c++综合实验报告友元
综合性、设计性实验报告
专业:计算机科学与技术
一、实验目的:
1.熟练掌握友元函数和友元类设计的方法
2.掌握友元函数的含义,友元函数和成员函数的区别。
3.掌握友元类的含义。
二、实验仪器或设备:微型计算机
三、总体设计(设计原理、设计方案及流程等)
实验内容:
定义Student类和Score类,输出一个学生的成绩单(包括学号、姓名、高等数学、英语成绩)。
【要求:】
方法1:非成员函数作为友元函数
方法2:成员函数作为友元函数
方法3:友元类
本实验运行环境:Microsoft Visual c++ 2010学习版,采用面向对象的程序设计方法。
四、实验步骤(包括主要步骤、代码分析等)
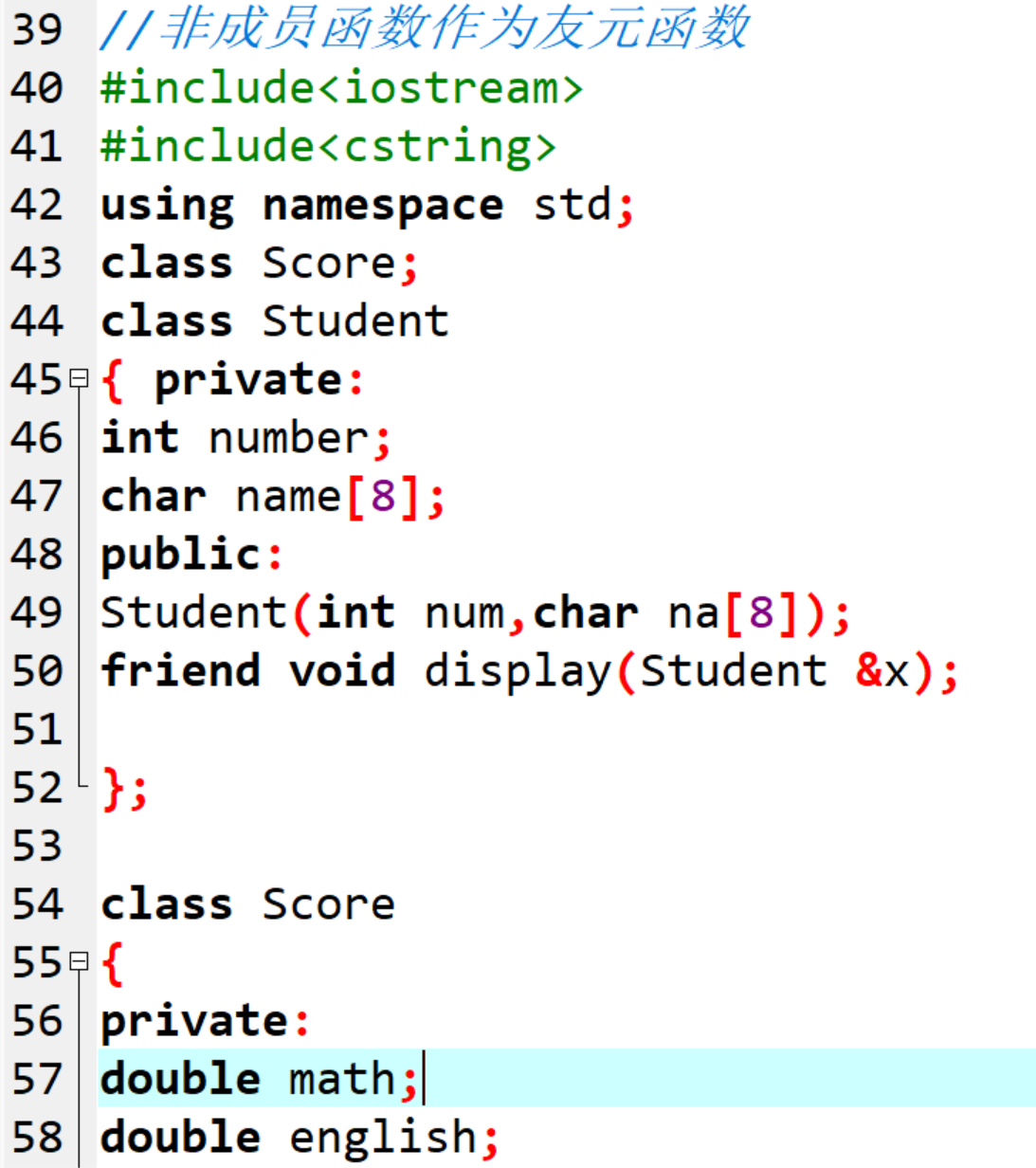
方法1://非成员函数作为友元函数
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
class Score;
class Student
{ private:
int number;
