Java-笔记13

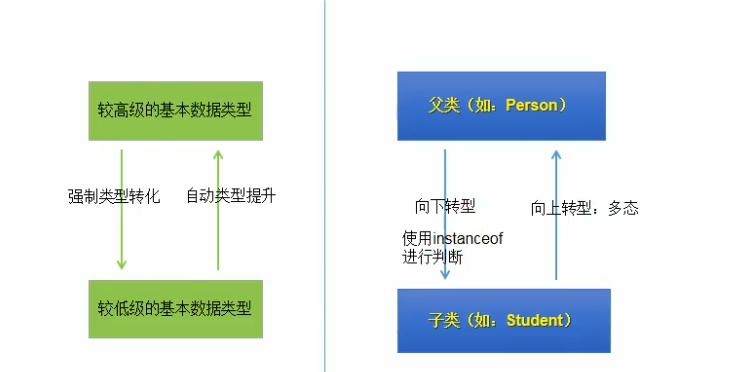
package com.atguigu.java; /* * 面向对象特征之三:多态性 * * 1.理解多态性:可以理解为一个事物的多种形态。 * 2.何为多态性: * 对象的多态性:父类的引用指向子类的对象(或子类的对象赋给父类的引用) * * 3. 多态的使用:虚拟方法调用 * 有了对象的多态性以后,我们在编译期,只能调用父类中声明的方法,但在运行期,我们实际执行的是子类重写父类的方法。 * 总结:编译,看左边;运行,看右边。 * * 4.多态性的使用前提: ① 类的继承关系 ② 方法的重写 * * 5.对象的多态性,只适用于方法,不适用于属性(编译和运行都看左边) * * ************************************************ * * */ public class PersonTest { public static void main(String[] args) { Person p1 = new Person(); p1.eat(); Man man = new Man(); man.eat(); man.age = 25; man.earnMoney(); //************************************************* System.out.println("*******************"); //对象的多态性:父类的引用指向子类的对象 Person p2 = new Man(); // Person p3 = new Woman(); //多态的使用:当调用子父类同名同参数的方法时,实际执行的是子类重写父类的方法 ---虚拟方法调用 p2.eat(); p2.walk(); // p2.earnMoney(); System.out.println(p2.id);//1001 System.out.println("*************************"); //不能调用子类所特有的方法、属性:编译时,p2是Person类型。 p2.name = "Tom"; // p2.earnMoney(); // p2.isSmoking = true; //有了对象的多态性以后,内存中实际上是加载了子类特有的属性和方法的,但是由于声明的变量为 //父类类型,导致编译时,只能调用父类中声明的属性和方法。子类特有的属性和方法不能被调用。 //如何才能调用子类中特有的属性和方法? //向下转型:使用强制类型转换符。 Man m1 = (Man)p2; m1.earnMoney(); m1.isSmoking = true; //使用强转时,可能出现ClassCastException的异常。 // Woman w1 = (Woman)p2; // w1.goShopping(); /* * instanceof 关键字的使用 * * a instanceof A:判断对象a是否是类A的实例。 如果是,返回true;如果不是,返回false; * * 使用情景:为了避免在向下转型是出现ClassCastException的异常,我们在向下转型之前, * 先进行instanof的判断,一旦返回true,就进行向下转型。如果返回false,不进行向下转型。 * * 如果 a instanceof A返回true,则 a instanceof B也返回true。 * * 其中,类B是类A的父类 * */ if(p2 instanceof Woman){ Woman w1 = (Woman)p2; w1.goShopping(); System.out.println("*****Woman*****"); } if(p2 instanceof Man){ Man m2 = (Man)p2; m2.earnMoney(); System.out.println("*****Man*****"); } if(p2 instanceof Person){ System.out.println("*****Person*****"); } if(p2 instanceof Object){ System.out.println("*****Object*****"); } //练习: //问题一:编译时通过,运行是不通过 // Person p3 = new Woman(); // Man m3 = (Man)p3; // Person p4 = new Person(); // Man m4 = (Man)p4; //两个无关的类 // Object o = new Person(); // String str1 = (String)o; // //问题二:编译时通过,运行时也通过 // Object obj = new Woman(); // Person p = (Person)obj; //问题三:编译不通过 // Man 5m = new Woman(); // String str = new Date(); } }
package com.atguigu.java; public class Person { String name; int age; int id = 1001; public void eat(){ System.out.println("人:吃饭"); } public void walk(){ System.out.println("人:走路"); } }
package com.atguigu.java; public class Man extends Person{ boolean isSmoking; int id = 1002; public void earnMoney(){ System.out.println("男人负责挣钱养家"); } public void eat(){ System.out.println("男人多吃肉,长肌肉"); } public void walk(){ System.out.println("男人霸气的走路"); } }
package com.atguigu.java; public class Woman extends Person{ boolean isBeauty; public void goShopping(){ System.out.println("女人喜欢购物"); } public void eat(){ System.out.println("女人少吃,为了减肥"); } public void walk(){ System.out.println("女人窈窕的走路"); } }
