链表问题(6)-----排序
一、题目:将单向链表按某值划分为左边小、中间相等、右边大的形式


简单的思路:时间O(N),空间O(N)
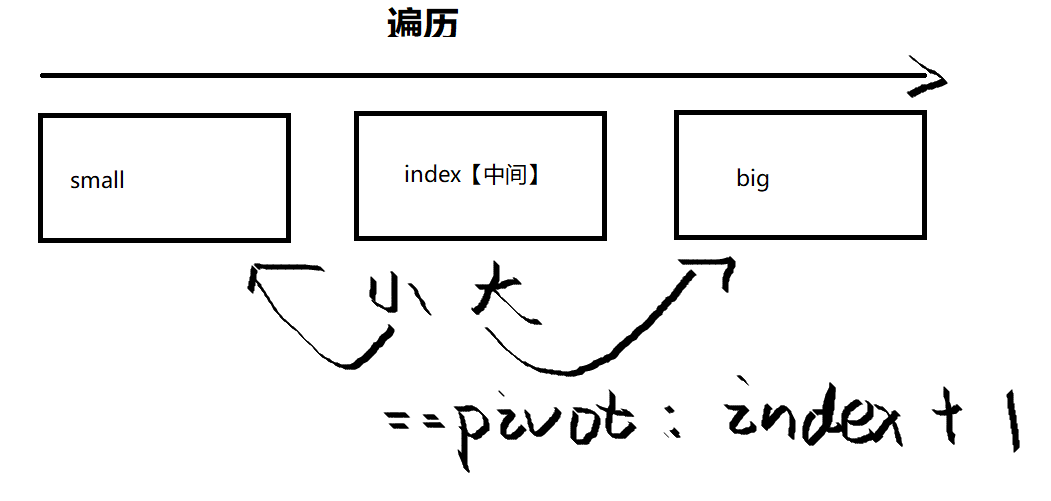
采用一个数组来存储链表中的值,然后对该数组进行快排,然后再连成链表,快排思想如下图所示:
代码:
class Node: def __init__(self,value): self.value = value self.next = None #快排思想 def partition(arr,pivot): small = -1 big = len(arr) index = 0 while index != big: if arr[index] < pivot: small += 1 arr[small] , arr[index] = arr[index] , arr[small] index += 1 elif arr[index] == pivot: index += 1 else: big -= 1 arr[index] , arr[big] = arr[big] , arr[index] return arr #链表操作 def listSort(head,pivot): if not head: return head #将链表存储在数组中 arr = [] while head: arr.append(head.value) head = head.next arr = partition(arr,pivot) #创建链表 node = Node(arr[0]) p = node for i in range(1,len(arr)): p.next = Node(arr[i]) p = p.next return node head = Node(9) head.next = Node(0) head.next.next = Node(4) head.next.next.next = Node(3) head.next.next.next.next = Node(1) pivot = 3 node = listSort(head,pivot)
进阶思想:时间O(N),空间O(1)

代码:
class Node: def __init__(self,value): self.value = value self.next = None def listPartition(head,pivot): if not head: return head sH = None sT = None eH = None eT = None bH = None bT = None while head: next = head.next head.next = None if head.value < pivot: if not sH: sH = head sT = head else: sT.next = head sT = head elif head.value == pivot: if not eH: eH = head eT = head else: eT.next = head eT = head else: if bH == None: bH = head bT = head else: bT.next = head bT = head head = next if sT: sT.next = eH eT = eT if eT else sT if eT: eT.next = bH return sH if sH else eH if eH else bH arr = [9,1,4,5,6,3,8] head = Node(arr[0]) p = head for i in range(1,len(arr)): p.next = Node(arr[i]) p = p.next pivot = 5 res = listPartition(head,pivot)
二、题目:实现单链表的选择排序:
要求:额外空间为O(1),时间复杂度为O(N2)
代码:
class Node: def __init__(self,val): self.val = val self.next = None def sortList(head): if not head: return head tail = None res = tail cur = head smallpre = Node(None) small = Node(None) while cur: small = cur smallPre = getSmallValue(cur) if smallPre: small = smallPre.next smallPre.next = small.next cur = cur.next if cur == small else cur if not tail: tail = small res = small else: tail.next = small tail = small def getSmallValue(cur): small = cur smallPre = None while cur.next: if cur.next.val < small.val: small = cur.next smallPre = cur cur = cur.next return smallPre head = Node(4) head.next = Node(5) head.next.next = Node(3) head.next.next.next = Node(1) head.next.next.next.next = Node(2) sortList(head)
三、题目:实现单链表的归并排序
在 O(n log n) 时间复杂度和常数级空间复杂度下,对链表进行排序。
思路:时间复杂度O(nlogn),空间复杂度O(1)
1、找到链表中间节点
2、递归排序左边链表和右边链表。
3、排序合并左右两边链表
class ListNode(object): def __init__(self, x): self.val = x self.next = None class Solution(object): def sortList(self, head): """ :type head: ListNode :rtype: ListNode """ if not head or not head.next: return head mid = self.get_mid(head) l = head r = mid.next mid.next = None return self.merge(self.sortList(l),self.sortList(r)) def get_mid(self,head): if not head or not head.next: return None slow = head fast = head while fast.next and fast.next.next: slow = slow.next fast = fast.next.next return slow def merge(self,l,r): head = ListNode(0) tmp = head while l and r: if l.val <= r.val: tmp.next = l l = l.next else: tmp.next = r r = r.next tmp = tmp.next if l: tmp.next = l if r: tmp.next = r return head.next
四、对链表进行插入排序
时间复杂度为O(n2),空间复杂度为O(1)
思路:
一个函数遍历原链表到当前元素,一个函数将当前元素插入到已经排好序的链表中,最终返回已经排好序的列表。
代码:
lass ListNode(object): # def __init__(self, x): # self.val = x # self.next = None class Solution(object): def insertionSortList(self, head): """ :type head: ListNode :rtype: ListNode """ if not head or not head.next: return head sortnode = None cur = head while cur: node = cur cur = cur.next node.next = None sortnode = self.sortList(sortnode,node) return sortnode def sortList(self,head,node): pre = None cur = head while cur and node.val > cur.val: pre = cur cur = cur.next node.next = cur if cur == head: head = node else: pre.next = node return head

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号