三SpringSecurity过滤器核心类
三 SpringSecurity过滤器核心类
spring security是基于AOP和servlet过滤器的安全框架。Spring Security在我们进行用户认证以及授予权限的时候,通过各种各样的拦截器来控制权限的访问。
对于基于HttpRequest的方式对端点进行保护,我们使用一个Filter Chain来保护;对于基于方法调用进行保护,我们使用AOP来保护。本篇重点讲Spring Security中过滤器链的种类及过滤器中如何实现的认证和授权。
SecurityFilterChain的构建过程是在WebSecurity.performBuild(),然后交由FilterChainProxy对象代理。
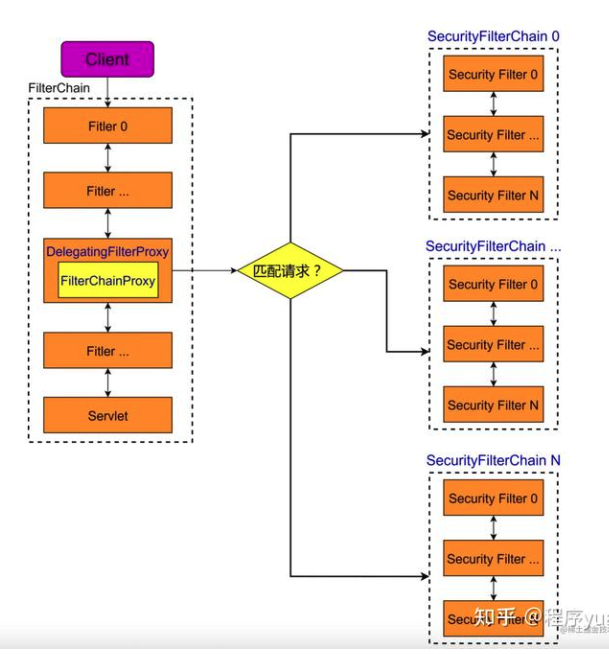
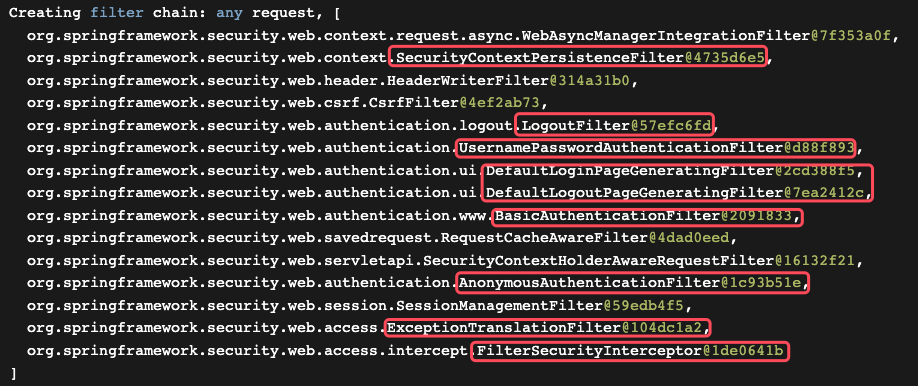
security的过滤器链,如下所示:
3.1 SecurityContextPersistenceFilter
public class SecurityContextPersistenceFilter extends GenericFilterBean {
static final String FILTER_APPLIED = "__spring_security_scpf_applied";
private SecurityContextRepository repo; //实质是本地session管理器
public SecurityContextPersistenceFilter() {
this(new HttpSessionSecurityContextRepository());
}
public SecurityContextPersistenceFilter(SecurityContextRepository repo) {
this.repo = repo;
}
public void doFilter(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res, FilterChain chain)
throws IOException, ServletException {
HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest) req;
HttpServletResponse response = (HttpServletResponse) res;
if (request.getAttribute(FILTER_APPLIED) != null) {
// ensure that filter is only applied once per request
// 如果已经执行过 该过滤器
chain.doFilter(request, response);
return;
}
final boolean debug = logger.isDebugEnabled();
// 标记改过滤器在本次请求过程中已经执行过
request.setAttribute(FILTER_APPLIED, Boolean.TRUE);
if (forceEagerSessionCreation) {
HttpSession session = request.getSession();
if (debug && session.isNew()) {
logger.debug("Eagerly created session: " + session.getId());
}
}
// 从SecurityContextRepository获取到SecurityContext
HttpRequestResponseHolder holder = new HttpRequestResponseHolder(request,
response);
/** 注意:SecurityContextRepository是一个httpsession管理器对象。
对于尚未认证的用户,这里返回一个空的SecurityContext;
如果会话为空,上下文对象为空,或者存储在会话中的上下文对象不是SecurityContext的实例,则生成并返回一个新的上下文对象。
*/
SecurityContext contextBeforeChainExecution = repo.loadContext(holder);
try {
//将SecurityContext存储到SecurityContextHolder,即线程变量threadlocal上
SecurityContextHolder.setContext(contextBeforeChainExecution);
//继续执行Filter
chain.doFilter(holder.getRequest(), holder.getResponse());
}
finally {
SecurityContext contextAfterChainExecution = SecurityContextHolder
.getContext();
// 这时应该 后续所有的Filter都已执行完后,有回到当前Filter中
// 请求执行完成后,清除SecurityContext
SecurityContextHolder.clearContext();
//把SecurityContextHolder的securitycontext保存的用户信息放到session,便于下次请求时共享数据
repo.saveContext(contextAfterChainExecution, holder.getRequest(),
holder.getResponse());
// 移除已执行标记
request.removeAttribute(FILTER_APPLIED);
if (debug) {
logger.debug("SecurityContextHolder now cleared, as request processing completed");
}
}
}
这个过滤器有两个作用:
- 用户发送请求时,从session对象提取用户信息,保存到SecurityContextHolder的securitycontext中
- 当前请求响应结束时,把SecurityContextHolder的securitycontext保存的用户信息放到session,便于下次请求时共享数据;同时将SecurityContextHolder的securitycontext清空
注意:这里SecurityContextRepository是一个httpsession管理器对象,在访问结束时,会话信息保存在这里。
/** 注意:SecurityContextRepository是一个httpsession管理器对象。
对于尚未认证的用户,这里返回一个空的SecurityContext;
