P4557 战争(闵可夫斯基和)
闵可夫斯基和
定义:
闵可夫斯基和 \((Minkowski\ sum)\)是两个欧几里得空间的点集的和,也称为这两个空间的膨胀集,以德国数学家闵可夫斯基命名。点集A与B的闵可夫斯基和被定义为:
\(A+B=\{ a+b|a∈A,b∈B\}\)
若推广至流形的连续集,闵可夫斯基和从几何上的直观体现即是A集合沿B的边际连续运动一周扫过的区域与B集合本身的并集,也可以是B沿着A的边界连续运动扫过区域与A自身的并集。
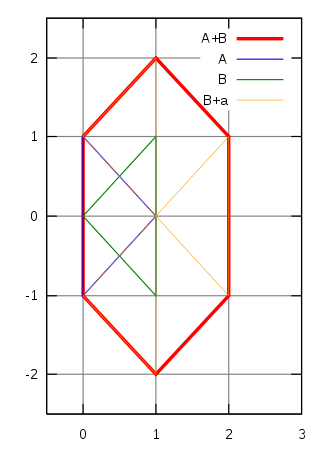
求法:
通过几何直观体现我们可以发现,其实闵可夫斯基和上的每一个边都是由原来的凸包平移得来的。于是我们的闵可夫斯基和其实就是要合并两个凸包。
针对其中任意一个凸包,首先极角已经是有序的了,于是在合并过程中,我们只需要进行归并排序,将两个凸包进行合并就可以了。
题意:给出两个点集A,B,以及q次询问。对于每次询问,给出一个向量,然后点集B向向量平移,若平移后的点集A与点集B构成的两个多边形存在交点则输出1,否则输出0。
通过读题我们可以知道,如果平移其中一个凸包后与另一个凸包有交点,那么一定满足:\(a∈A,b∈B\),若移动向量为\(c\),则存在\(b+c=a\),移项得到\(c=a-b\),,于是我们可以构造出一个闵可夫斯基和\(C=\{ a+(-b)\}\),之后我们只需要判断移动向量是否在我们构造的\(C\)中就可以了。
判断向量是否在凸包内:
判断方法:首先判断和边界的关系,之后找到与其极角相邻的两点,凭此判断即可。
需要注意的是,我们的原点\((0,0)\)是A[1]
ll inside(node a){
if(a*A[1]>0||A[tot]*a>0) return 0;
ll pos=lower_bound(A+1,A+tot+1,a,cmp2)-A-1;
return (a-A[pos])*(A[pos%tot+1]-A[pos])<=0;
}
求凸包:
inline void convex(node *B,ll &n){
sort(B+1,B+1+n,cmp1);
p=B[1];
st[top=1]=1;
for(re ll i=1;i<=n;i++){
B[i]=B[i]-p;
}
sort(B+2,B+1+n,cmp2);
for(re ll i=2;i<=n;i++){
while(top>1&&(B[i]-B[st[top-1]])*(B[st[top]]-B[st[top-1]])>=0)top--;
st[++top]=i;
}
for(re ll i=1;i<=top;i++){
B[i]=B[st[i]]+p;
}
n=top,B[n+1]=B[1];
}
合并两个凸包:
inline void Minkowski(){
for(re ll i=1;i<n;i++){
s1[i]=C1[i+1]-C1[i];
s1[n]=C1[1]-C1[n];
}
for(re ll i=1;i<m;i++){
s2[i]=C2[i+1]-C2[i];
s2[m]=C2[1]-C2[m];
}
A[tot=1]=C1[1]+C2[1];
ll cnt1=1,cnt2=1;
while(cnt1<=n&&cnt2<=m)++tot,A[tot]=A[tot-1]+(s1[cnt1]*s2[cnt2]>=0?s1[cnt1++]:s2[cnt2++]);
while(cnt1<=n)++tot,A[tot]=A[tot-1]+s1[cnt1++];
while(cnt2<=m)++tot,A[tot]=A[tot-1]+s2[cnt2++];
}
CODE:
//#define LawrenceSivan
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
#define re register
const int maxn=1e5+5;
const int maxm=1;
ll n,m,q;
ll st[maxn],top=1,tot;
struct node{
ll x,y;
node operator - (node A) {return (node){x-A.x,y-A.y};}
node operator + (node A) {return (node){x+A.x,y+A.y};}
ll operator * (node A) const {return x*A.y-y*A.x;}//vector_product
ll len() const {return x*x+y*y;}
}s1[maxn],s2[maxn],A[maxn],C1[maxn],C2[maxn],p;
inline bool cmp1(node A,node B){
return A.y<B.y||(A.y==B.y&&A.x<B.x);
}
inline bool cmp2(node A,node B){
return A*B>0||(A*B==0&&A.len()<B.len());
}
inline void convex(node *B,ll &n){
sort(B+1,B+1+n,cmp1);
p=B[1];
st[top=1]=1;
for(re ll i=1;i<=n;i++){
B[i]=B[i]-p;
}
sort(B+2,B+1+n,cmp2);
for(re ll i=2;i<=n;i++){
while(top>1&&(B[i]-B[st[top-1]])*(B[st[top]]-B[st[top-1]])>=0)top--;
st[++top]=i;
}
for(re ll i=1;i<=top;i++){
B[i]=B[st[i]]+p;
}
n=top,B[n+1]=B[1];
}
inline void Minkowski(){
for(re ll i=1;i<n;i++){
s1[i]=C1[i+1]-C1[i];
s1[n]=C1[1]-C1[n];
}
for(re ll i=1;i<m;i++){
s2[i]=C2[i+1]-C2[i];
s2[m]=C2[1]-C2[m];
}
A[tot=1]=C1[1]+C2[1];
ll cnt1=1,cnt2=1;
while(cnt1<=n&&cnt2<=m)++tot,A[tot]=A[tot-1]+(s1[cnt1]*s2[cnt2]>=0?s1[cnt1++]:s2[cnt2++]);
while(cnt1<=n)++tot,A[tot]=A[tot-1]+s1[cnt1++];
while(cnt2<=m)++tot,A[tot]=A[tot-1]+s2[cnt2++];
}
ll inside(node a){
if(a*A[1]>0||A[tot]*a>0) return 0;
ll pos=lower_bound(A+1,A+tot+1,a,cmp2)-A-1;
return (a-A[pos])*(A[pos%tot+1]-A[pos])<=0;
}
inline ll read(){
ll x=0, f=1;char ch=getchar();
while (!isdigit(ch)) {if(ch=='-')f=-1;ch=getchar();}
while (isdigit(ch)){x=x*10+(ch^48);ch=getchar();}
return x*f;
}
int main() {
#ifdef LawrenceSivan
freopen("aa.in", "r", stdin);
freopen("aa.out", "w", stdout);
#endif
n=read();m=read();q=read();
for(re ll i=1;i<=n;i++){
C1[i].x=read();C1[i].y=read();
}
convex(C1,n);
for(re ll i=1;i<=m;i++){
C2[i].x=-read();C2[i].y=-read();
}
convex(C2,m);
Minkowski();
convex(A,tot);
p=A[1];
for(re ll i=tot;i>=1;i--)A[i]=A[i]-A[1];
while(q--){
A[0].x=read();A[0].y=read();
printf("%lld\n",inside(A[0]-p));
}
return 0;
}
 计算几何,闵可夫斯基和
计算几何,闵可夫斯基和

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号