char name[8];
public:
Student(int num,char na[8]);
friend void display(Student &x);
};
class Score
{
private:
double math;
double english;
public:
Score(double m,double e);
friend void display(Score &s);
};
Student::Student(int num,char na[])
{
number=num;
strcpy(name,na);
}
Score::Score(double m,double e)
{
math=m;
english=e;
}
void display(Student &x)
{
cout<<"该学生的信息 \n学号num: "<< x.number<<" 名字name: "<<x.name<<"\n";
}
void display(Score &s)
{
cout<<"该学生的高考成绩math: "<<s.math<<"分 英语成绩english: "<<s.english<<"分\n";
}
int main()
{
Student st1(123456,"小陈");
Score sc1(100,123);
display(st1) ;
display(sc1) ;
return 0;
}


方法2://成员函数作为友元函数
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
class Score;
class Student
{
private:
int number;
char name[8];
public:
Student(int num,char na[8]);
void display(Score &s);
};
class Score
{
private:
double math;
double english;
public:
Score(double m,double e);
friend void Student::display(Score &s);
};
Student::Student(int num,char na[])
{
number=num;
strcpy(name,na);
}
Score::Score(double m,double e)
{
math=m;
english=e;
}
void Student::display(Score &s)
{
cout<<"该学生的信息 \n学号num: "<<number<<" 名字name: "<<name<<"\n";
cout<<"该学生的高考成绩math: "<<s.math<<"分 英语成绩english: "<<s.english<<"分\n";
}
int main()
{
Student st1(123456,"小陈");
Score sc1(100,123);
st1.display(sc1) ;
return 0;
}


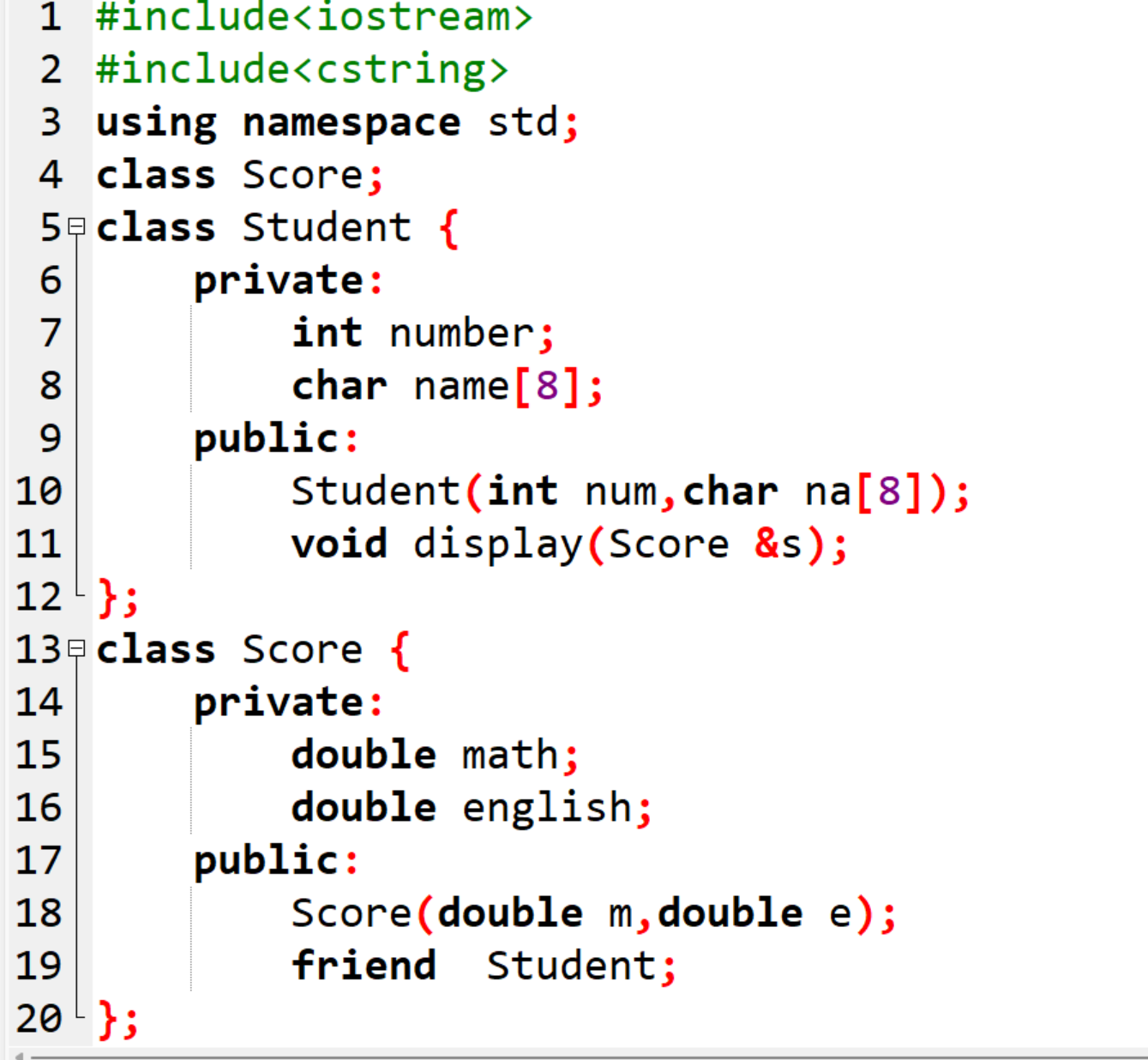
方法3://友元类
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
class Score;
