binary tree+tree order
二叉树的前中序确定后序:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1710
二叉树的后中序确定层序:https://pintia.cn/problem-sets/994805342720868352/problems/994805485033603072
二叉树的前中序确定后序变形:https://pintia.cn/problem-sets/994805342720868352/problems/994805380754817024
二叉树反转:https://pintia.cn/problem-sets/994805342720868352/problems/994805365537882112
二叉树遍历dfs:https://pintia.cn/problem-sets/994805342720868352/problems/994805388447170560
二叉树遍历dfs:https://pintia.cn/problem-sets/994805342720868352/problems/994805376476626944
二叉树遍历dfs:https://pintia.cn/problem-sets/994805342720868352/problems/994805362341822464
二叉树遍历bfs:https://pintia.cn/problem-sets/994805342720868352/problems/994805372601090048
1.二叉树中前序确定后序:
其实这个已经说过了,为了加深一下印象又做了一次;
前中序确定后序其实还是很简单的,
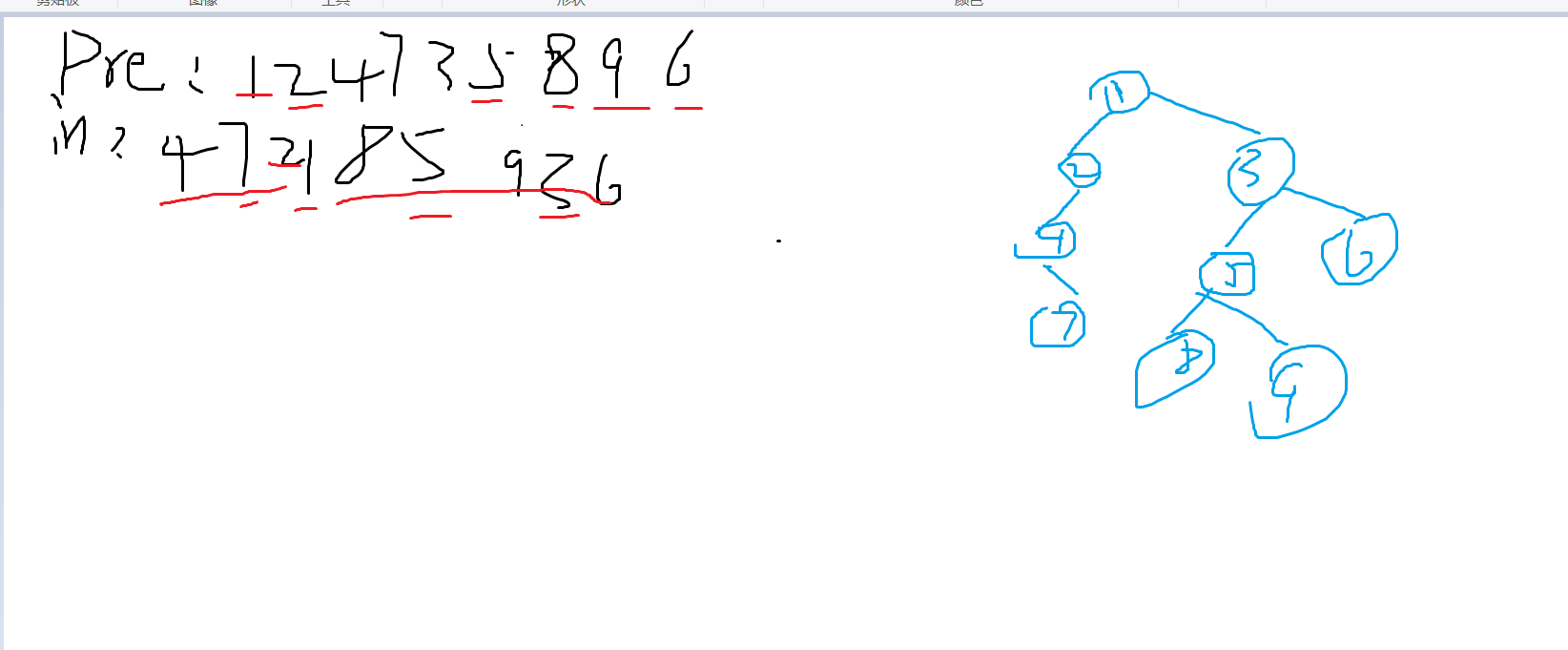
和上图所化差不多,从先序序列开始,依次在中序序列中找到相应位置,相应位置的左边就是左子树,右边是右子树,挨个遍历,直到把先序序列遍历完或者是把二叉树建树完成就可以了
而本题所说的是根据先序序列和中序序列确定后序序列,这样在进行一次后序遍历就可以了;
参考代码如下
// Problem: Binary Tree Traversals // Contest: HDOJ // URL: http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1710 // Memory Limit: 32 MB // Time Limit: 1000 ms // // Powered by CP Editor (https://cpeditor.org) #include<bits/stdc++.h>//hudoj 1710 using namespace std; #define int long long #define IOS ios_base::sync_with_stdio(0);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0); const int N=1010; int k;//统计个数 int n; int pre[N];//前序序列 int in[N];//中序序列 int post[N];//后序序列 struct node { int value; node *L; node *R; node(int value=0,node *L=NULL,node *R=NULL):value(value),L(L),R(R) {} //初始化 }; void buildtree(int L,int R,int &t,node * &root) { //建树,左子树,右子树,前序序列值的推进,根节点 int flag=-1; for(register int i=L; i<=R; i++) { if(in[i]==pre[t]) { //找到了线序序列的位置 flag=i;//对应中序序列的位置 break; } } if(flag==-1)//没有就返回 return ; root=new node(in[flag]);//新建子根节点 if(flag>L) { //如果是在左子树上,那中序序列遍历的根节点左边在左子树上 buildtree(L,flag-1,++t,root->L); } if(flag<R) { //如果是在右子树上,那中序序列遍历的根据二点右边在柚子树上,右子树需从i+1进行计数 buildtree(flag+1,R,++t,root->R); } } void preorder(node *root) { //前序遍历 if(root!=NULL) { post[k++]=root->value; preorder(root->L); preorder(root->R); } } void inorder(node *root) { //中序遍历 if(root!=NULL) { inorder(root->L); post[k++]=root->value; inorder(root->R); } } void postorder(node *root) { //后序遍历 if(root!