实验九异常、断言与日志
实验时间 2018-10-25
第一部分:理论部分
1.异常:在程序的执行过程中所发生的异常事件,它中断指令的正常执行。
Java的异常处理机制可以控制程序从错误产生的位置转移到能够进行错误处理的位置。
程序中出现的常见的错误和问题有:用户输入错误;设备错误;物理限制;代码错误。
Java把程序运行时可能遇到的错误分为两类:非致命异常:通过某种修正后程序还能继续执行。这类错误叫作异常。如:文件不存在、无效的数组下标、空引用、网络断开、打印机脱机、磁盘满等。 Java中提供了一种独特的处理异常的机制,通过异常来处理程序设计中出现的错误。致命异常:程序遇到了非常严重的不正常状态,不能简单恢复执行,是致命性错误。如:内存耗尽、系统内部错误等。这种错误程序本身无法解决。
2.Java中的异常类可分为两大类: Error :Error类层次结构描述了Java 运行时系统的内部错误和资源耗尽错误。应用程序不应该捕获这类异常,也不会抛出这种异常 。 Exception类: Exception层次结构又分解为两个分支:一个分支派生于 RuntimeException;另一个分支包含其他异常。3.RuntimeException为运行时异常类,一般是程序错误产生。派生于RuntimeException的异常包含下面几种情况:错误的类型转换;数组访问越界;访问空指针。
4.将派生于Error类或RuntimeException类的所有异常称为未检查异常,编译器允许不对它们做出异常处理。 注意:“如果出现RuntimeException异常,就一定是程序员的问题!!!”
5.非运行时异常,程序本身没有问题,但由于某种情况的变化,程序不能正常运行,导致异常出现。除了运行时异常之外的其它继承自Exception类的异常类包括:试图在文件尾部后面读取数据;试图打开一个错误格式的URL。 编译器要求程序必须对这类异常进行处理 (checked),称为已检查异常
6. RuntimeException运行时异常类:ArithmeticException: 算术异常类;ArrayStoreException: 数组存储异常类;ClassCastException: 类型强制转换异常类;IndexOutOfBoundsException: 下标越界异常类;NullPointerException: 空指针异常类;SecurityException: 违背安全原则异常类。
7.IOException:输入输出异常类:IOException:申请I/O操作没有正常完成。EOFException:在输入操作正常结束前遇见了文件结束符。FileNotFountException:在文件系统中,没有找到由文件名字符串指定的文件。
8.声明抛出异常:如果一个方法可能会生成一些异常,但是该方法并不确切知道如何对这些异常事件进行处理,此时,这个方法就需声明抛出这些异常。“一个方法不仅需要告诉编译器将要返回什么值,还要告诉编译器可能发生什么异常。”
9.声明抛出异常在方法声明中用throws子句中来指明。例如:public FileInputStream(String name ) throws FileNotFoundException
10。以下4种情况需要方法用throws子句声明抛出异常:1、方法调用了一个抛出已检查异常的方法。程序运行过程中可能会发生错误,并且利用throw语句抛出一个已检查异常对象。 3、程序出现错误。例如,a[-1] = 0/4、Java虚拟机和运行时库出现的内部异常。
11.一个方法必须声明该方法所有可能抛出的已检查异常,而未检查异常要么不可控制(Error),要么应该避免发生(RuntimeException)。如果方法没有声明所有可能发生的已检查异常,编译器会给出一个错误消息。当Java应用程序出现错误时,会根据错误类型产生一个异常对象,这个对象包含了异常的类型和错误出现时程序所处的状态信息。把异常对象递交给Java编译器的过程称为抛出。抛出异常要生成异常对象,异常对象可由某些类的实例生成,也可以由JVM生成。抛出异常对象通过throw语句来实现。
12.如何抛出异常:首先决定抛出异常类型。例如:当从一个长为 1024的文件中读取数据时,但读到733时遇到了文件结束标记,此时应抛出一个异常,EOFException比较合适。代码为:throw new EOFException(); 或者: EOFException e= new EOFException(); throw e;
13.对于已存在的异常类,抛出该类的异常对象非常容易,步骤是:找到一个合适的异常类;创建这个类的一个对象;将该对象抛出。一个方法抛出了异常后,它就不能返回调用者了。
14.创建异常类:自定义异常类:定义一个派生于Exception的直接或间接子类。如一个派生于IOException的类。自定义的异常类应该包括两个构造器:默认构造器;带有详细描述信息的构造器(超类Throwable的toString方法会打印出这些详细信息,有利于代码调程序运行期间,异常发生时,Java运行系统从异常生成的代码块开始,寻找相应的异常处理代码,并将异常交给该方法处理,这一过程叫作捕获。某个异常发生时,若程序没有在任何地方进行该异常的捕获,则程序就会终止执行,并在控制台上输出异常信息。若要捕获一个异常,需要在程序中设置一个try/catch/ finally块: try语句括住可能抛出异常的代码段。catch语句指明要捕获的异常及相应的处理代码。finally语句指明必须执行的程序
catch子句:catch块是对异常对象进行处理的代码;每个try代码块可以伴随一个或多个catch语句,用于处理 try代码块中所生成的各类异常事件;catch语句只需要一个形式参数指明它所能捕获的异常类对象,这个异常类必须是Throwable的子类,运行时系统通过参数值把被抛出的异常对象传递给catch块;catch块可以通过异常对象调用类Throwable所提供的方法。getMessage()用来得到有关异常事件的信息;printStackTrace()用来跟踪异常事件发生时执行堆栈的内容。
1、实验目的与要求
(1) 掌握java异常处理技术;
(2) 了解断言的用法;
(3) 了解日志的用途;
(4) 掌握程序基础调试技巧;
2、实验内容和步骤
实验1:用命令行与IDE两种环境下编辑调试运行源程序ExceptionDemo1、ExceptionDemo2,结合程序运行结果理解程序,掌握未检查异常和已检查异常的区别。
|
//异常示例1 public class ExceptionDemo1 { public static void main(String args[]) { int a = 0; System.out.println(5 / a); } } |
|
//异常示例2 import java.io.*;
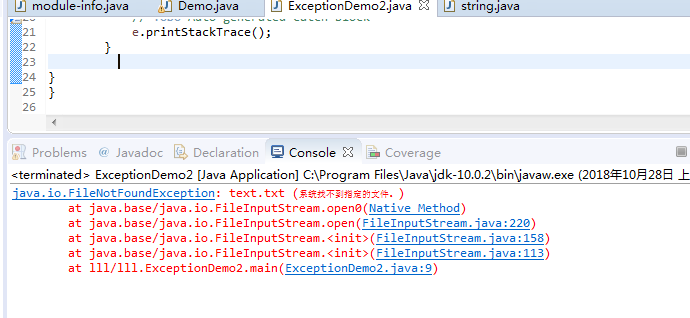
public class ExceptionDemo2 { public static void main(String args[]) { FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream("text.txt");//JVM自动生成异常对象 int b; while((b=fis.read())!=-1) { System.out.print(b); } fis.close(); } } |
