可视化库Seaborn
老唐数据分析机器学习
Seaborn-1Style
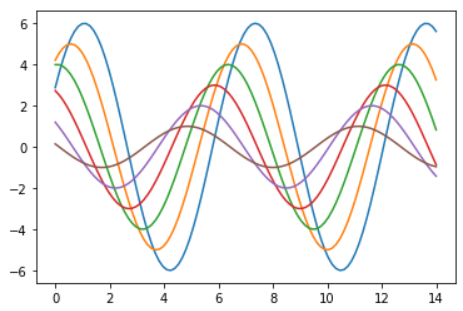
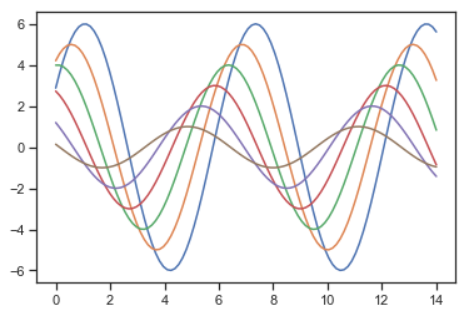
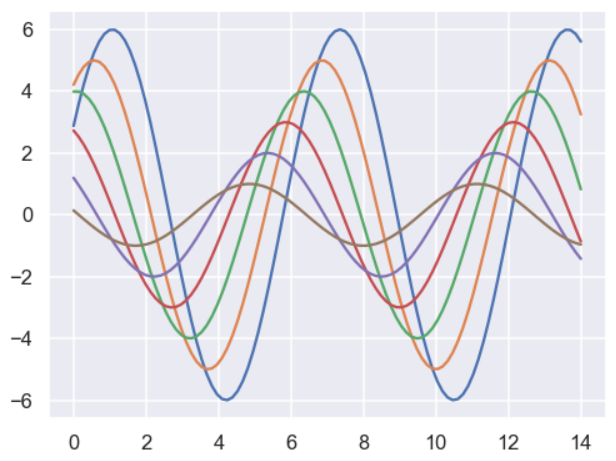
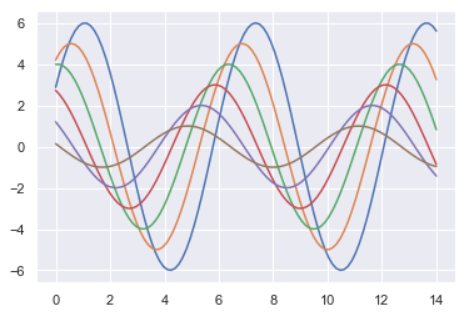
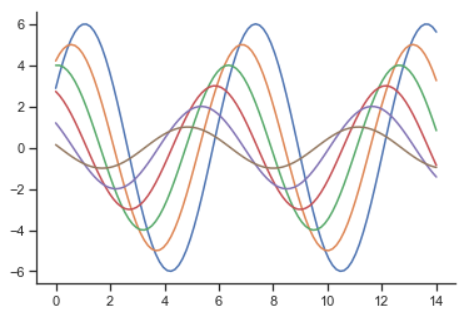
import seaborn as sns import numpy as np import matplotlib as mpl import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # %matplotlib inline def sinplot(flip=1): x = np.linspace(0, 14, 100) for i in range(1, 7): plt.plot(x, np.sin(x + i * .5) * (7 - i) * flip) sinplot()
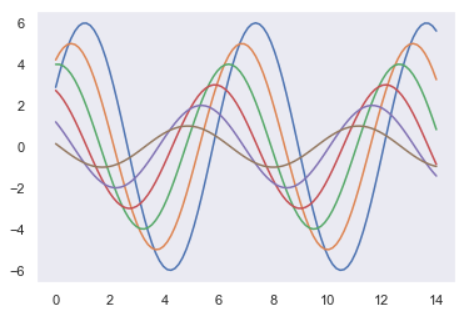
sns.set()
sinplot()
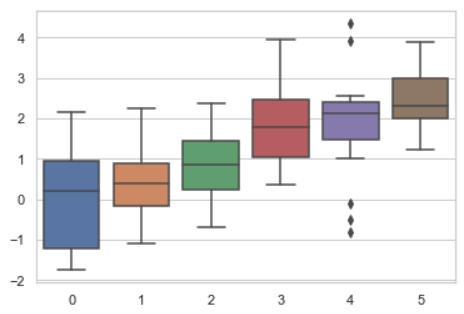
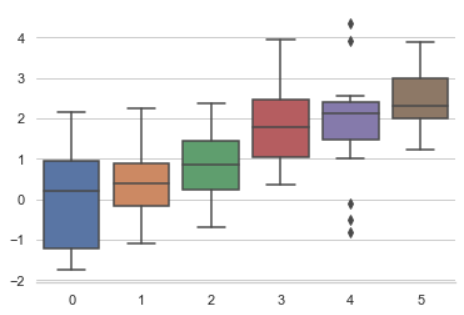
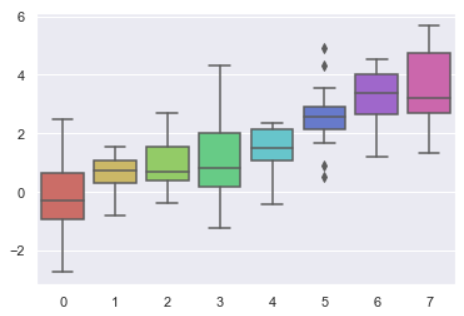
''' 5种主题风格 darkgrid whitegrid dark white ticks ''' sns.set_style("whitegrid") data = np.random.normal(size=(20, 6)) + np.arange(6) / 2 sns.boxplot(data=data)
data ''' array([[ 0.63986007, 2.14485399, 1.01131002, 1.40268475, 2.339169 , 3.22343471], [ 0.52113843, 0.83365849, 1.56715032, 0.7159742 , 0.35526665, 2.64698869], [ 0.26712799, 1.93107107, 0.11208568, -0.09777214, 1.0448611 , 2.89050072], [-0.23100111, -0.21345777, 0.45369097, 2.55874325, 2.02284598, 2.34599155], [ 0.13584382, 1.03477685, 1.65613141, 1.57249385, 1.26252323, 1.2502523 ], [-0.98887618, 2.12578215, 0.50486762, 1.07129467, 0.29844895, 2.83149809], [ 0.2791657 , 0.70301803, 1.68786681, -0.72639551, 3.02613673, 2.09390095], [ 0.97237265, 1.60585848, -0.23019449, 0.94411186, 2.47911711, 3.75833174], [ 2.36644874, 1.74865381, 0.49079692, 1.84241922, 2.13008836, 3.74685447], [ 1.49364838, 0.19296167, 0.75148434, 1.68317246, 2.3352623 , 2.77883528], [ 0.54814897, -0.03756201, 2.30158484, 0.35876512, 1.43424766, 1.20749153], [ 1.01546528, 0.70699355, 0.80075029, 1.92595054, -0.46382634, 2.35953131], [-0.68841373, 0.46816329, 1.62756676, 1.38552499, 1.99805172, 3.91744223], [-1.24971189, 2.30894878, 0.56885806, 1.61251681, 1.92630285, 4.16217846], [-0.77979552, -0.29186602, 1.21501248, 2.95481369, 0.82249344, 2.77935004], [ 0.05522944, -0.23371659, 1.62287008, 0.2330687 , 3.1935013 , 4.41159611], [ 3.37032537, -0.32074589, 3.84291451, 2.23170646, 1.11824526, 3.56219305], [ 2.23227077, 2.94561766, -1.28387574, 5.67984199, 1.72101898, 3.73012338], [ 1.36362738, 0.83392614, 0.09145057, 2.0837733 , 2.33104093, 3.14713488], [ 0.27535606, 0.61696806, 1.35029868, 0.95423693, 4.08083078, 1.63515582]]) ''' sns.set_style("dark") sinplot()
