Keras函数式 API
用Keras定义网络模型有两种方式,
之前我们介绍了Sequential顺序模型,今天我们来接触一下 Keras 的函数式API模型。
函数式API:全连接网络
from keras.layers import Input, Dense from keras.models import Model # 这部分返回一个张量 inputs = Input(shape=(784,)) # 层的实例是可调用的,它以张量为参数,并且返回一个张量 x = Dense(64, activation='relu')(inputs) x = Dense(64, activation='relu')(x) predictions = Dense(10, activation='softmax')(x) # 这部分创建了一个包含输入层和三个全连接层的模型 model = Model(inputs=inputs, outputs=predictions) model.compile(optimizer='rmsprop', loss='categorical_crossentropy', metrics=['accuracy']) model.fit(data, labels,batch_size=32, epochs=5) # 开始训练
多输入多输出模型
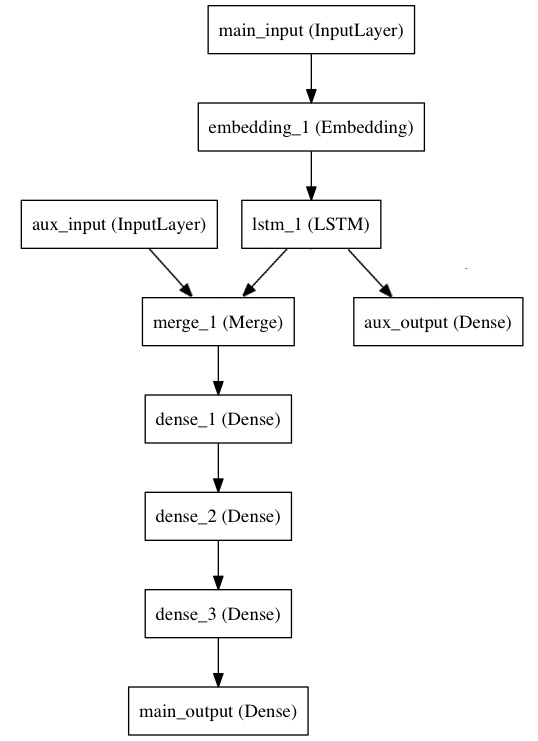
主要负责用函数式API来实现它
主要输入接收新闻标题本身,即一个整数序列(每个证书编码一个词),这些整数在1到10000之间(10000个词的词汇表),且序列长度为100个词
from keras.layers import Input, Embedding, LSTM, Dense from keras.models import Model # 标题输入:接收一个含有 100 个整数的序列,每个整数在 1 到 10000 之间。 # 注意我们可以通过传递一个 "name" 参数来命名任何层。 main_input = Input(shape=(100,), dtype='int32', name='main_input') # Embedding 层将输入序列编码为一个稠密向量的序列, # 每个向量维度为 512。 x = Embedding(output_dim=512, input_dim=10000, input_length=100)(main_input) # LSTM 层把向量序列转换成单个向量, # 它包含整个序列的上下文信息 lstm_out = LSTM(32)(x)
在这里,我们插入辅助损失,即使在模型主损失很高的情况下,LSTM层和Embedding层都能被平稳地训练。
auxiliary_output = Dense(1, activation='sigmoid', name='aux_output')(lstm_out)
此时,我们将辅助输入数据与 LSTM 层的输出连接起来,输入到模型中:
auxiliary_input = Input(shape=(5,), name='aux_input') x = keras.layers.concatenate([lstm_out, auxiliary_input]) # 堆叠多个全连接网络层 x = Dense(64, activation='relu')(x) x = Dense(64, activation='relu')(x) x = Dense(64, activation='relu')(x) # 最后添加主要的逻辑回归层 main_output = Dense(1, activation='sigmoid', name='main_output')(x)
然后定义一个具有两个输入和两个输出的模型:
model = Model(inputs=[main_input, auxiliary_input], outputs=[main_output, auxiliary_output])
现在编译模型,并给辅助损失分配一个 0.2 的权重。如果要为不同的输出指定不同的 loss_weights 或 loss,可以使用列表或字典。 在这里,我们给 loss 参数传递单个损失函数,这个损失将用于所有的输出。
model.compile(optimizer='rmsprop', loss='binary_crossentropy', loss_weights=[1., 0.2])
我们可以通过输入数组和目标数组的列表来训练模型:
model.fit([headline_data, additional_data], [labels, labels],
epochs=50, batch_size=32)
由于输入和输出均被命名了(在定义时传递了一个 name 参数),我们也可以通过以下方式编译模型:
model.compile(optimizer='rmsprop', loss={'main_output': 'binary_crossentropy', 'aux_output': 'binary_crossentropy'}, loss_weights={'main_output': 1., 'aux_output': 0.2}) # 然后使用以下方式训练: model.fit({'main_input': headline_data, 'aux_input': additional_data}, {'main_output': labels, 'aux_output': labels}, epochs=50, batch_size=32)
共享网络层
函数API的另一个用途是使用共享网络层的模型。
比如我们想建立一个模型来分辨两条推文是否来自同一个人,实现这个目标的方法是:将两条推文编码层两个向量,连接向量,然后添加逻辑回归层;这将输出推文来自通一个作者的概率。模型将接受一对对正负表示的推特数据。
太难了,我理解不了。以后这条博客慢慢更新。

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号