1 //异常示例1 2 public class ExceptionDemo1 { 3 public static void main(String args[]) { 4 int a = 0; 5 System.out.println(5 / a); 6 } 7 }
做出异常判断
1 package t; 2 public class ExceptionDemo1 { 3 public static void main(String args[]) { 4 int a = 0; 5 if(a==0){ 6 System.out.println("中断!"); 7 } 8 else{ 9 System.out.println(5 / a); 10 } 11 } 12 }
1 //异常示例2 2 import java.io.*; 3 4 public class ExceptionDemo2 { 5 public static void main(String args[]) 6 { 7 FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream("text.txt");//JVM自动生成异常对象 8 int b; 9 while((b=fis.read())!=-1) 10 { 11 System.out.print(b); 12 } 13 fis.close(); 14 } 15 }
做出处理
1 import java.io.*; 2 3 public class ExceptionDemo2 { 4 public static void main(String args[]) { 5 FileInputStream fis; 6 try { 7 fis = new FileInputStream("text.txt"); 8 // JVM自动生成异常对象 9 int b; 10 while ((b = fis.read()) != -1) { 11 System.out.print(b); 12 } 13 fis.close(); 14 } catch (Exception e) { 15 // TODO 自动生成的 catch 块 16 e.printStackTrace(); 17 } 18 } 19 }
实验2: 导入以下示例程序,测试程序并进行代码注释。
测试程序1:
l 在elipse IDE中编辑、编译、调试运行教材281页7-1,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
l 在程序中相关代码处添加新知识的注释;
l 掌握Throwable类的堆栈跟踪方法;
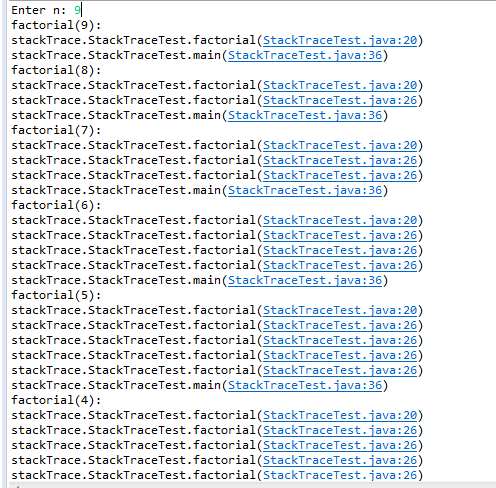
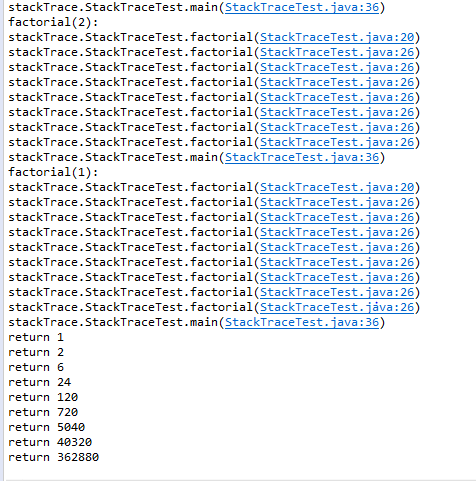
1 package stackTrace; 2 3 import java.util.*; 4 5 /** 6 * A program that displays a trace feature of a recursive method call. 7 * @version 1.01 2004-05-10 8 * @author Cay Horstmann 9 */ 10 public class StackTraceTest 11 { 12 /** 13 * Computes the factorial of a number 14 * @param n a non-negative integer 15 * @return n! = 1 * 2 * . . . * n 16 */ 17 public static int factorial(int n) 18 { 19 System.out.println("factorial(" + n + "):"); 20 Throwable t = new Throwable();//生成Throwable类对象 21 StackTraceElement[] frames = t.getStackTrace(); 22 //使用getStackTrace方法得到 StackTraceElement对象的一个数组 23 for (StackTraceElement f : frames) 24 System.out.println(f); 25 int r; 26 if (n <= 1) r = 1; 27 else r = n * factorial(n - 1); 28 System.out.println("return " + r); 29 return r; 30 } 31 32 public static void main(String[] args) 33 { 34 Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); 35 System.out.print("Enter n: "); 36 int n = in.nextInt();//读取下一行的内容 37 factorial(n); 38 } 39 }
测试程序2:
l Java语言的异常处理有积极处理方法和消极处理两种方式;
l 下列两个简答程序范例给出了两种异常处理的代码格式。在elipse IDE中编辑、调试运行源程序ExceptionalTest.java,将程序中的text文件更换为身份证号.txt,要求将文件内容读入内容,并在控制台显示;
l 掌握两种异常处理技术的特点。
|
//积极处理方式 import java.io.*;
class ExceptionTest { public static void main (string args[]) { try{ FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream("text.txt"); } catch(FileNotFoundExcption e) { …… } …… } } |
|
//消极处理方式
import java.io.*; class ExceptionTest { public static void main (string args[]) throws FileNotFoundExcption { FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream("text.txt"); } } |
1 //积极处理 2 import java.io.*; 3 class ExceptionDemo1 { 4 public static void main (String args[]) 5 { 6 File fis=new File("身份证号.txt"); 7 try{ 8 9 10 FileReader fr = new FileReader(fis); 11 BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(fr); 12 try { 13 String s, s2 = new String(); 14 while ((s = br.readLine()) != null) { 15 s2 += s + "\n "; 16 } 17 br.close(); 18 System.out.println(s2); 19 } catch (IOException e) { 20 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 21 e.printStackTrace(); 22 } 23 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { 24 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 25 e.printStackTrace(); 26 } 27 28 } 29 }