package com.atguigu.exer; /* * 练习: * 1.若子类重写了父类方法,就意味着子类里定义的方法彻底覆盖了父类里的同名方法, * 系统将不可能把父类里的方法转移到子类中:编译看左边,运行看右边 * * 2.对于实例变量则不存在这样的现象,即使子类里定义了与父类完全相同的实例变量, * 这个实例变量依然不可能覆盖父类中定义的实例变量:编译运行都看左边 * * * * */ class Base { int count = 10; public void display() { System.out.println(this.count); } } class Sub extends Base { int count = 20; public void display() { System.out.println(this.count); } } public class FieldMethodTest { public static void main(String[] args) { Sub s = new Sub(); System.out.println(s.count);//20 s.display();//20 Base b = s;//多态性 //==:对于引用数据类型来讲,比较的是两个引用数据类型变量的地址值是否相同 System.out.println(b == s);//true System.out.println(b.count);//10 b.display();//20 } }
package com.atguigu.exer; /* * 建立InstanceTest 类,在类中定义方法method(Person e); 在method中: (1)根据e的类型调用相应类的getInfo()方法。 (2)根据e的类型执行: 如果e为Person类的对象,输出: “a person”; 如果e为Student类的对象,输出: “a student” “a person ” 如果e为Graduate类的对象,输出: “a graduated student” “a student” “a person” * * * */ public class InstanceTest { public static void main(String[] args) { InstanceTest test = new InstanceTest(); test.method(new Student()); } public void method(Person e){ //虚拟方法调用 String info = e.getInfo(); System.out.println(info); //方式一 // if(e instanceof Graduate){ // System.out.println("a graduated student"); // System.out.println("a student"); // System.out.println("a person"); // }else if(e instanceof Student){ // System.out.println("a student"); // System.out.println("a person"); // }else{ // System.out.println("a person"); // } //方式二 if(e instanceof Graduate){ System.out.println("a graduated student"); } if(e instanceof Student){ System.out.println("a student"); } if(e instanceof Person){ System.out.println("a person"); } } } class Person { protected String name = "person"; protected int age = 50; public String getInfo() { return "Name: " + name + "\n" + "age: " + age; } } class Student extends Person { protected String school = "pku"; public String getInfo() { return "Name: " + name + "\nage: " + age + "\nschool: " + school; } } class Graduate extends Student { public String major = "IT"; public String getInfo() { return "Name: " + name + "\nage: " + age + "\nschool: " + school + "\nmajor:" + major; } }
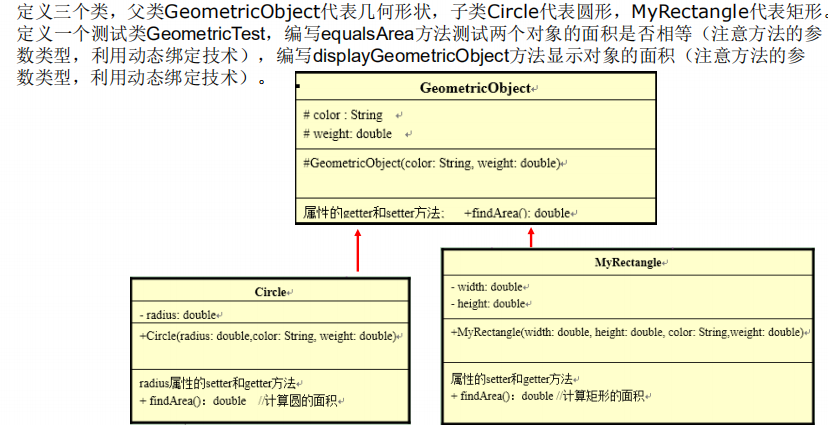
package com.atguigu.exer1; /* * * 定义一个测试类GeometricTest, * 编写equalsArea方法测试两个对象的面积是否相等(注意方法的参数类型,利用动态绑定技术), * 编写displayGeometricObject方法显示对象的面积(注意方法的参数类型,利用动态绑定技术)。 */ public class GeometricTest { public static void main(String[] args) { GeometricTest test = new GeometricTest(); Circle c1 = new Circle(3.3, "white", 1.0); test.displayGeometricObject(c1); Circle c2 = new Circle(3.3, "white", 1.0); test.displayGeometricObject(c2); boolean isEquals = test.equalsArea(c1, c2); System.out.println("c1 和 c2的面积是否相等:" + isEquals); MyRectangle rect = new MyRectangle(2.1, 3.4, "red", 2.0); test.displayGeometricObject(rect); } public void displayGeometricObject(GeometricObject o){//GeometricObject o = new Circle(...) System.out.println("面积为:" + o.findArea()); } //测试两个对象的面积是否相等 public boolean equalsArea(GeometricObject o1,GeometricObject o2){ return o1.findArea() == o2.findArea(); } }