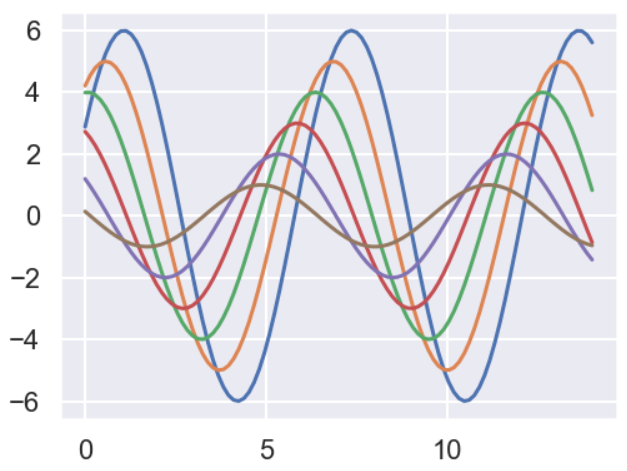
sns.set_style("white") sinplot()
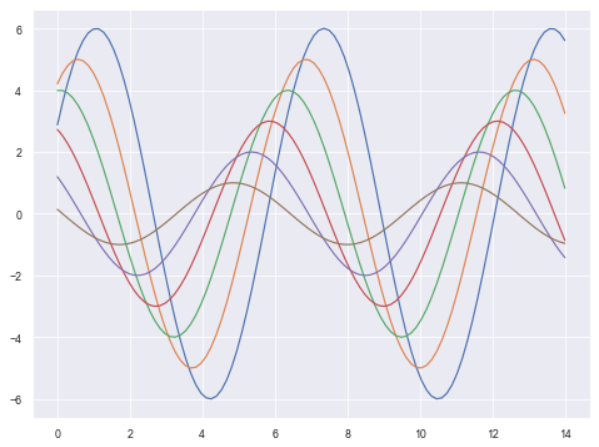
sns.set_style("ticks") sinplot()
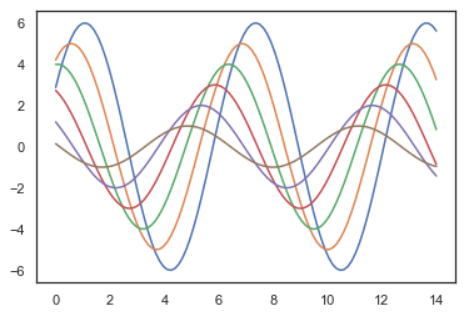
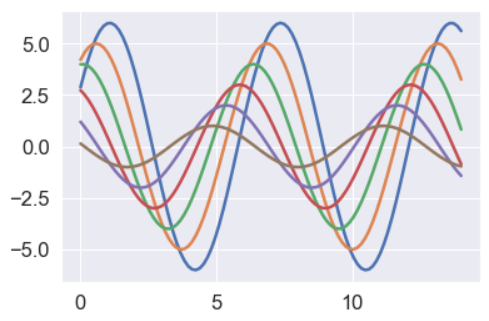
sinplot()
sns.despine()
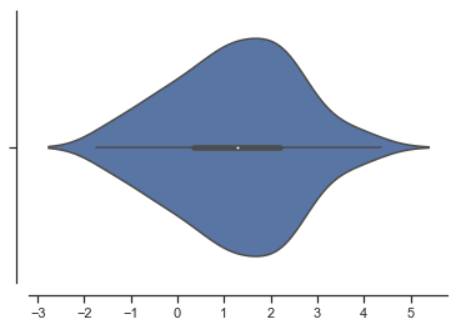
#f, ax = plt.subplots() sns.violinplot(data) sns.despine(offset=10) # offset 设置图像离轴线的距离
sns.set_style("whitegrid") sns.boxplot(data=data, palette="deep") sns.despine(left=True)
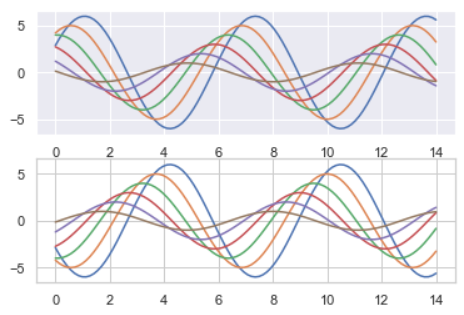
with sns.axes_style("darkgrid"): plt.subplot(211) sinplot() plt.subplot(212) sinplot(-1)
sns.set() sns.set_context("paper") plt.figure(figsize=(8, 6)) sinplot()
sns.set_context("talk") plt.figure(figsize=(8, 6)) sinplot()
sns.set_context("poster") plt.figure(figsize=(8, 6)) sinplot()
sns.set_context("notebook", font_scale=1.5, rc={"lines.linewidth": 2.5}) sinplot()
Seaborn-2Color
import numpy as np
import seaborn as sns
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
%matplotlib inline
sns.set(rc={"figure.figsize": (6, 6)})
调色板
颜色很重要
color_palette()能传入任何Matplotlib所支持的颜色
color_palette()不写参数则默认颜色
set_palette()设置所有图的颜色
分类色板
current_palette = sns.color_palette()
sns.palplot(current_palette)

10个默认的颜色循环主题
圆形画板
当你有10个以上的分类要区分时,最简单的方法就是在一个圆形的颜色空间中画出均匀间隔的颜色(这样的色调会保持亮度和饱和度不变)。这是大多数的当他们需要使用比当前默认颜色循环中设置的颜色更多时的默认方案。
最常用的方法是使用hls的颜色空间,这是RGB值的一个简单转换。
sns.palplot(sns.color_palette("hls", 8))

data = np.random.normal(size=(20, 8)) + np.arange(8) / 2
sns.boxplot(data=data,palette=sns.color_palette("hls", 8))
hls_palette()函数来控制颜色的亮度和饱和
l-亮度 lightness
s-饱和 saturation
sns.palplot(sns.hls_palette(8, l=.7, s=.9))

sns.palplot(sns.color_palette("Paired",8))

使用xkcd颜色来命名颜色
xkcd包含了一套众包努力的针对随机RGB色的命名。产生了954个可以随时通过xdcd_rgb字典中调用的命名颜色。
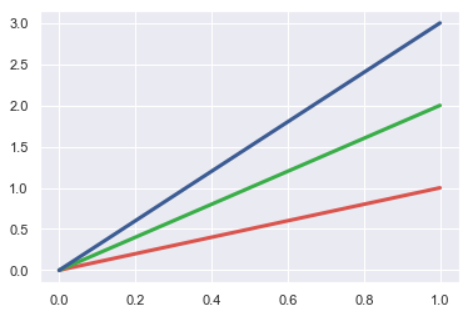
plt.plot([0, 1], [0, 1], sns.xkcd_rgb["pale red"], lw=3)
plt.plot([0, 1], [0, 2], sns.xkcd_rgb["medium green"], lw=3)
plt.plot([0, 1], [0, 3], sns.xkcd_rgb["denim blue"], lw=3)
colors = ["windows blue", "amber", "greyish", "faded green", "dusty purple"]
sns.palplot(sns.xkcd_palette(colors))
连续色板
色彩随数据变换,比如数据越来越重要则颜色越来越深
sns.palplot(sns.color_palette("Blues"))