=NULL) { postorder(root->L); postorder(root->R); post[k++]=root->value; } } void remove_tree(node *root) { //删除节点释放空间 if(root==NULL) return ; remove_tree(root->L); remove_tree(root->R); delete root; } signed main() { IOS; while(cin>>n) { for(register int i=1; i<=n; i++) cin>>pre[i]; for(register int i=1; i<=n; i++) cin>>in[i]; int t=1;//同步前序序列,确定根节点 node *root; buildtree(1,n,t,root);//建树 k=0; postorder(root);//后序遍历 for(register int i=0; i<k; i++) { printf("%d%c",post[i],i==k-1?'\n':' ');//输出 } remove_tree(root);//释放空间 } return 0; }
2.根据后序和中序序列确定层序序列
这道题和上面那道题的不同之处在于建树的过程
因为如果按照上面建树过程的话其实你会发现给定的两个序列到了一定深度就会return ,而得到的层序序列是4,2,5,因为这个结果我试验过,并且手动debug了一下就是会在某个数字造成return而建树会被构造成一个单支树
怎么建树是本题的关键;
可以这样想:
后序序列的最后一个元素将会是根节点
所以我们在建树的时候要让根节点的键值等于后序序列的右边界
然后很常规的查找在中序序列中哪个是后序序列的右边界的元素的下标;
7
2 3 1 5 7 6 4
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
比如这组样例,下标为4的中序序列和后序序列的右边界相等,标为flag
那么他左子树的数量就是num=flag-inl(inl代表中序序列的左边界)
那遍历左子树的时候就可以这样写了(postl,postl+num-1,inl,flag-1)//后序左边界,后序右边界,中序左边界,中序右边界
遍历右子树的时候就可以(postl+num,postr-1,flag+1,inr)//后序左边界,后序右边界,中序左边界,中序右边界
和上面那道题不一样的建树过程是return 的条件变了,变成了当后序序列推进完成的时候就结束了
还有就是建树方式变成了由后序边界和中序边界共同确定的建树算法
上面的是只有中序边界和正序推进先序序列
但思想上的基本规则还是不变的,可以和上面那道题进行对比;
参考代码:
1 #include<bits/stdc++.h> 2 using namespace std; 3 #define int long long 4 #define IOS ios_base::sync_with_stdio(0);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0); 5 const int N=100; 6 int n; 7 int k; 8 struct node 9 { 10 int value; 11 node *l; 12 node *r; 13 node(int value=0,node *l=NULL,node *r=NULL):value(value),l(l),r(r){} 14 }; 15 int post[N]; 16 int in[N]; 17 node *buildtree(int postl,int postr,int inl,int inr) 18 { 19 if(postr-postl<0) 20 return NULL; 21 node *root=new node(post[postr]); 22 int flag=-1; 23 for(int i=inl;i<=inr;i++) 24 { 25 if(in[i]==post[postr]) 26 { 27 flag=i; 28 break; 29 } 30 } 31 int numl=flag-inl; 32 root->l=buildtree(postl,postl+numl-1,inl,flag-1); 33 root->r=buildtree(postl+numl,postr-1,flag+1,inr); 34 return root; 35 36 } 37 void bfs(node *root) 38 { 39 queue<node *>q; 40 q.push(root); 41 while(!q.empty()) 42 { 43 node *newnode=q.front(); 44 q.pop(); 45 cout<<newnode->value; 46 k++; 47 if(k<n) 48 cout<<" "; 49 if(newnode->l!