package com.atguigu.exer1; public class GeometricObject {//几何图形 protected String color; protected double weight; public String getColor() { return color; } public void setColor(String color) { this.color = color; } public double getWeight() { return weight; } public void setWeight(double weight) { this.weight = weight; } public GeometricObject(String color, double weight) { super(); this.color = color; this.weight = weight; } public double findArea(){ return 0.0; } }
package com.atguigu.exer1; public class Circle extends GeometricObject { private double radius; public Circle(double radius,String color, double weight) { super(color, weight); this.radius = radius; } public double getRadius() { return radius; } public void setRadius(double radius) { this.radius = radius; } public double findArea(){ return 3.14 * radius * radius; } }
package com.atguigu.exer1; public class MyRectangle extends GeometricObject { private double width; private double height; public MyRectangle(double width,double height,String color, double weight) { super(color, weight); this.width = width; this.height = height; } public double getWidth() { return width; } public void setWidth(double width) { this.width = width; } public double getHeight() { return height; } public void setHeight(double height) { this.height = height; } @Override public double findArea() { return width * height; } }
package com.atguigu.java1; /* * java.lang.Object类 * 1.Object类是所有Java类的根父类 * 2.如果在类的声明中未使用extends关键字指明其父类,则默认父类为java.lang.Object类 * 3.Object类中的功能(属性、方法)就具有通用性。 * 属性:无 * 方法:equals() / toString() / getClass() /hashCode() / clone() / finalize() * wait() 、 notify()、notifyAll() * * 4. Object类只声明了一个空参的构造器 * * * * 面试题: * final、finally、finalize的区别? * */ public class ObjectTest { public static void main(String[] args) { Order order = new Order(); System.out.println(order.getClass().getSuperclass()); } } class Order{ }
package com.atguigu.java1; //Object类的clone()的使用 public class CloneTest { public static void main(String[] args) { Animal a1 = new Animal("花花"); try { Animal a2 = (Animal) a1.clone(); System.out.println("原始对象:" + a1); a2.setName("毛毛"); System.out.println("clone之后的对象:" + a2); } catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } class Animal implements Cloneable{ private String name; public Animal() { super(); } public Animal(String name) { super(); this.name = name; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } @Override public String toString() { return "Animal [name=" + name + "]"; } @Override protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return super.clone(); } }
//垃圾回收
