Vuex状态管理详解
什么是Vuex
专门为vue应用程序开发的状态管理模式,采用集中式存储管理应用的所有组件的状态(数据),以相应的规则保证状态以一种可预测的方式发生改变
Vuex的作用(什么样的情况下使用Vuex)
多个视图依赖于同一个状态(数据),来自不同视图的行为需要变更同一状态
Vuex的流程图和操作结构图
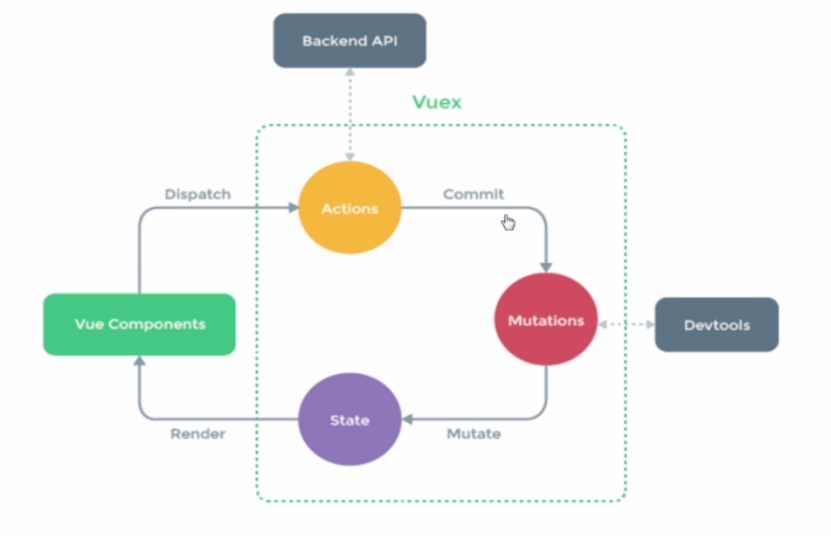
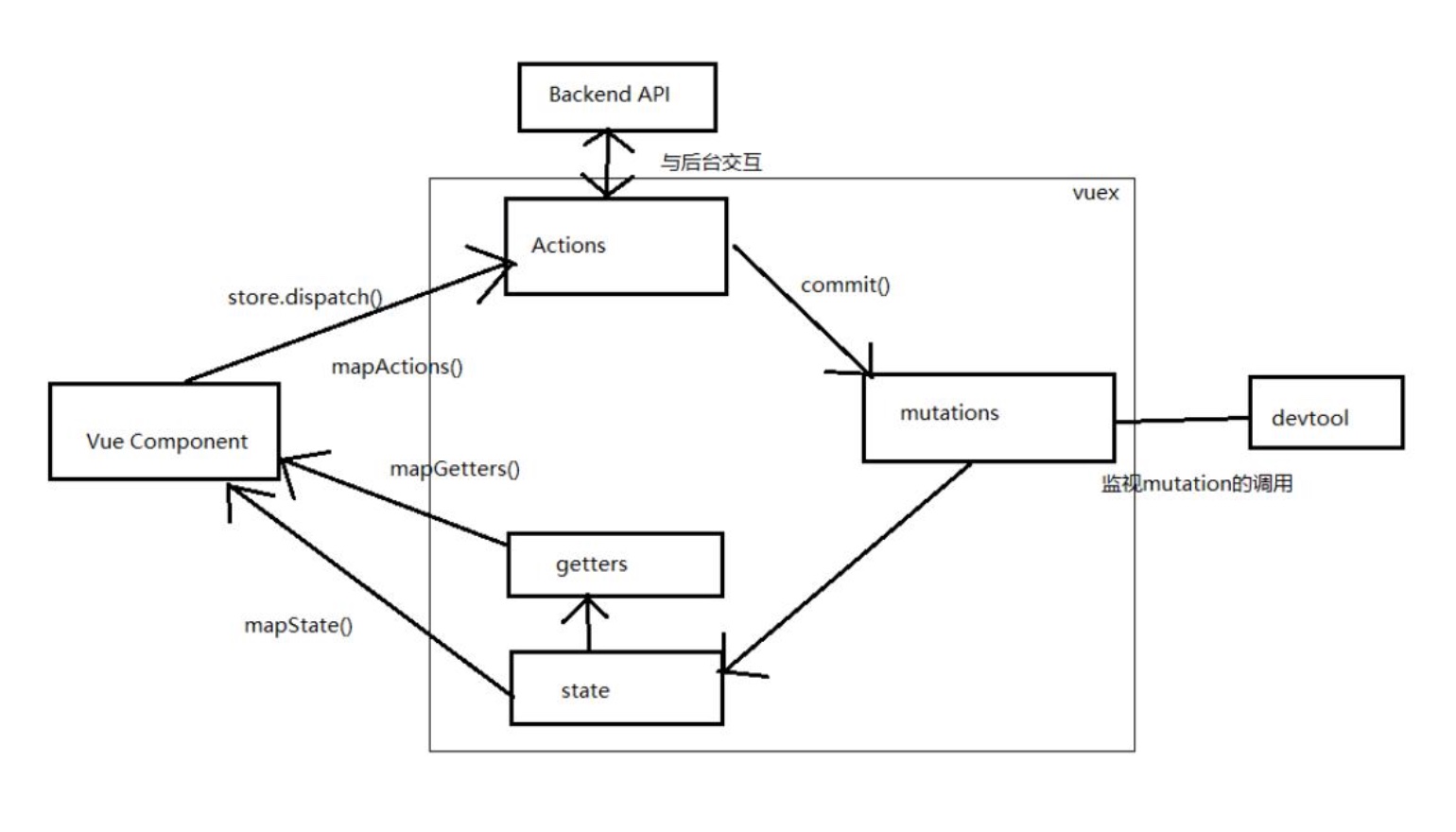
假设这个组件需要从后台拿到数据,那么就牵扯到异步操作,所以将异步操作定义在Actions中,组件中触发这个Actions,Actions中执行异步请求,拿到后台接口,然后拿到数据,需要将数据提交一个mutations改变状态,然后重新渲染组件中的状态
vuex 核心概念和 API
state:vuex 管理的状态对象,它应该是唯一的
const state = {
xxx: initValue
}
mutations:包含多个直接更新 state 的方法(回调函数)的对象,谁来触发: action 中的 commit('mutation 名称'),只能包含同步的代码, 不能写异步代码
const mutations = { yyy (state, {data1}) { // 更新 state 的某个属性 } }
actions:包含多个事件回调函数的对象,通过执行:commit()来触发 mutation 的调用, 间接更新 state,谁来触发: 组件中: $store.dispatch('action 名称', data1),可以包含异步代码(定时器, ajax)
const actions = { zzz ({commit, state}, data1) { commit('yyy', {data1}) } }
getters:包含多个计算属性(get)的对象,谁来读取: 组件中: $store.getters.xxx
const getters = { mmm (state) { return ... } }
modules:包含多个 module,一个 module 是一个 store 的配置对象,与一个组件(包含有共享数据)对应
Vuex的基本使用(通过一个简易计算器实例分析Vuex流程)
首先使用脚手架初始化一项vue的项目,并且App.vue组件中引入一个组件(简易计算器的这么一个组件)
<template> <div> <h2>简易加法计算器</h2> <div> <input type="button" value="-" /> <span>{{count}}</span> <input type="button" value="+" /> </div> </div> </template> <script> export default { } </script> <style> </style>
<template> <div id="app"> <increment></increment> </div> </template> <script> import Increment from './components/Increment' export default { name: 'app', components: { Increment } } </script> <style> #app { font-family: 'Avenir', Helvetica, Arial, sans-serif; -webkit-font-smoothing: antialiased; -moz-osx-font-smoothing: grayscale; text-align: center; color: #2c3e50; margin-top: 60px; } </style>
然后启动项目,可以看到下面的界面

接下来先安装vuex模块

然后src目录中创建一个vuex的目录,在里面创建一个store.js的一个文件,用于操作vuex,并且将vue和vuex导入进来,将vuex作为插件使用
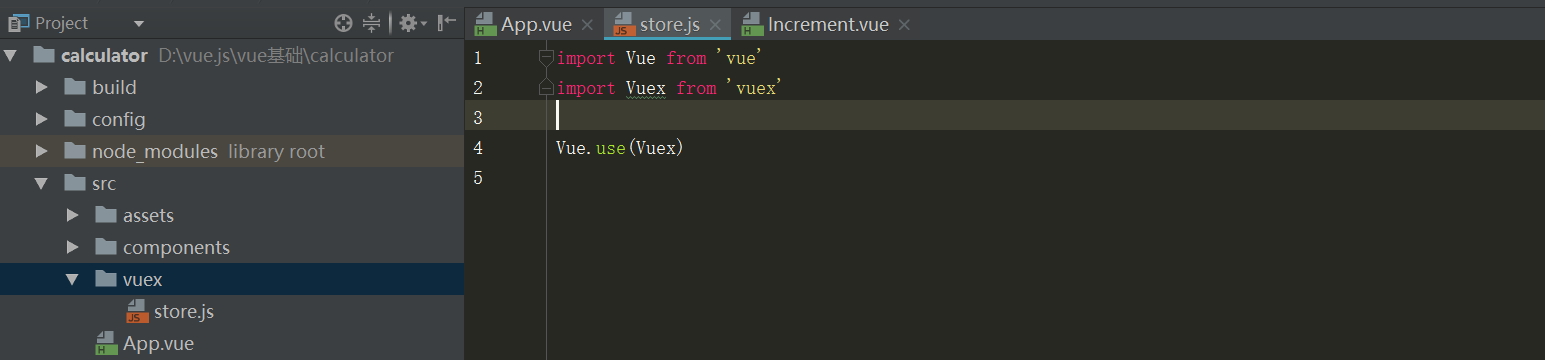
定义一个容器,并且将这个容器导出去,这个store容器,包含应用中的大部分状态,store的特点:
一个页面只能有一个store
状态存储是响应式的(就是说当state中的某个状态值发生改变的时候,使用了这个状态值的组件中的数据也会跟着改变,所以只要改变state中的状态就可以了)