class Student {
private:
int number;
char name[8];
public:
Student(int num,char na[8]);
void display(Score &s);
};
class Score {
private:
double math;
double english;
public:
Score(double m,double e);
friend Student;
};
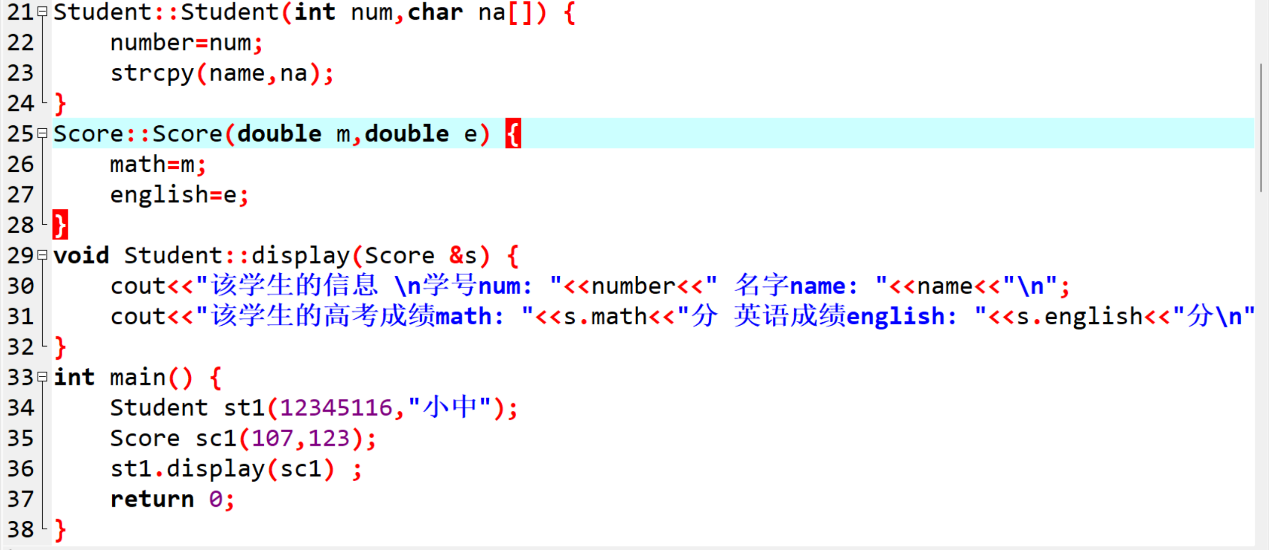
Student::Student(int num,char na[]) {
number=num;
strcpy(name,na);
}
Score::Score(double m,double e) {
math=m;
english=e;
}
void Student::display(Score &s) {
cout<<"该学生的信息 \n学号num: "<<number<<" 名字name: "<<name<<"\n";