=NULL) 50 q.push(newnode->l); 51 if(newnode->r!=NULL) 52 q.push(newnode->r); 53 } 54 } 55 signed main() 56 { 57 IOS; 58 cin>>n; 59 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) 60 cin>>post[i]; 61 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) 62 cin>>in[i]; 63 node *root=buildtree(1,n,1,n); 64 bfs(root); 65 return 0; 66 }
其实这道题更为详细的解释在这篇博客中也写过了其实:https://www.cnblogs.com/LQS-blog/p/16174901.html
再做一遍加深印象
3.
是这类题的变形
题目给的并不是常规的先序序列和中序序列;
它给的是一组数据的入栈和出站,其实也不难理解,入栈的顺序其实就是先序序列的遍历顺序,而出站的顺序就是中序序列的遍历顺序,这个其实在数据结构课上讲过了,非递归形式的四种遍历方式
无论是我的数据结构恩师还是mooc姥姥的讲解我觉得已经够清楚了,不明白的可以去mooc看一下姥姥对于这节课的讲解哦
回归正题,既然确定了中序和先序序列,那题目就变得和第一题一样了,前提是用栈处理好先序序列和中序序列
其余倒是和第一题没什么太大区别了
参考代码:
1 #include<bits/stdc++.h> 2 using namespace std; 3 #define int long long 4 #define IOS ios_base::sync_with_stdio(0);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0); 5 const int N=100; 6 int pre[N]; 7 int post[N]; 8 int in[N]; 9 int n; 10 int cnt1=1; 11 int cnt2=1; 12 int k; 13 stack<int>q; 14 struct node 15 { 16 int value; 17 node *l; 18 node *r; 19 node(int value=0,node *l=NULL,node *r=NULL):value(value),l(l),r(r){} 20 }; 21 void buildtree(int l,int r,int &t,node *&root) 22 { 23 int flag=-1; 24 for(int i=l;i<=r;i++) 25 { 26 if(in[i]==pre[t]) 27 { 28 flag=i; 29 break; 30 } 31 } 32 if(flag==-1) 33 return ; 34 root=new node(in[flag]); 35 t++; 36 if(flag>l) 37 buildtree(l,flag-1,t,root->l); 38 if(flag<r) 39 buildtree(flag+1,r,t,root->r); 40 } 41 void postorder(node *root) 42 { 43 if(root!=NULL) 44 { 45 postorder(root->l); 46 postorder(root->r); 47 post[k++]=root->value; 48 } 49 } 50 signed main() 51 { 52 IOS; 53 char ch[10]; 54 int num; 55 cin>>n; 56 for(int i=1;i<=2*n;i++) 57 { 58 cin>>ch; 59 if(strcmp(ch,"Push")==0) 60 { 61 cin>>num; 62 pre[cnt1++]=num; 63 q.push(num); 64 } 65 else 66 { 67 in[cnt2++]=q.top(); 68 q.pop(); 69 } 70 } 71 int t=1; 72 node *root; 73 buildtree(1,n,t,root); 74 postorder(root); 75 for(int i=0;i<k;i++) 76 { 77 cout<<post[i]; 78 if(i<k-1) 79 cout<<" "; 80 } 81 /* for(int i=1;i<=cnt1;i++) 82 cout<<pre[i]<<" "; 83 cout<<endl; 84 for(int i=1;i<=cnt2;i++) 85 cout<<in[i]<<" ";*/ 86 return 0; 87 }
4.二叉树反转
这道题是一道什么样的题呢?
