AtCoder Beginner Contest 289
A - flip (abc289 a)
题目大意
给定一个\(01\)字符串,翻转 \(01\)输出
解题思路
模拟即可
神奇的代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
using LL = long long;
int main(void) {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0);
string s;
cin >> s;
for(auto &i : s){
cout << ((i - '0') ^ 1);
}
return 0;
}
B - V (abc289 b)
题目大意
给定一张无向图,\(n\)个点, \(m\)条边。第 \(i\)条边连接点 \(c_i\)和 \(c_i + 1\)。
现在轮流出点,从最小的点所在的连通块开始,从该连通块标号最大的点开始出。
问出点顺序。
解题思路
因为连边顺序都是递增加一的。用并查集维护连通,往序号大的合并,或者注意到连通块序号都是递增的,维护下每个连通块的左右区间都可以。
神奇的代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
using LL = long long;
int main(void) {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0);
int n, m;
cin >> n >> m;
int st = 1, ed = 1;
for(int i = 0; i < m; ++ i){
int a;
cin >> a;
while(ed < a){
for(int j = ed; j >= st; -- j)
cout << j << ' ';
++ ed;
st = ed;
}
++ ed;
}
while(ed <= n){
for(int j = ed; j >= st; -- j)
cout << j << ' ';
++ ed;
st = ed;
}
return 0;
}
C - Coverage (abc289 c)
题目大意
\(m\)个集合,问有多少种选择方式,使得选择的集合的并集覆盖了 \(1 \sim n\)
解题思路
范围不大,直接暴力即可。
神奇的代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
using LL = long long;
int main(void) {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0);
int n, m;
cin >> n >> m;
vector<bitset<10>> qwq(m);
for(auto &i : qwq){
int c;
cin >> c;
while(c--){
int x;
cin >> x;
i.set(x - 1);
}
}
int ok = (1 << n) - 1;
bitset<10> good;
int ans = 0;
for(int i = 1; i < (1 << m); ++ i){
good.reset();
for(int j = 0; j < m; ++ j){
if ((i >> j) & 1)
good |= qwq[j];
}
ans += (good.to_ulong() == ok);
}
cout << ans << '\n';
return 0;
}
D - Step Up Robot (abc289 d)
题目大意
走楼梯,某些阶梯不能踩。有\(n\)种方式,一次可以登上 \(x_i\)层。
问能不能从第 \(0\)层走到第 \(n\)层。
解题思路
设\(dp[i]\)表示能否走到第 \(i\)层。转移枚举方式即可。
神奇的代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
using LL = long long;
int main(void) {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0);
int n;
cin >> n;
vector<int> op(n);
for(auto &i : op)
cin >> i;
int m;
cin >> m;
vector<int> danger(m);
for(auto &i : danger)
cin >> i;
int x;
cin >> x;
vector<int> dp(x + 1, 0);
vector<int> ok(x + 1, 1);
for(auto &i : danger)
ok[i] = 0;
dp[0] = 1;
for(int i = 1; i <= x; ++ i){
if (!ok[i])
continue;
for(auto &j : op){
if (i >= j)
dp[i] |= dp[i - j];
}
}
if (dp[x])
cout << "Yes" << '\n';
else
cout << "No" << '\n';
return 0;
}
