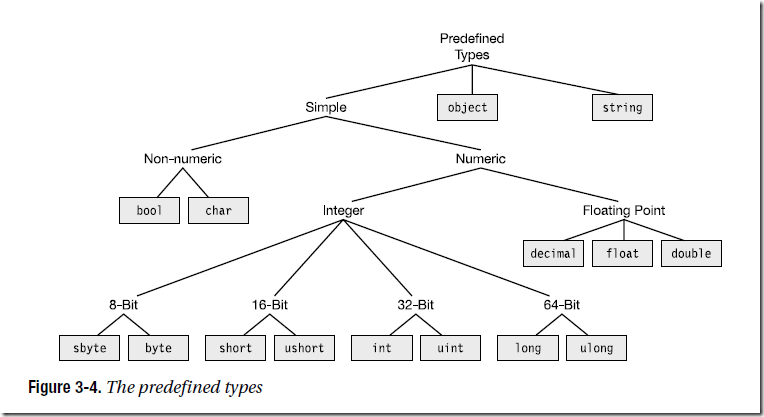
预定义类型
自定义类型
• class types
• struct types
• array types
• enum types
• delegate types
• interface types
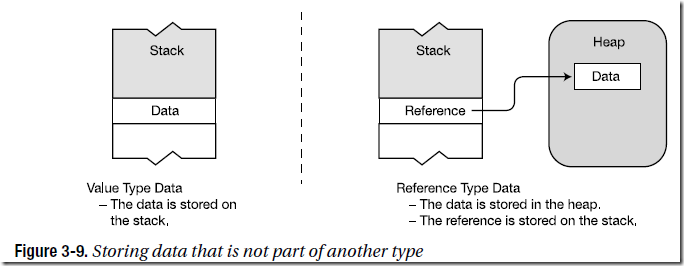
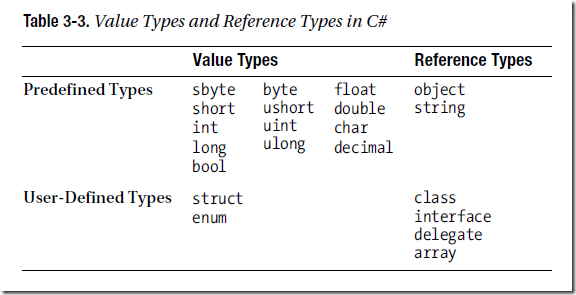
Types are divided into two categories: value types and reference types.
• Value types require only a single segment of memory—which stores the actual data.
• Reference types require two segments of memory:
– The first contains the actual data—and is always located in the heap.
– The second is a reference that points to where in the heap the data is stored.
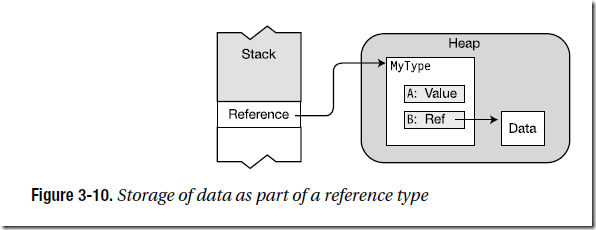
Suppose, for example, that you have an instance of a reference type, called MyType, that has
two members—a value type member and a reference type member. How is it stored? Is the
value type member stored on the stack and the reference type split between the stack and the
heap as shown in Figure 3-9? The answer is no.
Remember that for a reference type, the data of an instance is always stored in the heap.
Since both members are part of the object’s data, they are both stored in the heap, regardless
of whether they are value or reference types. Figure 3-10 illustrates the case of type MyType.