题目是这样讲的:给定二叉树的节点数量
输入n行
从0~n-1进行节点标号
如果存在左或者右孩子就输入数字,没有就输入‘-’
问确定层序序列和中序序列
思路其实可以先不看输入的,因为你看输入不怎么容易确定这颗树是怎样的
可以先看输出
输出给定的当然是层序序列和中序序列
根据层序序列和中序序列确定这颗二叉树的大体模样
3 7 2 6 4 0 5 1
6 5 7 4 3 2 0 1、
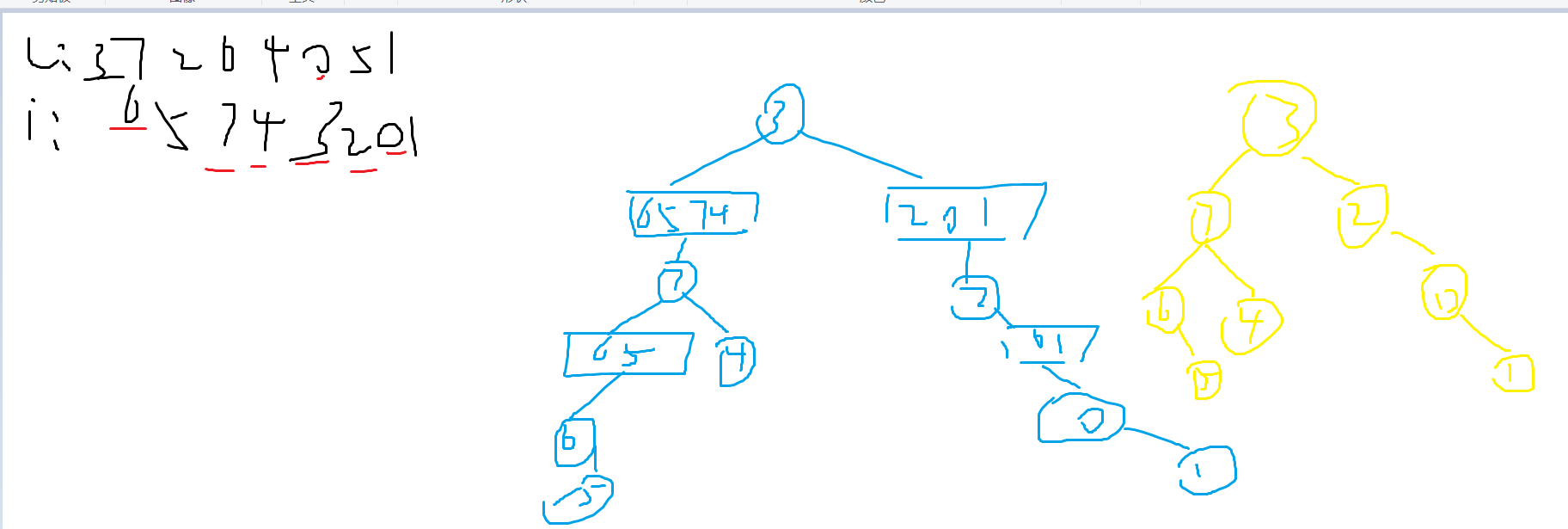
根据层序序列在中序序列中不断找到根节点直到把树构造出来就可以了
剩下的问题是确定根节点和反转二叉树
第一、如何确定根节点,我们可以用标记数组标记
输入的时候,如果是数字的话就标记,如果是‘-’return -1,最后遍历一下数组找没被标记的就是根节点了
第二、如何反转二叉树,我们可以后序遍历交换
为什么不用先序序列交换?因为先序序列上来就把左右子树交换,所以访问左子树的时候实际上访问的是右子树,这样是不符合根-左-右的先序遍历方式的,当然,在效果上和后序交换还是一样的,但这样不遵循先序的规则了
其余的遍历方式还是一样的
参考代码:
1 #include<bits/stdc++.h>//1102 2 using namespace std; 3 #define int long long 4 #define IOS ios_base::sync_with_stdio(0);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0); 5 const int N=20; 6 struct node 7 { 8 //int key; 9 int l; 10 int r; 11 node(int l=0,int r=0):l(l),r(r){} 12 }t[N]; 13 int n; 14 bool vis[N];//标记数组 15 int cnt1; 16 int cnt2; 17 void bfs(int root) 18 { 19 queue<int>q; 20 q.push(root); 21 while(!q.empty()) 22 { 23 int f=q.front(); 24 q.pop(); 25 cout<<f; 26 cnt1++; 27 if(cnt1<n) 28 cout<<" "; 29 if(t[f].l!=-1) 30 q.push(t[f].l); 31 if(t[f].r!=-1) 32 q.push(t[f].r); 33 } 34 cout<<endl; 35 } 36 void inorder(int root) 37 { 38 if(root!=-1) 39 { 40 inorder(t[root].l); 41 cout<<root; 42 cnt2++; 43 if(cnt2<n) 44 cout<<" "; 45 inorder(t[root].r); 46 } 47 } 48 int findroot()//找到根节点 49 { 50 for(int i=0;i<n;i++) 51 { 52 if(!vis[i]) 53 { 54 return i; 55 } 56 } 57 } 58 int findnochild(char c )//找没有孩子的节点,其实是为了找根节点做准备 59 { 60 if(c=='-') 61 return -1; 62 else 63 { 64 vis[c-'0']=true; 65 return (c-'0'); 66 } 67 } 68 void swchild(int root)//后序遍历置换 69 { 70 if(root!