二叉树二刷
今天先整理二叉树,dijkstra和链表二刷过几天有空会整理
首先二叉树的几个性质就不说了,其中一个我认为比较好用的是满足二叉树连通,边数等于顶点数-1的结构就一定是一棵树
这次二刷的新的收获是分辨*root=NULL与root=NULL的不同之处,首先*root=NULL是不合法的
因为*root=NULL的含义是获取地址root指向的空间的内容,但无法说明root是否为空
相当于节点不存在和节点存在但是没有内容的区别
并且对于层序遍历中为什么是queue<node*>q而不是node型,队列保存的是原元素的一个副本,因此如果队列直接存放了node型,当需要修改队首元素时,就无法对原元素进行修改(只修改了副本)
然后是根据先序,中序确定一棵树或者是后序中序确定一棵树
先序,中序:
1 node *build_tree(int prel,int prer,int inl,int inr) 2 { 3 if(prel>prer) 4 { 5 return NULL; 6 } 7 node *root=new node(pre[prel]); 8 int k; 9 for(k=inl;k<=inr;k++) 10 { 11 if(in[k]==pre[prel]) 12 { 13 break; 14 } 15 } 16 int numleft=k-inl; 17 root->l=build_tree(prel+1,prel+numleft,inl,k-1);//从先序的第二个节点开始是左子树的左边 18 root->r=build_tree(prel+numleft+1,prer,k+1,inr); 19 return root; 20 }
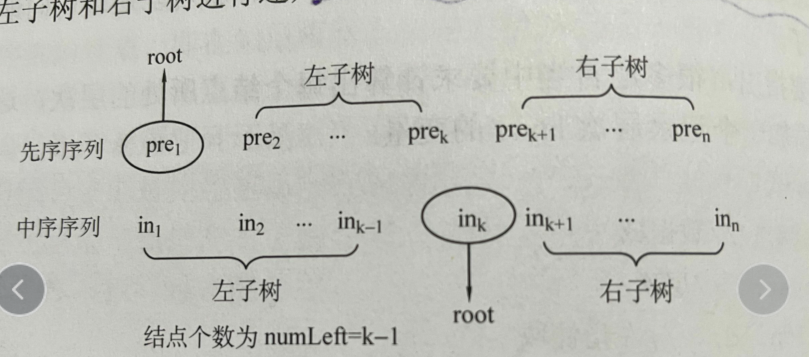
后序中序确定一棵树:
1 node *build_tree(int postl,int postr,int inl,int inr) 2 { 3 if(postl>postr) 4 { 5 return NULL; 6 } 7 node *root=new node; 8 root->data=post[postr]; 9 int k; 10 for(k=inl;k<=inr;k++) 11 { 12 if(in[k]==post[postr]) 13 { 14 break; 15 } 16 } 17 int numleft=k-inl; 18 root->l=build_tree(postl,postl+numleft-1,inl,k-1); 19 root->r=build_tree(postl+numleft,postr-1,k+1,inr); 20 return root; 21 22 }
解释一下:后序序列的最后一个元素是根节点,所以说需要在中序中找k,在求左子树的个数
然后左子树的后序序列区间是[postl,postl+numleft-1]
右子树的后序序列区间是[postl+numleft,postr-1]
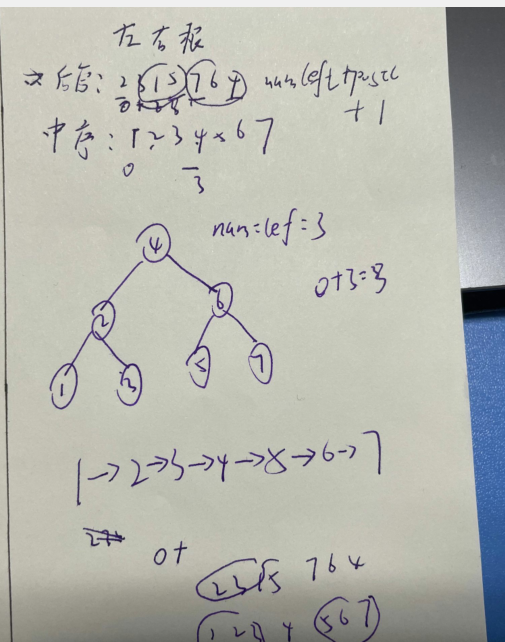
一些二刷的题目:
1020:https://pintia.cn/problem-sets/994805342720868352/exam/problems/994805485033603072
1 //基本的根据中序和后序确定一颗树的题 2 //需要注意的几个点 3 //后序和中序的左右子树的位置要确定好 4 //numleft=k-inl的原因是找到了根节点以后往左的节点都是左子树,所以说个数为k-inl 5 //因为是从0开始的,所以说左子树的右边界是postl_numledt-1,如果从1开始可+1,自己画画图就懂了 6 #include<bits/stdc++.h> 7 using namespace std; 8 #define int long long 9 #define IOS ios_base::sync_with_stdio(0);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0); 10 const int N=40; 11 vector<int>level; 12 int n; 13 struct node 14 { 15 int data; 16 node *l; 17 node *r; 18 node(int data=0,node *l=NULL,node *r=NULL):data(data),l(l),r(r){} 19 }; 20 int post[N]; 21 int in[N]; 22 node *build_tree(int postl,int postr,int inl,int inr) 23 { 24 if(postl>postr) 25 { 26 return NULL; 27 } 28 node *root=new node; 29 root->data=post[postr]; 30 int k; 31 for(k=inl;k<=inr;k++) 32 { 33 if(in[k]==post[postr]) 34 { 35 break; 36 } 37 } 38 int numleft=k-inl; 39 root->l=build_tree(postl,postl+numleft-1,inl,k-1); 40 root->r=build_tree(postl+numleft,postr-1,k+1,inr); 41 return root; 42 43 } 44 void bfs(node *&root) 45 { 46 queue<node*>q; 47 q.push(root); 48 while(!q.empty()) 49 { 50 root=q.front(); 51 q.pop(); 52 level.push_back(root->data); 53 if(root->l!