STL标准库-容器-set与multiset
技术在于交流、沟通,转载请注明出处并保持作品的完整性。
set与multiset关联容器
结构如下

set是一种关联容器,key即value,value即key.它是自动排序,排序特点依据key
set的key不能相同.multiset的key相同.关联容器的查找效率要高于顺序容器很多很多.
set和multiset不提供用来直接存取元素的任何操作函数,取值需要通过迭代器
一 定义
1.set/mulitiset以红黑树为底层结构,因此有元素自动排序的特性,排序是根据key,而set.multiset的元素的value和key相同
2.set/multiset提供遍历即迭代器操作,获得排序后的状态
3.我们无法使用迭代器改变set/multiset改变元素值,实现原理是RB tree 的const iterator
4.set元素的key必须对无二,因此其insert()用的rb_tree的insert_unique()
5.multiset的元素key可以重复,因此其insert()用的是rb_tree的insert_equal()
set的源码
template <class _Key, class _Compare = less<_Key>, class _Allocator = allocator<_Key> > class _LIBCPP_TYPE_VIS_ONLY set { ... private: typedef __tree<value_type, value_compare, allocator_type> __base; ... __base __tree_; ... }
第一参数 key 是key的类型 ,
第二参数 compare 比较函数,key的排序函数
第三参数 默认的分配器
使用介绍
//1.定义 set<int> c; for(auto i : c) { cout << i << endl; } cout << "ctor" <<endl; //2.initializer ctor set<int> c1 = {1,2,3,7,6,4,5};//set当插入相同元素时,会插入不成功,但是不会有任何提示 for(auto i : c1) { cout << i << endl; } cout << "initializer_ctor" <<endl;//会发现set有自动排序的功能,因为他的底层实现使红黑树 //3.数组转换 int arrayOfSet[] = {10,20,30,40,50}; std::set<int> c2(arrayOfSet,arrayOfSet+5); for(auto i : c2) { cout << i << endl; } cout << "initializer_ctor" <<endl; //4.operator = c = c1; for(auto i : c) { cout << i << endl; } cout << "operator= " <<endl;
二 set迭代器
//迭代器操作 正向迭代器 set<int>::iterator iteBegin = c.begin(); set<int>::iterator iteEnd = c.end(); cout<< "*iteBegin: "<< *iteBegin << endl; iteEnd--; cout<< "*iteEnd: "<< *iteEnd << endl; //正向const迭代器,不能改变,其实不需要知道正向迭代器和反向,反正都不能使用迭代器直接修改其元素 set<int>::const_iterator iteCBegin = c.cbegin(); set<int>::const_iterator iteCEnd = c.cend(); cout<< "*iteCBegin: "<< *iteCBegin << endl; iteCEnd--; cout<< "*iteCEnd: "<< *iteCEnd << endl; //反向迭代器 set<int>::reverse_iterator iteRBegin = c.rbegin(); set<int>::reverse_iterator iteREnd = c.rend(); cout<< "*iteRBegin: "<< *iteRBegin << endl; iteREnd--; cout<< "*iteCEnd: "<< *iteREnd << endl; //反向cosnt迭代器 set<int>::const_reverse_iterator iteCRBegin = c.crbegin(); set<int>::const_reverse_iterator iteCREnd = c.crend(); cout<< "*iteCRBegin: "<< *iteCRBegin << endl; iteCREnd--; cout<< "*iteCEnd: "<< *iteCREnd << endl;
