Pytorch深入学习阶段二(一)
Pytorch学习二阶段
一、自动求导
训练神经网络包含两步:
- 前向传播
- 后向传播:后向传播中,NN将调整他的参数,并通过loss_function来自计算误差,并通过优化器来优化参数。
import torch, torchvision
model = torchvision.models.resnet18(pretrained=True)
data = torch.rand(1, 3, 64, 64)
labels = torch.rand(1, 1000)
prediction = model(data) # forward pass
>>>data
tensor([[[[0.0792, 0.3683, 0.3258, ..., 0.8572, 0.9326, 0.5032],
[0.3238, 0.3992, 0.6769, ..., 0.7879, 0.6261, 0.4239],
[0.0839, 0.7466, 0.7469, ..., 0.0616, 0.5267, 0.0221],
...,
[0.4114, 0.2793, 0.4946, ..., 0.3337, 0.0151, 0.9790],
[0.4874, 0.2718, 0.3890, ..., 0.6204, 0.2941, 0.9589],
[0.8202, 0.3904, 0.9375, ..., 0.1282, 0.2416, 0.0420]],
[[0.2958, 0.6416, 0.2069, ..., 0.0054, 0.3710, 0.8716],
[0.2861, 0.6640, 0.3595, ..., 0.4552, 0.6691, 0.9000],
[0.1908, 0.1988, 0.0502, ..., 0.9516, 0.0986, 0.2951],
...,
[0.3542, 0.6152, 0.8829, ..., 0.7102, 0.7418, 0.2471],
[0.1259, 0.4121, 0.4195, ..., 0.0277, 0.7919, 0.1961],
[0.6761, 0.1635, 0.6317, ..., 0.5082, 0.8117, 0.4959]],...
>>>labels
tensor([[9.7649e-01, 7.4230e-01, 8.9876e-01, 3.9301e-01, 4.3104e-01, 2.5916e-01,
2.1638e-01, 2.3715e-01, 3.6239e-01, 5.1230e-02, 5.0033e-01, 9.3420e-01,
7.3738e-01, 5.1232e-01, 6.1602e-01, 3.1946e-01, 3.3043e-01, 6.6394e-01,
6.5134e-01, 4.4163e-01, 3.2559e-01, 1.1167e-01, 9.5033e-01, 2.6302e-01,
4.9590e-01, 1.1047e-01, 6.7810e-01, 1.6822e-01, 3.9666e-01, 9.3511e-01,...
计算完毕前向传播后,通过与真实标签计算误差(目前常用交叉熵去计算)。然后下一步就是后向传播误差在网络参数中,自动梯度计算并存储了梯度为每个参数,通过.grad属性。
loss = (prediction - labels).sum()
loss.backward() # backward pass
>>> loss
tensor(-491.3782, grad_fn=<SumBackward0>)
接下来定义优化器,用随机梯度下降,SGD,并且Learning_rate设置为0.01,动量设置为0.9。
optim = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=1e-2, momentum=0.9)
>>> optim
SGD (
Parameter Group 0
dampening: 0
lr: 0.01
momentum: 0.9
nesterov: False
weight_decay: 0
)
最后我们调用.step()来初始玩成梯度下降,优化器最后会调整参数通过模型属性.grad。
optim.step() #gradient descent
(一)Autograd中的微分
autograd是怎样收集梯度的呢?