如果想要翻转渐变,可以在面板名称中添加一个_r后缀
sns.palplot(sns.color_palette("BuGn_r"))

cubehelix_palette()调色板
色调线性变换
sns.palplot(sns.color_palette("cubehelix", 8))

sns.palplot(sns.cubehelix_palette(8, start=.5, rot=-.75))

sns.palplot(sns.cubehelix_palette(8, start=.75, rot=-.150))

light_palette() 和dark_palette()调用定制连续调色板
sns.palplot(sns.light_palette("green"))

sns.palplot(sns.dark_palette("purple"))

sns.palplot(sns.light_palette("navy", reverse=True))

x, y = np.random.multivariate_normal([0, 0], [[1, -.5], [-.5, 1]], size=300).T
pal = sns.dark_palette("green", as_cmap=True)
sns.kdeplot(x, y, cmap=pal);
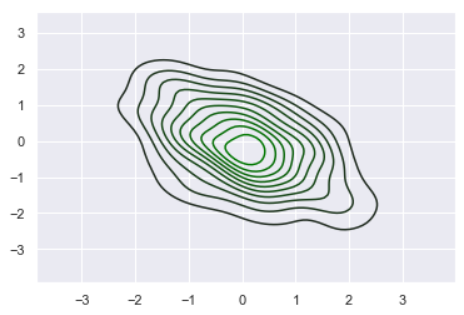
sns.palplot(sns.light_palette((210, 90, 60), input="husl"))

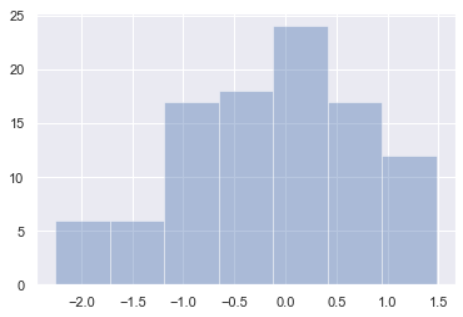
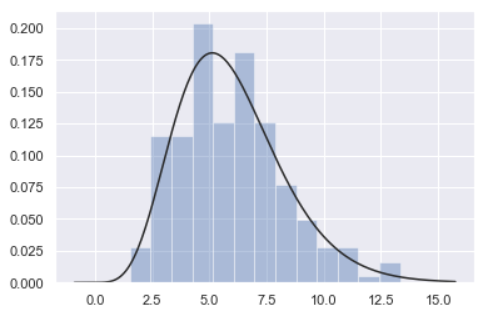
Seaborn-3Var %matplotlib inline import numpy as np import pandas as pd from scipy import stats, integrate import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import seaborn as sns sns.set(color_codes=True) np.random.seed(sum(map(ord, "distributions"))) x = np.random.normal(size=100) sns.distplot(x,kde=False)
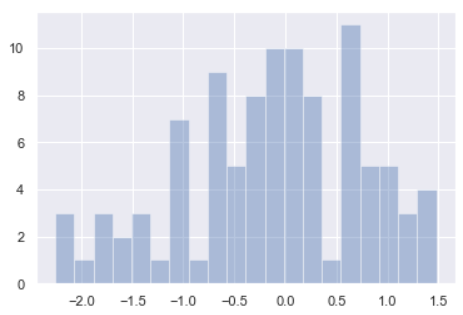
x ''' array([ 0.97752209, 0.21994529, 1.15613215, 0.65223291, -0.5748041 , 0.15529892, 0.32819136, -0.52983823, 0.60642604, -0.75095403, -0.15975087, 0.13873173, -0.37420078, -0.66933013, 0.97879031, 1.39975046, -0.69109644, -1.71275999, -0.98069174, 0.04053801, -0.08993049, -0.21894432, 0.95007978, 0.04834565, 0.7594089 , 0.60660518, -1.04920173, -0.11541744, -0.15526694, 1.47822792, -1.36072685, -0.45489649, -0.3327011 , 0.61143769, -1.64781917, 0.04655565, -0.09984121, 0.23188707, -1.18274658, -0.66297796, -0.80121788, -0.25074193, 0.13970127, 0.82166008, -0.12297872, 0.2372636 , 1.46122763, 0.59616042, -1.85714625, 1.27880682, -1.45718971, -0.68239548, 0.0419499 , -0.38886254, -0.36657596, -0.5210484 , 0.59571555, 0.26732394, -0.67206209, -1.9304416 , 0.59615679, -1.00097477, 0.80460921, -0.10346389, 0.60495096, -1.0529459 , 0.96063664, 0.77417928, -1.80310065, -2.25505873, -0.10676567, -1.60643438, 0.6203414 , -1.05387172, -0.24499961, -1.35825235, -1.02115073, 1.02619575, 0.31307791, 1.12870088, -0.05591163, 0.88423656, 0.47052053, 0.00631765, -0.64831749, -2.17714683, -0.3308601 , 0.68436603, 0.32375091, -0.21378255, 0.1867279 , -2.07346476, 0.10669616, -0.72691788, 1.42268722, -0.71936773, 0.65605735, 0.13668725, -0.17619063, -0.97891862]) ''' sns.distplot(x, bins=20, kde=False) # bins=20 设置切分 20 份
