24、Swap Nodes in Pairs
题目
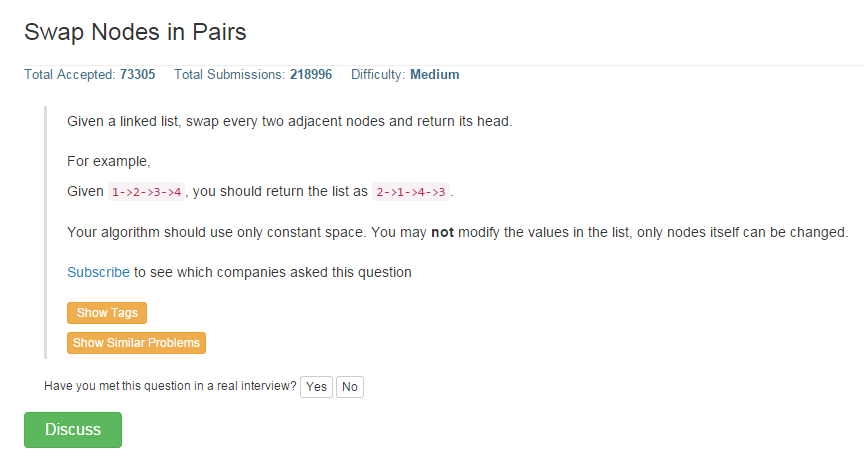
看到此题,第一想法是利用两个指针,分别将其所指向的节点的value交换。然后同时向后移动2个节点,代码如下:
1 struct ListNode { 2 int val; 3 ListNode *next; 4 ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {} 5 }; 6 7 class Solution { 8 public: 9 ListNode* swapPairs(ListNode* head) { 10 ListNode *first,*second; 11 if(NULL == head || NULL == head->next)//空或者只有一个节点 12 return head; 13 first = head; 14 second = head->next; 15 int temp; 16 while (NULL != second) 17 { 18 temp = first->val; 19 first->val = second->val; 20 second->val = temp; 21 22 first = second->next; 23 if(NULL == first) 24 return head; 25 second = first->next; 26 if (NULL == second) 27 return head; 28 } 29 } 30 };
但是题目明确要求不能通过交换值的方式,只能对整个节点操作。因此在上面的代码中,需要利用一个指针指向second之后的节点,然后交换first和second,代码如下:
1 //Definition for singly-linked list. 2 struct ListNode { 3 int val; 4 ListNode *next; 5 ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {} 6 }; 7 8 class Solution { 9 public: 10 ListNode* swapPairs(ListNode* head) { 11 ListNode *first,*second; 12 if(NULL == head || NULL == head->next)//空或者只有一个节点 13 return head; 14 first = head; 15 second = head->next; 16 ListNode *temp; 17 ListNode *pHead,*pre; 18 pHead = second;//虚头节点指向第二个节点,因为第二个节点在交换后会作为头结点; 19 while (NULL != second) 20 { 21 temp = second->next; 22 first->next = second->next; 23 second->next = first; 24 pre = first; 25 if(NULL == temp) 26 break; 27 first = temp; 28 29 second = first->next; 30 if (NULL == second) 31 break; 32 pre->next = second; 33 } 34 head = pHead; 35 return head; 36 } 37 };
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------分割线----------------------------------------------------------------------------
25、Reverse Nodes in k-Group
题目
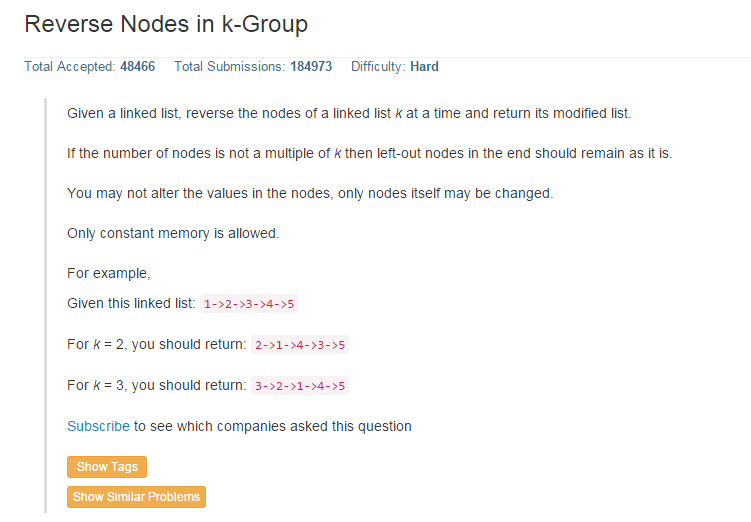
这一题是24题的升级,如果解决了这一题,当k=2就是24题。因此该题更通用更具一般性。其解决方法是利用一个stack,依次将k个节点放入stack,代码如下:
1 struct ListNode { 2 int val; 3 ListNode *next; 4 ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {} 5 }; 6 7 class Solution { 8 public: 9 ListNode* reverseKGroup(ListNode* head, int k) { 10 if(k <= 1 || NULL == head) 11 return head; 12 stack<ListNode*> myStack; 13 ListNode *pre,*tail,*current,*temp,*phead; 14 current = head; 15 int i; 16 tail = new ListNode(-1);//构造一个伪头结点 17 phead = tail; 18 19 while (NULL != current) 20 { 21 for (i=0;i<k;i++) 22 { 23 if(current == NULL)//说明不够k节点 24 break; 25 pre = current; 26 current = current->next; 27 pre->next = NULL; 28 myStack.push(pre); 29 30 } 31 if(i == k) 32 { 33 while(!myStack.empty()) 34 { 35 temp = myStack.top(); 36 myStack.pop(); 37 tail->next = temp;//tail是当前已经交换好的链表的最后一个节点 38 tail = tail->next; 39 } 40 } 41 else//stack中不够k个节点,顺序不变 42 { 43 pre = NULL; 44 while(!myStack.empty()) 45 { 46 temp = myStack.top(); 47 myStack.pop(); 48 temp->next = pre; 49 pre = temp; 50 } 51 tail->next = pre; 52 } 53 if(!flag) 54 { 55 head = phead->next; 56 flag = true; 57 } 58 } 59 60 return phead->next; 61 } 62 };
因为代码中使用了栈,如果k比较大的话。辅助空间也是比较大的,并且在最后的翻转中,如果个数不足k个,是不需要翻转,而上面的代码需要先拆掉又重新链接起来,相当于做了无用功,因此改进实现如下(网上查找的代码):
class Solution { public: ListNode *reverseKGroup(ListNode *head, int k) { ListNode *newHead = new ListNode(0); newHead->next = head; int cnt = 0; ListNode *cur_node = head; ListNode *last_tail = newHead; while(cur_node) { cnt++; if(cnt == k) { ListNode *cp = cur_node->next; cur_node->next = NULL; last_tail = reverseList(last_tail->next, last_tail); last_tail->next = cp; cur_node = cp; cnt = 0; continue; } cur_node = cur_node->next; } return newHead->next; } ListNode *reverseList(ListNode*head, ListNode*last_tail) { ListNode *next_node = head->next; ListNode *res = head; while(next_node) { ListNode *tmp = next_node->next; next_node->next = head; head = next_node; next_node = tmp; } last_tail->next = head; return res; } };