E - Swap Places (abc289 e)
题目大意
给定一张\(n\)个点\(m\)条边的无向图,点有红蓝两种颜色。
高橋从\(1\)号点出发,青木从 \(n\)号点出发。
每个时刻,两人同时移动至其相邻点,要求每次移动之后,两人所在点的颜色不同。
问两人能否同时抵达\(n\)号点和 \(1\)号点,若能的话,输出最小耗时。
解题思路
考虑爆搜(也算是dp?),设\(dp[i][j]\)表示高橋抵达\(i\)号点出发,青木抵达\(j\)号点所需要的最小时刻。然后枚举两人下一个抵达的点,BFS。
分析其复杂度,发现其惊奇地可过,于是就做完了(
该搜索,状态总共有\(O(n^2)\),但每个状态的转移代价都不是固定的,我们考虑所有转移的代价。
转移的代价来自于边的遍历,对于一条边来说,它最多可被遍历\(m\)次(对于青木走的每条边,我们每考虑一条高橋走的边,该边就会被遍历一次),因此所有边的遍历次数和为\(O(m^2)\),这即为转移的代价。
因为我们考虑了转移代价的和,而不是每个状态的转移代价,因此总的复杂度应为状态代价+转移代价。
因此该搜索的时间复杂度为 \(O(n^2 + m^2)\),而\(n, m \leq 2000\),是可以通过的。
神奇的代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
using LL = long long;
const int inf = 1e9 + 7;
int main(void) {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0);
int t;
cin >> t;
while(t--){
int n, m;
cin >> n >> m;
vector<int> color(n);
for(auto &i : color)
cin >> i;
vector<vector<int>> edge(n);
for(int i = 0; i < m; ++ i){
int u, v;
cin >> u >> v;
-- u;
-- v;
edge[u].push_back(v);
edge[v].push_back(u);
}
auto bfs = [&](int l, int r){
queue<pair<int, int>> team;
vector<vector<int>> dis(n, vector<int>(n, inf));
dis[l][r] = 0;
team.push({l, r});
while(!team.empty()){
auto [u, v] = team.front();
team.pop();
for(auto x : edge[u]){
for(auto y : edge[v]){
if (color[x] != color[y] && dis[x][y] > dis[u][v] + 1){
dis[x][y] = dis[u][v] + 1;
team.push({x, y});
}
}
}
}
return dis[n - 1][0];
};
int ans = bfs(0, n - 1);
if (ans == inf)
ans = -1;
cout << ans << '\n';
}
return 0;
}
F - Teleporter Takahashi (abc289 f)
题目大意
二维平面,要求从点\(s\)到点 \(t\) 。
给定一个矩形区域,每次操作从区域里选择一个点\(m\),然后点 \(s\)就跑到与 点\(m\)的镜像点。
给定一个操作序列,或告知不可能。不要求最小化操作次数。
解题思路
考虑一维情况。
如果区域是一个点,很显然点\(s\)只有两个位置可以选择。
如果区域不是一个点,假设是\([a,b]\)。既然不要求最小化操作次数,那么考虑是否有基本的移动操作。
可以观察到,两次操作分别选择点\(a\)和点 \(a+1\),那么当前点 \(s\)相对操作前,坐标 \(+2\)了。反之选择点 \(a+1\)和点 \(a\)就会 \(-2\)。那就可以依靠此基本操作一步一步移向终点。由坐标范围限制,操作次数不会超过上限。
注意到,原点坐标\(s\),选择点坐标 \(m\),那镜像点坐标\(t = 2m - s\)的奇偶性和 \(s\)相同。故操作不会改变坐标奇偶性。因此如果起点和终点的奇偶性不同,则不可达。
一维解决了,二维的话两个维度是相互独立的,因此分别考虑两个维度移动即可。注意区域变成一个点或一条线的情况。
神奇的代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
using LL = long long;
int main(void) {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0);
int sx, sy, tx, ty, a, b, c, d;
cin >> sx >> sy >> tx >> ty >> a >> b >> c >> d;
vector<pair<int, int>> ans;
auto move = [&](int x, int y){
sx = 2 * x - sx;
sy = 2 * y - sy;
ans.push_back({x, y});