1 //消极处理方式 2 3 import java.io.*; 4 class ExceptionDemo1 { 5 public static void main (String args[]) throws IOException 6 { 7 File fis=new File("身份证号.txt"); 8 FileReader fr = new FileReader(fis); 9 BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(fr); 10 String s, s2 = new String(); 11 12 while ((s = br.readLine()) != null) { 13 s2 += s + "\n "; 14 } 15 br.close(); 16 System.out.println(s2); 17 } 18 }
实验3: 编程练习
练习1:
l 编制一个程序,将身份证号.txt 中的信息读入到内存中;
l 按姓名字典序输出人员信息;
l 查询最大年龄的人员信息;
l 查询最小年龄人员信息;
l 输入你的年龄,查询身份证号.txt中年龄与你最近人的姓名、身份证号、年龄、性别和出生地;
l 查询人员中是否有你的同乡;
l 在以上程序适当位置加入异常捕获代码。
1 import java.io.BufferedReader; 2 import java.io.File; 3 import java.io.FileInputStream; 4 import java.io.FileNotFoundException; 5 import java.io.IOException; 6 import java.io.InputStreamReader; 7 import java.util.ArrayList; 8 import java.util.Arrays; 9 import java.util.Collections; 10 import java.util.Scanner; 11 12 13 public class Test{ 14 15 private static ArrayList<Person> Personlist1; 16 public static void main(String[] args) { 17 18 Personlist1 = new ArrayList<>(); 19 20 Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); 21 File file = new File("C:\\Users\\lenovo\\Documents\\身份证"); 22 23 try { 24 FileInputStream F = new FileInputStream(file); 25 BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(F)); 26 String temp = null; 27 while ((temp = in.readLine()) != null) { 28 29 Scanner linescanner = new Scanner(temp); 30 31 linescanner.useDelimiter(" "); 32 String name = linescanner.next(); 33 String id = linescanner.next(); 34 String sex = linescanner.next(); 35 String age = linescanner.next(); 36 String place =linescanner.nextLine(); 37 Person Person = new Person(); 38 Person.setname(name); 39 Person.setid(id); 40 Person.setsex(sex); 41 int a = Integer.parseInt(age); 42 Person.setage(a); 43 Person.setbirthplace(place); 44 Personlist1.add(Person); 45 46 } 47 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { 48 System.out.println("查找不到信息"); 49 e.printStackTrace(); 50 } catch (IOException e) { 51 System.out.println("信息读取有误"); 52 e.printStackTrace(); 53 } 54 boolean isTrue = true; 55 while (isTrue) { 56 System.out.println("1:按姓名字典序输出人员信息;"); 57 System.out.println("2:查询最大年龄与最小年龄人员信息;"); 58 System.out.println("3.输入你的年龄,查询身份证号.txt中年龄与你最近人的姓名、身份证号、年龄、性别和出生地"); 59 System.out.println("4:按省份找你的同乡;"); 60 System.out.println("5:退出"); 61 int type = scanner.nextInt(); 62 switch (type) { 63 case 1: 64 Collections.sort(Personlist1); 65 System.out.println(Personlist1.toString()); 66 break; 67 case 2: 68 69 int max=0,min=100;int j,k1 = 0,k2=0; 70 for(int i=1;i<Personlist1.size();i++) 71 { 72 j=Personlist1.get(i).getage(); 73 if(j>max) 74 { 75 max=j; 76 k1=i; 77 } 78 if(j<min) 79 { 80 min=j; 81 k2=i; 82 } 83 84 } 85 System.out.println("年龄最大:"+Personlist1.get(k1)); 86 System.out.println("年龄最小:"+Personlist1.get(k2)); 87 break; 88 case 3: 89 System.out.println("place?"); 90 String find = scanner.next(); 91 String place=find.substring(0,3); 92 String place2=find.substring(0,3); 93 