=NULL) 54 { 55 q.push(root->l); 56 } 57 if(root->r!=NULL) 58 { 59 q.push(root->r); 60 } 61 } 62 } 63 signed main() 64 { 65 IOS; 66 cin>>n; 67 for(int i=0;i<n;i++) 68 { 69 cin>>post[i]; 70 } 71 for(int i=0;i<n;i++) 72 { 73 cin>>in[i]; 74 } 75 node *root=build_tree(0,n-1,0,n-1); 76 bfs(root); 77 for(int i=0;i<level.size();i++) 78 { 79 cout<<level[i]; 80 if(i<level.size()-1) 81 cout<<" "; 82 } 83 return 0; 84 }
1102:https://pintia.cn/problem-sets/994805342720868352/exam/problems/994805365537882112
1 //题目的意思就是求交换左右子树的二叉树之后求他的层序和中序序列即可 2 //几个注意的点 3 //找根的方式是找一个没有父亲的节点,即他不是任何节点的孩子,所以这里用标记数组解决 4 //交换左右子树这里采用的后序交换,其实前序交换也是可以的,但是前序交换后就是访问左子树的时候其实扫的是右子树 5 //右子树同理,不符合根->左->右的遍历方式了,但效果是同后序交换一样的 6 //由于输入的特殊性,所以用cin.get()或者getchar()来吸收空格 7 //采用二叉树的静态表示法,下标即地址 8 #include<bits/stdc++.h> 9 using namespace std; 10 #define int long long 11 #define IOS ios_base::sync_with_stdio(0);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0); 12 const int N=50; 13 struct node 14 { 15 int data; 16 int l; 17 int r; 18 node(int data=0,int l=0,int r=0):data(data),l(l),r(r){} 19 }t[N]; 20 int n; 21 vector<int>le,in; 22 bool vis[N]; 23 int findchild(char c) 24 { 25 if(c=='-') 26 return -1; 27 else 28 { 29 vis[c-'0']=true; 30 return (c-'0'); 31 } 32 } 33 int findroot() 34 { 35 for(int i=0;i<n;i++) 36 { 37 if(!vis[i]) 38 { 39 return i; 40 } 41 } 42 } 43 void bfs(int root) 44 { 45 queue<int>q; 46 q.push(root); 47 while(!q.empty()) 48 { 49 int tmp=q.front(); 50 q.pop(); 51 le.push_back(tmp); 52 if(t[tmp].l!=-1) 53 { 54 q.push(t[tmp].l); 55 } 56 if(t[tmp].r!=-1) 57 q.push(t[tmp].r); 58 } 59 } 60 void inorder(int root) 61 { 62 if(root!=-1) 63 { 64 inorder(t[root].l); 65 in.push_back(root); 66 inorder(t[root].r); 67 68 } 69 } 70 void swapchild(int root) 71 { 72 if(root!=-1) 73 { 74 swapchild(t[root].l); 75 swapchild(t[root].r); 76 swap(t[root].l,t[root].r); 77 } 78 } 79 signed main() 80 { 81 IOS; 82 cin>>n; 83 char lc,rc; 84 for(int i=0;i<n;i++) 85 { 86 cin.get(); 87 cin>>lc>>rc; 88 t[i].l=findchild(lc); 89 t[i].r=findchild(rc); 90 } 91 int root=0; 92 root=findroot(); 93 swapchild(root); 94 bfs(root); 95 inorder(root); 96 for(int i=0;i<le.size();i++) 97 { 98 cout<<le[i]; 99 if(i<le.size()-1) 100 { 101 cout<<" "; 102 } 103 } 104 cout<<endl; 105 for(int i=0;i<in.size();i++) 106 { 107 cout<<in[i]; 108 if(i<in.size()-1) 109 { 110 cout<<" "; 111 } 112 } 113 return 0; 114 }
1086:https://pintia.cn/problem-sets/994805342720868352/exam/problems/994805380754817024