三 容量
//容量 //判断是否为null cout << "empty: " << c.empty() <<endl; //大小size cout << "size: " << c.size() <<endl; //最大容量max_size cout << "max_size: " << c.max_size() <<endl;
四 基本操作
//操作 //插入 c.insert(10); for(auto i : c) { cout << i << endl; } cout << "insert" <<endl; //指定元素删除 c.erase(10); for(auto i : c) { cout << i << endl; } cout << "erase" <<endl; //指定位置删除 advance(iteBegin, 3); c.erase(iteBegin); for(auto i : c) { cout << i << endl; } cout << "erase" <<endl; //交换 c.swap(c2); for(auto i : c) { cout << i << endl; } cout << "swap" <<endl; //清除 set<int> c3 = c2; c3.clear(); for(auto i : c3) { cout << i << endl; } cout << "clear" <<endl; //判断是否存在1 ,存在返回false, 不存在返回1 for(auto i : c) { cout << i << endl; } auto ret = c.emplace(1); if (!ret.second) cout << "1 already exists in myset\n"; else cout << "1 non-exists in myset\n"; //如果不存在元素1 则插入1,如果存在则什么也不做 c.emplace(1); for(auto i : c) { cout << i << endl; } //key_comp返回存储的函数对象 //set 的默认比较key函数是 less()函数,且set中value和key是同一元素,即从小到大排序 cout << c.key_comp()(1,2) <<endl; //会返回1 因为1<2 cout << c.key_comp()(2,1) <<endl; //会返回0 因为2>1 cout << c.key_comp()(1,1) <<endl; //会返回0 因为1=1 //key_comp返回比较key的函数对象,即返回比较函数相同功能的函数 cout << c.value_comp()(1,2) <<endl; //会返回1 因为1<2 cout << c.value_comp()(2,1) <<endl; //会返回0 因为2>1 cout << c.value_comp()(1,1) <<endl; //会返回0 因为1=1
五 基本算法
//算法类 //find 查看是否含有该元素 如果有返回指向该点的迭代器 如果没有返回 end() auto findObj = c.find(40); if(*findObj) cout<<*findObj<<endl; else cout<< "not found" << endl; //元素出现个数 cout << "count: " << c.count(1) <<endl; //lower_bound(key_value) ,返回第一个大于等于key_value的迭代器 auto lower_boundObj = c.lower_bound(25); if(*lower_boundObj) cout<<*lower_boundObj<<endl; else