不能直接改变store中的状态,唯一途径就是显示地提交mutations
import Vue from 'vue' import Vuex from 'vuex' Vue.use(Vuex) // 定义一个容器 const store = new Vuex.Store({ }) export default store
然后再mian.js中注入(注入根实例),之后就可以使用vuex来管理状态了,注入的时候需要注意,store小写
// The Vue build version to load with the `import` command // (runtime-only or standalone) has been set in webpack.base.conf with an alias. import Vue from 'vue' import App from './App' import store from './vuex/store' Vue.config.productionTip = false /* eslint-disable no-new */ new Vue({ el: '#app', store, template: '<App/>', components: { App } })
在store容器中定义一个对象,叫做state,里面存放的都是应用中共享的状态(数据),也就是说包含所有应用级别状态的对象,比如下面定义一个count的状态
import Vue from 'vue' import Vuex from 'vuex' Vue.use(Vuex) // 定义一个容器 const store = new Vuex.Store({ state: { count: 100 } }) export default store
然后在需要这个状态值的组件中拿到这个状态值,就是在组件中使用this(当前组件的实例对象).$store(因为这个store已经在main.js中注入进来了,所以每个组件都可以访问到这个store).state
然后在这个state中拿到想要的那个状态值
<template> <div> <h2>简易加法计算器</h2> <div> <input type="button" value="-" /> <span>{{ num }}</span> <input type="button" value="+"/> </div> </div> </template> <script> export default { computed: { num () { return this.$store.state.count } } } </script>
接着在组件中通过事件来触发改变state里面的某个状态值,改变state中的状态值需要通过Mutations(唯一修改状态的事件回调函数)
状态存储是响应式的(就是说当state中的某个状态值发生改变的时候,使用了这个状态值的组件中的数据也会跟着改变,所以只要改变state中的状态就可以了)
不能直接改变store中的状态,唯一途径就是显示地提交mutations
import Vue from 'vue' import Vuex from 'vuex' Vue.use(Vuex) // 定义一个容器 const store = new Vuex.Store({ state: { count: 100 }, mutations: { // 这里里面定义改变状态值的一些函数(需要接收一个state作为参数,也就是state容器) addincrement (state) { state.count += 1 }, deincrement (state) { state.count -= 1 } } }) export default store
然后再组件中通过事件来提交一个mutations并且触发里面相应函数
<template> <div> <h2>简易加法计算器</h2> <div> <input type="button" value="-" @click="deHandler"/> <span>{{ num }}</span> <input type="button" value="+" @click="addHandler"/> </div> </div> </template> <script> export default { computed: { num () { return this.$store.state.count } }, methods: { addHandler () { this.$store.commit('addincrement') }, deHandler () { this.$store.commit('deincrement') } } } </script>