举例如下:
import torch
a = torch.tensor([2., 3.], requires_grad=True)
b = torch.tensor([6., 4.], requires_grad=True)
假设a,b都是NN的参数,Q是损失,在训练过程,优化参数求导:
当调用.backward()在Q上,autograd计算这些梯度和分数,在参数的.grad属性。
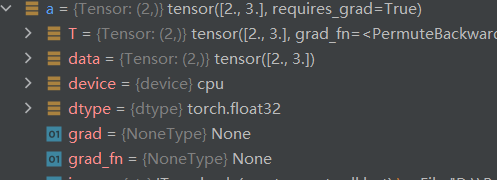
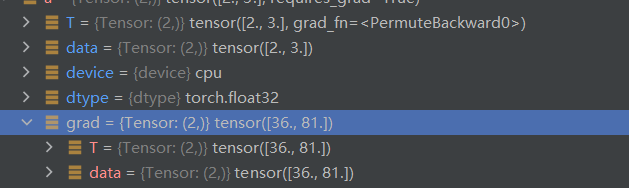
在idea中可以看到,未学习前,grad为0空,下图是autograd计算后,得到的a的值,b同理可得。
(二)向量计算使用autograd
在数学里,雅各比行列式被用来存储函数的导数:
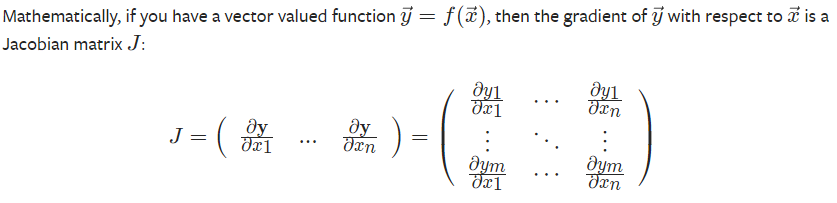
而autograd也可以用来计算雅各比行列式。
(三)计算图
计算图是autograd的一种计算方法,称之为directed acyclic graph,在DAG中,叶子是输入张量,根是输出张量,通过追踪计算图的叶子到根,我们可以自动计算出梯度,使用链式法则。
前向传播中,autograd同时做两件事情:
- 运行必要的计算操作
- 保持梯度函数的操作,在DAG中
后向传播当.backward()被调用在DAG的根上,autograd则:
- 计算梯度的每个
.grad_fn - 加快张量的
.grad属性计算 - 使用链式法则,传播给所连的叶子张量
DAG记录了每个张量的操作,当其requires_grad标志位设置为True,反之,将不会记录。在NN中,参数不更新叫做冻结参数(frozen parameters),如果你事先直到不需要梯度更新参数,这将是有用的。
from torch import nn, optim
model = torchvision.models.resnet18(pretrained=True)
# Freeze all the parameters in the network
for param in model.parameters():
param.requires_grad = False
二、NEURAL NETWORKS
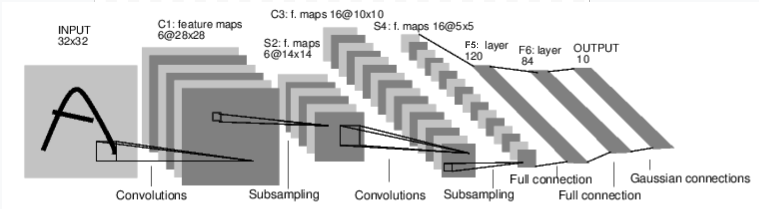
一个典型的神经网络训练过程:
- 定义NN(一些可以学习的参数)
- 迭代输入的数据集
- 计算损失
- 运用后向传播和梯度
- 更新权重,一般简单的运用公式:
weight = weight - learning_rate * gradient
(一)定义网络
class Net(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Net, self).__init__()
# 1 input image channel, 6 output channels, 5x5 square convolution
# kernel
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(1, 6, 5)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(6, 16, 5)
# an affine operation: y = Wx + b
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(16 * 5 * 5, 120) # 5*5 from image dimension
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(120, 84)
self.fc3 = nn.Linear(84, 10)
def forward(self, x):
# Max pooling over a (2, 2) window
x = F.max_pool2d(F.relu(self.conv1(x)), (2, 2))
# If the size is a square, you can specify with a single number
x = F.max_pool2d(F.relu(self.conv2(x)), 2)
x = torch.flatten(x, 1) # flatten all dimensions except the batch dimension
x = F.relu(self.fc1(x))
x = F.relu(self.fc2(x))
x = self.fc3(x)
return x
net = Net()
print(net)
>>>Net(
(conv1): Conv2d(1, 6, kernel_size=(5, 5), stride=(1, 1))
(conv2): Conv2d(6, 16, kernel_size=(5, 5), stride=(1, 1))
(fc1): Linear(in_features=400, out_features=120, bias=True)
(fc2): Linear(in_features=120, out_features=84, bias=True)
(fc3): Linear(in_features=84, out_features=10, bias=True)
)
forward必须被定义,但是backward函数不需要,因为已经被自动定义。forward可以被用于任何张量操作。
Note:
torch.nn仅支持mini-batches。nn.Conv2d将喂入一个4dimension的张量,如nSamples x nChannels x Height x Width。如果是一个单个样本,使用input.unsqueeze(0)去增加一个虚拟batch维度。
Recap:
-
