SpringCache
<!--导入springCache依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-cache</artifactId>
</dependency>

spring.cache.type=redis
并在启动类上添加注解
//springCache缓存开启
@EnableCaching
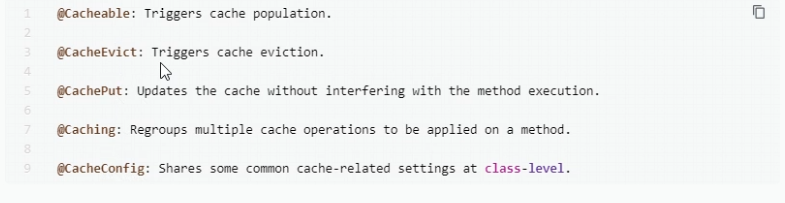
@cacheable 触发缓存的操作 缓存中有数据 就直接返回 没有数据 查询出数据 放进缓存
@cacheEvict 触发把数据从缓存中删除的操作
@cachePut 不影响方法执行的情况下 更新缓存
@chching 以上操作的组合操作
@cacheconfig 在类级别共享缓存的相关数据
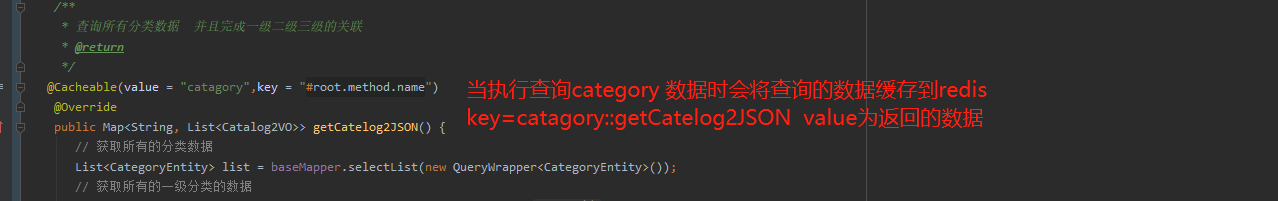
/** * 查询出所有的商品大类 * @return * 在注解中我们可以指定缓存的名称 起到一个分区的作用 一般按照业务区分 * @Cacheable({"category","product"}) * 代表当前的方法返回结果是需要缓存的 调用该方法的时候 如果缓存中有数据 那么该方法就不会执行 * 如果缓存中没有数据 那么就执行该方法 并且把查询的结果缓存起来 * * 缓存处理 * 1存储在redis中的缓存数据的key是默认生成的 缓存名称::simpleKey * 2默认缓存的数据的过期时间是永久 -1 * 3 缓存的数据 默认使用jdk的序列号机制 * * 改进 * 1 生成的缓存数据 我们需要自定义的key 自定义key在双引号中写spel表达式 但是如果定义字符串 需要在加上单引号 * 2 指定缓存数据的存活时间 spring cache time-to-live: 60000 * 3 把缓存的数据保存为json数据 * */ @Cacheable(key = "#root.method.name",value = {"catagory","product"}) @Override public List<CategoryEntity> getLeve1Categroy() { //long start=System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println("查询了数据库操作....."); List<CategoryEntity> list=baseMapper.queryLeve1Category(); //System.out.println("查询queryLeve1Category所需要的时间为:"+(System.currentTimeMillis()-start)); return list; }
自定义序列化
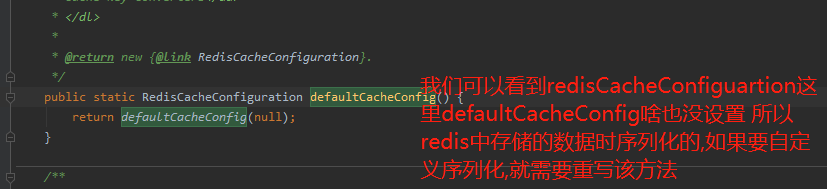
@Configuration
public class MyCacheConfig {
@Bean
public RedisCacheConfiguration redisCacheConfiguration(){
RedisCacheConfiguration config = RedisCacheConfiguration.defaultCacheConfig();
//指定自定义序列化的方式
