树(8)----路径和
1、输出树的所有路径:(前序遍历,深度遍历的特例)
def allPath(root):
'''
root为TreeNode类
输出:['1->2->5','1->3']
'''
res=[]
strPre=''
def helper(Tree,strPre):
if Tree:
strPre+=str(Tree.val)+'->'
#若左右子树都为空的时候就把结果加入列表中
if not Tree.left and not Tree.right:
res.append(strPre[:-2])
#否则递归将左右子树的路径加进来
else:
helper(Tree.left,strPre)
helper(Tree.right,strPre)
helper(root,strPre)
return res
1、二叉树中的最大路径和
给定一个非空二叉树,返回其最大路径和。
本题中,路径被定义为一条从树中任意节点出发,达到任意节点的序列。该路径至少包含一个节点,且不一定经过根节点。
示例 1:
输入: [1,2,3]
1
/ \
2 3
输出: 6
示例 2:
输入: [-10,9,20,null,null,15,7] -10 / \ 9 20 / \ 15 7 输出: 42
class Solution:
def __init__(self): self.maxRes=-2**31 def helper (self,root): if root: l=max(0,self.helper(root.left)) r=max(0,self.helper(root.right)) self.maxRes=max(self.maxRes,l+r+root.val) return max(l,r)+root.val return 0 def maxPathSum(self, root): if not root: return 0 self.helper(root) return self.maxRes
############超出时间限制
class Solution(object): def maxPathSum(self, root): """ :type root: TreeNode :rtype: int """ temp,res=self.helper(root) return res #计算最长路径和 def path(self,root,maxres,sumval): if root: sumval+=root.val maxres=max(maxres,sumval) left=right=maxres if root.left: left=self.path(root.left,maxres,sumval) if root.right: right=self.path(root.right,maxres,sumval) return max(left,right) return 0 #(root,左路+root,右路+root,左最大值,右最大值)比较得到最大值 def helper(self,root): if not root: return -10000,-10000 maxres=root.val sumval=0 lpath,lre=self.helper(root.left) rpath,rre=self.helper(root.right) return self.path(root,maxres,sumval),max(lre,rre,lpath+rpath+root.val,root.val,lpath+root.val,rpath+root.val)
2、路径求和等于给定值(两个递归求解)
给定一个二叉树,它的每个结点都存放着一个整数值。
找出路径和等于给定数值的路径总数。
路径不需要从根节点开始,也不需要在叶子节点结束,但是路径方向必须是向下的(只能从父节点到子节点)。
二叉树不超过1000个节点,且节点数值范围是 [-1000000,1000000] 的整数。
示例:
root = [10,5,-3,3,2,null,11,3,-2,null,1], sum = 8
10
/ \
5 -3
/ \ \
3 2 11
/ \ \
3 -2 1
返回 3。和等于 8 的路径有:
1. 5 -> 3
2. 5 -> 2 -> 1
3. -3 -> 11