torch.Tensor是一个多维向量,支持autograd -
nn.Moduleneural network模型,转化参数类型,可以移步到GPU去计算 -
nn.Parameter一种张量,可以自动地注册 -
autograd.Function实现了autograd操作的前后传播定义,每一个张量操作创造至少一个Function节点,以此链接特殊的函数,这个特殊的函数创建了一个张量,并且编码了它的生命记录
(二)损失函数
损失函数需要输出和目标值作为一对输入,并且计算他们俩之间的差距。
output = net(input)
target = torch.randn(10) # a dummy target, for example
target = target.view(1, -1) # make it the same shape as output
criterion = nn.MSELoss()
loss = criterion(output, target)
print(loss)
>>>
tensor(0.6493, grad_fn=<MseLossBackward0>)
如果我们跟随Loss在后向传播方向,使用Loss的.grad_fn,可以看到计算图。
input -> conv2d -> relu -> maxpool2d -> conv2d -> relu -> maxpool2d
-> flatten -> linear -> relu -> linear -> relu -> linear
-> MSELoss
-> loss
(三)权重更新
最简单的随机梯度下降(SGD),更新方法:
weight = weight - learning_rate * gradient
运用代码:
learning_rate = 0.01
for f in net.parameters():
f.data.sub_(f.grad.data * learning_rate)
更多的更新方法在包torch.optim中。
三、CIFAR-10训练
import torch
from torch import nn
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
from torch.utils.tensorboard import SummaryWriter
from torchvision import datasets
from torchvision.transforms import ToTensor
torch.manual_seed(1)
# hyper parameters
Epoch = 10
Batch_size = 64
Learning_rate = 0.001
# Download training data from open datasets.
training_data = datasets.FashionMNIST(
root="data",
train=True,
download=True,
transform=ToTensor(),
)
# Download test data from open datasets.
test_data = datasets.FashionMNIST(
root="data",
train=False,
download=True,
transform=ToTensor(),
)
# Create data loaders.
train_dataloader = DataLoader(training_data, batch_size=Batch_size)
test_dataloader = DataLoader(test_data, batch_size=Batch_size)
for X, y in test_dataloader:
print(f"Shape of X [N, C, H, W]: {X.shape}")
print(f"Shape of y: {y.shape} {y.dtype}")
break
# Get cpu or gpu device for training.
device = "cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu"
print(f"Using {device} device")
class CNN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(CNN, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Sequential( # input shape (1,28,28)
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=1, # input height
out_channels=16, # n_filter
kernel_size=5, # filter size
stride=1, # filter step
padding=2 # con2d出来的图片大小不变
), # output shape (16,28,28)
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2) # 2x2采样,output shape (16,14,14)
)
self.conv2 = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(16, 32, 5, 1, 2), # output shape (32,7,7)
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(2))
self.out = nn.Linear(32 * 7 * 7, 10)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv1(x)