config=config.serializeKeysWith(RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair.fromSerializer(new StringRedisSerializer()));
config=config.serializeValuesWith(RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair.fromSerializer(new GenericFastJsonRedisSerializer()));
return config;
}
}
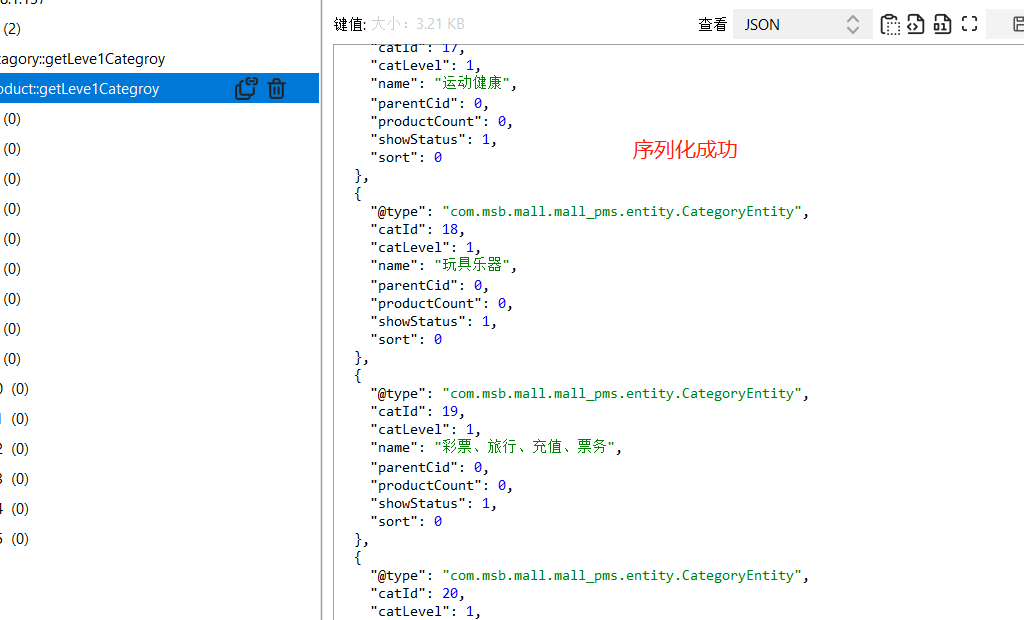
添加以下完整配置类
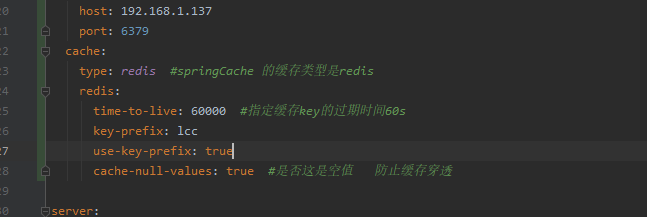
@Configuration public class MyCacheConfig { @Bean public RedisCacheConfiguration redisCacheConfiguration(CacheProperties cacheProperties){ RedisCacheConfiguration config = RedisCacheConfiguration.defaultCacheConfig(); //指定自定义序列化的方式 config=config.serializeKeysWith(RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair.fromSerializer(new StringRedisSerializer())); config=config.serializeValuesWith(RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair.fromSerializer(new GenericFastJsonRedisSerializer())); CacheProperties.Redis redisProperties = cacheProperties.getRedis(); if (redisProperties.getTimeToLive() != null) { config = config.entryTtl(redisProperties.getTimeToLive()); } if (redisProperties.getKeyPrefix() != null) { config = config.prefixKeysWith(redisProperties.getKeyPrefix()); } if (!redisProperties.isCacheNullValues()) { config = config.disableCachingNullValues(); } if (!redisProperties.isUseKeyPrefix()) { config = config.disableKeyPrefix(); } return config; } }
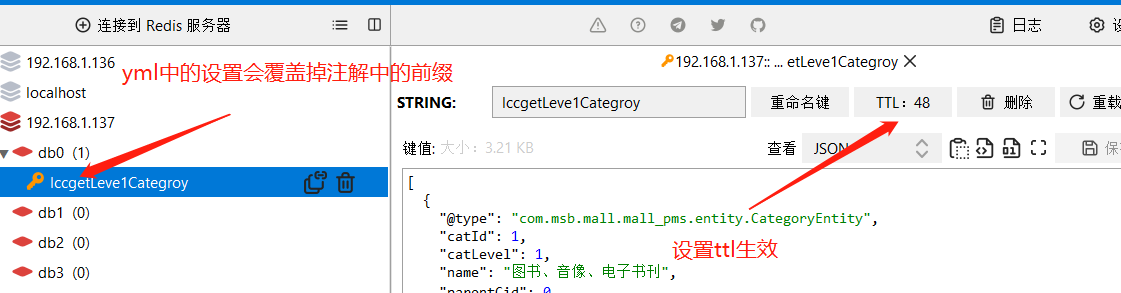
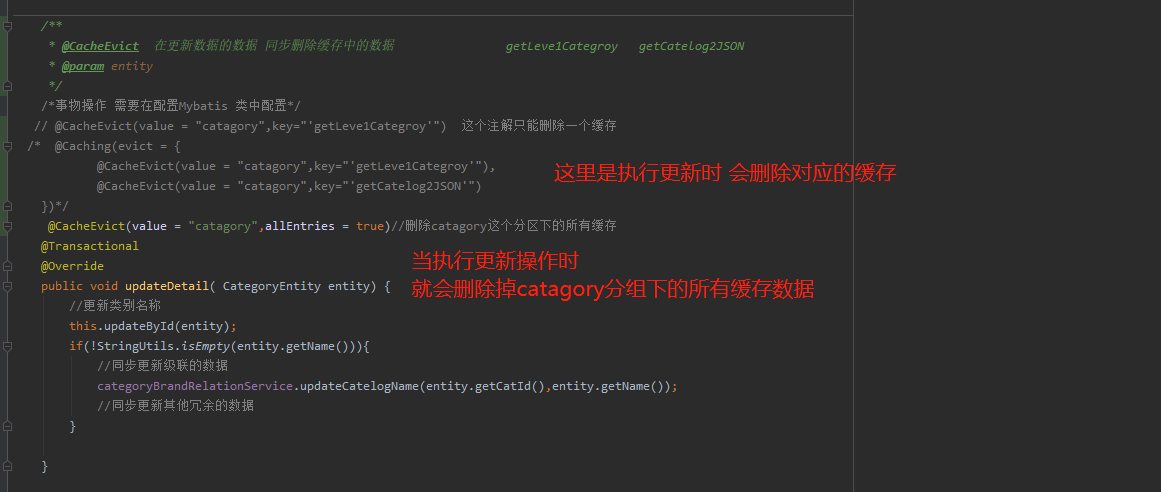
