Codeforces Round #616 (Div. 2)
A. Even But Not Even (CF 1291 A)
题目大意
给定一个数,要求删去其中的一些数字后所得的数是奇数但各位数的和为偶数。
解题思路
保留两位奇数即可,其中一个奇数在末位。
神奇的代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h> #define MIN(a,b) ((((a)<(b)?(a):(b)))) #define MAX(a,b) ((((a)>(b)?(a):(b)))) #define ABS(a) ((((a)>0?(a):-(a)))) using namespace std; typedef long long LL; typedef vector<int> VI; typedef pair<int,int> PII; typedef vector<PII> VPII; typedef vector<LL> VL; typedef pair<LL,LL> PLL; typedef vector<PLL> VPLL; template <typename T> void read(T &x) { int s = 0, c = getchar(); x = 0; while (isspace(c)) c = getchar(); if (c == 45) s = 1, c = getchar(); while (isdigit(c)) x = (x << 3) + (x << 1) + (c ^ 48), c = getchar(); if (s) x = -x; } template <typename T> void write(T x, char c = ' ') { int b[40], l = 0; if (x < 0) putchar(45), x = -x; while (x > 0) b[l++] = x % 10, x /= 10; if (!l) putchar(48); while (l) putchar(b[--l] | 48); putchar(c); } int main(void) { int kase; read(kase); for (int i = 1; i <= kase; i++) { int n; char s[3006]={0}; read(n); scanf("%s",s); int fir=-1,sec=-1; for(int i=0;i<n;++i) if ((s[i]-'0')&1) if (fir==-1) fir=i; else if (sec==-1) sec=i; else break; if (sec==-1) puts("-1"); else s[sec+1]=0,printf("%s\n",s); } return 0; }
B. Array Sharpening (CF 1291 B)
题目大意
给定一个有个数的数字序列,可以对序列里的任意正数多次减一,要求将序列变成先严格递增后严格递减,也可以单增或单减,问能否做到。
解题思路
我们让波峰尽可能靠右,波峰左边的就看它是否(从开始),第一个不满足该不等式的位置当做波峰,波峰的右边包括波峰看其是否满足,都满足则可,否则不可。因为我们让波峰尽可能靠右,这样对于波峰右边的数所需要满足的条件就不会那么苛刻。
神奇的代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h> #define MIN(a,b) ((((a)<(b)?(a):(b)))) #define MAX(a,b) ((((a)>(b)?(a):(b)))) #define ABS(a) ((((a)>0?(a):-(a)))) using namespace std; typedef long long LL; typedef vector<int> VI; typedef pair<int,int> PII; typedef vector<PII> VPII; typedef vector<LL> VL; typedef pair<LL,LL> PLL; typedef vector<PLL> VPLL; template <typename T> void read(T &x) { int s = 0, c = getchar(); x = 0; while (isspace(c)) c = getchar(); if (c == 45) s = 1, c = getchar(); while (isdigit(c)) x = (x << 3) + (x << 1) + (c ^ 48), c = getchar(); if (s) x = -x; } template <typename T> void write(T x, char c = ' ') { int b[40], l = 0; if (x < 0) putchar(45), x = -x; while (x > 0) b[l++] = x % 10, x /= 10; if (!l) putchar(48); while (l) putchar(b[--l] | 48); putchar(c); } bool solve(int n,int a[]){ int qwq=0; while(qwq<n&&a[qwq]>=qwq) ++qwq; if (qwq==n) return true; --qwq; while(qwq<n&&a[qwq]>=n-qwq-1) ++qwq; if (qwq==n) return true; return false; } int main(void) { int kase; read(kase); for (int i = 1; i <= kase; i++) { int n; read(n); int a[n]; for(int i=0;i<n;++i) read(a[i]); if (solve(n,a)) puts("Yes"); else puts("No"); } return 0; }