for (int i = 0; i <Personlist1.size(); i++) 94 { 95 if(Personlist1.get(i).getbirthplace().substring(1,4).equals(place)) 96 { 97 System.out.println("你的同乡:"+Personlist1.get(i)); 98 } 99 } 100 101 break; 102 case 4: 103 System.out.println("年龄:"); 104 int yourage = scanner.nextInt(); 105 int close=ageclose(yourage); 106 int d_value=yourage-Personlist1.get(close).getage(); 107 System.out.println(""+Personlist1.get(close)); 108 109 break; 110 case 5: 111 isTrue = false; 112 System.out.println("再见!"); 113 break; 114 default: 115 System.out.println("输入有误"); 116 } 117 } 118 } 119 public static int ageclose(int age) { 120 int m=0; 121 int max=53; 122 int d_value=0; 123 int k=0; 124 for (int i = 0; i < Personlist1.size(); i++) 125 { 126 d_value=Personlist1.get(i).getage()-age; 127 if(d_value<0) d_value=-d_value; 128 if (d_value<max) 129 { 130 max=d_value; 131 k=i; 132 } 133 134 } return k; 135 136 } 137 } 138
1 public class Person implements Comparable<Person> { 2 private String name; 3 private String id; 4 private int age; 5 private String sex; 6 private String birthplace; 7 8 public String getname() { 9 return name; 10 } 11 public void setname(String name) { 12 this.name = name; 13 } 14 public String getid() { 15 return id; 16 } 17 public void setid(String id) { 18 this.id= id; 19 } 20 public int getage() { 21 22 return age; 23 } 24 public void setage(int age) { 25 // int a = Integer.parseInt(age); 26 this.age= age; 27 } 28 public String getsex() { 29 return sex; 30 } 31 public void setsex(String sex) { 32 this.sex= sex; 33 } 34 public String getbirthplace() { 35 return birthplace; 36 } 37 public void setbirthplace(String birthplace) { 38 this.birthplace= birthplace; 39 } 40 41 public int compareTo(Person o) { 42 return this.name.compareTo(o.getname()); 43 44 } 45 46 public String toString() { 47 return name+"\t"+sex+"\t"+age+"\t"+id+"\t"; 48 49 }
注:以下实验课后完成
练习2:
l 编写一个计算器类,可以完成加、减、乘、除的操作;
l 利用计算机类,设计一个小学生100以内数的四则运算练习程序,由计算机随机产生10道加减乘除练习题,学生输
入答案,由程序检查答案是否正确,每道题正确计10分,错误不计分,10道题测试结束后给出测试总分;
l 将程序中测试练习题及学生答题结果输出到文件,文件名为test.txt;
l 在以上程序适当位置加入异常捕获代码。
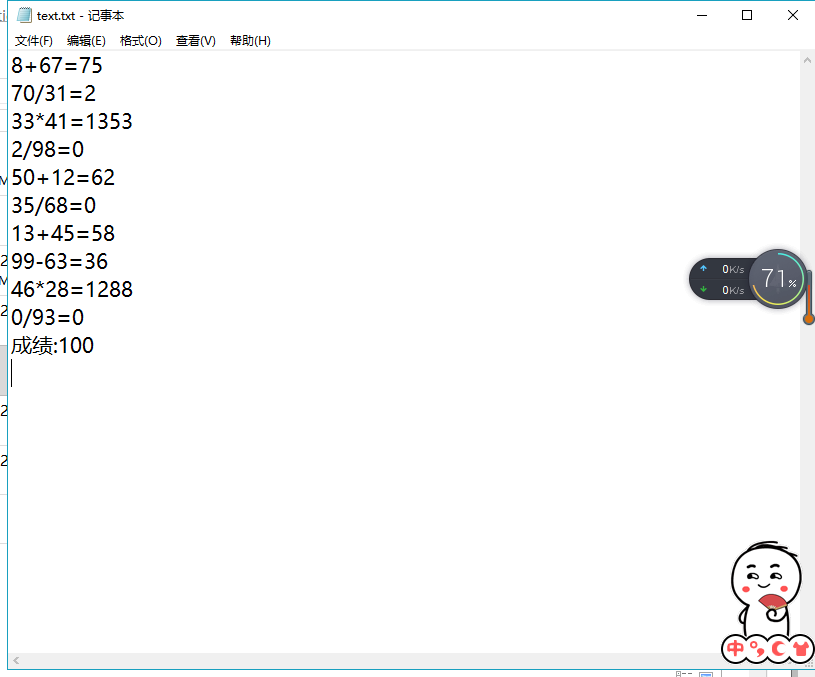
1 import java.util.Scanner; 2 import java.io.FileNotFoundException; 3 import java.io.PrintWriter; 4 import java.util.Random; 5 6 public class Demo { 7 public static void main(String[] args) { 8 9 Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); 10 Number counter = new Number(); 11 PrintWriter out = null; 12 try { 13 out = new PrintWriter("text.txt"); 14 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { 15 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 16 e.printStackTrace(); 17 } 18 int sum = 0; 19 20 for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) { 21 22 int a = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100); 23 int b = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100); 24 int m = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 3); 25 Random n = new Random(); 26 27 switch (m) { 28 case 0: 29 System.out.println(i + ": " + a + "/" + b + "="); 30 31 while (b == 0) { 32 b = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100); 33 } 34 35 int c = in.nextInt(); 36 out.println(a + "/" + b + "=" + c); 37 if (c == counter.division(a, b)) { 38 sum += 