如果会话为空,上下文对象为空,或者存储在会话中的上下文对象不是SecurityContext的实例,则生成并返回一个新的上下文对象。
*/
SecurityContext contextBeforeChainExecution = repo.loadContext(holder);
//把SecurityContextHolder的securitycontext保存的用户信息放到session,便于下次请求时共享数据
repo.saveContext(contextAfterChainExecution, holder.getRequest(),
holder.getResponse());
在使用stateless状态时,禁用session功能,此时SecurityContextRepository的load和saveContext无效。所以该过滤器只剩一个作用即把SecurityContextHolder的securitycontext清空。举例来说明为何要清空securitycontext:用户1发送一个请求,由线程M处理,当响应完成线程M放回线程池;用户2发送一个请求,本次请求同样由线程M处理,由于securitycontext没有清空,理应储存用户2的信息但此时储存的是用户1的信息,造成用户信息不符。
3.2 LogoutFilter
处理用户登出请求。
public void doFilter(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res, FilterChain chain)
throws IOException, ServletException {
HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest) req;
HttpServletResponse response = (HttpServletResponse) res;
// 判断请求是否是注销登录 默认匹配/logout请求路径
if (requiresLogout(request, response)) {
Authentication auth = SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication();
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Logging out user '" + auth
+ "' and transferring to logout destination");
}
// 调用登出方法
this.handler.logout(request, response, auth);
// 跳转到登出成功后指定的页面
logoutSuccessHandler.onLogoutSuccess(request, response, auth);
return;
}
//不需要则继续向下执行
chain.doFilter(request, response);
}
3.3 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter---某种token认证的实现
AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter的子类,AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter的作用是,用于提供针对某种类型AbstractAuthenticationToken的用户认证的具体实现
public abstract class AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter extends GenericFilterBean
implements ApplicationEventPublisherAware, MessageSourceAware {
public void doFilter(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res, FilterChain chain)
throws IOException, ServletException {
HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest) req;
HttpServletResponse response = (HttpServletResponse) res;
// 判断请求是否是需要请求用户认证的 默认是 POST /login
if (!requiresAuthentication(request, response)) {
// 如果不是请求认证的请求,则继续执行后面的filter
chain.doFilter(request, response);
return; //直接返回
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Request is to process authentication");
}
// 如果是请求用户认证的请求
Authentication authResult;
try {
// 调用子类的attemptAuthentication实现,尝试去认证,这里调用的是UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter.attemptAuthentication方法
// attemptAuthentication有可能会抛出认证相关的异常 AuthenticationException
authResult = attemptAuthentication(request, response);
// 如果此时返回的结果是null 表示认证尚未完成
if (authResult == null) {
//直接返回,暂停后续chain过滤操作
return;
}
sessionStrategy.onAuthentication(authResult, request, response);
}
catch (InternalAuthenticationServiceException failed) {
logger.error(
"An internal error occurred while trying to authenticate the user.",
failed);
unsuccessfulAuthentication(request, response, failed);
return;
}
catch (AuthenticationException failed) {
// Authentication failed
unsuccessfulAuthentication(request, response, failed);
return;
}
// false