package com.atguigu.java1; public class FinalizeTest { public static void main(String[] args) { Person p = new Person("Peter", 12); System.out.println(p); p = null;//此时对象实体就是垃圾对象,等待被回收。但时间不确定。 System.gc();//强制性释放空间 } } class Person{ private String name; private int age; public Person(String name, int age) { super(); this.name = name; this.age = age; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } //子类重写此方法,可在释放对象前进行某些操作 @Override protected void finalize() throws Throwable { System.out.println("对象被释放--->" + this); } @Override public String toString() { return "Person [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + "]"; } }
package com.atguigu.java1; import java.util.Date; /* * * 面试题: == 和 equals() 区别 * * 一、回顾 == 的使用: * == :运算符 * 1. 可以使用在基本数据类型变量和引用数据类型变量中 * 2. 如果比较的是基本数据类型变量:比较两个变量保存的数据是否相等。(不一定类型要相同) * 如果比较的是引用数据类型变量:比较两个对象的地址值是否相同.即两个引用是否指向同一个对象实体 * 补充: == 符号使用时,必须保证符号左右两边的变量类型一致。 * * 二、equals()方法的使用: * 1. 是一个方法,而非运算符 * 2. 只能适用于引用数据类型 * 3. Object类中equals()的定义: * public boolean equals(Object obj) { return (this == obj); } * 说明:Object类中定义的equals()和==的作用是相同的:比较两个对象的地址值是否相同.即两个引用是否指向同一个对象实体 * * 4. 像String、Date、File、包装类等都重写了Object类中的equals()方法。重写以后,比较的不是 * 两个引用的地址是否相同,而是比较两个对象的"实体内容"是否相同。 * * 5. 通常情况下,我们自定义的类如果使用equals()的话,也通常是比较两个对象的"实体内容"是否相同。那么,我们 * 就需要对Object类中的equals()进行重写. * 重写的原则:比较两个对象的实体内容是否相同. */ public class EqualsTest { public static void main(String[] args) { //基本数据类型 int i = 10; int j = 10; double d = 10.0; System.out.println(i == j);//true System.out.println(i == d);//true boolean b = true; // System.out.println(i == b); char c = 10; System.out.println(i == c);//true char c1 = 'A'; char c2 = 65; System.out.println(c1 == c2);//true //引用类型: Customer cust1 = new Customer("Tom",21); Customer cust2 = new Customer("Tom",21); System.out.println(cust1 == cust2);//false String str1 = new String("atguigu"); String str2 = new String("atguigu"); System.out.println(str1 == str2);//false System.out.println("****************************"); System.out.println(cust1.equals(cust2));//false--->true System.out.println(str1.equals(str2));//true Date date1 = new Date(32432525324L); Date date2 = new Date(32432525324L); System.out.println(date1.equals(date2));//true } }
package com.atguigu.java1; public class Customer { private String name; private int age; public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } public Customer() { super(); } public Customer(String name, int age) { super(); this.name = name; this.age = age; } //自动生成的equals() @Override public boolean equals(Object obj) { if (this == obj) return true; if (obj == null) return false; if (getClass() != obj.getClass()) return false; Customer other = (Customer) obj; if (age != other.age) return false; if (name == null) { if (other.name != null) return false; } else if (!name.equals(other.name)) return false; return true; } //重写的原则:比较两个对象的实体内容(即:name和age)是否相同 //手动实现equals()的重写 // @Override // public boolean equals(Object obj) { // //// System.out.println("Customer equals()...."); // if (this == obj) { // return true; // } // // if(obj instanceof Customer){ // Customer