10; 39 System.out.println("恭喜答案正确"); 40 } else { 41 System.out.println("抱歉,答案错误"); 42 } 43 44 break; 45 46 case 1: 47 System.out.println(i + ": " + a + "*" + b + "="); 48 int c1 = in.nextInt(); 49 out.println(a + "*" + b + "=" + c1); 50 if (c1 == counter.multiplication(a, b)) { 51 sum += 10; 52 System.out.println("恭喜答案正确"); 53 } else { 54 System.out.println("抱歉,答案错误"); 55 } 56 break; 57 case 2: 58 System.out.println(i + ": " + a + "+" + b + "="); 59 int c2 = in.nextInt(); 60 out.println(a + "+" + b + "=" + c2); 61 if (c2 == counter.add(a, b)) { 62 sum += 10; 63 System.out.println("恭喜答案正确"); 64 } else { 65 System.out.println("抱歉,答案错误"); 66 } 67 68 break; 69 case 3: 70 System.out.println(i + ": " + a + "-" + b + "="); 71 int c3 = in.nextInt(); 72 out.println(a + "-" + b + "=" + c3); 73 if (c3 == counter.reduce(a, b)) { 74 sum += 10; 75 System.out.println("恭喜答案正确"); 76 } else { 77 System.out.println("抱歉,答案错误"); 78 } 79 break; 80 81 } 82 83 } 84 System.out.println("成绩" + sum); 85 out.println("成绩:" + sum); 86 out.close(); 87 88 } 89 } 90
1 public class Number { 2 private int a; 3 private int b; 4 5 public int add(int a, int b) { 6 return a + b; 7 } 8 9 public int reduce(int a, int b) { 10 return a - b; 11 } 12 13 public int multiplication(int a, int b) { 14 return a * b; 15 } 16 17 public int division(int a, int b) { 18 if (b != 0) 19 return a / b; 20 else 21 return 0; 22 } 23 24 }

实验4:断言、日志、程序调试技巧验证实验。
实验程序1:
l 在elipse下调试程序AssertDemo,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
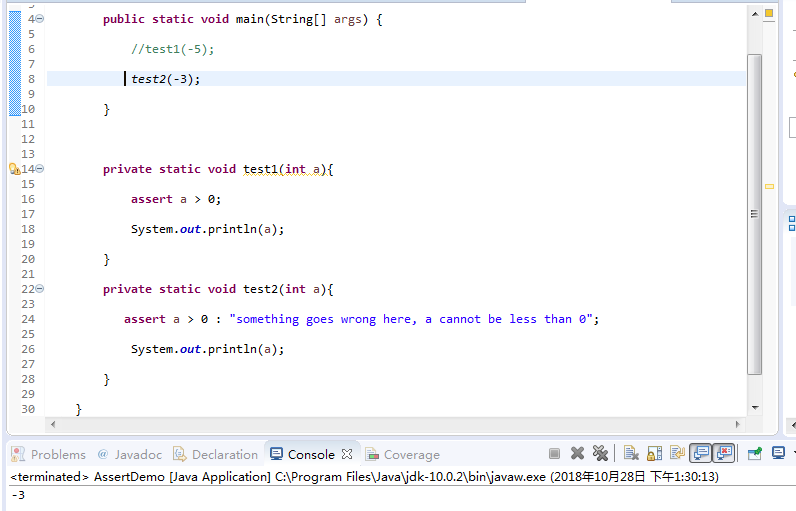
l 注释语句test1(-5);后重新运行程序,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
l 掌握断言的使用特点及用法。
|
//断言程序示例 public class AssertDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { test1(-5); test2(-3); }
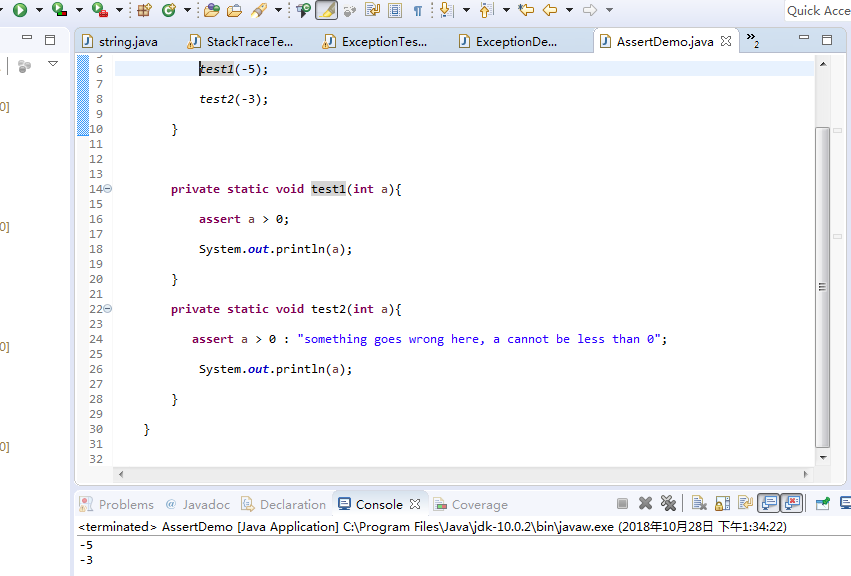
private static void test1(int a){ assert a > 0; System.out.println(a); } private static void test2(int a){ assert a > 0 : "something goes wrong here, a cannot be less than 0"; System.out.println(a); } } |
1 public class AssertDemo { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 test1(-5); 4 test2(-3); 5 } 6 7 private static void test1(int a){ 8 assert a > 0;//assert宏的原型定义在<assert.h>中,作用是如果它的条件返回错误,则终止程序执行 9 System.out.println(a); 10 } 11 private static void test2(int a){ 12 assert a > 0 : "这里出错了,a不能小于0"; 13 System.out.println(a); 14 } 15 }
注释前结果
1 public class AssertDemo { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 // test1(-5); 4 test2(-3); 5 } 6 7 private static void test1(int a){ 8 assert a > 0;//assert宏的原型定义在<assert.h>中,作用是如果它的条件返回错误,则终止程序执行 9 System.out.println(a); 10 } 11 private static void test2(int a){ 12 assert a > 0 : "这里出错了,a不能小于0"; 13 System.out.println(a); 14 } 15 }
注释后结果
实验程序2:
l 用JDK命令调试运行教材298页-300页程序7-2,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
l 并掌握Java日志系统的用途及用法。
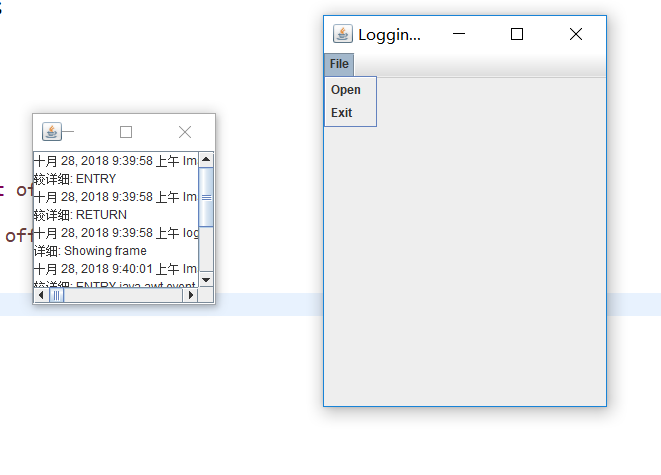