# 数据分布情况 x = np.random.gamma(6, size=200) sns.distplot(x, kde=False, fit=stats.gamma)
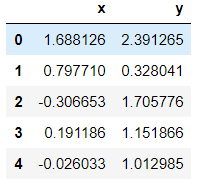
# 根据均值和协方差生成数据 mean, cov = [0, 1], [(1, .5), (.5, 1)] data = np.random.multivariate_normal(mean, cov, 200) df = pd.DataFrame(data, columns=["x", "y"]) # 将 numpy.ndarray 转化为 pandas.core.frame.DataFrame df.head()
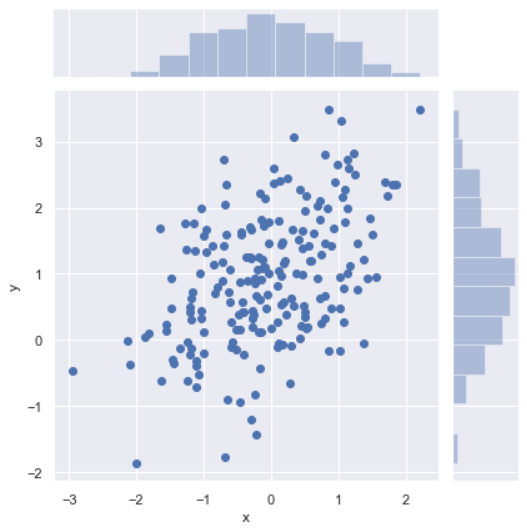
观测两个变量之间的分布关系最好用散点图 sns.jointplot(x="x", y="y", data=df);
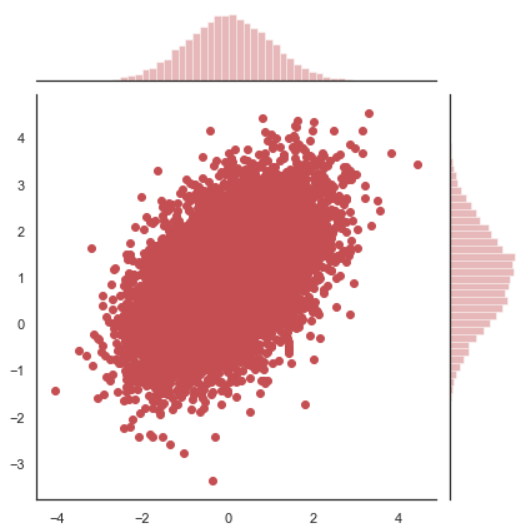
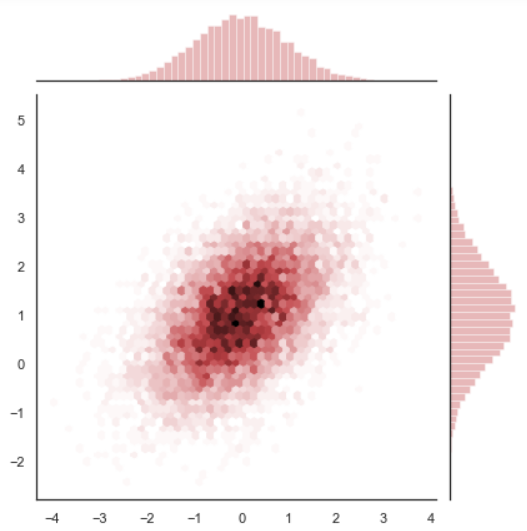
x, y = np.random.multivariate_normal(mean, cov, 10000).T with sns.axes_style("white"): sns.jointplot(x=x, y=y, color="r")
# 当散点图的点太多,占满整张图时,可以使用 hex 图,通过颜色深浅来判断 x, y = np.random.multivariate_normal(mean, cov, 10000).T with sns.axes_style("white"): sns.jointplot(x=x, y=y, kind="hex", color="r")
4-REG
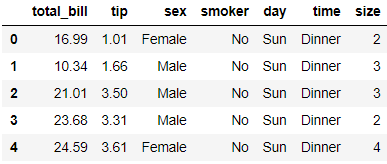
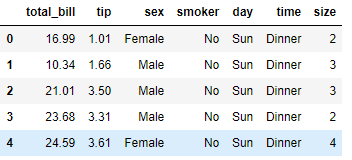
%matplotlib inline import numpy as np import pandas as pd import matplotlib as mpl import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import seaborn as sns sns.set(color_codes=True) np.random.seed(sum(map(ord, "regression"))) tips = sns.load_dataset("tips") tips.head()
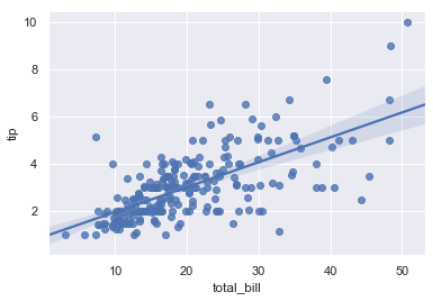
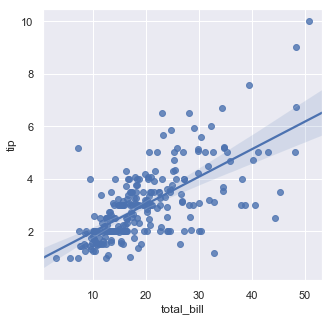
# regplot()和lmplot()都可以绘制回归关系,推荐regplot() sns.regplot(x="total_bill", y="tip", data=tips)
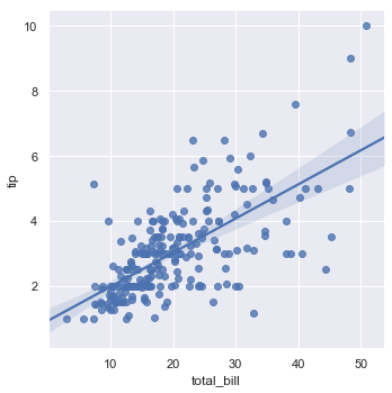
sns.lmplot(x="total_bill", y="tip", data=tips);
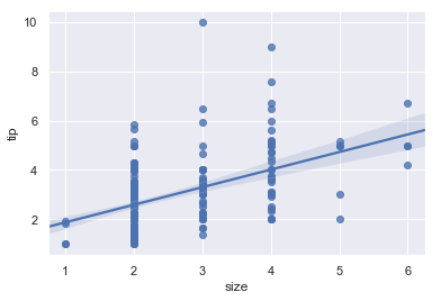
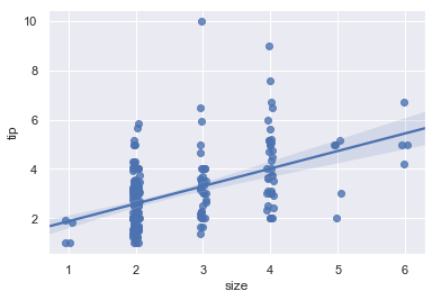
sns.regplot(data=tips,x="size",y="tip")
sns.regplot(x="size", y="tip", data=tips, x_jitter=.05) # x_jitter 在原始的数据值范围内抖动
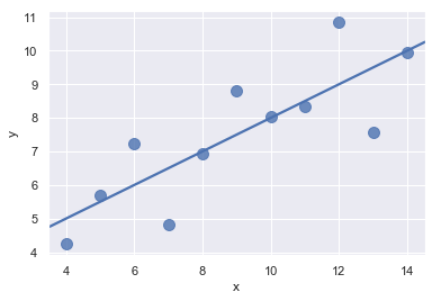
anscombe = sns.load_dataset("anscombe") sns.regplot(x="x", y="y", data=anscombe.query("dataset == 'I'"), ci=None, scatter_kws={"s": 100})
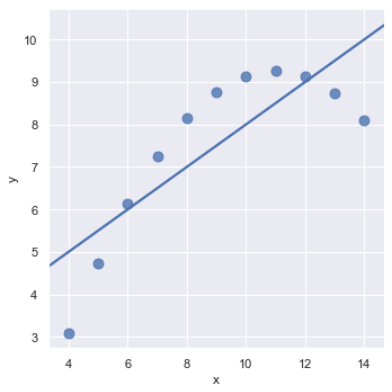
sns.lmplot(x="x", y="y", data=anscombe.query("dataset == 'II'"), ci=None, scatter_kws={"s": 80})
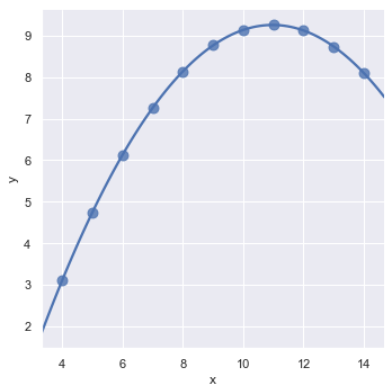
sns.lmplot(x="x", y="y", data=anscombe.query("dataset == 'II'"), order=2, ci=None, scatter_kws={"s": 80});