cust = (Customer)obj; // //比较两个对象的每个属性是否都相同 //// if(this.age == cust.age && this.name.equals(cust.name)){ //// return true; //// }else{ //// return false; //// } // // //或 // return this.age == cust.age && this.name.equals(cust.name); // }else{ // return false; // // } // // } //手动实现 // @Override // public String toString() { // return "Customer[name = " + name + ",age = " + age + "]"; // } //自动实现 @Override public String toString() { return "Customer [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + "]"; } }


package com.atguigu.exer2; /* * 编写Order类,有int型的orderId,String型的orderName, * 相应的getter()和setter()方法,两个参数的构造器, * 重写父类的equals()方法:public boolean equals(Object obj), * 并判断测试类中创建的两个对象是否相等。 */ public class OrderTest { public static void main(String[] args) { Order order1 = new Order(1001, "AA"); Order order2 = new Order(1001, new String("BB")); System.out.println(order1.equals(order2)); Order order3 = new Order(1001, "BB"); System.out.println(order2.equals(order3)); // String s1 = "BB"; // String s2 = "BB"; // System.out.println(s1 == s2);//true } } class Order{ private int orderId; private String orderName; public int getOrderId() { return orderId; } public void setOrderId(int orderId) { this.orderId = orderId; } public String getOrderName() { return orderName; } public void setOrderName(String orderName) { this.orderName = orderName; } public Order(int orderId, String orderName) { super(); this.orderId = orderId; this.orderName = orderName; } @Override public boolean equals(Object obj) { if(this == obj){ return true; } if(obj instanceof Order){ Order order = (Order)obj; //正确的: return this.orderId == order.orderId && this.orderName.equals(order.orderName); //错误的: // return this.orderId == order.orderId && // this.orderName == order.orderName; } return false; } }
package com.atguigu.exer2; public class MyDateTest { public static void main(String[] args) { MyDate m1 = new MyDate(14, 3, 1976); MyDate m2 = new MyDate(14, 3, 1976); if (m1 == m2) { System.out.println("m1==m2"); } else { System.out.println("m1!=m2"); // m1 != m2 } if (m1.equals(m2)) { System.out.println("m1 is equal to m2");// m1 is equal to m2 } else { System.out.println("m1 is not equal to m2"); } } } class MyDate{ private int day; private int month; private int year; public MyDate(int day, int month, int year) { super(); this.day = day; this.month = month; this.year = year; } public int getDay() { return day; } public void setDay(int day) { this.day = day; } public int getMonth() { return month; } public void setMonth(int month) { this.month = month; } public int getYear() { return year; } public void setYear(int year) { this.year = year; } @Override public boolean equals(Object obj) { if(this == obj){ return true; } if(obj instanceof MyDate){ MyDate myDate = (MyDate)obj; return this.day == myDate.day && this.month == myDate.month && this.year == myDate.year; } return false; } // @Override // public boolean equals(Object obj) { // if (this == obj) // return true; // if (obj == null) // return false; // if (getClass() != obj.getClass()) // return false; // MyDate other = (MyDate) obj; // if (day != other.day) // return false; // if (month != other.month) // return false; // if (year != other.year) // return false; // return true; // } }