测试,点击加号或者就可以改变count这个状态值,并且查看vue调试工具可以看到数据的变化

在点击事件提交一个mutations的时候,可以传入第二个参数,比如下面我想要点击一次加5或者减5
addHandler () { this.$store.commit('addincrement', 5) }, deHandler () { this.$store.commit('deincrement', 5) }
在容器中的mutations可以接收第二个参数,这个参数叫做payload
mutations: { // 这里里面定义改变状态值的一些函数(需要接收一个state作为参数,也就是state容器) addincrement (state, n) { state.count += n }, deincrement (state, n) { state.count -= n } }
运行测试可以看到,点击一次以5来计算

当需要传递很多个参数的时候,第二个参数写成对象的形式
methods: { addHandler () { this.$store.commit('addincrement', { n: 5 }) }, deHandler () { this.$store.commit('deincrement', { n: 5 }) } }
mutations: { // 这里里面定义改变状态值的一些函数(需要接收一个state作为参数,也就是state容器) addincrement (state, payload) { state.count += payload.n }, deincrement (state, payload) { state.count -= payload.n } }
运行测试:
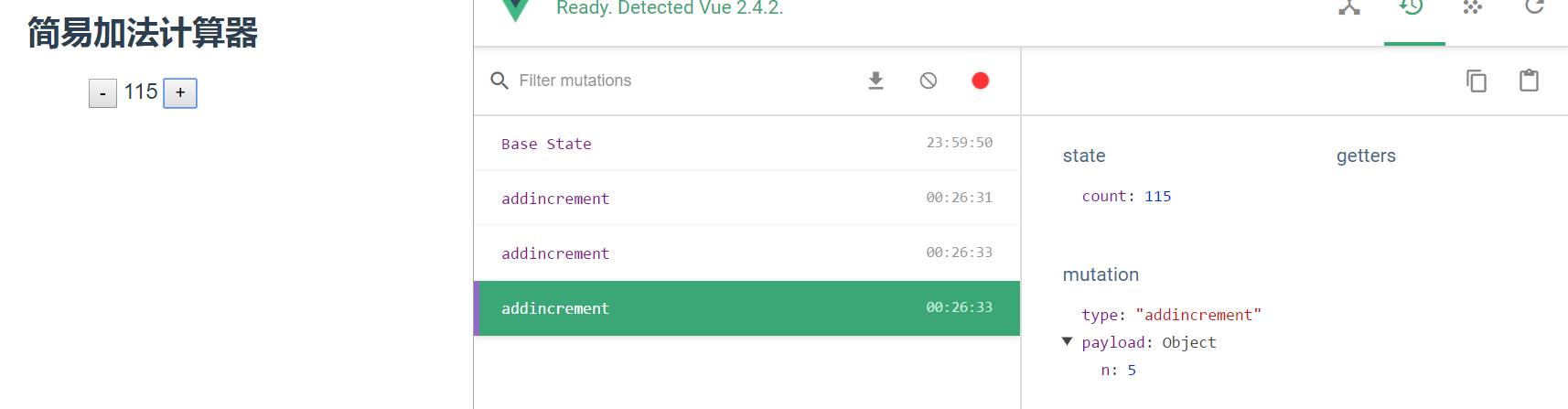
还可以使用下面这种写法:mutations中接收参数也是一样的写法接收一个payload,然后获取payload下的某个参数值
methods: { addHandler () { this.$store.commit({ type: 'addincrement', n: 5 }) }, deHandler () { this.$store.commit({ type: 'deincrement', n: 5 }) } }
Action异步操作
当点击某个按钮需要从后台请求数据的时候,这个时候有异步的操作,这里就使用上面的例子来模拟一下异步的操作
import Vue from 'vue' import Vuex from 'vuex' Vue.use(Vuex) // 定义一个容器 const store = new Vuex.Store({ state: { count: 100 }, mutations: { // 这里里面定义改变状态值的一些函数(需要接收一个state作为参数,也就是state容器) addincrement (state, payload) { state.count += payload.n }, deincrement (state, payload) { state.count -= payload.n } }, actions: { addAction (context) { setTimeout(() => { // 改变状态,提交mutations context.commit('addincrement', { n: 5 }) }, 1000) } } }) export default store
在组件中触发的时候,先触发actions,然后在提交mutations