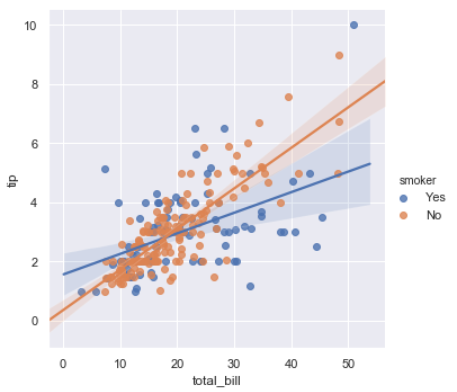
sns.lmplot(x="total_bill", y="tip", hue="smoker", data=tips);
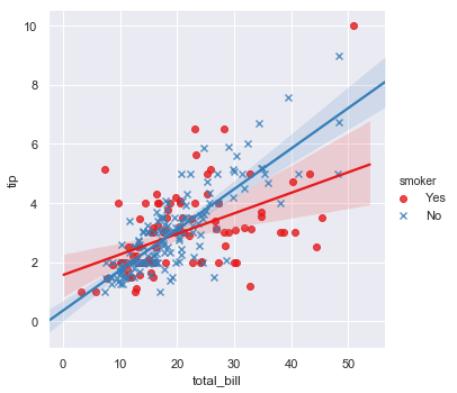
sns.lmplot(x="total_bill", y="tip", hue="smoker", data=tips, markers=["o", "x"], palette="Set1");
sns.lmplot(x="total_bill", y="tip", hue="smoker", col="time", data=tips);
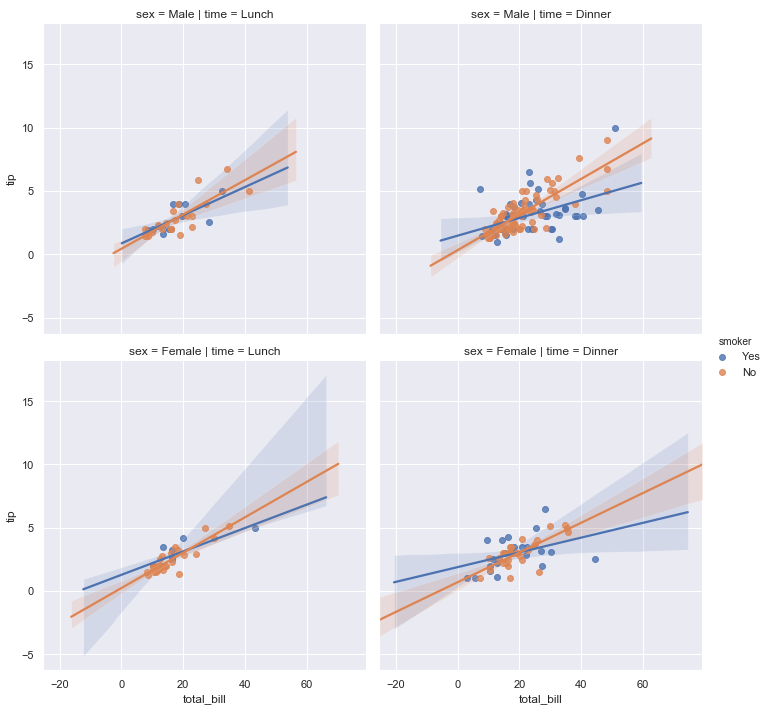
sns.lmplot(x="total_bill", y="tip", hue="smoker", col="time", row="sex", data=tips);
f, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(5, 5)) sns.regplot(x="total_bill", y="tip", data=tips, ax=ax);
col_wrap:“Wrap” the column variable at this width, so that the column facets span multiple rows size :Height (in inches) of each facet
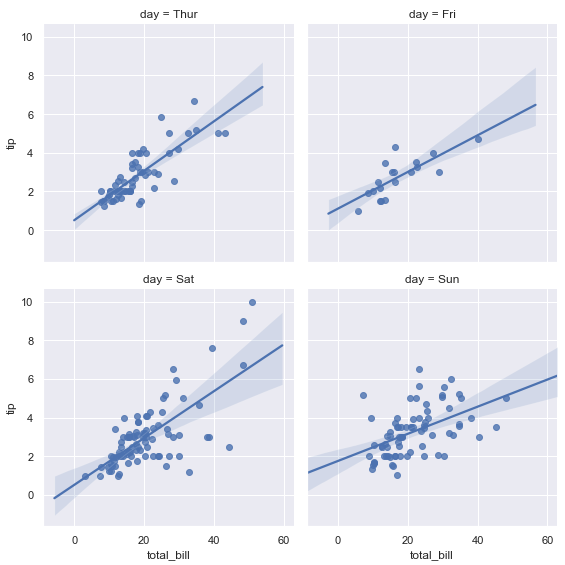
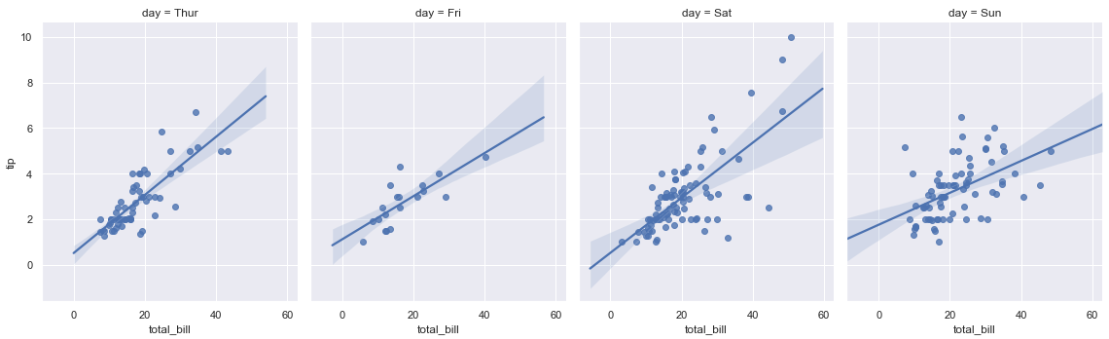
sns.lmplot(x="total_bill", y="tip", col="day", data=tips, col_wrap=2, size=4);
sns.lmplot(x="total_bill", y="tip", col="day", data=tips, aspect=.8);
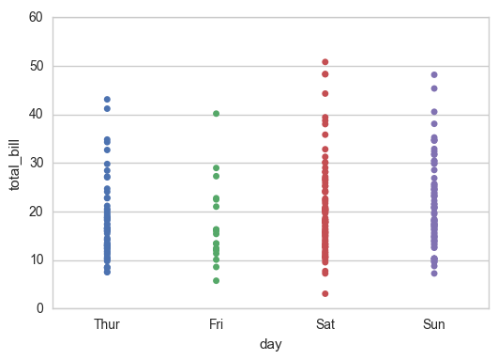
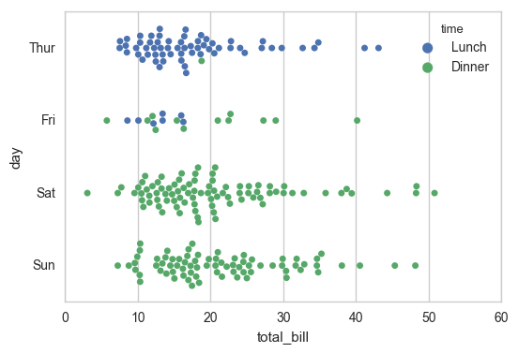
5-category %matplotlib inline import numpy as np import pandas as pd import matplotlib as mpl import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import seaborn as sns sns.set(style="whitegrid", color_codes=True) np.random.seed(sum(map(ord, "categorical"))) titanic = sns.load_dataset("titanic") tips = sns.load_dataset("tips") iris = sns.load_dataset("iris") sns.stripplot(x="day", y="total_bill", data=tips, jitter=False);
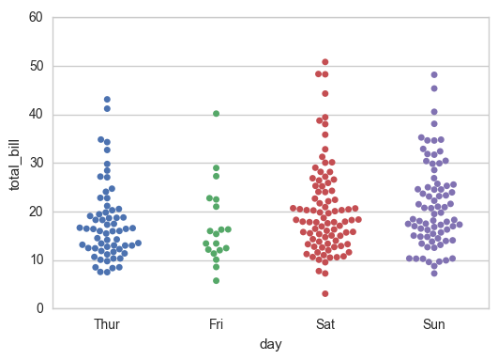
# 重叠是很常见的现象,但是重叠影响我观察数据的量了 sns.stripplot(x="day", y="total_bill", data=tips, jitter=True)
sns.swarmplot(x="day", y="total_bill", data=tips)
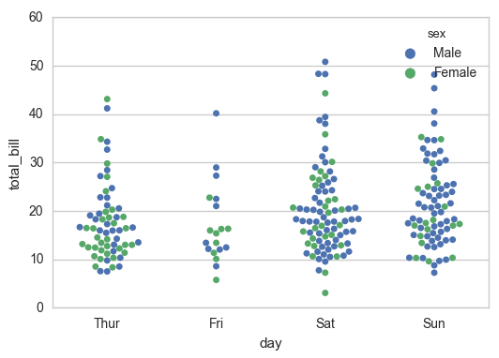
sns.swarmplot(x="day", y="total_bill", hue="sex",data=tips)
sns.swarmplot(x="total_bill", y="day", hue="time", data=tips);
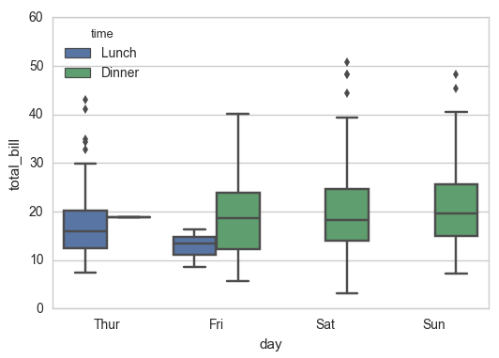
盒图 IQR即统计学概念四分位距,第一/四分位与第三/四分位之间的距离 N = 1.5IQR 如果一个值>Q3+N或 < Q1-N,则为离群点 sns.boxplot(x="day", y="total_bill", hue="time", data=tips);
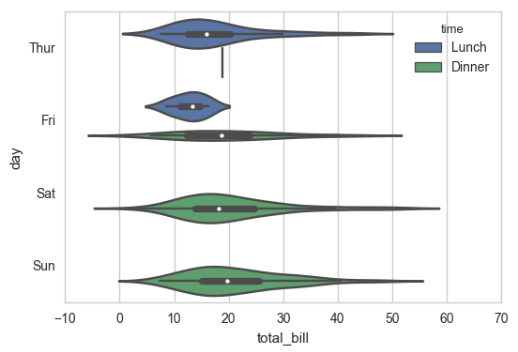
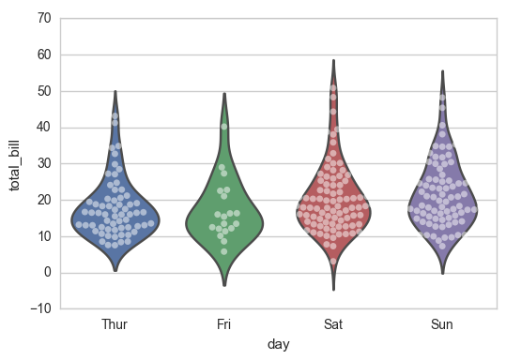
sns.violinplot(x="total_bill", y="day", hue="time", data=tips);
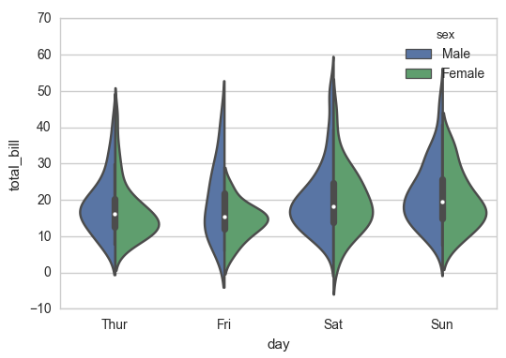
sns.violinplot(x="day", y="total_bill", hue="sex", data=tips, split=True);