package com.atguigu.java1; import java.util.Date; /* * Object类中toString()的使用: * * 1. 当我们输出一个对象的引用时,实际上就是调用当前对象的toString() * * 2. Object类中toString()的定义: * public String toString() { return getClass().getName() + "@" + Integer.toHexString(hashCode()); } * * 3. 像String、Date、File、包装类等都重写了Object类中的toString()方法。 * 使得在调用对象的toString()时,返回"实体内容"信息 * * 4. 自定义类也可以重写toString()方法,当调用此方法时,返回对象的"实体内容" */ public class ToStringTest { public static void main(String[] args) { Customer cust1 = new Customer("Tom",21); System.out.println(cust1.toString());//com.atguigu.java1.Customer@15db9742-->Customer[name = Tom,age = 21] System.out.println(cust1);//com.atguigu.java1.Customer@15db9742-->Customer[name = Tom,age = 21] String str = new String("MM"); System.out.println(str);//MM Date date = new Date(4534534534543L); System.out.println(date.toString());//Mon Sep 11 08:55:34 GMT+08:00 2113 } }
package com.atguigu.exer3; /* * 写一个测试类,创建两个Circle对象,判断其颜色是否相等; * 利用equals方法判断其半径是否相等;利用toString()方法输出其半径。 */ public class CircleTest { public static void main(String[] args) { Circle circle1 = new Circle(2.3);
// Circle circle2 = new Circle(3.3, "white", 2.0); Circle circle2 = new Circle(3.3, new String("white"), 2.0); System.out.println("颜色是否相等:" + circle1.getColor().equals(circle2.getColor())); System.out.println("半径是否相等:" + circle1.equals(circle2)); System.out.println(circle1); System.out.println(circle2.toString()); } }
package com.atguigu.exer3; public class GeometricObject { protected String color; protected double weight; public GeometricObject() { super(); this.color = "white"; this.weight = 1.0; } public GeometricObject(String color, double weight) { super(); this.color = color; this.weight = weight; } public String getColor() { return color; } public void setColor(String color) { this.color = color; } public double getWeight() { return weight; } public void setWeight(double weight) { this.weight = weight; } }
package com.atguigu.exer3; public class Circle extends GeometricObject { private double radius; public Circle() { super(); radius = 1.0; // color = "white"; //父类中已经初始化 // weight = 1.0; } public Circle(double radius) { super(); this.radius = radius; } public Circle(double radius,String color,double weight) { super(color,weight); this.radius = radius; } public double getRadius() { return radius; } public void setRadius(double radius) { this.radius = radius; } //求圆的面积 public double findArea(){ return 3.14 * radius * radius; } //比较两个圆的半径是否相等,如相等,返回true。 @Override public boolean equals(Object obj) { if(this == obj){ return true; } if(obj instanceof Circle){ Circle c = (Circle)obj; return this.radius == c.radius; } return false; } @Override public String toString() { return "Circle [radius=" + radius + "]"; } }
