
(1)将ProxyCreationEnabled和LazyLoadingEnabled 2个属性设为false(默认都是true)。延迟加载(LazyLoading)主要是指当对象间的关联配置成导航属性暴露给外界的时候,那么这个属性的会在用到它的时候(在前台foreach的时候)才加载,那么极有可能成为性能杀手,我们项目中希望立即加载。而ProxyCreation是配合LazyLoading一起用的,因此当我们把这两个属性值设为false时,那么“LearningContext”就不会去加载导航属性除非调用了“Include”方法(下一章会有演示)。
(2)为数据库配置初始化和迁移策略,如果模型的属性被改变(添加了新的属性),就把数据库迁移到最新版本。为了实现这个功能,我们新建一个类LearningContextMigrationConfiguration继承自System.Data.Entity.Migrations.DbMigrationsConfiguration<TContext>
class LearningContextMigrationConfiguration : DbMigrationsConfiguration<LearningContext> { public LearningContextMigrationConfiguration() { this.AutomaticMigrationsEnabled = true; this.AutomaticMigrationDataLossAllowed = true; } #if DEBUG protected override void Seed(LearningContext context) { new LearningDataSeeder(context).Seed(); } #endif }
LearningContextMigrationConfiguration这个类主要有2个任务:
(1)在构造函数中,我们设置AutomaticMigrationsEnabled 属性为true,那么就意味着EF会为我们自动迁移数据库而不考虑版本问题。同时我们把AutomaticMigrationDataLossAllowed属性也设为true但这样做在开发环境中是很危险的,因为如果这个属性设为false时,一旦数据库在自动迁移时发生数据丢失,那么就会抛出一个异常。但在这次的系列中我们确保没问题。
(2)重写Seed方法来为我们的数据库添加初始数据,这个函数在我们应用程序每次启动时执行。“LearningDataSeeder”这个类主要用于提供需要的数据,具体代码在本章结束时提供。
本章总结
到目前为止,我们已经把用于创建数据库的Model和配置都实现了。在这个时候我们应该想一想:数据访问层是否已经完成?当我们使用Web Api操作的时候是否方便 快捷 高效?我们是否应该对已有的数据访问层再做一次封装?。。。 因此下一章我们将使用“Repository”模式应用在我们的项目中。
随堂代码:http://yun.baidu.com/share/link?shareid=1763536438&uk=17559114
目录
背景返回目录
Heap 可以用来实现优先级队列,也可以用来做堆排序,本文简单的做个介绍。
Heap返回目录
规则返回目录
- 是一个完全二叉树,隐含的意思是:他是平衡的、使用数组进行存储也是连续的。
- 给定的任意节点,该节点小于等于其父亲节点,大于他们的孩子节点。
基础知识返回目录
对于一个完全二叉树,如果将其存储到数组中,给定父节点的索引为:x,则:
- left child's index is:2*x + 1。
- right child's index is:2*x + 2。
- root's index is:0.
说明:上面的公式很容易自己推到出来,有兴趣的朋友可以推到一下,这样就不用记住这个特性了。
图示

存储到数组的顺序为:先存储第一层,然后是第二层,直到第 N 层。
操作返回目录
添加和删除后还必须保证 Heap 满足规则。
添加返回目录
添加前

添加 6

先将 6 添加到完全树的下一个节点,然后沿着祖先路径,将其插入到合适的节点(不一定是根节点)。
代码
1 public void Insert(T item) 2 { 3 if (this.IsFull()) 4 { 5 throw new InvalidOperationException("容量已满,不能插入!"); 6 } 7 8 _items[_length++] = item; 9 this.MoveUp(_length - 1); 10 }
结果

删除最大值返回目录
接着上面的例子执行删除
先将删除根节点(6),再将完全树最后的节点(2)直接移动到根节点。

接着将 2 向下插入到合适的节点,比如:5 > 4 && 5 > 2,因此结果是:

代码
1 public T Remove() 2 { 3 if (this.IsEmpty()) 4 { 5 throw new InvalidOperationException("容量已空,不能删除!"); 6 } 7 8 var result = _items[0]; 9 _items[0] = _items[--_length]; 10 11 this.MoveDown(0); 12 13 return result; 14 }
完整代码返回目录
1 using System; 2 using System.Collections.Generic; 3 using System.Linq; 4 using System.Text; 5 using System.Threading.Tasks; 6 7 namespace DataStuctureStudy.Heaps 8 { 9 class HeapTest 10 { 11 public static void Test() 12 { 13 var heap = new Heap<int>(10); 14 heap.Insert(1); 15 heap.Insert(2); 16 heap.Insert(3); 17 heap.Insert(4); 18 heap.Insert(5); 19 heap.Insert(6); 20 heap.Display(); 21 heap.Remove(); 22 heap.Display(); 23 } 24 25 class Heap<T> 26 where T : IComparable<T> 27 { 28 private T[] _items; 29 private int _length; 30 31 public Heap(int size) 32 { 33 _items = new T[size]; 34 } 35 36 public void Display() 37 { 38 Console.WriteLine("数组表示"); 39 Console.Write("["); 40 for (var i = 0; i < _items.Length; i++) 41 { 42 if (i < _length) 43 { 44 Console.Write(_items[i]); 45 } 46 else 47 { 48 Console.Write('-'); 49 } 50 } 51 Console.WriteLine("]"); 52 Console.WriteLine(); 53 54 Console.WriteLine("树形表示"); 55 var row = 0; 56 var column = 0; 57 var level = (int)Math.Ceiling(Math.Log(_length + 1, 2)); 58 var width = (int)Math.Pow(2, level); 59 for (var i = 0; i < _length; i++) 60 { 61 this.Display(_items[i], width, row, column); 62 63 if ((i + 1) == Math.Pow(2, row + 1) - 1) 64 { 65 row++; 66 column = 0; 67 Console.WriteLine(); 68 } 69 else 70 { 71 column++; 72 if (i == _length - 1) 73 { 74 Console.WriteLine(); 75 } 76 } 77 } 78 79 Console.WriteLine(); 80 } 81 82 private void Display(T item, int width, int row, int column) 83 { 84 var step = (int)((width * 3) / Math.Pow(2, row)); 85 var itemLength = item.ToString().Length; 86 Console.Write(item.ToString().PadLeft((step + itemLength) / 2).PadRight(step)); 87 } 88 89 public void Insert(T item) 90 { 91 if (this.IsFull()) 92 { 93 throw new InvalidOperationException("容量已满,不能插入!"); 94 } 95 96 _items[_length++] = item; 97 this.MoveUp(_length - 1); 98 } 99 100 private void MoveUp(int index) 101 { 102 var bottom = _items[index]; 103 var current = index; 104 105 while (current > 0) 106 { 107 var parent = (current - 1) / 2; 108 if (_items[parent].CompareTo(bottom) > 0) 109 { 110 break; 111 } 112 113 _items[current] = _items[parent]; 114 current = parent; 115 } 116 117 _items[current] = bottom; 118 } 119 120 public T Remove() 121 { 122 if (this.IsEmpty()) 123 { 124 throw new InvalidOperationException("容量已空,不能删除!"); 125 } 126 127 var result = _items[0]; 128 _items[0] = _items[--_length]; 129 130 this.MoveDown(0); 131 132 return result; 133 } 134 135 private void MoveDown(int index) 136 { 137 var top = _items[index]; 138 var current = index; 139 140 while (current < _length) 141 { 142 var large = 0; 143 var left = 2 * current + 1; 144 var right = left + 1; 145 146 if (left < _length && right < _length) 147 { 148 if (_items[left].CompareTo(_items[right]) >= 0) 149 { 150 large = left; 151 } 152 else 153 { 154 large = right; 155 } 156 } 157 else if (left < _length) 158 { 159 large = left; 160 } 161 else 162 { 163 break; 164 } 165 166 if (_items[large].CompareTo(top) <= 0) 167 { 168 break; 169 } 170 171 _items[current] = _items[large]; 172 current = large; 173 } 174 175 _items[current] = top; 176 } 177 178 public bool IsFull() 179 { 180 return _length == _items.Length; 181 } 182 183 public bool IsEmpty() 184 { 185 return _length == 0; 186 } 187 } 188 } 189 }
备注返回目录
下篇简单的介绍一下堆排序。