sns.violinplot(x="day", y="total_bill", data=tips, inner=None) sns.swarmplot(x="day", y="total_bill", data=tips, color="w", alpha=.5)
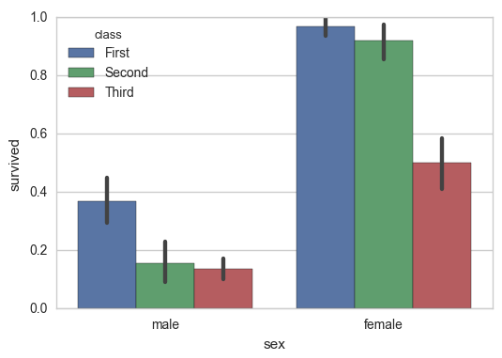
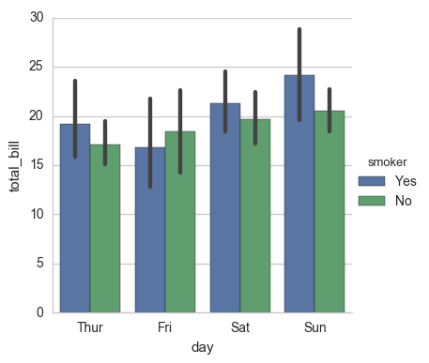
# 显示值的集中趋势可以用条形图 sns.barplot(x="sex", y="survived", hue="class", data=titanic);
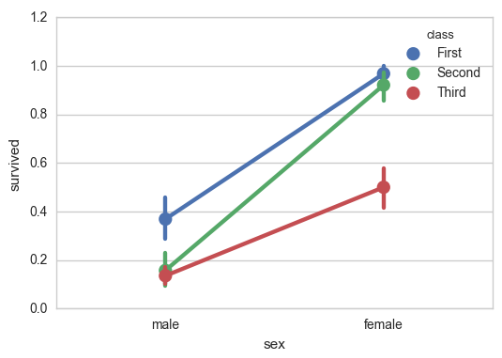
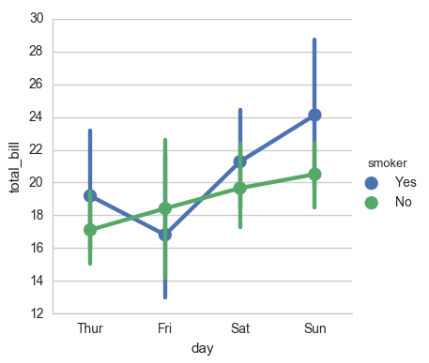
# 点图可以更好的描述变化差异 sns.pointplot(x="sex", y="survived", hue="class", data=titanic);
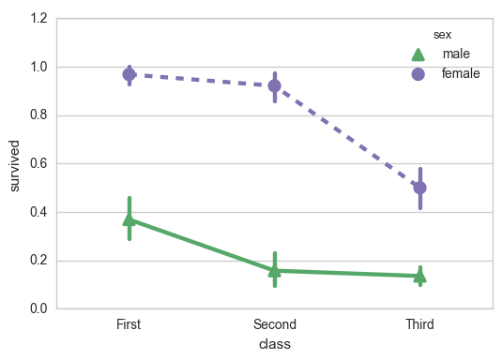
sns.pointplot(x="class", y="survived", hue="sex", data=titanic, palette={"male": "g", "female": "m"}, markers=["^", "o"], linestyles=["-", "--"]);
# 宽形数据 sns.boxplot(data=iris,orient="h");
# 多层面板分类图 sns.factorplot(x="day", y="total_bill", hue="smoker", data=tips)
sns.factorplot(x="day", y="total_bill", hue="smoker", data=tips, kind="bar")
sns.factorplot(x="day", y="total_bill", hue="smoker", col="time", data=tips, kind="swarm")
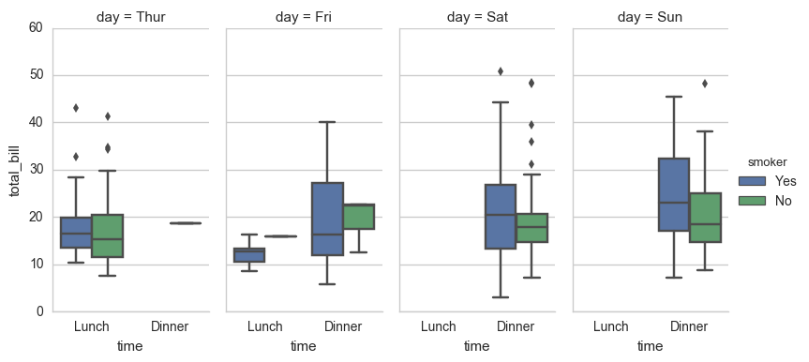
sns.factorplot(x="time", y="total_bill", hue="smoker", col="day", data=tips, kind="box", size=4, aspect=.5)
seaborn.factorplot(x=None, y=None, hue=None, data=None, row=None, col=None, col_wrap=None, estimator=, ci=95, n_boot=1000, units=None, order=None, hue_order=None, row_order=None, col_order=None, kind='point', size=4, aspect=1, orient=None, color=None, palette=None, legend=True, legend_out=True, sharex=True, sharey=True, margin_titles=False, facet_kws=None, **kwargs) Parameters: x,y,hue 数据集变量 变量名 date 数据集 数据集名 row,col 更多分类变量进行平铺显示 变量名 col_wrap 每行的最高平铺数 整数 estimator 在每个分类中进行矢量到标量的映射 矢量 ci 置信区间 浮点数或None n_boot 计算置信区间时使用的引导迭代次数 整数 units 采样单元的标识符,用于执行多级引导和重复测量设计 数据变量或向量数据 order, hue_order 对应排序列表 字符串列表 row_order, col_order 对应排序列表 字符串列表 kind : 可选:point 默认, bar 柱形图, count 频次, box 箱体, violin 提琴, strip 散点,swarm 分散点 size 每个面的高度(英寸) 标量 aspect 纵横比 标量 orient 方向 "v"/"h" color 颜色 matplotlib颜色 palette 调色板 seaborn颜色色板或字典 legend hue的信息面板 True/False legend_out 是否扩展图形,并将信息框绘制在中心右边 True/False share{x,y} 共享轴线 True/False
6-FacetGrid %matplotlib inline import numpy as np import pandas as pd import seaborn as sns from scipy import stats import matplotlib as mpl import matplotlib.pyplot as plt sns.set(style="ticks") np.random.seed(sum(map(ord, "axis_grids"))) tips = sns.load_dataset("tips") tips.head()
g = sns.FacetGrid(tips, col="time")