1 //还是日常根据前序和中序建一颗二叉树求后序 2 //需要注意的点 3 //这里用栈模拟了树的建立,其实对于树和栈而言,栈的入栈其实就是先序遍历如数组,出栈就是中序遍历如数组 4 #include<bits/stdc++.h> 5 using namespace std; 6 #define int long long 7 #define IOS ios_base::sync_with_stdio(0); 8 const int N=40; 9 struct node 10 { 11 int data; 12 node *l; 13 node *r; 14 node(int data=0,node *l=NULL,node *r=NULL):data(data),l(l),r(r){} 15 }; 16 vector<int>pre,in,post; 17 int n; 18 stack<int>q; 19 node *build_tree(int prel,int prer,int inl,int inr) 20 { 21 if(prel>prer) 22 { 23 return NULL; 24 } 25 node *root=new node(pre[prel]); 26 int k; 27 for(k=inl;k<=inr;k++) 28 { 29 if(in[k]==pre[prel]) 30 { 31 break; 32 } 33 } 34 int numleft=k-inl; 35 root->l=build_tree(prel+1,prel+numleft,inl,k-1);//从先序的第二个节点开始是左子树的左边 36 root->r=build_tree(prel+numleft+1,prer,k+1,inr); 37 return root; 38 } 39 void postorder(node *&root) 40 { 41 if(root!=NULL) 42 { 43 postorder(root->l); 44 postorder(root->r); 45 post.push_back(root->data); 46 } 47 } 48 signed main() 49 { 50 IOS; 51 cin>>n; 52 string s; 53 int tmp; 54 for(int i=0;i<2*n;i++) 55 { 56 cin>>s; 57 if(s=="Push") 58 { 59 cin>>tmp; 60 pre.push_back(tmp); 61 q.push(tmp); 62 } 63 else{ 64 in.push_back(q.top()); 65 q.pop(); 66 } 67 } 68 node *root=build_tree(0,n-1,0,n-1); 69 postorder(root); 70 for(int i=0;i<post.size();i++){ 71 cout<<post[i]; 72 if(i<post.size()-1) 73 cout<<" "; 74 } 75 return 0; 76 }
1138:https://pintia.cn/problem-sets/994805342720868352/exam/problems/994805345078067200
1 //没啥技术含量,输出后序的第一个即可 2 #include<bits/stdc++.h> 3 using namespace std; 4 #define int long long 5 #define IOS ios_base::sync_with_stdio(0);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0); 6 const int N=5e4+10; 7 int pre[N]; 8 int in[N]; 9 int n; 10 vector<int>post; 11 struct node 12 { 13 int data; 14 node *l; 15 node *r; 16 node(int data=0,node *l=NULL,node *r=NULL):data(data),l(l),r(r){} 17 }; 18 node *build_tree(int prel,int prer,int inl,int inr) 19 { 20 if(prel>prer) 21 return NULL; 22 node *root=new node(pre[prel]); 23 int k; 24 for(k=inl;k<=inr;k++) 25 { 26 if(in[k]==pre[prel]) 27 break; 28 } 29 int numleft=k-inl; 30 root->l=build_tree(prel+1,prel+numleft,inl,k-1); 31 root->r=build_tree(prel+numleft+1,prer,k+1,inr); 32 return root; 33 } 34 void postorder(node *&root) 35 { 36 if(root!=NULL) 37 { 38 postorder(root->l); 39 postorder(root->r); 40 post.push_back(root->data); 41 } 42 } 43 signed main() 44 { 45 IOS; 46 cin>>n; 47 for(int i=0;i<n;i++) 48 { 49 cin>>pre[i]; 50 } 51 for(int i=0;i<n;i++) 52 { 53 cin>>in[i]; 54 } 55 node *root=build_tree(0,n-1,0,n-1); 56 postorder(root); 57 /*for(int i=0;i<post.size();i++) 58 { 59 cout<<post[i]; 60 if(i<post.size()-1) 61 cout<<" "; 62 }*/ 63 cout<<post[0]; 64 return 0; 65 }