if (continueChainBeforeSuccessfulAuthentication) {
chain.doFilter(request, response);
}
//认证成功处理器
successfulAuthentication(request, response, chain, authResult);
}
public class UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter extends
AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter {
public Authentication attemptAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response) throws AuthenticationException {
if (postOnly && !request.getMethod().equals("POST")) {
throw new AuthenticationServiceException(
"Authentication method not supported: " + request.getMethod());
}
String username = obtainUsername(request);
String password = obtainPassword(request);
if (username == null) {
username = "";
}
if (password == null) {
password = "";
}
username = username.trim();
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authRequest = new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(
username, password);
// Allow subclasses to set the "details" property
setDetails(request, authRequest);
return this.getAuthenticationManager().authenticate(authRequest);
}
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter继承自AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter,处理逻辑在doFilter方法中:
1. 当请求被`UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter`拦截时,判断请求路径是否匹配登录URL,若不匹配继续执行下个过滤器;否则,执行步骤2
2. 调用`attemptAuthentication`方法进行认证。`UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter`重写了`attemptAuthentication`方法,负责读取表单登录参数,委托`AuthenticationManager`进行认证,返回一个认证过的token(null表示认证失败)
3. 判断token是否为null,非null表示认证成功,null表示认证失败
4. 若认证成功,调用`successfulAuthentication`。该方法把认证过的token放入securitycontext供后续请求授权,同时该方法预留一个扩展点(`AuthenticationSuccessHandler.onAuthenticationSuccess方法`),进行认证成功后的处理
5. 若认证失败,同样可以扩展`uthenticationFailureHandler.onAuthenticationFailure`进行认证失败后的处理
6. 只要当前请求路径匹配登录URL,那么无论认证成功还是失败,当前请求都会响应完成,不再执行过滤器链
注意:
只要当前请求路径匹配登录URL,那么无论认证成功还是失败,当前请求都会响应完成,不再执行过滤器链。
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter的attemptAuthentication方法,执行逻辑如下:
1. 从请求中获取表单参数。因为使用`HttpServletRequest.getParameter`方法获取参数,它只能处理Content-Type为application/x-www-form-urlencoded或multipart/form-data的请求,若是application/json则无法获取值
2. 把步骤1获取的账号、密码封装成`UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken`对象,创建未认证的token。`UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken`有两个重载的构造方法,其中`public UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(Object principal, Object credentials)`创建未经认证的token,`public UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(Object principal, Object credentials, Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> authorities)`创建已认证的token
3. 获取认证管理器`AuthenticationManager`,其缺省实现为`ProviderManager`,调用其`authenticate`进行认证
4. `ProviderManager`的`authenticate`是个模板方法,它遍历所有`AuthenticationProvider`,直至找到支持认证某类型token的`AuthenticationProvider`,调用`AuthenticationProvider.authenticate`方法认证,`AuthenticationProvider.authenticate`加载正确的账号、密码进行比较验证
5. `AuthenticationManager.authenticate`方法返回一个已认证的token
3.4 DefaultLoginPageGeneratingFilter
public void doFilter(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res, FilterChain chain)