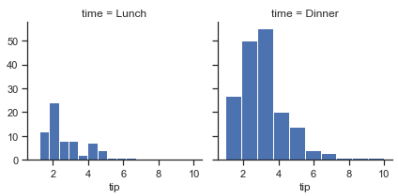
g = sns.FacetGrid(tips, col="time") g.map(plt.hist, "tip");
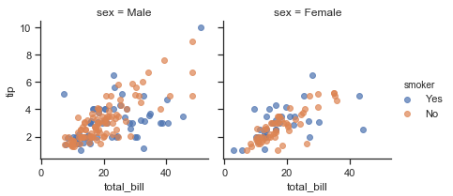
g = sns.FacetGrid(tips, col="sex", hue="smoker") g.map(plt.scatter, "total_bill", "tip", alpha=.7) g.add_legend();
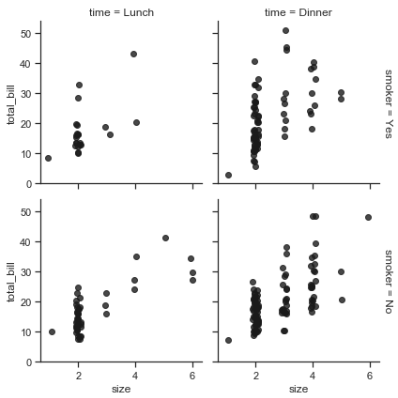
g = sns.FacetGrid(tips, row="smoker", col="time", margin_titles=True) g.map(sns.regplot, "size", "total_bill", color=".1", fit_reg=False, x_jitter=.1);
g = sns.FacetGrid(tips, col="day", size=4, aspect=.5) g.map(sns.barplot, "sex", "total_bill");
from pandas import Categorical ordered_days = tips.day.value_counts().index print (ordered_days) ordered_days = Categorical(['Thur', 'Fri', 'Sat', 'Sun']) g = sns.FacetGrid(tips, row="day", row_order=ordered_days, size=1.7, aspect=4,) g.map(sns.boxplot, "total_bill");
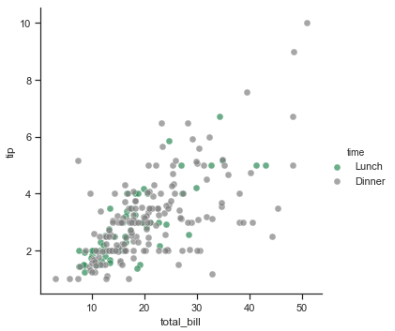
pal = dict(Lunch="seagreen", Dinner="gray") g = sns.FacetGrid(tips, hue="time", palette=pal, size=5) g.map(plt.scatter, "total_bill", "tip", s=50, alpha=.7, linewidth=.5, edgecolor="white") g.add_legend();
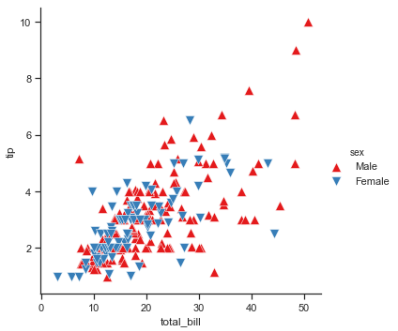
g = sns.FacetGrid(tips, hue="sex", palette="Set1", size=5, hue_kws={"marker": ["^", "v"]}) g.map(plt.scatter, "total_bill", "tip", s=100, linewidth=.5, edgecolor="white") g.add_legend();
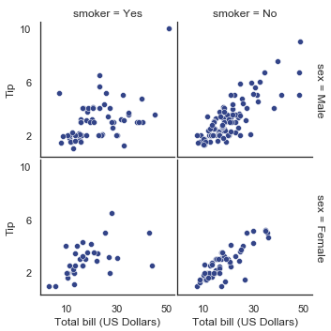
with sns.axes_style("white"): g = sns.FacetGrid(tips, row="sex", col="smoker", margin_titles=True, size=2.5) g.map(plt.scatter, "total_bill", "tip", color="#334488", edgecolor="white", lw=.5); g.set_axis_labels("Total bill (US Dollars)", "Tip"); g.set(xticks=[10, 30, 50], yticks=[2, 6, 10]); g.fig.subplots_adjust(wspace=.02, hspace=.02); #g.fig.subplots_adjust(left = 0.125,right = 0.5,bottom = 0.1,top = 0.9, wspace=.02, hspace=.02)
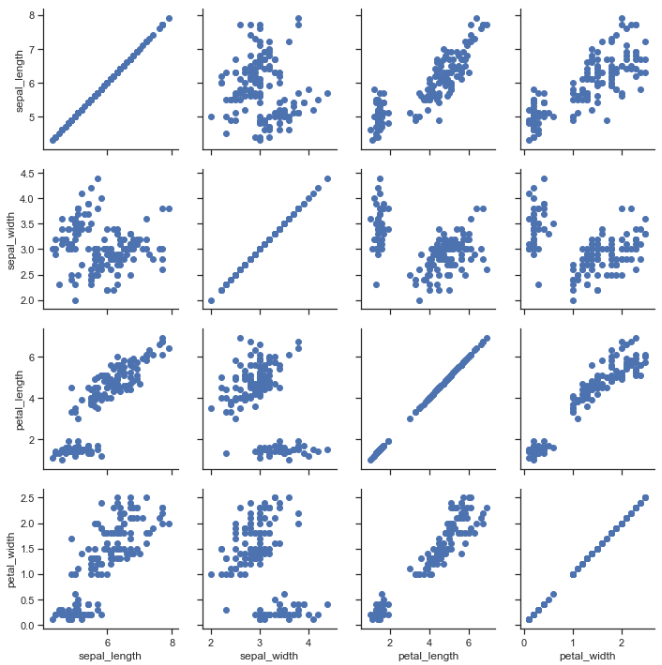
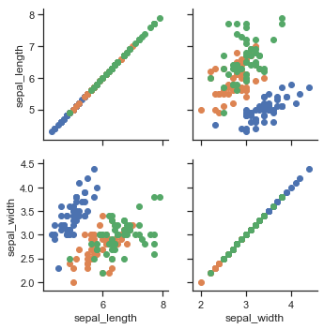
iris = sns.load_dataset("iris") g = sns.PairGrid(iris) g.map(plt.scatter);
g = sns.PairGrid(iris) g.map_diag(plt.hist) g.map_offdiag(plt.scatter);
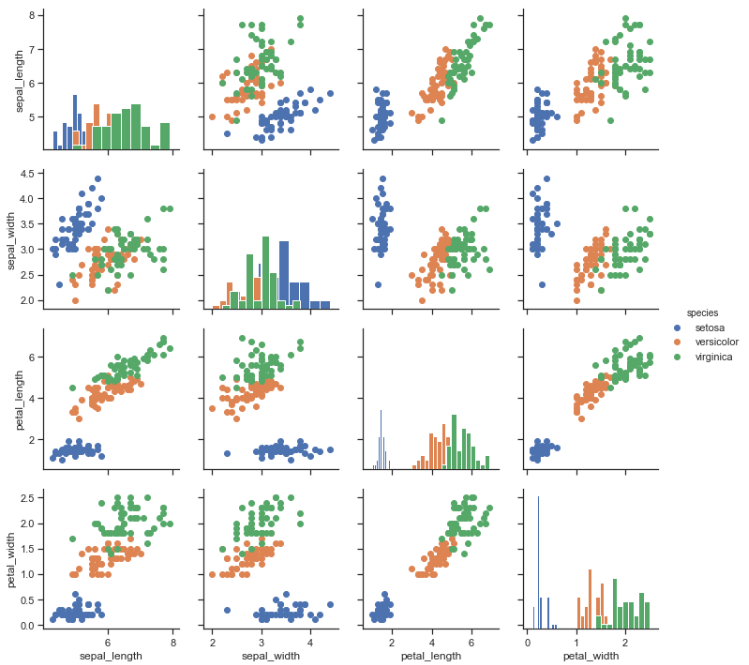
g = sns.PairGrid(iris, hue="species") g.map_diag(plt.hist) g.map_offdiag(plt.scatter) g.add_legend();
g = sns.PairGrid(iris, vars=["sepal_length", "sepal_width"], hue="species") g.map(plt.scatter);
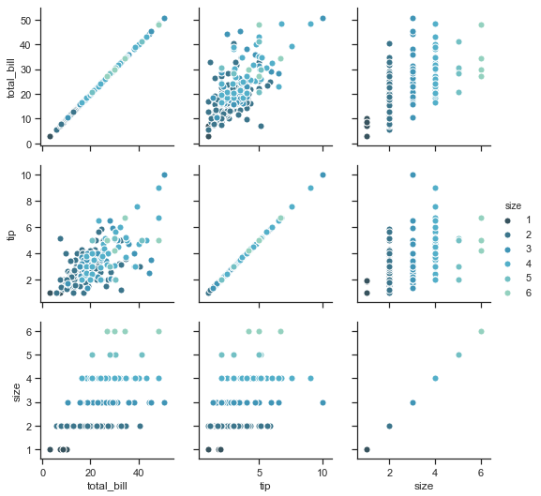