=-1) 71 { 72 swchild(t[root].l); 73 swchild(t[root].r); 74 swap(t[root].l,t[root].r); 75 } 76 } 77 signed main() 78 { 79 IOS; 80 cin>>n; 81 for(int i=0;i<n;i++) 82 { 83 char lc,rc; 84 cin.get(); 85 cin>>lc>>rc; 86 t[i].l=findnochild(lc); 87 t[i].r=findnochild(rc); 88 } 89 int root=0; 90 root=findroot(); 91 swchild(root); 92 bfs(root); 93 inorder(root); 94 return 0; 95 }
----------------------------------------------------------------------------2022-8-11 22:24
今天就早休息了,明天在把剩下的几道题更一下//分割线
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
------------------------------------------------------------更新分割线。。。。2022-8-12 4:25
1090:https://pintia.cn/problem-sets/994805342720868352/problems/994805376476626944
题目大意是这样的:一条供应链上存在多个供应商和被供应商,其中,第二个供应商从首个供应商那里得到原始售价,并且随着每一层的供应关系的递增,价格随之递增%r,求做大售价和达到最大售价的节点个数
题目给定了节点个数和原始售价p,递增价格%r,然后给定n个元素,并且当某元素为-1的时这个元素的下标是根节点,而每个所代表的值是他们的父节点
9 1.80 1.00
1 5 4 4 -1 4 5 3 6
可以这样解释:
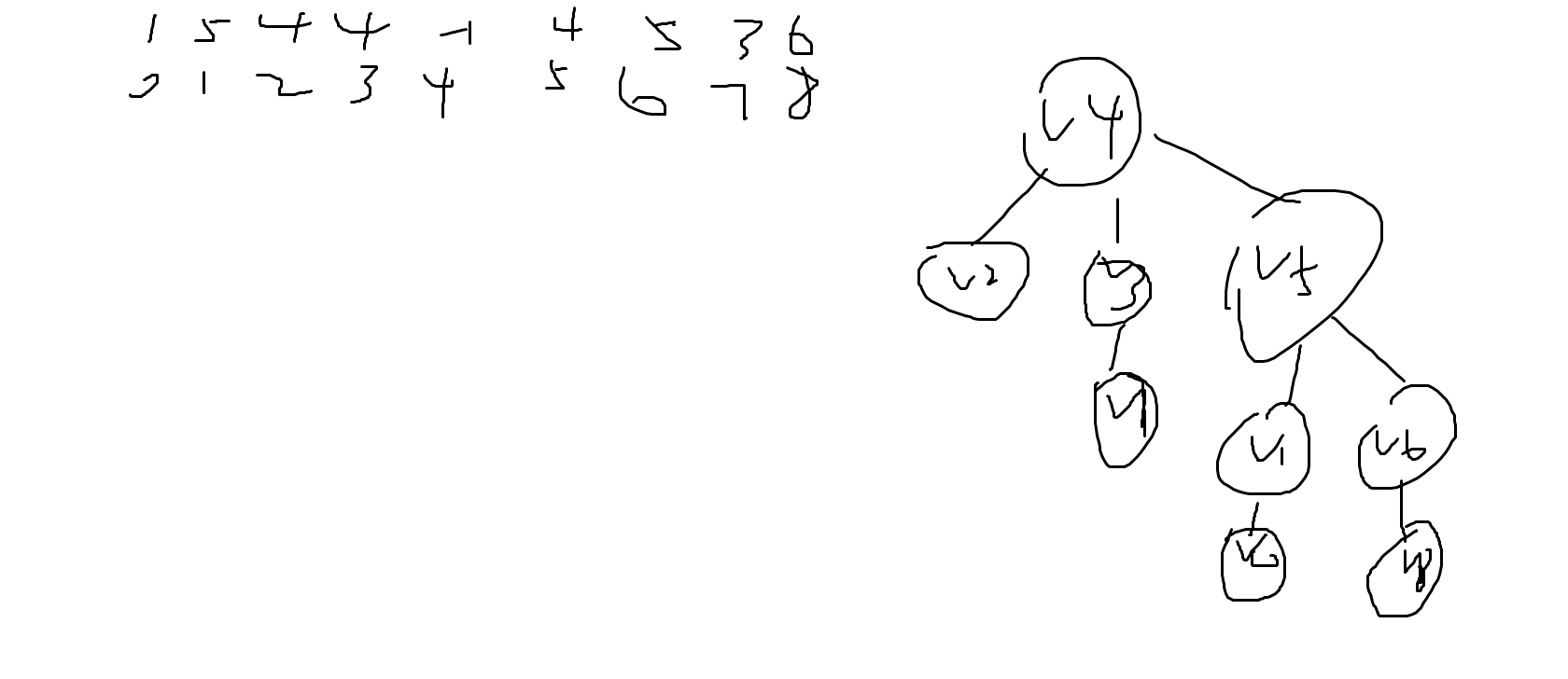
根据样例构造出树,树最深有4层,从首层到末层是3层,所以说最高价ans=p*(1+%r)^maxdepth;
同时达到此的有节点6与8,所以说有两个节点
参考代码:
1 #include<bits/stdc++.h>//1090 2 using namespace std; 3 #define int long long 4 #define IOS ios_base::sync_with_stdio(0);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0); 5 const int N=1e5+10; 6 int n; 7 double p; 8 //int r; 9 vector<int>f[N]; 10 int cnt; 11 int maxdepth=-1; 12 double ans; 13 double r; 14 