@CacheEvict 在更新数据的数据 同步删除缓存中的数据
/**
* @CacheEvict 在更新数据的数据 同步删除缓存中的数据
* @param entity
*/
/*事物操作 需要在配置Mybatis 类中配置*/
@CacheEvict(value = "catagory",key="'getLeve1Categroy'") //在执行这个方法时候 会删除redis中对应的 catagory::getLeve1Category 为key的数据
@Transactional
@Override
public void updateDetail( CategoryEntity entity) {
//更新类别名称
this.updateById(entity);
if(!StringUtils.isEmpty(entity.getName())){
//同步更新级联的数据
categoryBrandRelationService.updateCatelogName(entity.getCatId(),entity.getName());
//同步更新其他冗余的数据
}
}
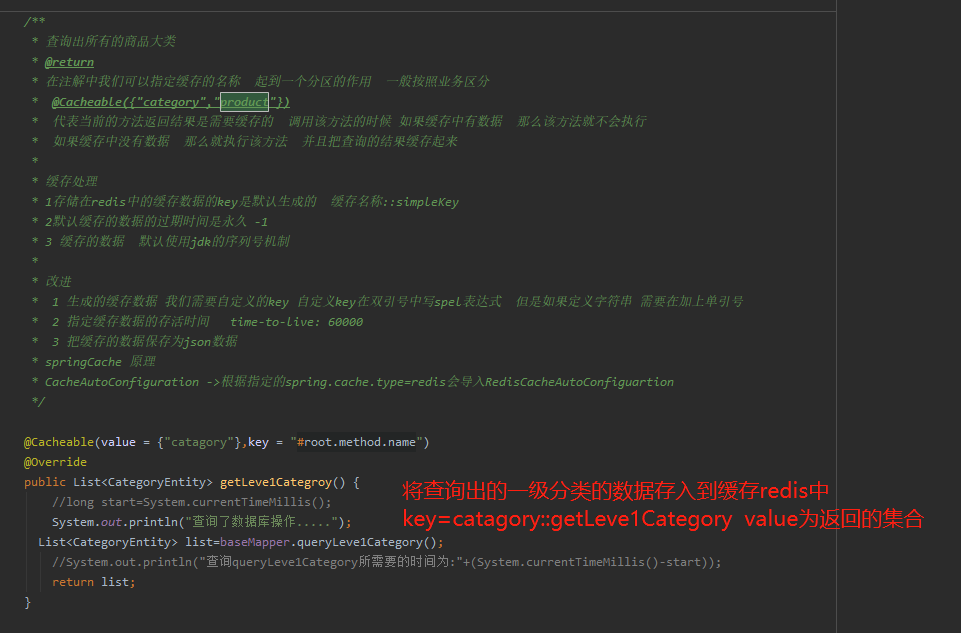
/** * @CacheEvict 在更新数据的数据 同步删除缓存中的数据 getLeve1Categroy getCatelog2JSON * @param entity */ /*事物操作 需要在配置Mybatis 类中配置*/ // @CacheEvict(value = "catagory",key="'getLeve1Categroy'") 这个注解只能删除一个缓存 /* @Caching(evict = { @CacheEvict(value = "catagory",key="'getLeve1Categroy'"), @CacheEvict(value = "catagory",key="'getCatelog2JSON'") })*/ @CacheEvict(value = "catagory",allEntries = true)//删除catagory这个分区下的所有缓存 @Transactional @Override public void updateDetail( CategoryEntity entity) { //更新类别名称 this.updateById(entity); if(!StringUtils.isEmpty(entity.getName())){ //同步更新级联的数据 categoryBrandRelationService.updateCatelogName(entity.getCatId(),entity.getName()); //同步更新其他冗余的数据 } } /** * 查询出所有的商品大类 * @return * 在注解中我们可以指定缓存的名称 起到一个分区的作用 一般按照业务区分 * @Cacheable({"category","product"}) * 代表当前的方法返回结果是需要缓存的 调用该方法的时候 如果缓存中有数据 那么该方法就不会执行 * 如果缓存中没有数据 那么就执行该方法 并且把查询的结果缓存起来 * * 缓存处理 * 1存储在redis中的缓存数据的key是默认生成的 缓存名称::simpleKey * 2默认缓存的数据的过期时间是永久 -1 * 3 