<template> <div> <h2>简易加法计算器</h2> <div> <input type="button" value="-" @click="deHandler"/> <span>{{ num }}</span> <input type="button" value="+" @click="addHandler"/> </div> </div> </template> <script> export default { computed: { num () { return this.$store.state.count } }, methods: { addHandler () { // 触发Actions this.$store.dispatch('addAction') }, deHandler () { this.$store.commit({ type: 'deincrement', n: 5 }) } } } </script>
getters计算属性
包含多个计算属性(get)的对象,谁来读取: 组件中: $store.getters.xxx
import Vue from 'vue' import Vuex from 'vuex' Vue.use(Vuex) // 定义一个容器 const store = new Vuex.Store({ state: { count: 100 }, mutations: { // 这里里面定义改变状态值的一些函数(需要接收一个state作为参数,也就是state容器) addincrement (state, payload) { state.count += payload.n }, deincrement (state, payload) { state.count -= payload.n } }, actions: { addAction (context) { setTimeout(() => { // 改变状态,提交mutations context.commit('addincrement', { n: 5 }) }, 1000) } }, getters: { oddOrEven (state) { return state.count % 2 === 0 ? '偶数' : '奇数' } } }) export default store
<template> <div> <h2>简易加法计算器</h2> <div> <input type="button" value="-" @click="deHandler"/> <span>{{ num }}, is {{ oddOrEven2 }}</span> <input type="button" value="+" @click="addHandler"/> </div> </div> </template> <script> export default { computed: { num () { return this.$store.state.count }, oddOrEven2 () { return this.$store.getters.oddOrEven } }, methods: { addHandler () { // 触发Actions this.$store.dispatch('addAction') }, deHandler () { this.$store.commit({ type: 'deincrement', n: 5 }) } } } </script>
vuex的API使用
mapState的使用:直接获取state中的某个数据
mapGetters的使用:获取getters中的对应的get名称的返回值
mapActions的使用:触发store下的actios下对应的action,事件名称跟action的名称需要一样(开发中一般不这么写,不可以传递参数)
mapMutations的使用:跟mapActions的使用一样
import Vue from 'vue' import Vuex from 'vuex' Vue.use(Vuex) // 定义一个容器 const store = new Vuex.Store({ state: { count: 100 }, mutations: { // 这里里面定义改变状态值的一些函数(需要接收一个state作为参数,也就是state容器) addincrement (state, payload) { state.count += payload.n }, deHandler (state) { state.count -= 1 } }, actions: { addHandler (context) { setTimeout(() => { // 改变状态,提交mutations context.commit('addincrement', { n: 5 }) }, 1000) } }, getters: { oddOrEven (state) { return state.count % 2 === 0 ? '偶数' : '奇数' } } }) export default store