C. Mind Control (CF 1291 C)
题目大意
给定个数,有个人,你第次拿,对于每个人来说,他们可以拿第一个数或最后一个数,现在在取数开始前,你可以指定最多个人,当他们拿的时候规定他们分别是拿第一个数还是最后一个数。而没有被你指定的人,当他们取的时候,他们有可能拿第一个数也可能拿最后一个数。现在需要你指定最多个人,来使得不管其他人怎么取,到你取的时候,你取到的数始终大于等于,且这个尽可能大。
解题思路
前个人取后,剩下的是连续的个数。如果的话,那么到我取的时候情况数就有种,而答案就是这种情况中第一个和最后一个数的最大值的最小值。我们考虑如果指定了一个人的话,对最终的情况数会有什么影响。
我们把这个取数过程的状态树画出来,会有层,进而能发现,如果对其中任意一个人进行指定,那么最边边上的状态就会取不到了,最终的情况数就只有种,而这种就有两种可能。如果指定个人,那么最终的情况数就只有种,且这种情况在状态树中是连续的。
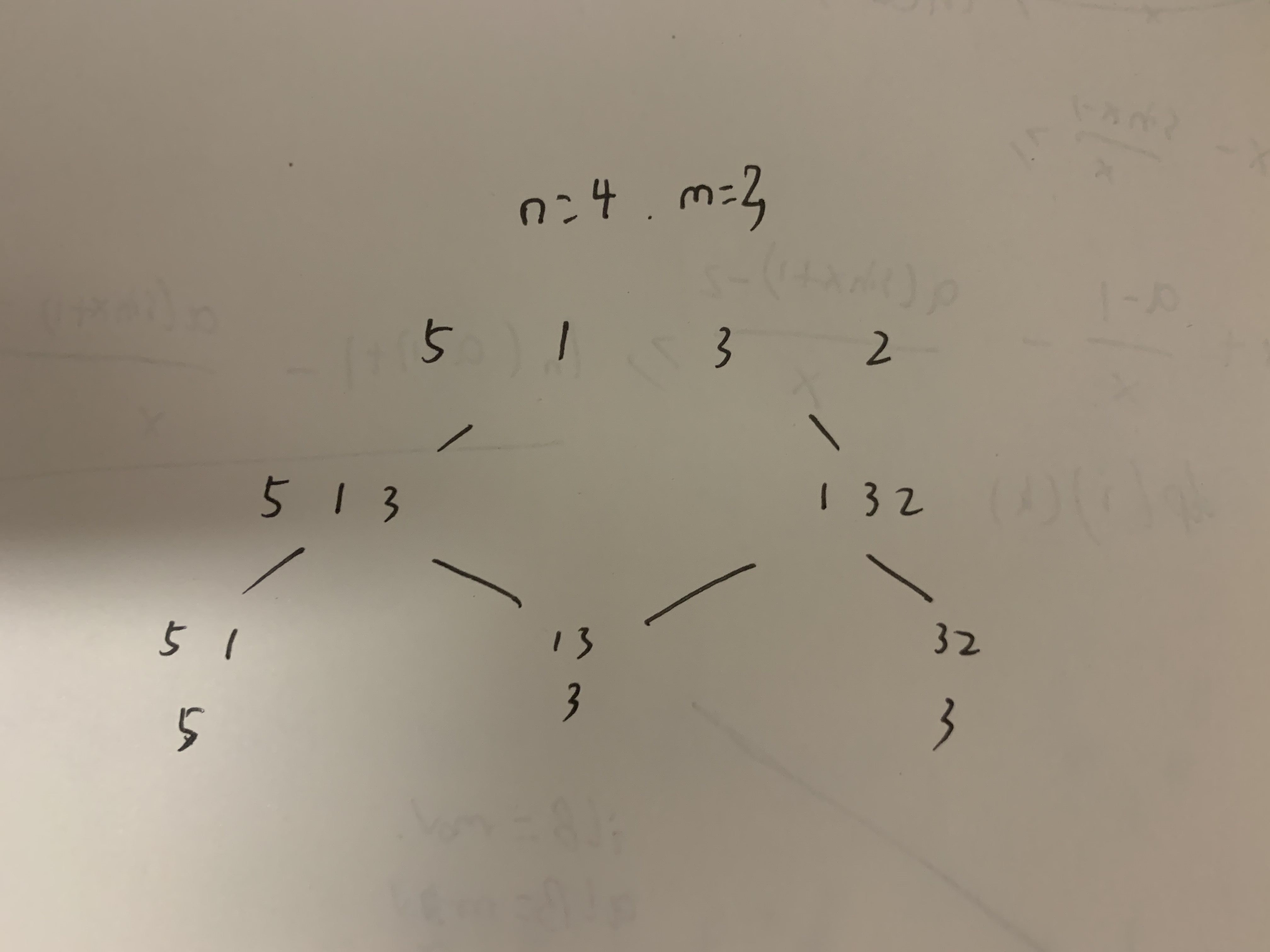
那么我们先把所有最终情况求出来,即,然后我们取连续的个数求最小值,答案就是这些最小值中的最大值。
暴力,线段树或表,单调队列都可以。
神奇的代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h> #define MIN(a,b) ((((a)<(b)?(a):(b)))) #define MAX(a,b) ((((a)>(b)?(a):(b)))) #define ABS(a) ((((a)>0?(a):-(a)))) using namespace std; typedef long long LL; typedef vector<int> VI; typedef pair<int,int> PII; typedef vector<PII> VPII; typedef vector<LL> VL; typedef pair<LL,LL> PLL; typedef vector<PLL> VPLL; template <typename T> void read(T &x) { int s = 0, c = getchar(); x = 0; while (isspace(c)) c = getchar(); if (c == 45) s = 1, c = getchar(); while (isdigit(c)) x = (x << 3) + (x << 1) + (c ^ 48), c = getchar(); if (s) x = -x; } template <typename T> void write(T x, char c = ' ') { int b[40], l = 0; if (x < 0) putchar(45), x = -x; while (x > 0) b[l++] = x % 10, x /= 10; if (!l) putchar(48); while (l) putchar(b[--l] | 48); putchar(c); } int main(void) { int kase; read(kase); for (int ii = 1; ii <= kase; ii++) { int n,m,k; read(n); read(m); read(k); k=min(k,m-1); int a[n+1]; for(int i=1;i<=n;++i) read(a[i]); int len=n-m; deque<pair<int,int>> team; int ans=0; for(int i=1;i<=m;++i){ int qwq=max(a[i],a[i+len]); while(!team.empty()&&team.front().second<i-m+k+1) team.pop_front(); while(!team.empty()&&team.back().first>=qwq) team.pop_back(); team.push_back(make_pair(qwq,i)); if (i>m-k-1) ans=max(ans,team.front().first); } write(ans,'\n'); } return 0; }
D. Irreducible Anagrams (CF 1291 D)
题目大意
给定一个串,有次询问,每次询问给定两个正整数,问子串是否有一个不可约的同构串。两个串互为同构串就是说可以通过重新排列串字母使得变为。若存在一个串是的一个同构串,,且可以分为个子串,也相应位置分为个子串,每个对应的子串都是同构串,则串是可约的,否则是不可约的。
解题思路
我们考虑一下一个串是否是可约的。