class Solution(object): def pathSum(self, root, sum): """ :type root: TreeNode :type sum: int :rtype: int """ self.res=0 def ans(root,cur,sum): cur+=root.val if cur==sum: self.res+=1 if root.left: ans(root.left,cur,sum) if root.right: ans(root.right,cur,sum) def helper(root,sum): if root: ans(root,0,sum) if root.left: helper(root.left,sum) if root.right: helper(root.right,sum) helper(root,sum) return self.res
#方案二:时间复杂度和空间复杂度都是O(n)。存放当前节点若为某条目标路径的终点其可能的取值集和,避免重复计算 def pathSum(root, sum): if not root: return 0 sum_res = [sum] return helper(root, sum_res) def helper(root, sum_res): count = 0 sum = sum_res[-1] if not root: return count count += sum_res.count(root.val) sum_res = [x-root.val for x in sum_res] sum_res.append(sum) count += helper(root.left, sum_res) count += helper(root.right, sum_res) return count
14、路径总和(递归)【用列表的深拷贝】
def pathSum(self, root, sum):
"""
:type root: TreeNode
:type sum: int
:rtype: List[List[int]]
"""
if not root:
return []
res=[]
temp= []
def helper(root,sum,temp,res):
if root:
# temp += str(root.val) + ','
temp.append(root.val)
if not root.left and not root.right:
# temp = temp.split(',')[:-1]
# temp = map(lambda x: int(x), temp)
a=reduce(lambda x,y:x+y,temp)
if a==sum:
res.append(temp)
else:
temp_copy = copy.deepcopy(temp)
helper(root.left,sum,temp_copy,res)
helper(root.right,sum,temp,res)
helper(root,sum,temp,res)
return res
15、二叉树路径求和(可加可减):
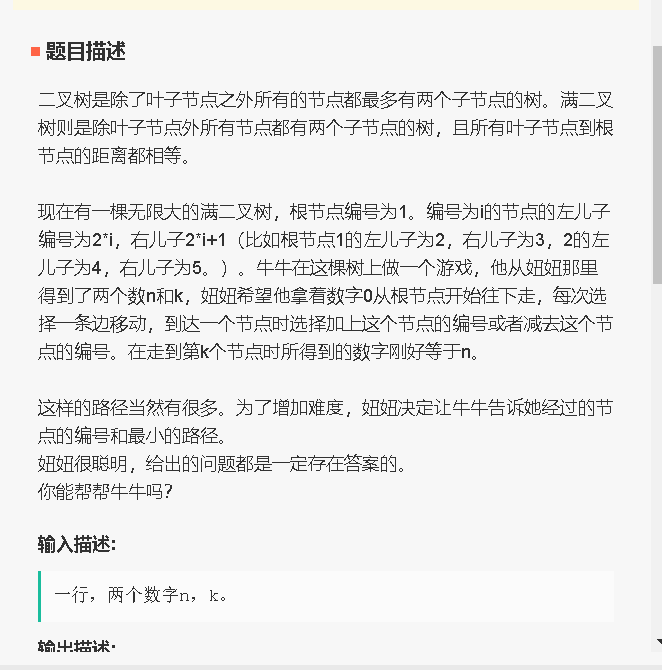
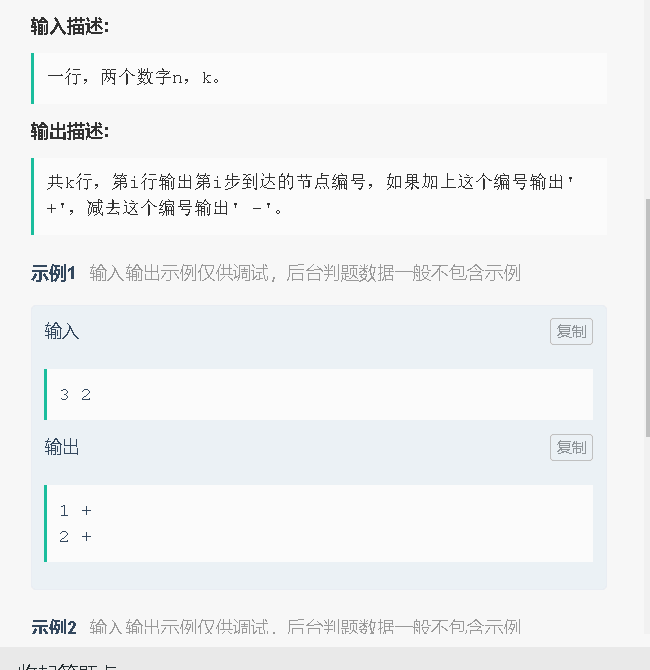
代码:
class Solution: def __init__(self): self.res = [] def find_path(self,i,n,k): if n == 0 and k == 0: return True if n != 0 and k == 0: return if self.find_path(2*i,n-2*i,k-1):#+,走左 self.res.append(str(2*i) + '+') return True if self.find_path (2*i,n+2*i,k-1):#-,走左 self.res.append (str(2*i) + '-') return True if self.find_path(2*i+1,n-2*i-1,k-1):#+,走右 self.res.append(str(2*i+1) + '+') return True if self.find_path(2*i+1,n+2*i+1,k-1):#-,走右 self.res.append(str(2*i+1)+'-') return True return False S = Solution() S.find_path(0,6,3) print(S.res)