缓存的数据 默认使用jdk的序列号机制 * * 改进 * 1 生成的缓存数据 我们需要自定义的key 自定义key在双引号中写spel表达式 但是如果定义字符串 需要在加上单引号 * 2 指定缓存数据的存活时间 time-to-live: 60000 * 3 把缓存的数据保存为json数据 * springCache 原理 * CacheAutoConfiguration ->根据指定的spring.cache.type=redis会导入RedisCacheAutoConfiguartion */ @Cacheable(value = {"catagory"},key = "#root.method.name") @Override public List<CategoryEntity> getLeve1Categroy() { //long start=System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println("查询了数据库操作....."); List<CategoryEntity> list=baseMapper.queryLeve1Category(); //System.out.println("查询queryLeve1Category所需要的时间为:"+(System.currentTimeMillis()-start)); return list; } /** * 根据父编号 获取对应的子菜单信息 * @param list * @param parentCid * @return */ private List<CategoryEntity> queryByParentCid(List<CategoryEntity> list,Long parentCid){ List<CategoryEntity> collect = list.stream().filter(item -> { return item.getParentCid().equals(parentCid); }).collect(Collectors.toList()); return collect; } /* //本地缓存 private Map<String,Map<String,List<Catalog2VO>>> cache=new HashMap<>();*/ /** * 查询所有分类数据 并且完成一级二级三级的关联 * @return */ @Cacheable(value = "catagory",key = "#root.method.name") @Override public Map<String, List<Catalog2VO>> getCatelog2JSON() { // 获取所有的分类数据 List<CategoryEntity> list = baseMapper.selectList(new QueryWrapper<CategoryEntity>()); // 获取所有的一级分类的数据 List<CategoryEntity> leve1Category = this.queryByParentCid(list, 0l); // 把一级分类的数据转换为Map容器 key就是一级分类的编号, value就是一级分类对应的二级分类的数据 Map<String, List<Catalog2VO>> map = leve1Category.