1027:https://pintia.cn/problem-sets/994805342720868352/exam/problems/994805349394006016
1 //比较难做的树类题 2 //其中思想是很清晰的,就是根据后中序来确定层序,并且层序的输出是一个Z形的输出 3 //根据后中序确定一棵树就不说了,来说一说这里不同的bfs 4 //根据题意要设置一个lay来表示深度,设初始深度为1,且每深入一层就加一层,并且在深入中不断去求最大深度 5 //对于如何储存层序序列,可以设一个二维数组,第一维度来表示深度,第二维度表示序列是几 6 //之后根据奇偶性质来输出层序序列 7 //代码较为繁琐,但思路其实是很清晰的 8 #include<bits/stdc++.h> 9 using namespace std; 10 #define int long long 11 #define IOS ios_base::sync_with_stdio(0);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0); 12 const int N=40; 13 struct node 14 { 15 int data; 16 node *r; 17 node *l; 18 int lay; 19 node(int data=0,node *l=NULL,node *r=NULL,int lay=1):data(data),l(l),r(r),lay(lay){} 20 }; 21 int n; 22 int in[N]; 23 int post[N]; 24 vector<int>le[N]; 25 int cnt; 26 int max_level=INT_MIN; 27 node *build_tree(int postl,int postr,int inl,int inr) 28 { 29 if(postl>postr) 30 { 31 return NULL; 32 } 33 node *root=new node; 34 root->data=post[postr]; 35 int k; 36 for(k=inl;k<=inr;k++) 37 { 38 if(in[k]==post[postr]) 39 { 40 break; 41 } 42 } 43 int numleft=k-inl; 44 root->l=build_tree(postl,postl+numleft-1,inl,k-1); 45 root->r=build_tree(postl+numleft,postr-1,k+1,inr); 46 return root; 47 48 } 49 void bfs(node *&root) 50 { 51 queue<node*>q; 52 q.push(root); 53 root->lay=1; 54 while(!q.empty()) 55 { 56 node *tmp=q.front(); 57 q.pop(); 58 le[tmp->lay].push_back(tmp->data); 59 if(tmp->lay>max_level) 60 max_level=tmp->lay; 61 if(tmp->l!=NULL) 62 { 63 tmp->l->lay=tmp->lay+1; 64 q.push(tmp->l); 65 } 66 if(tmp->r!=NULL) 67 { 68 tmp->r->lay=tmp->lay+1; 69 q.push(tmp->r); 70 } 71 } 72 } 73 signed main() 74 { 75 IOS; 76 cin>>n; 77 for(int i=0;i<n;i++) 78 { 79 cin>>in[i]; 80 } 81 for(int i=0;i<n;i++) 82 { 83 cin>>post[i]; 84 } 85 node *root=build_tree(0,n-1,0,n-1); 86 bfs(root); 87 for(int i=1;i<=max_level;i++) 88 { 89 if(i&1) 90 { 91 for(int j=le[i].size()-1;j>=0;j--) 92 { 93 cout<<le[i][j]; 94 cnt++; 95 if(cnt<n) 96 cout<<" "; 97 } 98 } 99 else 100 { 101 for(int j=0;j<le[i].size();j++) 102 { 103 cout<<le[i][j]; 104 cnt++; 105 if(cnt<n) 106 cout<<" "; 107 } 108 } 109 } 110 return 0; 111 } 112
1151:https://pintia.cn/problem-sets/994805342720868352/exam/problems/1038430130011897856
没做出来
总结:
单考二叉树的考点是考建树和输出序列,但很显然,一般树的问题还是综合性的,结合其他考点比如镜像树或者是树的遍历
所以说树的遍历和bst树可以进行二刷
本文来自博客园,作者:江上舟摇,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/LQS-blog/p/16904850.html