throws IOException, ServletException {
HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest) req;
HttpServletResponse response = (HttpServletResponse) res;
/**loginPageUrl=/login;logoutSuccessUrl=/login?logout; failureUrl=/login?error */
// 判断是不是登录失败跳转页面
boolean loginError = isErrorPage(request);
// 判断是不是退出登录成功跳转页面
boolean logoutSuccess = isLogoutSuccess(request);
// 判断是否需要需要生成登录页面
if (isLoginUrlRequest(request) || loginError || logoutSuccess) {
String loginPageHtml = generateLoginPageHtml(request, loginError,
logoutSuccess);
response.setContentType("text/html;charset=UTF-8");
response.setContentLength(loginPageHtml.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8).length);
response.getWriter().write(loginPageHtml);
return;
}
chain.doFilter(request, response);
}
如果request访问URL是loginPageUrl=/login;logoutSuccessUrl=/login?logout; failureUrl=/login?error其中之一,生成默认login登录页面并返回。
3.5 DefaultLogoutPageGeneratingFilter
与DefaultLoginPageGeneratingFilter类似,这个过滤器 提供在默认配置下生成一个登出页面的能力
public class DefaultLogoutPageGeneratingFilter extends OncePerRequestFilter {
private RequestMatcher matcher = new AntPathRequestMatcher("/logout", "GET");
private Function<HttpServletRequest, Map<String, String>> resolveHiddenInputs = request -> Collections
.emptyMap();
@Override
protected void doFilterInternal(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain filterChain)
throws ServletException, IOException {
// 判断是否是 /logout 页面
if (this.matcher.matches(request)) {
renderLogout(request, response);// 生成页面返回到浏览器
} else {
// 不是 /logout 继续执行后续的过滤器
filterChain.doFilter(request, response);
}
}
3.6 BasicAuthenticationFilter--Basic认证(较少用)
Basic认证是HTTP协议中的一个基本的认证协议,其基本原理是客户端在请求资源时,将用户名和密码组成一个字符串,进行Base64编码后,放入HTTP请求头中,服务端收到请求后,将用户名和密码解码后进行验证,如果验证成功,返回请求的资源;否则返回错误信息。
Base64编码是一种将二进制数据转换成ASCII字符的编码方式。通过Base64编码后,传输的数据可以在HTTP头中直接传输,避免了一些问题。
Basic认证的HTTP请求头格式如下:
Authorization: Basic 用户名:密码的Base64编码
这个过滤器时用来做BASIC认证的。与表单认证的作用一样,都是一种用户认证的方式。目前该basic认证方法,比较少用。
public abstract class OncePerRequestFilter extends GenericFilterBean {
@Override
public final void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, FilterChain filterChain)
throws ServletException, IOException {
if (!(request instanceof HttpServletRequest) || !(response instanceof HttpServletResponse)) {
throw new ServletException("OncePerRequestFilter just supports HTTP requests");
}
HttpServletRequest httpRequest = (HttpServletRequest) request;
HttpServletResponse httpResponse = (HttpServletResponse) response;
String alreadyFilteredAttributeName = getAlreadyFilteredAttributeName();
boolean hasAlreadyFilteredAttribute = request.getAttribute(alreadyFilteredAttributeName) != null;
if (skipDispatch(httpRequest) || shouldNotFilter(httpRequest)) {
// Proceed without invoking this filter...
filterChain.doFilter(request, response);
}
else if (hasAlreadyFilteredAttribute) {
if (DispatcherType.ERROR.equals(request.getDispatcherType())) {
doFilterNestedErrorDispatch(httpRequest, httpResponse, filterChain);
return;
}
// Proceed without invoking this filter...