int root; 15 void dfs(int index,int depth) 16 { 17 if(f[index].size()==0) 18 { 19 if(depth>maxdepth) 20 { 21 maxdepth=depth; 22 cnt=1; 23 } 24 else if(depth==maxdepth) 25 cnt++; 26 return; 27 } 28 for(int i=0;i<f[index].size();i++) 29 dfs(f[index][i],depth+1); 30 } 31 signed main() 32 { 33 // IOS; 34 cin>>n>>p>>r; 35 for(int i=0;i<n;i++) 36 { 37 int fa; 38 cin>>fa; 39 if(fa!=-1) 40 { 41 f[fa].push_back(i); 42 } 43 else 44 root=i; 45 } 46 dfs(root,0); 47 r=(r/100); 48 ans=p*pow((1.0+r),maxdepth); 49 printf("%.2f %lld",ans,cnt); 50 return 0; 51 }
1079:https://pintia.cn/problem-sets/994805342720868352/problems/994805388447170560
这道题是和上道题目没多大差别的,差别在于加了一个供货量的问题,其实也是一样的,按照题目就是说,当这个节点没有子节点的时候他的供货量是唯一的;
而如果它有子节点,就按照父节点依次输入子节点,然后进行bfs就可以了
参考代码
1 #include<bits/stdc++.h>//1079 2 using namespace std; 3 #define int long long 4 #define IOS ios_base::sync_with_stdio(0);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0); 5 const int N=1e5+10; 6 int n; 7 double ans; 8 double p; 9 double r; 10 struct node 11 { 12 double num; 13 vector<int>f; 14 }goods[N]; 15 int maxdepth=-1; 16 void dfs(int index,int depth) 17 { 18 if(goods[index].f.size()==0) 19 { 20 ans+=(goods[index].num*pow((1.0+r),depth)); 21 return ; 22 } 23 for(int i=0;i<goods[index].f.size();i++) 24 { 25 dfs(goods[index].f[i],depth+1); 26 } 27 } 28 signed main() 29 { 30 IOS; 31 cin>>n>>p>>r; 32 for(int i=0;i<n;i++) 33 { 34 int t; 35 cin>>t; 36 if(t==0) 37 { 38 int a; 39 cin>>a; 40 goods[i].num=a; 41 } 42 else 43 { 44 for(int j=0;j<t;j++) 45 { 46 int a; 47 cin>>a; 48 goods[i].f.push_back(a); 49 } 50 } 51 } 52 r=r/100; 53 dfs(0,0); 54 //ans=ans*pow((1.0+r),maxdepth); 55 printf("%.1f",ans*p); 56 return 0; 57 }