首先长度为一的串是不可约的,因为它无法分割成两部分或以上,前提为假命题为真。
然后一个串中只含有一个字母的也是不可约的,因为它的同构串只有它本身。
然后我们从字母出现的位置顺序考虑。如果一个的同构串是不可约的,那就意味着我无法将分成两部分或以上,否则存在一个子串使得和不同构。换句话说,就是我在取的前位时,这前位中出现的字母在中出现的最远位置要大于,这才使得我要增大,才有可能使得串的第一部分与串的第一部分同构,而无法做到这一点就意味着我取了前位时,这其中出现的字母在中的最远距离已经是的尾端,这就要我们把取完,才使得的第一部分与的第一部分同构,而此时没有第二部分了,那么此时就是个不可约的同构串。
从上面的思路我们就将问题转换成,这里有从左到右标号分别为到的个格子,以及我们有组数(个字母),每组数里有若干个从小到大排好的数且各不相同(该字母出现的位置),共有个数。现在要把这个数放到个格子里,对于一组数来说要先放小的数才能放大的数。问能否有一种放法,使得最大的数不在最后一个格子,且对于最大的数所在格子的前面每个格子,里面放的数满足。
最大的数所在的那一组中,如果最小的数不是,那么就一定存在该种放法,即我们直接把最大的数所在的那组数都放到前面的格子里即可。也就是说时,就存在不可约的同构串。
而如果最小的数是,如果有两组的话,可以发现我们无法满足上述的条件,而如果有三组及以上,都可以满足。
神奇的代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h> #define MIN(a,b) ((((a)<(b)?(a):(b)))) #define MAX(a,b) ((((a)>(b)?(a):(b)))) #define ABS(a) ((((a)>0?(a):-(a)))) using namespace std; typedef long long LL; typedef vector<int> VI; typedef pair<int,int> PII; typedef vector<PII> VPII; typedef vector<LL> VL; typedef pair<LL,LL> PLL; typedef vector<PLL> VPLL; template <typename T> void read(T &x) { int s = 0, c = getchar(); x = 0; while (isspace(c)) c = getchar(); if (c == 45) s = 1, c = getchar(); while (isdigit(c)) x = (x << 3) + (x << 1) + (c ^ 48), c = getchar(); if (s) x = -x; } template <typename T> void write(T x, char c = ' ') { int b[40], l = 0; if (x < 0) putchar(45), x = -x; while (x > 0) b[l++] = x % 10, x /= 10; if (!l) putchar(48); while (l) putchar(b[--l] | 48); putchar(c); } bool check(int pos[][26],int l,int r){ int cnt=0; for(int i=0;i<26;++i) cnt+=(pos[r][i]-pos[l-1][i])>0; return cnt>2; } int main(void) { char s[200006]; scanf("%s",s+1); int n=strlen(s+1); int pos[n+1][26]={0}; for(int i=1;i<=n;++i){ pos[i][s[i]-'a']++; for(int j=0;j<26;++j) pos[i][j]+=pos[i-1][j]; } int q; read(q); for(int l,r,i=1;i<=q;++i){ read(l); read(r); if (l==r) puts("Yes"); else if (s[l]!=s[r]) puts("Yes"); else if (check(pos,l,r)) puts("Yes"); else puts("No"); } return 0; }
本文作者:~Lanly~
本文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/Lanly/p/12257762.html
版权声明:本作品采用知识共享署名-非商业性使用-禁止演绎 2.5 中国大陆许可协议进行许可。



【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· go语言实现终端里的倒计时
· 如何编写易于单元测试的代码
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语,封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· 分享一个免费、快速、无限量使用的满血 DeepSeek R1 模型,支持深度思考和联网搜索!
· 基于 Docker 搭建 FRP 内网穿透开源项目(很简单哒)
· ollama系列01:轻松3步本地部署deepseek,普通电脑可用
· 25岁的心里话
· 按钮权限的设计及实现