<template> <div> <h2>简易加法计算器</h2> <div> <input type="button" value="-" @click="deHandler"/> <span>{{ count }}, is {{ oddOrEven2 }}</span> <input type="button" value="+" @click="addHandler"/> </div> </div> </template> <script> import {mapState, mapGetters, mapActions, mapMutations} from 'vuex' export default { computed: { ...mapState(['count']), // 直接获取state下的count这个数据,相当于这个组件中有了count这个变量,可以任意地方this.count获取这个数据,但是不能直接修改 ...mapGetters({ // 直接获取getters返回的值,可以获取多个对应的getters oddOrEven2: 'oddOrEven' }) }, methods: { ...mapActions(['addHandler']), // 事件名称跟actions名称一样 ...mapMutations(['deHandler']) // 事件名跟对应的Mutations名称一致 } } </script>
实际开发项目中应该如何使用vuex
实际开发项目中我们不会像上面那样去使用vuex,首先我们会将每个功能模块对应一个stote文件,然后通过module来合并到store.js文件中,下面来做一个实例
目录结构
这里是两个模块feeds和movies
store
│ index.js
│
├─feeds.js
│
└─movies.js
第一步:在store文件夹下的index.js入口文件写入
import Vue from 'vue' import Vuex from 'vuex' import Vue from 'vue'; import Vuex from 'vuex'; import feeds from './feeds'; import Movies from './movies'; Vue.use(Vuex) // 全局状态对象 const state = {} // 全局mutations let mutations = {} let getters = {} let actions = {} export default new Vuex.Store({ state: state, mutations: mutations, getters: getters, actions: actions, modules: { feeds, movies: Movies } })
第二步:在每个模块内的index文件这组装所有的零件(state,actions,mutations,getters),并且输出
注意上面多出的一行,我们在组件里怎么区分不同模块呢?namespaced写成true,意思就是可以用这个module名作为区分了(也就是module所在的文件夹名)
export default { namespaced: true, state: {}, actions: {}, mutations: {}, getters: {} }
第三步:在组件里使用获取state中的数据,在组件的计算属性中写
如果是全局下的state
...mapState(['userInfo', 'isInNative'])
如果是模块下的state,这里表示获取movies模块下的projectApplyId这个数据
...mapState('movies', ['projectApplyId'])
第四步:触发actions操作,在组件的methods中写
store.dispatch('pi/taskSaveAndSubmit', {projectLockKey: that.projectLockKey})
...mapActions('movies',[
'foo',
'bar'
])




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号