1 import java.awt.*; 2 import java.awt.event.*; 3 import java.io.*; 4 import java.util.logging.*; 5 import javax.swing.*; 6 7 /** 8 * A modification of the image viewer program that logs various events. 9 * @version 1.03 2015-08-20 10 * @author Cay Horstmann 11 */ 12 public class LoggingImageViewer 13 { 14 public static void main(String[] args) 15 { 16 //将所有消息记录到应用程序特定的文件中 17 if (System.getProperty("java.util.logging.config.class") == null 18 && System.getProperty("java.util.logging.config.file") == null) 19 { 20 try//放入可能出错的语句 21 { 22 Logger.getLogger("com.horstmann.corejava").setLevel(Level.ALL);//得到日志记录器 23 final int LOG_ROTATION_COUNT = 10; 24 Handler handler = new FileHandler("%h/LoggingImageViewer.log", 0, LOG_ROTATION_COUNT); 25 Logger.getLogger("com.horstmann.corejava").addHandler(handler); 26 } 27 catch (IOException e) 28 { 29 Logger.getLogger("com.horstmann.corejava").log(Level.SEVERE, 30 "Can't create log file handler", e); 31 } 32 } 33 34 EventQueue.invokeLater(() ->//使事件派发线程上的可运行对象排队 35 { 36 Handler windowHandler = new WindowHandler(); 37 windowHandler.setLevel(Level.ALL); 38 Logger.getLogger("com.horstmann.corejava").addHandler(windowHandler); 39 40 JFrame frame = new ImageViewerFrame(); 41 frame.setTitle("LoggingImageViewer"); 42 frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); 43 44 Logger.getLogger("com.horstmann.corejava").fine("Showing frame"); 45 frame.setVisible(true); 46 }); 47 } 48 } 49 50 /** 51 * 显示图像的帧。 52 */ 53 class ImageViewerFrame extends JFrame 54 { 55 private static final int DEFAULT_WIDTH = 300; 56 private static final int DEFAULT_HEIGHT = 400; 57 58 private JLabel label; 59 private static Logger logger = Logger.getLogger("com.horstmann.corejava"); 60 61 public ImageViewerFrame() 62 { 63 logger.entering("ImageViewerFrame", "<init>"); 64 setSize(DEFAULT_WIDTH, DEFAULT_HEIGHT); 65 66 //设置菜单栏 67 JMenuBar menuBar = new JMenuBar(); 68 setJMenuBar(menuBar); 69 70 JMenu menu = new JMenu("File"); 71 menuBar.add(menu); 72 73 JMenuItem openItem = new JMenuItem("Open"); 74 menu.add(openItem); 75 openItem.addActionListener(new FileOpenListener()); 76 77 JMenuItem exitItem = new JMenuItem("Exit"); 78 menu.add(exitItem); 79 exitItem.addActionListener(new ActionListener() 80 { 81 public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent event) 82 { 83 logger.fine("Exiting."); 84 System.exit(0); 85 } 86 }); 87 88 //使用标签显示图像 89 label = new JLabel(); 90 add(label); 91 logger.exiting("ImageViewerFrame", "<init>"); 92 } 93 94 private class FileOpenListener implements ActionListener 95 { 96 public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent event) 97 { 98 logger.entering("ImageViewerFrame.FileOpenListener", "actionPerformed", event); 99 100 //设置文件选择器 101 JFileChooser chooser = new JFileChooser(); 102 chooser.setCurrentDirectory(new File(".")); 103 104 //接受以.gif结尾的所有文件 105 chooser.setFileFilter(new javax.swing.filechooser.FileFilter() 106 { 107 public boolean accept(File f) 108 { 109 return f.getName().toLowerCase().endsWith(".gif") || f.isDirectory(); 110 } 111 112 public String getDescription() 113 { 114 return "GIF Images"; 115 } 116 }); 117 118 //显示文件选择器对话框 119 int r = chooser.showOpenDialog(ImageViewerFrame.this); 120 121 // 如果图像文件被接受,将其设置为标签的图标 122 if (r == JFileChooser.APPROVE_OPTION) 123 { 124 String name = chooser.getSelectedFile().getPath(); 125 logger.log(Level.FINE, "Reading file {0}", name); 126 label.setIcon(new ImageIcon(name)); 127 } 128 else logger.fine("File open dialog canceled."); 129 logger.exiting("ImageViewerFrame.FileOpenListener", "actionPerformed"); 130 } 131 } 132 } 133 134 /** 135 * 用于在窗口中显示日志记录的处理程序。 