cout<<"该学生的高考成绩math: "<<s.math<<"分 英语成绩english: "<<s.english<<"分\n";
}
int main() {
Student st1(12345116,"小中");
Score sc1(107,123);
st1.display(sc1) ;
return 0;
}
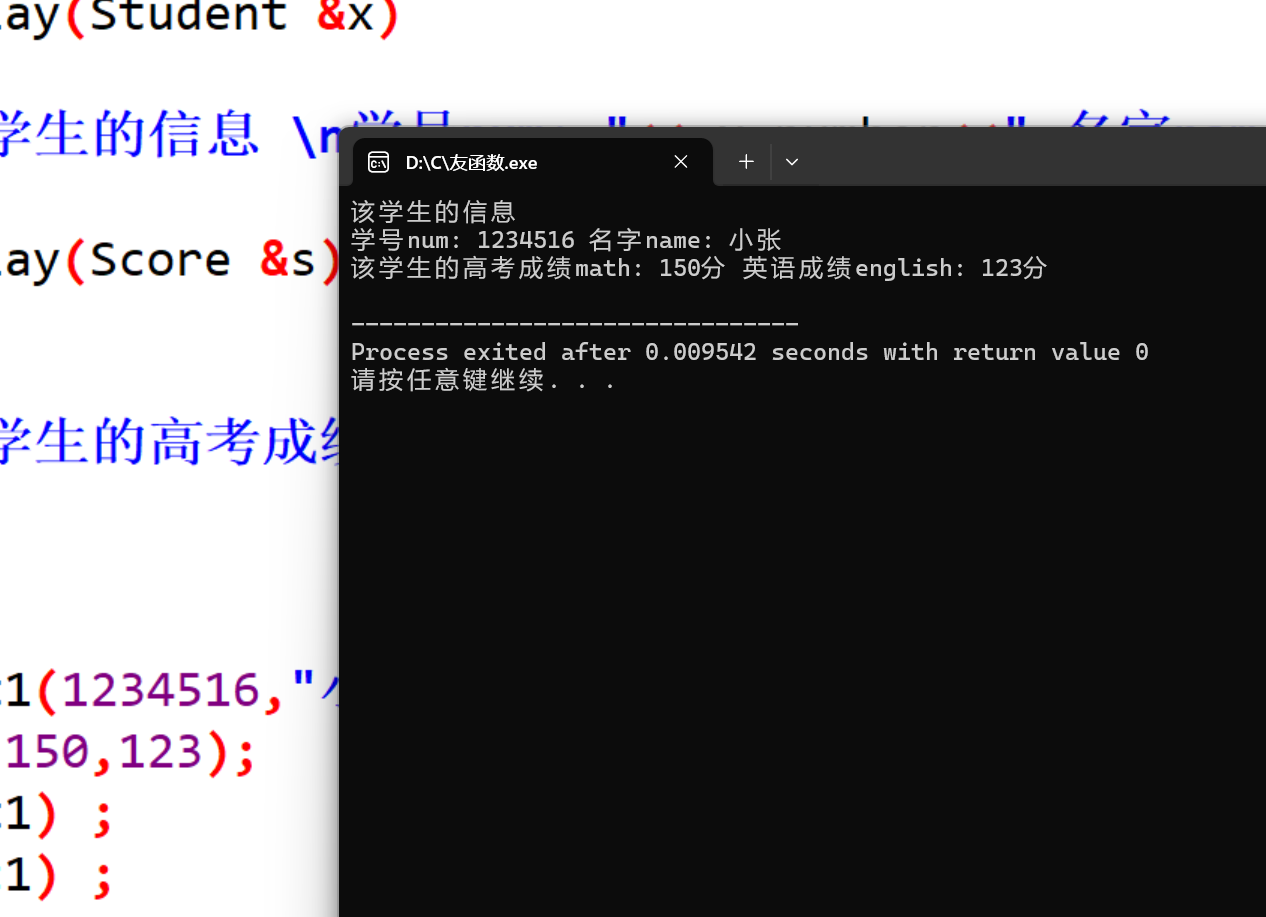
五、结果分析与总结
方法1:
方法2:
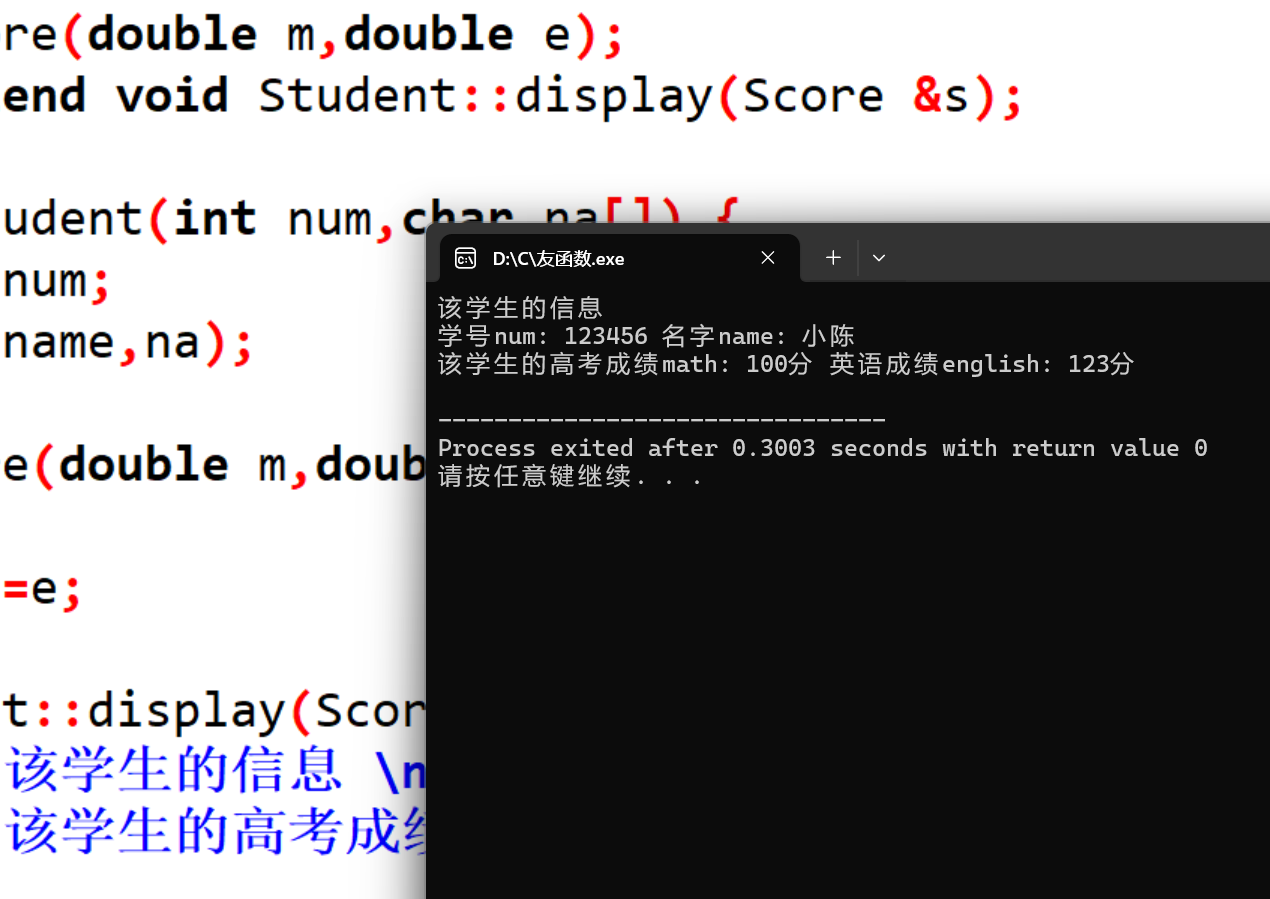
方法3:
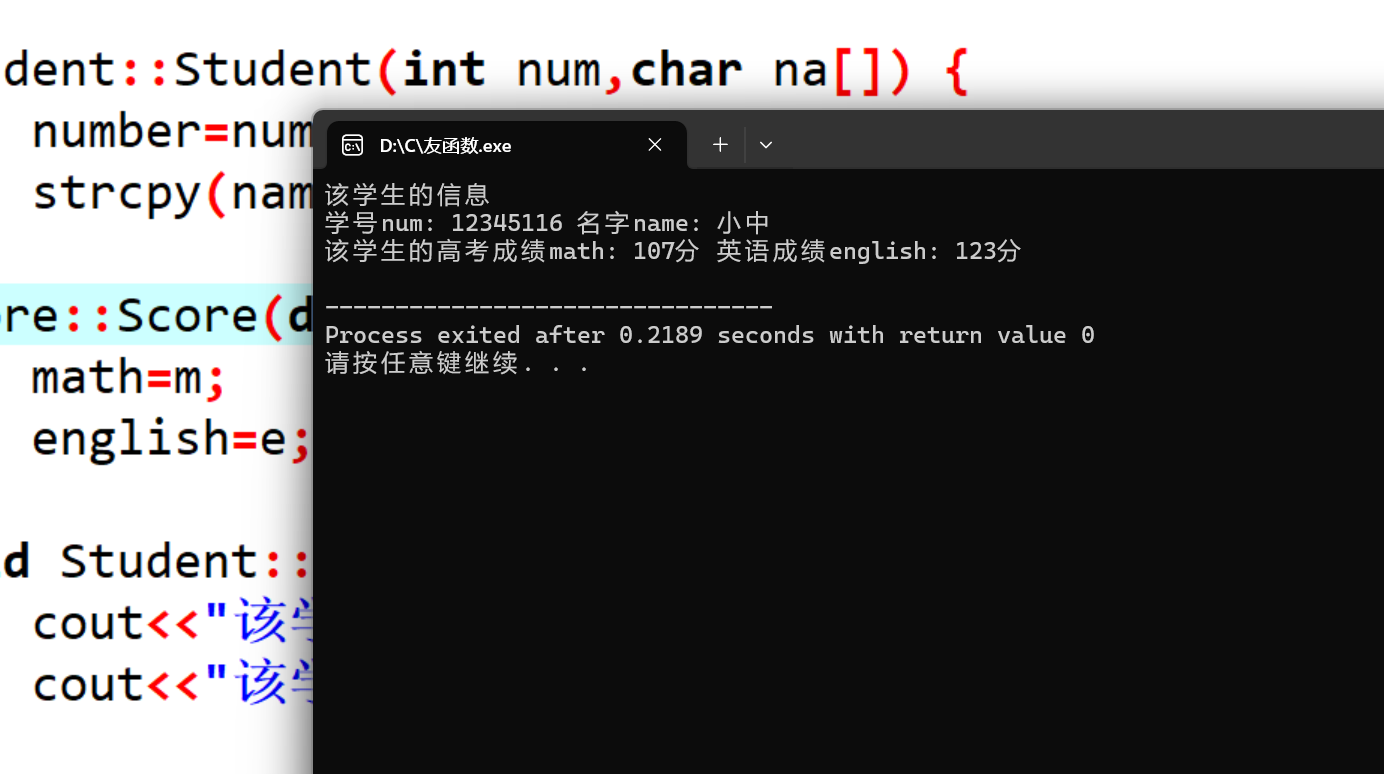 (运行结果截图,简短的体会总结)
(运行结果截图,简短的体会总结)
简短的体会总结:非成员函数作为友元函数适用于封装与类相关但不属于类的逻辑;成员函数作为友元函数适用于在不同类之间实现紧密耦合和协作;而友元类则适用于需要深度交互和合作的两个类之间。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号