「2019冬令营提高组」堆
二叉堆计数显然可以递归处理
考虑两个二叉堆合并时的情况:
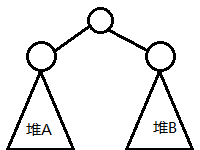
最小的数肯定在根的位置
设此时总的节点数为 $tot$,堆$A$的节点数为 $a$,我们显然可以从 $tot-1$ 个数中随意选出 $a$ 个数放到堆$A$中,剩下的数放到堆$B$中($tot-1$是因为根的值已经确定了)
考虑堆$A$原本的一种可能情况,发现如果我们把随意选出的 $a$ 个数按排名标号,把相应排名的数放到堆$A$原本相应的值的位置刚好为一种情况
堆$B$显然也可以同样考虑
设 $f[i]$ 表示有 $i$ 个节点的二叉堆的方案数,那么根据乘法原理有如下转移
$f[tot]=C^{a}_{tot-1}*f[a]*f[b]$
因为二叉堆是完全二叉树所以对于每一个 $tot$,它的 $a$ 和 $b$ 都是固定的
然后预处理一波阶乘就可以得到 60 分的好成绩:
#include<iostream> #include<cstdio> #include<algorithm> #include<cstring> #include<cmath> using namespace std; typedef long long ll; inline int read() { int x=0,f=1; char ch=getchar(); while(ch<'0'||ch>'9') { if(ch=='-') f=-1; ch=getchar(); } while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9') { x=(x<<1)+(x<<3)+(ch^48); ch=getchar(); } return x*f; } const int N=4e6+7,mo=1e9+7;; int n,f[N],sz[N]; int fac[N],inv[N]; inline int C(int x,int y) { return 1ll*fac[x]*inv[x-y]%mo*inv[y]%mo; } void dfs(int o) { sz[o]=1; int lc=o<<1,rc=lc|1; if(lc<=n) dfs(lc),sz[o]+=sz[lc]; else f[lc]=1; if(rc<=n) dfs(rc),sz[o]+=sz[rc]; else f[rc]=1; f[o]=1ll*f[lc]*f[rc]%mo*C(sz[o]-1,sz[lc])%mo; } inline int ksm(int x,int y) { int res=1; while(y) { if(y&1) res=1ll*res*x%mo; x=1ll*x*x%mo; y>>=1; } return res; } int main() { freopen("heap.in","r",stdin); freopen("heap.out","w",stdout); n=read(); fac[0]=1,inv[0]=1; for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) { fac[i]=1ll*fac[i-1]*i%mo; inv[i]=ksm(fac[i],mo-2); } dfs(1); cout<<f[1]; return 0; }
继续考虑优化,发现我们还有一条重要的性质没有好好利用:二叉堆是一颗完全二叉树
完全二叉树中,左右儿子至少有一个儿子是满二叉树,这条性质用反证法容易证明
所以我们可以先预处理出所有满二叉树的堆的方案数,然后递归时只要往一边儿子走就好了
递归复杂度 $log_n$
但是有一个很大的问题,组合数太大了阶乘无法预处理
怎么办?
分块打表!
先在本机中求出所以阶乘并每 $100000$ 个阶乘就输出一次,文件大小大概 97MB(比赛时代码长度要求小于100MB)
然后就过了23333

#include<iostream> #include<algorithm> #include<cstdio> #include<cmath> #include<cstring> using namespace std; typedef long long ll; const int N=1e9,mo=1e9+7,M=1e5; int main() { freopen("data.out","w",stdout); int fac=1; cout<<1<<","; for(int i=1;i<=N;i++) { fac=1ll*fac*i%mo; if(i%M==0) { if(i!=N) printf("%d,",fac); else printf("%d\n",fac); } } return 0; }
#include<iostream> #include<algorithm> #include<cstdio> #include<cmath> #include<cstring> using namespace std; typedef long long ll; const int N=1e9,mo=1e9+7,M=1e5; int fac[100007]={}//表 inline int Fac(int pos)//分块求阶乘 { int res=fac[pos/M]; for(int i=pos/M*M+1;i<=pos;i++) res=1ll*res*i%mo; return res; } inline int ksm(int x,int y)//快速幂求逆元 { int res=1; while(y) { if(y&1) res=1ll*res*x%mo; x=1ll*x*x%mo; y>>=1; } return res; } inline int C(int x,int y) { return 1ll*Fac(x) * ksm(Fac(x-y),mo-2)%mo * ksm(Fac(y),mo-2)%mo; }//求组合数(x个数中选y个数的方案数) int n,f[107];//f[i]表示层数为i的满二叉堆的方案数 int dfs(int x) { int i=1; while( (1<<i)-1<x ) i++; if( (1<<i)-1==x ) return f[i]; if( (1<<i)-1 - (1<<i-2) >= x )//判断左右子树哪个是满的 return 1ll*dfs(x-(1<<i-2)) * f[i-2]%mo * C(x-1,(1<<i-2)-1)%mo; else return 1ll*dfs(x-(1<<i-1)) * f[i-1]%mo * C(x-1,(1<<i-1)-1)%mo; } int main() { freopen("heap.in","r",stdin); freopen("heap.out","w",stdout); scanf("%d",&n); f[0]=f[1]=1; for(int i=2;i<=30;i++)//预处理f f[i]=1ll*f[i-1]*f[i-1]%mo*C((1<<i)-2,(1<<i-1)-1)%mo; printf("%d",dfs(n)); return 0; }



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号