136 */ 137 class WindowHandler extends StreamHandler//继承 138 { 139 private JFrame frame; 140 141 public WindowHandler() 142 { 143 frame = new JFrame(); 144 final JTextArea output = new JTextArea(); 145 output.setEditable(false); 146 frame.setSize(200, 200); 147 frame.add(new JScrollPane(output)); 148 frame.setFocusableWindowState(false); 149 frame.setVisible(true); 150 setOutputStream(new OutputStream() 151 { 152 public void write(int b) 153 { 154 } 155 156 public void write(byte[] b, int off, int len) 157 { 158 output.append(new String(b, off, len)); 159 } 160 }); 161 } 162 163 public void publish(LogRecord record) 164 { 165 if (!frame.isVisible()) return; 166 super.publish(record); 167 flush(); 168 } 169 }
实验结果
实验程序3:
l 用JDK命令调试运行教材298页-300页程序7-2,结合程序运行结果理解程序;,
l 按课件66-77内容练习并掌握Elipse的常用调试技术。
1 import java.awt.*; 2 import java.awt.event.*; 3 import java.io.*; 4 import java.util.logging.*; 5 import javax.swing.*; 6 7 /** 8 * A modification of the image viewer program that logs various events. 9 * @version 1.03 2015-08-20 10 * @author Cay Horstmann 11 */ 12 public class LoggingImageViewer 13 { 14 public static void main(String[] args) 15 { 16 //将所有消息记录到应用程序特定的文件中 17 if (System.getProperty("java.util.logging.config.class") == null 18 && System.getProperty("java.util.logging.config.file") == null) 19 { 20 try//放入可能出错的语句 21 { 22 Logger.getLogger("com.horstmann.corejava").setLevel(Level.ALL);//得到日志记录器 23 final int LOG_ROTATION_COUNT = 10; 24 Handler handler = new FileHandler("%h/LoggingImageViewer.log", 0, LOG_ROTATION_COUNT); 25 Logger.getLogger("com.horstmann.corejava").addHandler(handler); 26 } 27 catch (IOException e) 28 { 29 Logger.getLogger("com.horstmann.corejava").log(Level.SEVERE, 30 "Can't create log file handler", e); 31 } 32 } 33 34 EventQueue.invokeLater(() ->//使事件派发线程上的可运行对象排队 35 { 36 Handler windowHandler = new WindowHandler(); 37 windowHandler.setLevel(Level.ALL); 38 Logger.getLogger("com.horstmann.corejava").addHandler(windowHandler); 39 40 JFrame frame = new ImageViewerFrame(); 41 frame.setTitle("LoggingImageViewer"); 42 frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); 43 44 Logger.getLogger("com.horstmann.corejava").fine("Showing frame"); 45 frame.setVisible(true); 46 }); 47 } 48 } 49 50 /** 51 * 显示图像的帧。 52 */ 53 class ImageViewerFrame extends JFrame 54 { 55 private static final int DEFAULT_WIDTH = 300; 56 private static final int DEFAULT_HEIGHT = 400; 57 58 private JLabel label; 59 private static Logger logger = Logger.getLogger("com.horstmann.corejava"); 60 61 public ImageViewerFrame() 62 { 63 logger.entering("ImageViewerFrame", "<init>"); 64 setSize(DEFAULT_WIDTH, DEFAULT_HEIGHT); 65 66 //设置菜单栏 67 JMenuBar menuBar = new JMenuBar(); 68 setJMenuBar(menuBar); 69 70 JMenu menu = new JMenu("File"); 71 menuBar.add(menu); 72 73 JMenuItem openItem = new JMenuItem("Open"); 74 menu.add(openItem); 75 openItem.addActionListener(new FileOpenListener()); 76 77 JMenuItem exitItem = new JMenuItem("Exit"); 78 menu.add(exitItem); 79 exitItem.addActionListener(new ActionListener() 80 { 81 public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent event) 82 { 83 logger.fine("Exiting."); 84 System.exit(0); 85 } 86 }); 87 88 //使用标签显示图像 89 