x = self.conv2(x)
x = x.view(x.size(0), -1) # flat (batch_size, 32*7*7)
output = self.out(x)
return output
cnn = CNN().to(device)
print(cnn)
# optimizer
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(cnn.parameters(), lr=Learning_rate)
# loss_fun
loss_func = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
write = SummaryWriter('logs')
def train(dataloader, cnn, loss_fn, optimizer):
size = len(dataloader.dataset)
cnn.train()
for batch, (X, y) in enumerate(dataloader):
X, y = X.to(device), y.to(device)
# Compute prediction error
pred = cnn(X)
loss = loss_fn(pred, y)
# Backpropagation
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
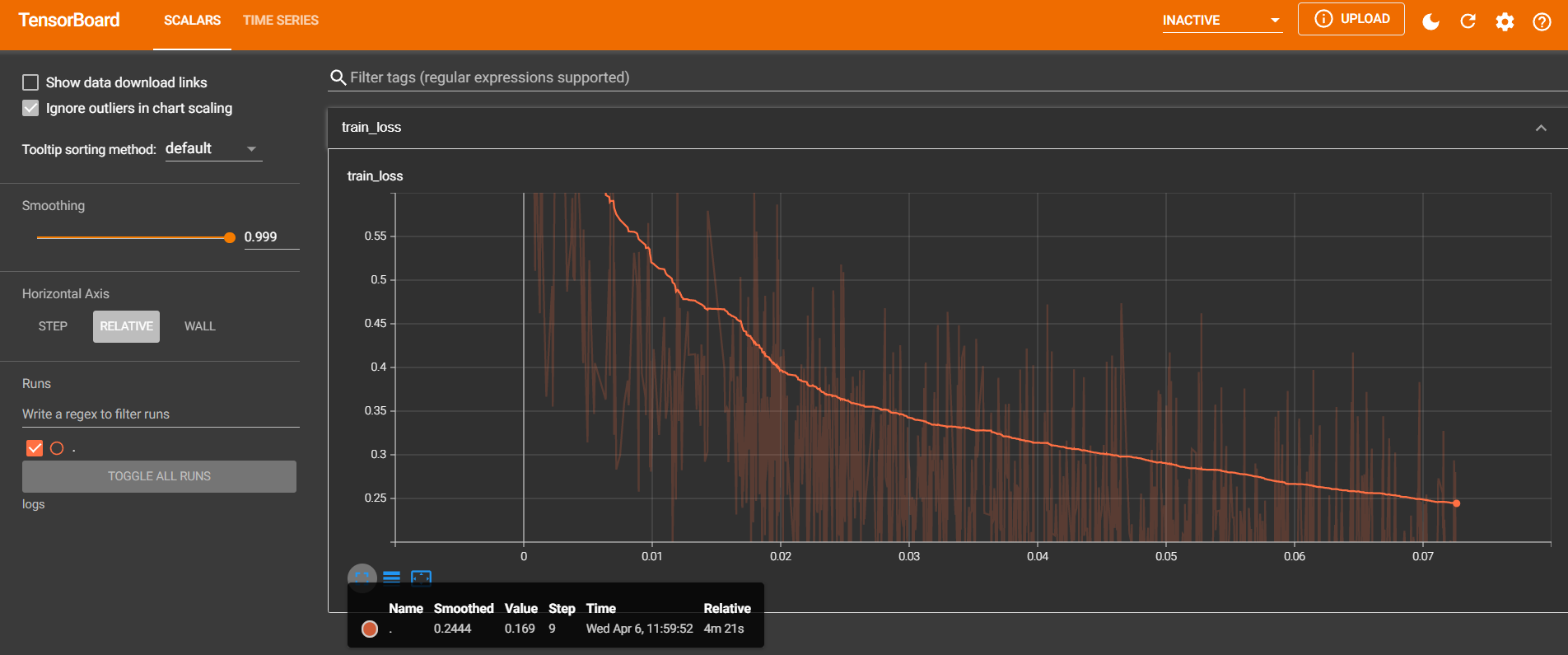
write.add_scalar("train_loss",loss.item())
if batch % 100 == 0:
loss, current = loss.item(), batch * len(X)
print(f"loss: {loss:>7f} [{current:>5d}/{size:>5d}]")
def test(dataloader, cnn, loss_fn):
size = len(dataloader.dataset)
num_batches = len(dataloader)
cnn.eval()
test_loss, correct = 0, 0
with torch.no_grad():
for X, y in dataloader:
X, y = X.to(device), y.to(device)
pred = cnn(X)
test_loss += loss_fn(pred, y).item()
correct += (pred.argmax(1) == y).type(torch.float).sum().item()
test_loss /= num_batches
correct /= size
print(f"Test Error: \n Accuracy: {(100*correct):>0.1f}%, Avg loss: {test_loss:>8f} \n")
print("------start training------")
for epoch in range(Epoch):
print(f"Epoch {epoch + 1}\n-------------------------------")
train(train_dataloader, cnn, loss_func, optimizer)
test(test_dataloader, cnn, loss_func)
print("Done!")
out:
Shape of X [N, C, H, W]: torch.Size([64, 1, 28, 28])
Shape of y: torch.Size([64]) torch.int64
Using cuda device
CNN(
(conv1): Sequential(
(0): Conv2d(1, 16, kernel_size=(5, 5), stride=(1, 1), padding=(2, 2))
(1): ReLU()
(2): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)
)
(conv2): Sequential(
(0): Conv2d(16, 32, kernel_size=(5, 5), stride=(1, 1), padding=(2, 2))
(1): ReLU()
(2): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)
)
(out): Linear(in_features=1568, out_features=10, bias=True)
)
------start training------
Epoch 1
-------------------------------
loss: 2.307641 [ 0/60000]
loss: 0.737086 [ 6400/60000]
loss: 0.368927 [12800/60000]
loss: 0.530034 [19200/60000]
loss: 0.556181 [25600/60000]
loss: 0.511927 [32000/60000]
loss: 0.382789 [38400/60000]
loss: 0.543811 [44800/60000]
loss: 0.516559 [51200/60000]
loss: 0.427986 [57600/60000]
Test Error:
Accuracy: 85.4%, Avg loss: 0.404072
运行后在cmd输入以下命令查看训练状态:
tensorboard --logdir=logs --port=8080


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号