package com.atguigu.java2; import java.util.Date; import org.junit.Test; /* * Java中的JUnit单元测试 * * 步骤: * 1.选中当前工程 - 右键选择:build path - add libraries - JUnit 4 - 下一步 * 2.创建Java类,进行单元测试。 * 此时的Java类要求:① 此类是public的 ②此类提供公共的无参的构造器 * 3.此类中声明单元测试方法。 * 此时的单元测试方法:方法的权限是public,没有返回值,没有形参 * * 4.此单元测试方法上需要声明注解:@Test,并在单元测试类中导入:import org.junit.Test; * * 5.声明好单元测试方法以后,就可以在方法体内测试相关的代码。 * 6.写完代码以后,左键双击单元测试方法名,右键:run as - JUnit Test * * 说明: * 1.如果执行结果没有任何异常:绿条 * 2.如果执行结果出现异常:红条 */ public class JUnitTest { int num = 10; @Test public void testEquals(){ String s1 = "MM"; String s2 = "MM"; System.out.println(s1.equals(s2)); //ClassCastException的异常 // Object obj = new String("GG"); // Date date = (Date)obj; System.out.println(num); show(); } public void show(){ num = 20; System.out.println("show()...."); } @Test public void testToString(){ String s2 = "MM"; System.out.println(s2.toString()); } }

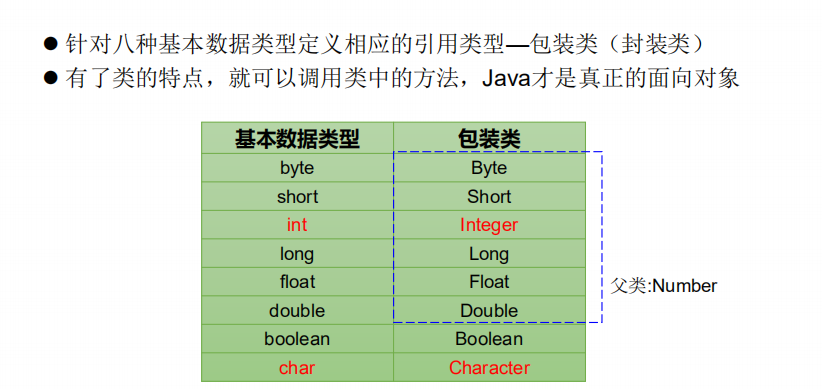


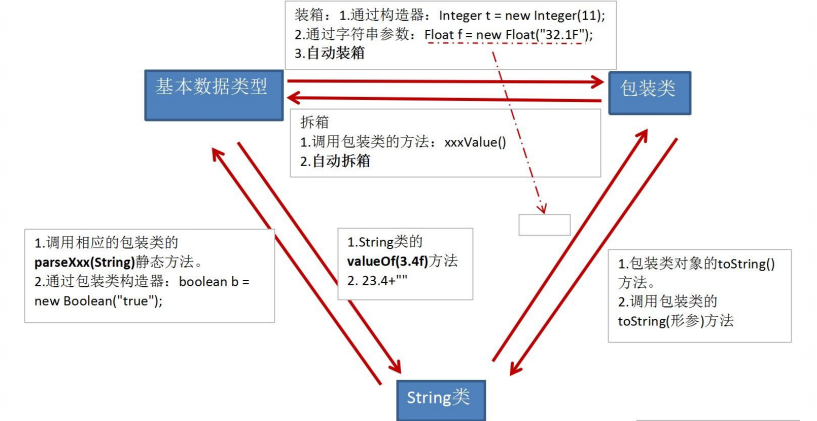
package com.atguigu.java2; import org.junit.Test; /* * 包装类的使用: * 1.java提供了8种基本数据类型对应的包装类,使得基本数据类型的变量具有类的特征 * * 2.掌握的:基本数据类型、包装类、String三者之间的相互转换 * * * */ public class WrapperTest { //String类型 --->基本数据类型、包装类:调用包装类的parseXxx(String s) @Test public void test5(){ String str1 = "123"; //错误的情况: // int num1 = (int)str1; // Integer in1 = (Integer)str1; //可能会报NumberFormatException int num2 = Integer.parseInt(str1); System.out.println(num2 + 1); String str2 = "true1"; boolean b1 = Boolean.parseBoolean(str2); System.out.println(b1); } //基本数据类型、包装类--->String类型:调用String重载的valueOf(Xxx xxx) @Test public void test4(){ int num1 = 10; //方式1:连接运算 String str1 = num1 + ""; //方式2:调用String的valueOf(Xxx xxx) float f1 = 12.3f; String str2 = String.valueOf(f1);//"12.3" Double d1 = new Double(12.4); String str3 = String.valueOf(d1); System.out.println(str2); System.out.println(str3);//"12.4" } /* * JDK 5.0 新特性:自动装箱 与自动拆箱 */ @Test public void test3(){ // int num1 = 10; // //基本数据类型-->包装类的对象 // method(num1); //自动装箱:基本数据类型 --->包装类 int num2 = 10; Integer in1 = num2;//自动装箱 boolean b1 = true; Boolean b2 = b1;//自动装箱 //自动拆箱:包装类--->基本数据类型 System.out.println(in1.toString()); int num3 = in1;//自动拆箱 } public void method(Object obj){ System.out.println(obj); } //包装类--->基本数据类型:调用包装类Xxx的xxxValue() @Test public void test2(){ Integer in1 = new Integer(12); Integer in2 = in1 + 1; int i1 = in1.intValue(); System.out.println(i1 + 1); Float f1 = new Float(12.3); float f2 = f1.floatValue(); System.out.println(f2 + 1); } //基本数据类型 --->包装类:调用包装类的构造器 @Test public void test1(){ int num1 = 10; // System.out.println(num1.toString()); Integer in1 = new Integer(num1); System.out.println(in1.toString()); Integer in2 = new Integer("123"); in2++; System.out.println(in2.toString()); //报异常 // Integer in3 = new