label = new JLabel(); 90 add(label); 91 logger.exiting("ImageViewerFrame", "<init>"); 92 } 93 94 private class FileOpenListener implements ActionListener 95 { 96 public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent event) 97 { 98 logger.entering("ImageViewerFrame.FileOpenListener", "actionPerformed", event); 99 100 //设置文件选择器 101 JFileChooser chooser = new JFileChooser(); 102 chooser.setCurrentDirectory(new File(".")); 103 104 //接受以.gif结尾的所有文件 105 chooser.setFileFilter(new javax.swing.filechooser.FileFilter() 106 { 107 public boolean accept(File f) 108 { 109 return f.getName().toLowerCase().endsWith(".gif") || f.isDirectory(); 110 } 111 112 public String getDescription() 113 { 114 return "GIF Images"; 115 } 116 }); 117 118 //显示文件选择器对话框 119 int r = chooser.showOpenDialog(ImageViewerFrame.this); 120 121 // 如果图像文件被接受,将其设置为标签的图标 122 if (r == JFileChooser.APPROVE_OPTION) 123 { 124 String name = chooser.getSelectedFile().getPath(); 125 logger.log(Level.FINE, "Reading file {0}", name); 126 label.setIcon(new ImageIcon(name)); 127 } 128 else logger.fine("File open dialog canceled."); 129 logger.exiting("ImageViewerFrame.FileOpenListener", "actionPerformed"); 130 } 131 } 132 } 133 134 /** 135 * 用于在窗口中显示日志记录的处理程序。 136 */ 137 class WindowHandler extends StreamHandler//继承 138 { 139 private JFrame frame; 140 141 public WindowHandler() 142 { 143 frame = new JFrame(); 144 final JTextArea output = new JTextArea(); 145 output.setEditable(false); 146 frame.setSize(200, 200); 147 frame.add(new JScrollPane(output)); 148 frame.setFocusableWindowState(false); 149 frame.setVisible(true); 150 setOutputStream(new OutputStream() 151 { 152 public void write(int b) 153 { 154 } // not called 155 156 public void write(byte[] b, int off, int len) 157 { 158 output.append(new String(b, off, len)); 159 } 160 }); 161 } 162 163 public void publish(LogRecord record) 164 { 165 if (!frame.isVisible()) return; 166 super.publish(record); 167 flush(); 168 } 169 }
1)条件断点(有一定条件的断点):在Eclipse Java 编辑区的行头双击就会得到一个断点,代码会运行到此处时停止。
在断点处点击鼠标右键,选择最后一个“Breakpoint Properties”。
2)变量断点:在变量的值初始化,或是变量值改变时可以停止。
3)方法断点:方法断点就是将断点打在方法的入口处。
4)异常断点:当异常发生时,代码会停在异常发生处。
5)重新调试:回退时,请在需要回退的线程方法上点右键,选择“Drop to Frame”。
6)单步执行程序
7)检查变量
8)改变变量值
实验总结:
1.异常
所有异常类型都是 Throwable 类的子类,它包含Exception类和Error类,Exception又包括checked exception和unchecked exception。
unchecked exception:Java编译器不要求对未检查异常一定捕获或抛出,可以不做处理。此类异常通常是在逻辑上有错误,可以通过修改代码避免。在eclipse中(保存即编译)编译后此类异常发生处会报错。
checked exception:Java编译器要求对检查异常必须捕获或抛出,代码逻辑没有错误,但程序运行时会因为IO等错误导致异常,你在编写程序阶段是预料不到的。如果不处理这些异常,程序将来肯定会出错。所以编译器会提示你要去捕获并处理这种可能发生的异常,不处理就不能通过编译。
2.Throwable类的堆栈信息跟踪。
堆栈跟踪是一个方法调用过程的立标,它包含了程序执行过程中方法的调用的特定位置。可以使用Throwable的接口获取堆栈信息,进行分析调用情况。
3.断言
assert。在程序开发过程中使用它创建一个断言(assertion),它的
语法形式有如下所示的两种形式:
1、assert condition;
这里condition是一个必须为真(true)的表达式。如果表达式的结果为true,那么断言为真,并且无任何行动
如果表达式为false,则断言失败,则会抛出一个AssertionError对象。这个AssertionError继承于Error对象,
而Error继承于Throwable,Error是和Exception并列的一个错误对象,通常用于表达系统级运行错误。
2、asser condition:expr;
这里condition是和上面一样的,这个冒号后跟的是一个表达式,通常用于断言失败后的提示信息,说白了,它是一个传到AssertionError构造函数的值,如果断言失败,该值被转化为它对应的字符串,并显示出来。
3.在本周学习了程序产生的异常以及如何解决程序中产生的异常。异常时在程序的执行过程中所发生的非正常事件,它中断指令的正常执行。因此在编写代码时需要及时处理这些错误。基本理解了异常的产生的原因和解决方法。但对于断言以及日志等内容不太理解。因此在运行后面几个相关程序时,对程序不是很理解。以后自己也会多练习程序去了解这些知识。