filterChain.doFilter(request, response);
}
else {
// Do invoke this filter...
request.setAttribute(alreadyFilteredAttributeName, Boolean.TRUE);
try {
doFilterInternal(httpRequest, httpResponse, filterChain);
}
finally {
// Remove the "already filtered" request attribute for this request.
request.removeAttribute(alreadyFilteredAttributeName);
}
}
}
@Override
protected void doFilterInternal(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain chain)
throws IOException, ServletException {
final boolean debug = this.logger.isDebugEnabled();
//从request请求头中Authorization获取token
String header = request.getHeader("Authorization");
if (header == null || !header.toLowerCase().startsWith("basic ")) {
//如果尚未认证,继续执行
chain.doFilter(request, response);
return;
}
try {
//解析basic的header头信息,获取
String[] tokens = extractAndDecodeHeader(header, request);
assert tokens.length == 2;
//获取用户名
String username = tokens[0];
if (debug) {
this.logger
.debug("Basic Authentication Authorization header found for user '"
+ username + "'");
}
// 从SecurityContextHolder中获取认证信息,判断用户名是否需要认证 如果已经认证过 就不再认证
/**需要认证情况: existingAuth = SecurityContextHolder.getContext()
.getAuthentication()
auth为null,或者auth标注未被认证过、或者auth是authenticationToken但是其和目前用户名不一致、或者auth为AnonymousAuthenticationToken*/
if (authenticationIsRequired(username)) {
//创建新的token
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authRequest = new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(
username, tokens[1]);
authRequest.setDetails(
this.authenticationDetailsSource.buildDetails(request));
// 调用认证接口-----重新执行UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter内的认证逻辑
Authentication authResult = this.authenticationManager
.authenticate(authRequest);
if (debug) {
this.logger.debug("Authentication success: " + authResult);
}
//设置认证到当前线程变量
SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(authResult);
this.rememberMeServices.loginSuccess(request, response, authResult);
// 调用认证成功后的处理方法
onSuccessfulAuthentication(request, response, authResult);
}
}
//认证失败,return
catch (AuthenticationException failed) {
SecurityContextHolder.clearContext();
if (debug) {
this.logger.debug("Authentication request for failed: " + failed);
}
this.rememberMeServices.loginFail(request, response);
onUnsuccessfulAuthentication(request, response, failed);
if (this.ignoreFailure) {
chain.doFilter(request, response);
}
else {
this.authenticationEntryPoint.commence(request, response, failed);
}
return;
}
//认证成功后,继续执行chain
chain.doFilter(request, response);
}
BasicAuthenticationFilter主要完成对于basic模式的登录的认证处理。
3.7 AnonymousAuthenticationFilter
该过滤器的作用:如果在经过该过滤器时,依然没有获取到用户的认证信息,则创建一个匿名用户。
public void doFilter(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res, FilterChain chain)
throws IOException, ServletException {
//如果当前还没有用户认证信息
if (SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication() == null) {
//创建匿名authentication,并传入本地线程变量
SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(
createAuthentication((HttpServletRequest) req));
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Populated SecurityContextHolder with anonymous token: '"
+ SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication() + "'");
}
}
else {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("SecurityContextHolder not populated with anonymous token, as it already contained: '"
+ SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication() + "'");
}
}
//继续向下执行
chain.doFilter(req, res);
}
protected Authentication createAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request) {
//创建AnonymousAuthenticationToken,密码anonymousUser,角色ROLE_ANONYMOUS
AnonymousAuthenticationToken auth = new AnonymousAuthenticationToken(key,
principal, authorities);
auth.setDetails(authenticationDetailsSource.buildDetails(request));
return auth;
}