Integer("123abc"); // System.out.println(in3.toString()); Float f1 = new Float(12.3f); Float f2 = new Float("12.3"); System.out.println(f1); System.out.println(f2); Boolean b1 = new Boolean(true); Boolean b2 = new Boolean("TrUe"); System.out.println(b2); Boolean b3 = new Boolean("true123"); System.out.println(b3);//false Order order = new Order(); System.out.println(order.isMale);//false System.out.println(order.isFemale);//null } } class Order{ boolean isMale; Boolean isFemale; }
package com.atguigu.java2; import org.junit.Test; /* * 关于包装类使用的面试题 * * */ public class InterviewTest { @Test public void test1() { Object o1 = true ? new Integer(1) : new Double(2.0); System.out.println(o1);// 1.0 } @Test public void test2() { Object o2; if (true) o2 = new Integer(1); else o2 = new Double(2.0); System.out.println(o2);// 1 } @Test public void test3() { Integer i = new Integer(1); Integer j = new Integer(1); System.out.println(i == j);//false //Integer内部定义了IntegerCache结构,IntegerCache中定义了Integer[], //保存了从-128~127范围的整数。如果我们使用自动装箱的方式,给Integer赋值的范围在 //-128~127范围内时,可以直接使用数组中的元素,不用再去new了。目的:提高效率 Integer m = 1; Integer n = 1; System.out.println(m == n);//true Integer x = 128;//相当于new了一个Integer对象 Integer y = 128;//相当于new了一个Integer对象 System.out.println(x == y);//false } }
package com.atguigu.exer4; import java.util.Scanner; import java.util.Vector; /* * 利用Vector代替数组处理:从键盘读入学生成绩(以负数代表输入结束),找出最高分,并输出学生成绩等级。 提示:数组一旦创建,长度就固定不变,所以在创建数组前就需要知道它的长度。 而向量类java.util.Vector可以根据需要动态伸缩。 创建Vector对象:Vector v=new Vector(); 给向量添加元素:v.addElement(Object obj); //obj必须是对象 取出向量中的元素:Object obj=v.elementAt(0); 注意第一个元素的下标是0,返回值是Object类型的。 计算向量的长度:v.size(); 若与最高分相差10分内:A等;20分内:B等; 30分内:C等;其它:D等 * * * * */ public class ScoreTest { public static void main(String[] args) { //1.实例化Scanner,用于从键盘获取学生成绩 Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in); //2.创建Vector对象:Vector v=new Vector();相当于原来的数组 Vector v = new Vector(); //3.通过for(;;)或while(true)方式,给Vector中添加数组 int maxScore = 0; for(;;){ System.out.println("请输入学生成绩(以负数代表输入结束)"); int score = scan.nextInt(); //3.2 当输入是负数时,跳出循环 if(score < 0){ break; } if(score > 100){ System.out.println("输入的数据非法,请重新输入"); continue; } //3.1 添加操作::v.addElement(Object obj) //jdk5.0之前: // Integer inScore = new Integer(score); // v.addElement(inScore);//多态 //jdk5.0之后: v.addElement(score);//自动装箱 //4.获取学生成绩的最大值 if(maxScore < score){ maxScore = score; } } //5.遍历Vector,得到每个学生的成绩,并与最大成绩比较,得到每个学生的等级。 char level; for(int i = 0;i < v.size();i++){ Object obj = v.elementAt(i); //jdk 5.0之前: // Integer inScore = (Integer)obj; // int score = inScore.intValue(); //jdk 5.0之后: int score = (int)obj; if(maxScore - score <= 10){ level = 'A'; }else if(maxScore - score <= 20){ level = 'B'; }else if(maxScore - score <= 30){ level = 'C'; }else{ level = 'D'; } System.out.println("student-" + i + " score is " + score + ",level is " + level); } } }
请你一定不要停下来 成为你想成为的人
感谢您的阅读,我是LXL


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号