};
auto check = [&](){
bool ok0 = ((sx ^ tx) % 2 == 0 && (a != b || (sx == tx || a + b == sx + tx)));
bool ok1 = ((sy ^ ty) % 2 == 0 && (c != d || (sy == ty || c + d == sy + ty)));
if (!ok0 || !ok1)
return false;
if (a == b && sx != tx){
move(a, c);
}
if (c == d && sy != ty){
move(a, c);
}
if (a == b && sx != tx)
return false;
while(sx < tx){
move(a, c);
move(a + 1, c);
}
while(sx > tx){
move(a + 1, c);
move(a, c);
}
while(sy < ty){
move(a, c);
move(a, c + 1);
}
while(sy > ty){
move(a, c + 1);
move(a, c);
}
return true;
};
if (check()){
cout << "Yes" << '\n';
for(auto &i : ans)
cout << i.first << ' ' << i.second << '\n';
}else {
cout << "No" << '\n';
}
return 0;
}
G - Shopping in AtCoder store (abc289 g)
题目大意
给定\(n\)个数 \(b_i\),有 \(q\)个询问,每个询问给定一个 \(c\),问最大的 \(p\),使得 \(p \times f(p)\)最大。输出该乘积最大值。
其中 \(f(p)\)表示满足\(b_i + c \geq p\)的 \(i\)的数量。
解题思路
很显然\(f(p)\)是个分段函数,因此其选择的\(p\)肯定满足:存在某个\(b_i\)有\(b_i + c = p\)。
首先对\(b\)降序排序,对于第 \(i\)个(从\(1\)开始) \(b_i\) ,如果它是那个\(b_i\)满足 \(b_i + c = p\)的话,则 \(p \times f(p) = (b_i + c) \times i = b_i \times i + c \times i\)。这里\(b_i \times i\)是个常数,变数是 \(c\)。
有个感性的观察就是 \(c\)越大的时候,越后面的 \(b\)成为答案的可能性就越可能大。且如果\(b_i\)成为 \(c\)的答案\(ans_i\),那么对于 \(c^\prime > c\)的答案\(b_j\),肯定满足 \(j > i\)(决策单调),但因为存在 \(ans_i > ans_{i + 1}\)并不意味着 \(ans_i > ans_{i + 2}\),所以也无法解决。
对问题更进一步的抽象,每个\(b_i\)就是 \(y_i = b_i \times i + c \times i\),其中 \(y_i\)就是选择其时的答案, \(b_i \times i\) 是定值,只有 \(c\)变量,也就是一个一次函数 \(y = kx + b\)。给定一个 \(c\),其实就是带入所有的一次函数,取最大的 \(y\)

斜率越大的在\(x\)越大时越有可能成为最大值。因此一次函数在成为最大值对应的 \(x\)区间要么只有一个,要么就没有。
由此我们可以维护一个由这些一次函数做围成的一个凸包,凸包上的边就是取最大值的那个一次函数的部分。
如何维护呢?
首先注意到,给定两个斜率不同的一次函数,它们有一个交点,交点前是斜率小的函数值较大,交点后是斜率大的函数值较大
因此对于此时凸包上最末尾的一次函数\(y_1\),次末尾的是\(y_2\),一个新加入的一次函数 \(y_0\),\(y_0\)与 \(y_2\)的交点 \(x_{02}\),\(y_1\)与 \(y_2\) 的交点\(x_{12}\),如果交点的横坐标,\(x_{02} \leq x_{12}\),那么\(y_1\)就没用了(\(y_0\)会比\(y_1\)更早的(\(x_{02} \leq x_{12})\) 超过\(y_2\)成为最大)。
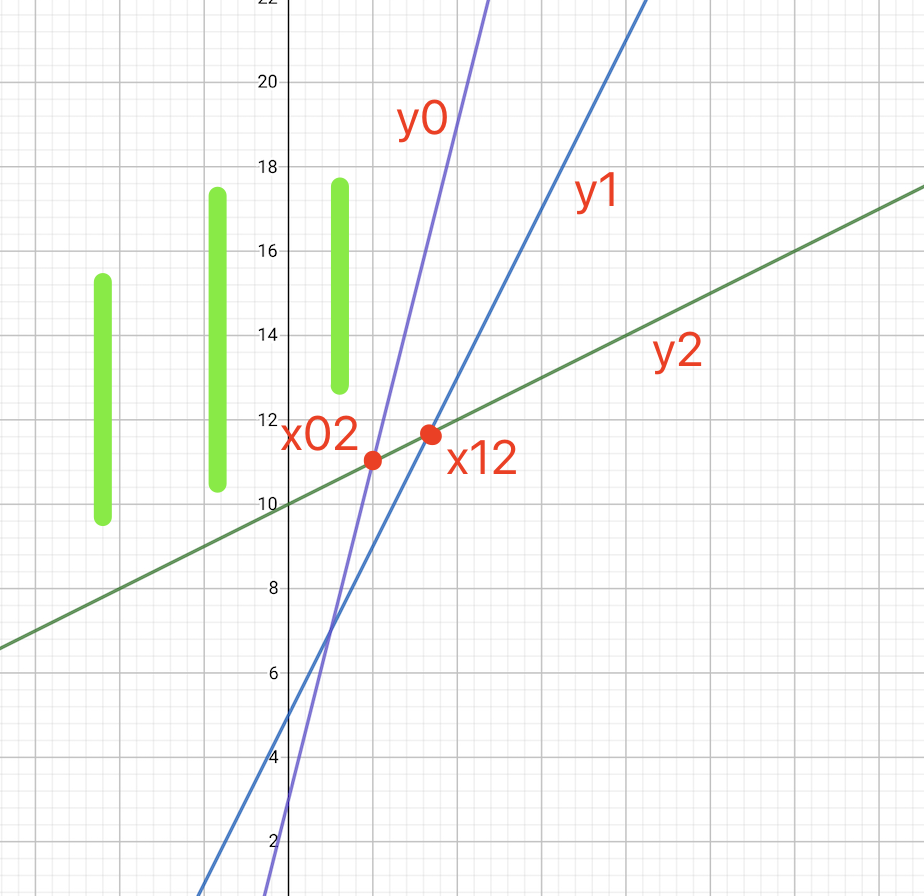
通过解方程,交点的横坐标\(x = \frac{b_i - b_j}{k_j - k_i}\),则 \(x_{02}\)和 \(x_{12}\)的比较,通过把分母移动到另一边就变成跟求凸包时判断点 \((k,b)\)差积一样的形式 。
得到凸包后对于一个\(c\),二分找到其所在的一次函数,代入其值求得答案即可。
神奇的代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
using LL = long long;
using db = double;
const db EPS = 1e-9;
inline int sign(db a) { return a < -EPS ? -1 : a > EPS; }
inline int cmp(db a, db b){ return sign(a-b); }