如果当前用户没有认证,会创建一个匿名token,用户是否能读取资源交由FilterSecurityInterceptor过滤器委托给决策管理器判断是否有权限读取
3.8 ExceptionTranslationFilter----处理filterChain中抛出的异常
ExceptionTranslationFilter主要作用是用来处理 过滤器链中抛出来的权限校验异常。
如果检测到AuthenticationException这种认证异常,过滤器将启动authenticationEntryPoint 跳转到登录页面去认证。
如果检测到AccessDeniedException,过滤器将确定用户是否是匿名用户。如果是匿名用户,authenticationEntryPoint将启动,跳转到登录页面去,如果他们不是匿名用户,过滤器将委托给AccessDeniedHandler。默认情况下,过滤器将使用AccessDeniedHandlerImpl。
public class ExceptionTranslationFilter extends GenericFilterBean {
public void doFilter(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res, FilterChain chain)
throws IOException, ServletException {
HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest) req;
HttpServletResponse response = (HttpServletResponse) res;
try {
// 执行doFilter 继续执行后续过滤器 如果后续的过滤器抛出异常,也会被catch到
chain.doFilter(request, response);
logger.debug("Chain processed normally");
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw ex;// 不处理IO异常
}
catch (Exception ex) {
// Try to extract a SpringSecurityException from the stacktrace
Throwable[] causeChain = throwableAnalyzer.determineCauseChain(ex);
// 先尝试获取AuthenticationException异常
RuntimeException ase = (AuthenticationException) throwableAnalyzer
.getFirstThrowableOfType(AuthenticationException.class, causeChain);
if (ase == null) {
// 在尝试获取AccessDeniedException异常
ase = (AccessDeniedException) throwableAnalyzer.getFirstThrowableOfType(
AccessDeniedException.class, causeChain);
}
if (ase != null) {
if (response.isCommitted()) {
throw new ServletException("Unable to handle the Spring Security Exception because the response is already committed.", ex);
}
//处理异常
handleSpringSecurityException(request, response, chain, ase);
}
else {
// Rethrow ServletExceptions and RuntimeExceptions as-is
if (ex instanceof ServletException) {
throw (ServletException) ex;
}
else if (ex instanceof RuntimeException) {
throw (RuntimeException) ex;
}
// Wrap other Exceptions. This shouldn't actually happen
// as we've already covered all the possibilities for doFilter
throw new RuntimeException(ex);
}
}
}
private void handleSpringSecurityException(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain chain, RuntimeException exception)
throws IOException, ServletException {
//如果是AuthenticationException异常
if (exception instanceof AuthenticationException) {
logger.debug(
"Authentication exception occurred; redirecting to authentication entry point",
exception);
sendStartAuthentication(request, response, chain,
(AuthenticationException) exception);
}
//如果是AccessDeniedException异常
else if (exception instanceof AccessDeniedException) {
//获取当前authentication
Authentication authentication = SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication();
//如果auth为匿名或者rememberMe时
if (authenticationTrustResolver.isAnonymous(authentication) || authenticationTrustResolver.isRememberMe(authentication)) {
logger.debug(
"Access is denied (user is " + (authenticationTrustResolver.isAnonymous(authentication) ? "anonymous" : "not fully authenticated") + "); redirecting to authentication entry point",
exception);
sendStartAuthentication(
request,
response,
chain,
new InsufficientAuthenticationException(
messages.getMessage(
"ExceptionTranslationFilter.insufficientAuthentication",
"Full authentication is required to access this resource")));
}
//此时用户已经登录,但是仍然AccessDeniedException,说明无权访问
else {
logger.debug(
"Access is denied (user is not anonymous); delegating to AccessDeniedHandler",
exception);
//3.8.2 accessDeniedHandler 自己实现,返回错误码、错误信息
//调用accessDeniedHandler处理拒绝访问逻辑
accessDeniedHandler.handle(request, response,
(AccessDeniedException) exception);
}
}
}
3.8.1 authenticationEntryPoint处理认证异常-- 需要自己实现(跳转到login)
如果检测到AuthenticationException这种认证异常,过滤器将启动authenticationEntryPoint 跳转到登录页面去认证。
如果检测到AccessDeniedException,过滤器将确定用户是否是匿名用户。如果是匿名用户,authenticationEntryPoint将启动,跳转到登录页面去,