1094:https://pintia.cn/problem-sets/994805342720868352/problems/994805372601090048
23 13
21 1 23
01 4 03 02 04 05
03 3 06 07 08
06 2 12 13
13 1 21
08 2 15 16
02 2 09 10
11 2 19 20
17 1 22
05 1 11
07 1 14
09 1 17
10 1 18
题目大意:给定总结点和有孩子的节点n,m接下来m行输入的第一个是父节点,第二个是孩子数量,然后依次输入子节点。
求有做多孩子的层数和这一层的孩子数
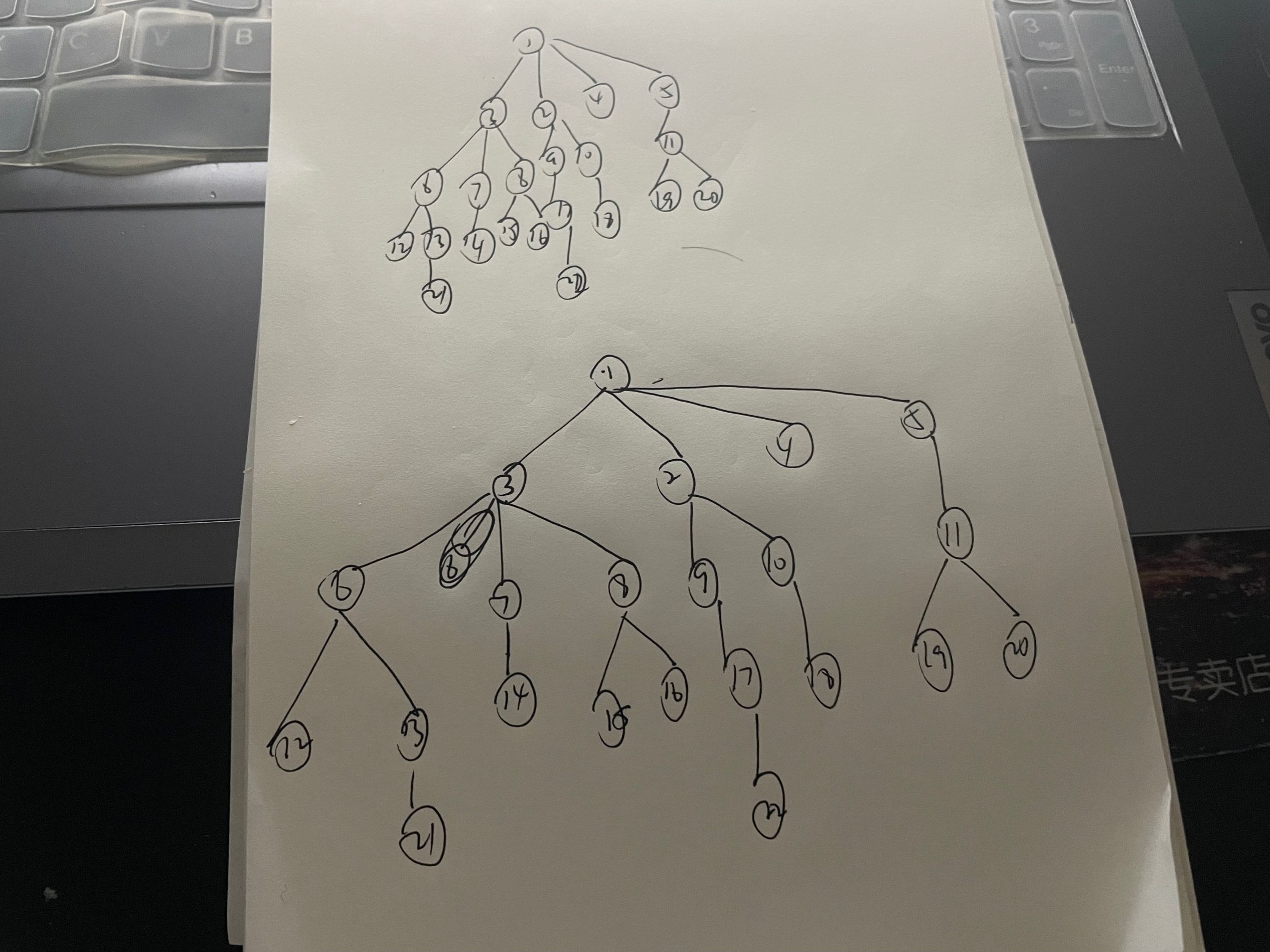
可以这样先建个树,如果是深入求,建议dfs,如果是横向求,建议bfs,
这里选用bfs,其实dfs也可以实现
和常规bfs差不多,记得要对每一层的节点数目进行统计即depth_num[person[t].depth]++,即是这一层的节点数++;
然后进入下一层;
就可以了
注意这里可能在设置节点数和最大深度的时候应该注意,这里的初始化是存在限制的,如果设置任意值比如0或者-1只能拿23分
因为这里忽略了当节点只有根节点的时候,所以说说如果只剩一个根节点都要设置成1;
参考代码:
1 #include<bits/stdc++.h> 2 using namespace std; 3 #define int long long 4 #define IOS ios_base::sync_with_stdio(0);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0); 5 const int N=1e2+10; 6 int n,m; 7 struct node 8 { 9 int depth;//深度 10 vector<int>fa;//记录子节点 11 }person[N]; 12 int cnt=1; 13 int max_depth=1;//和cnt都要设置成1因为只有根节点也是一种情况 14 int depth_num[N];//表示该层有多少节点 15 void bfs(int root) 16 { 17 person[root].depth=1; 18 queue<int>q; 19 q.push(root); 20 while(!q.empty()) 21 { 22 int t=q.front(); 23 q.pop(); 24 depth_num[person[t].depth]++;//统计该层的节点个数 25 for(int i=0;i<person[t].fa.size();i++) 26 { 27 int ch=person[t].fa[i]; 28 person[ch].depth=person[t].depth+1; 29 q.push(ch); 