struct P {
db x, y;
P() {}
P(db _x, db _y) : x(_x), y(_y) {}
P(LL _x, LL _y) : x(_x), y(_y) {}
P operator+(P p) { return {x + p.x, y + p.y}; }
P operator-(P p) { return {x - p.x, y - p.y}; }
P operator*(db d) { return {x * d, y * d}; }
P operator/(db d) { return {x / d, y / d}; }
bool operator<(P p) const { // 字典序小于
int c = cmp(x, p.x);
if (c) return c == -1;
return cmp(y, p.y) == -1;
}
bool operator==(P o) const{ // 判断点相等
return cmp(x,o.x) == 0 && cmp(y,o.y) == 0;
}
db dot(P p) { return x * p.x + y * p.y; } // 点积
db det(P p) { return x * p.y - y * p.x; } // 叉积
db distTo(P p) { return (*this-p).abs(); } // 两点距离
db alpha() { return atan2(y, x); } // 斜率
void read() { cin>>x>>y; } // 读取
void write() {cout<<"("<<x<<","<<y<<")"<<endl;} // 输出
db abs() { return sqrt(abs2());} // 距离原点的距离,向量长度
db abs2() { return x * x + y * y; } // 原点距离平方
P rot90() { return P(-y,x);} // 逆时针旋转90度
P unit() { return *this/abs(); } // 单位向量
int quad() const { return sign(y) == 1 || (sign(y) == 0 && sign(x) >= 0); } // 是否在0~179度?点在上半边,极角排序用的
P rot(db an){ return {x*cos(an)-y*sin(an),x*sin(an) + y*cos(an)}; } // 逆时针旋转an度
};
// p1->p2 叉积 p1->p3
inline db cross(const P& p1, const P& p2, const P& p3) {
return (p2.x-p1.x)*(p3.y-p1.y)-(p3.x-p1.x)*(p2.y-p1.y);
}
// p1->p2 叉积 p1->p3 的符号
inline int crossOp(const P& p1, const P& p2, const P& p3) {
return sign(cross(p1,p2,p3));
}
int main(void) {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0);
int n, m;
cin >> n >> m;
vector<LL> b(n);
for(auto &i : b)
cin >> i;
sort(b.begin(), b.end(), greater<LL>());
vector<pair<double, P>> l;
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++ i){
P p{i + 1, (i + 1) * b[i]};
while(l.size() >= 2 && cross(p, (l.rbegin()->second), (next(l.rbegin()))->second) <= 0)
l.pop_back();
db x = 0;
if (!l.empty()){
P p1 = l.back().second;
x = (p1.y - p.y) / (p.x - p1.x);
}
l.push_back({x, p});
}
for(int i = 0; i < m; ++ i){
int c;
cin >> c;
P p = prev(upper_bound(l.begin(), l.end(), make_pair(1.0 * c, P{0.0,0.0}), [](const auto& a, const auto& b){
return a.first < b.first;
}))->second;
LL ans = p.x * c + p.y;
cout << ans << ' ';
}
return 0;
}
Ex - Trio (abc289 h)
题目大意
三个人在数轴上随机游走,问\(t\)时刻三者第一次相遇的概率。
随机游走指每个时刻,等概率往左走一个或往右走一个。
概率对\(998244353\)取模。
解题思路
<++>
神奇的代码


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号