g = sns.PairGrid(tips, hue="size", palette="GnBu_d") g.map(plt.scatter, s=50, edgecolor="white") g.add_legend();
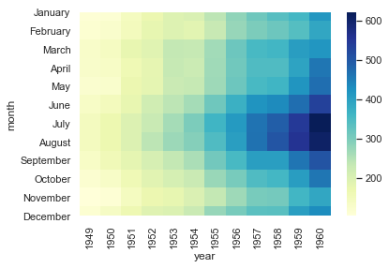
7-Heatmap %matplotlib inline import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np; np.random.seed(0) import seaborn as sns; sns.set() uniform_data = np.random.rand(3, 3) print (uniform_data) heatmap = sns.heatmap(uniform_data) ''' [[0.5488135 0.71518937 0.60276338] [0.54488318 0.4236548 0.64589411] [0.43758721 0.891773 0.96366276]] '''
ax = sns.heatmap(uniform_data, vmin=0.2, vmax=0.5)
normal_data = np.random.randn(3, 3) print (normal_data) ax = sns.heatmap(normal_data, center=0) ''' [[ 1.26611853 -0.50587654 2.54520078] [ 1.08081191 0.48431215 0.57914048] [-0.18158257 1.41020463 -0.37447169]] '''
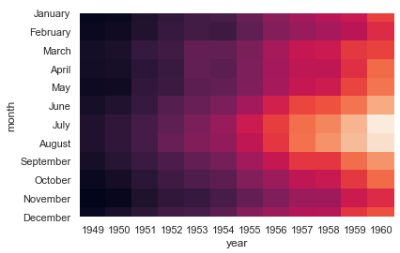
flights = sns.load_dataset("flights") flights.head()
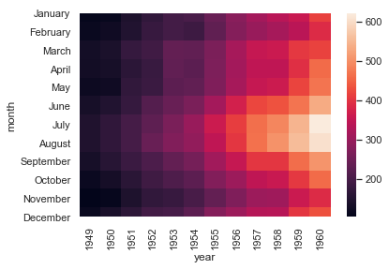
flights = flights.pivot("month", "year", "passengers") print (flights) ax = sns.heatmap(flights) ''' year 1949 1950 1951 1952 1953 1954 1955 1956 1957 1958 1959 \ month January 112 115 145 171 196 204 242 284 315 340 360 February 118 126 150 180 196 188 233 277 301 318 342 March 132 141 178 193 236 235 267 317 356 362 406 April 129 135 163 181 235 227 269 313 348 348 396 May 121 125 172 183 229 234 270 318 355 363 420 June 135 149 178 218 243 264 315 374 422 435 472 July 148 170 199 230 264 302 364 413 465 491 548 August 148 170 199 242 272 293 347 405 467 505 559 September 136 158 184 209 237 259 312 355 404 404 463 October 119 133 162 191 211 229 274 306 347 359 407 November 104 114 146 172 180 203 237 271 305 310 362 December 118 140 166 194 201 229 278 306 336 337 405 year 1960 month January 417 February 391 March 419 April 461 May 472 June 535 July 622 August 606 September 508 October 461 November 390 December 432 '''
ax = sns.heatmap(flights, annot=True,fmt="d") # annot=True,fmt="d" 显示数值
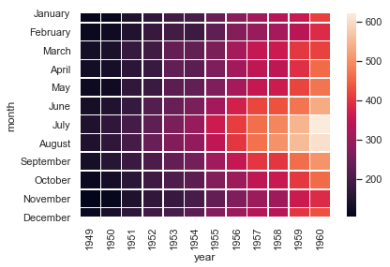
ax = sns.heatmap(flights, linewidths=.5) # linewidths=.1 指定每方格之间的间距
ax = sns.heatmap(flights, cmap="YlGnBu") # cmap="YlGnBu" 指定调色
ax = sns.heatmap(flights, cbar=False) # cbar=False 隐藏调色板
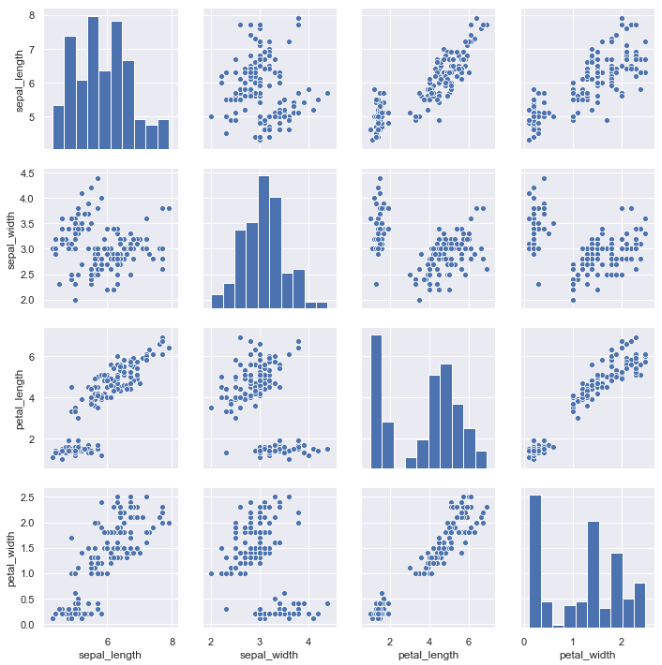
iris = sns.load_dataset("iris") sns.pairplot(iris)
请你一定不要停下来 成为你想成为的人
感谢您的阅读,我是LXL