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap( key -> key.getCatId().toString() , value -> { // 根据一级分类的编号,查询出对应的二级分类的数据 List<CategoryEntity> l2Catalogs = this.queryByParentCid(list, value.getCatId()); List<Catalog2VO> Catalog2VOs = null; if (l2Catalogs != null) { Catalog2VOs = l2Catalogs.stream().map(l2 -> { // 需要把查询出来的二级分类的数据填充到对应的Catelog2VO中 Catalog2VO catalog2VO = new Catalog2VO(l2.getParentCid().toString(), null, l2.getCatId().toString(), l2.getName()); // 根据二级分类的数据找到对应的三级分类的信息 List<CategoryEntity> l3Catelogs = this.queryByParentCid(list, l2.getCatId()); if (l3Catelogs != null) { // 获取到的二级分类对应的三级分类的数据 List<Catalog2VO.Catalog3VO> catalog3VOS = l3Catelogs.stream().map(l3 -> { Catalog2VO.Catalog3VO catalog3VO = new Catalog2VO.Catalog3VO(l3.getParentCid().toString(), l3.getCatId().toString(), l3.getName()); return catalog3VO; }).collect(Collectors.toList()); // 三级分类关联二级分类 catalog2VO.setCatalog3List(catalog3VOS); } return catalog2VO; }).collect(Collectors.toList()); } return Catalog2VOs; } )); return map; }
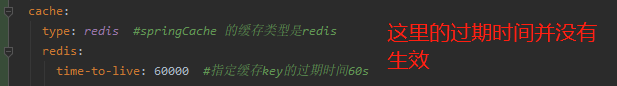
SpringCache SpringCache的不足: 1).读模式 * 缓存穿透:查询一个null的数据。可以解决 cache-null-values=true * 缓存击穿:大量并发进来同时查询一个正好过期的数据。解决方案:分布式锁 sync=true 本地锁 * 缓存雪崩:大量的key同一个时间点失效。解决方案:添加过期时间 time-to-live=60000 指定过期时间 2).写模式 * 读写锁 * 引入canal,监控binlog日志文件来同步更新数据 * 读多写多,直接去数据库中读取数据即可 总结: * 常规数据(读多写少):而且对及时性和数据的一致性要求不高的情况,我们完全可以使用SpringCache * 特殊情况:特殊情况特殊处理。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号