30 } 31 } 32 } 33 signed main() 34 { 35 IOS; 36 cin>>n>>m; 37 for(int i=0;i<m;i++) 38 { 39 int f,num; 40 cin>>f>>num; 41 for(int j=0;j<num;j++) 42 { 43 int c; 44 cin>>c; 45 person[f].fa.push_back(c); 46 } 47 } 48 bfs(1); 49 for(int i=2;i<n;i++) 50 { 51 if(depth_num[i]>cnt)//更新最大层数和节点数 52 { 53 cnt=depth_num[i]; 54 max_depth=i; 55 } 56 } 57 cout<<cnt<<" "<<max_depth; 58 return 0; 59 }
1106:https://pintia.cn/problem-sets/994805342720868352/problems/994805362341822464
同1090差不多,这个是最小零售商问题;
其实思路也是一样的,这个只要统计最小层数和价格就可以了
参考代码:
1 #include<bits/stdc++.h> 2 using namespace std; 3 #define int long long 4 #define IOS ios_base::sync_with_stdio(0);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0); 5 const int N=1e5+10; 6 int cnt; 7 vector<int>f[N]; 8 int n; 9 double p; 10 double r; 11 double ans=INT_MAX; 12 double np; 13 void dfs(int index,int depth) 14 { 15 if(f[index].size()==0) 16 { 17 np=p*pow((1+r),depth); 18 if(np<ans) 19 { 20 ans=np; 21 cnt=1; 22 } 23 else if(np==ans) 24 { 25 cnt++; 26 } 27 } 28 for(int i=0;i<f[index].size();i++) 29 { 30 dfs(f[index][i],depth+1); 31 } 32 } 33 signed main() 34 { 35 IOS; 36 cin>>n>>p>>r; 37 for(int i=0;i<n;i++) 38 { 39 int t; 40 cin>>t; 41 if(t!=0) 42 { 43 for(int j=0;j<t;j++) 44 { 45 int c; 46 cin>>c; 47 f[i].push_back(c); 48 } 49 } 50 51 } 52 r=r/100; 53 dfs(0,0); 54 printf("%.4f %lld",ans,cnt); 55 return 0; 56 }
本文来自博客园,作者:江上舟摇,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/LQS-blog/p/16578150.html