cout<< "lower_boundObj" << endl; //upper_bound(key_value),返回最后一个大于等于key_value的迭代器 auto upper_boundObj = c.upper_bound(25); if(*upper_boundObj) cout<<*upper_boundObj<<endl; else cout<< "upper_boundObj" << endl; //equal_range()返回该元素所在区间(闭区间),返回值是一个pair类型,first代表所在区间的起点,second表示所在区间的重点 //如set<int> c {1,2,3,4,5} //c.equal_range(3) ,first就是指向3的迭代器 second就是指向4的迭代器 auto equal_rangeObj = c.equal_range(30); if(*equal_rangeObj.first) cout<<*equal_rangeObj.first<<endl; else cout<< "NOT equal_rangeObj.first" << endl; if(*equal_rangeObj.second) cout<<*equal_rangeObj.second<<endl; else cout<< "NOT equal_rangeObj.second" << endl;
六 自定义比较函数
//自定义比较函数 //set的默认比较key函数是less 下面我演示一下用自定义比较函数 // class my_comp // { // public: // bool operator()(int a, int b) // { // return a > b; // } // }; set<int, my_comp> my_set = {5,2,3,4,1}; for(auto i : my_set) { cout << i << endl; }
source code
类图
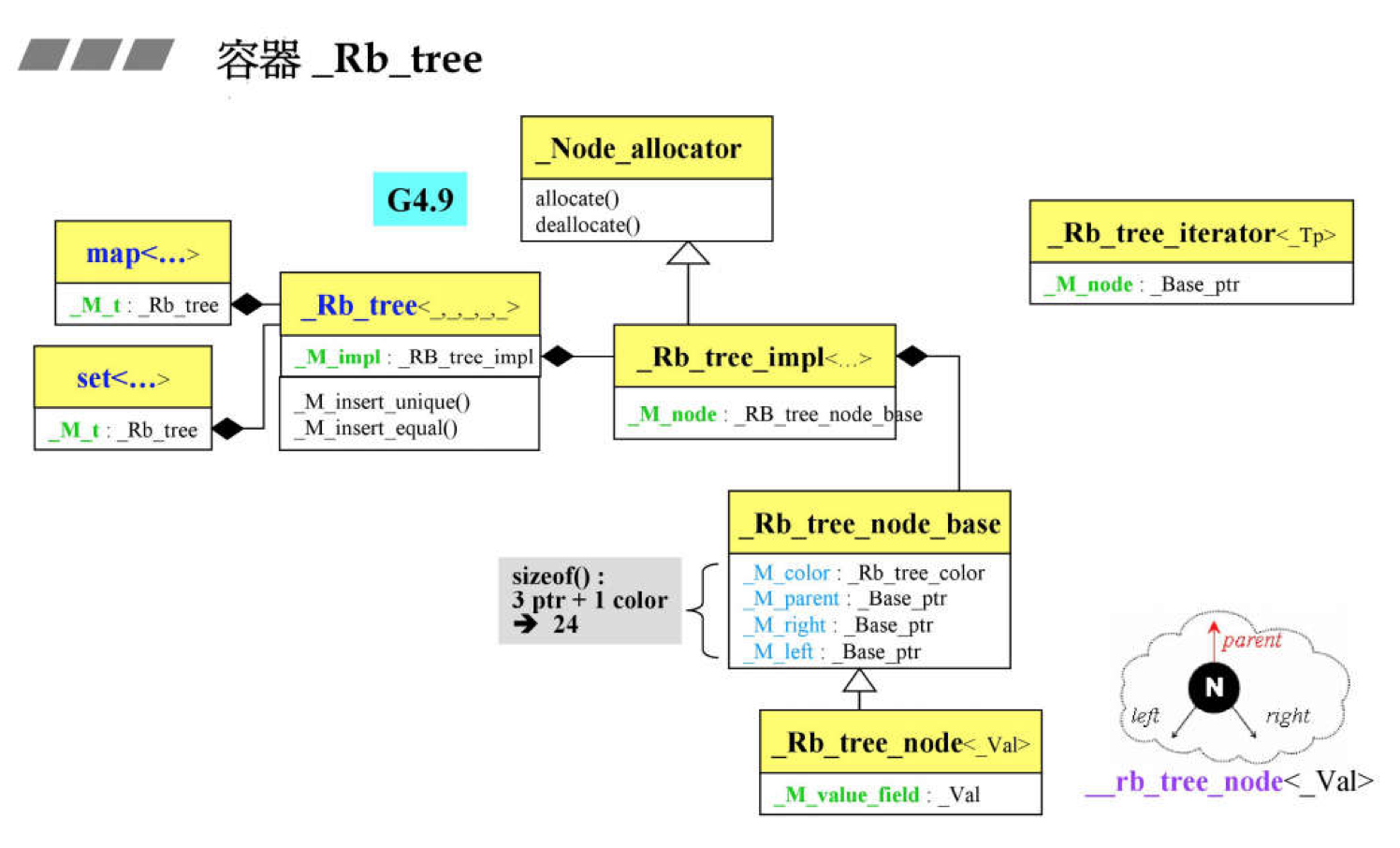
set的底层结构是rb_tree(),应该说set是一个容器适配器.它封装了rb_tree的方法,先介绍一下set的参数含义
template<typename _Key, typename _Compare = std::less<_Key>, typename _Alloc = std::allocator<_Key> > class set { public: // typedefs: //@{ /// Public typedefs. typedef _Key key_type; // Key value typedef _Key value_type; //(key+value的数据包) typedef _Compare key_compare; // key的比较函数 typedef _Compare value_compare; // typedef _Alloc allocator_type; // 分配器 //@} private: typedef typename __gnu_cxx::__alloc_traits<_Alloc>::template rebind<_Key>::other _Key_alloc_type; typedef _Rb_tree<key_type, value_type, _Identity<value_type>, key_compare, _Key_alloc_type> _Rep_type; _Rep_type _M_t; // Red-black tree representing set. ... set() : _M_t() { } ... std::pair<iterator, bool> insert(const value_type& __x) { std::pair<typename _Rep_type::iterator, bool> __p = _M_t._M_insert_unique(__x); return std::pair<iterator, bool>(__p.first, __p.second); } ... }
更详细实现我会在rb_tree介绍
参考<<侯捷STL标准库>>


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号