protected void sendStartAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain chain,
AuthenticationException reason) throws ServletException, IOException {
SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(null);
requestCache.saveRequest(request, response);
logger.debug("Calling Authentication entry point.");
//3.8.1 authenticationEntryPoint 需要自己实现(跳转到login)
//启动authenticationEntryPoint,跳转到login页面
authenticationEntryPoint.commence(request, response, reason);
}
3.8.2 accessDeniedHandler处理授权异常-- 自己实现,返回错误码、错误信息
这里可以自定义实现,完成spring security的全局异常处理,返回前端可以识别、友好的错误状态码、错误信息
3.9 FilterSecurityInterceptor
他的主要作用是判断当前的用户用没有权限可以访问目标资源。
如果用户没有权限访问当前资源 会抛出 AccessDeniedException。异常会被ExceptionTranslationFilter处理。
public class FilterSecurityInterceptor extends AbstractSecurityInterceptor implements Filter {
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response,
FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException {
FilterInvocation fi = new FilterInvocation(request, response, chain);
invoke(fi);
}
public void invoke(FilterInvocation fi) throws IOException, ServletException {
//判断当前request是否执行过该处理器
if ((fi.getRequest() != null)
&& (fi.getRequest().getAttribute(FILTER_APPLIED) != null)
&& observeOncePerRequest) {
// filter already applied to this request and user wants us to observe
// once-per-request handling, so don't re-do security checking
//当前filter保证request请求只被执行一次,超过的继续向chain下执行
fi.getChain().doFilter(fi.getRequest(), fi.getResponse());
}
else {
// request第一次执行filter,执行check
if (fi.getRequest() != null && observeOncePerRequest) {
fi.getRequest().setAttribute(FILTER_APPLIED, Boolean.TRUE); //设置已经执行过
}
//调用前
InterceptorStatusToken token = super.beforeInvocation(fi);
//调用
try {
fi.getChain().doFilter(fi.getRequest(), fi.getResponse());
}
finally {
//调用回调
super.finallyInvocation(token);
}
//调用后
super.afterInvocation(token, null);
}
}
public abstract class AbstractSecurityInterceptor implements InitializingBean,
ApplicationEventPublisherAware, MessageSourceAware {
protected InterceptorStatusToken beforeInvocation(Object object) {
Assert.notNull(object, "Object was null");
final boolean debug = logger.isDebugEnabled();
if (!getSecureObjectClass().isAssignableFrom(object.getClass())) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"Security invocation attempted for object "
+ object.getClass().getName()
+ " but AbstractSecurityInterceptor only configured to support secure objects of type: "
+ getSecureObjectClass());
}
// 1. 通过 SecurityMetadataSource 获取属性,用来给认证授权对象添加配置属性(ConfigAttribute)
Collection<ConfigAttribute> attributes = this.obtainSecurityMetadataSource()
.getAttributes(object);
// 1.1 属性为空,啥都不做,返回
if (attributes == null || attributes.isEmpty()) {
if (rejectPublicInvocations) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"Secure object invocation "
+ object
+ " was denied as public invocations are not allowed via this interceptor. "
+ "This indicates a configuration error because the "
+ "rejectPublicInvocations property is set to 'true'");
}
if (debug) {
logger.debug("Public object - authentication not attempted");
}
publishEvent(new PublicInvocationEvent(object));
return null; // no further work post-invocation
}
if (debug) {
logger.debug("Secure object: " + object + "; Attributes: " + attributes);
}
// auth为null,未登录
if (SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication() == null) {
credentialsNotFound(messages.getMessage(
"AbstractSecurityInterceptor.authenticationNotFound",
"An Authentication object was not found in the SecurityContext"),
object, attributes);
}
// 2. 认证,成功后并放入 SecurityContext
/**看是否有必要认证:
如果当前线程变量中authentication已经认证过,直接返回;
如果auth不为null,但是尚未认证过,authenticationManager.authenticate(authentication),然后存入线程变量*/
Authentication authenticated = authenticateIfRequired();
// 3. 授权 ,通过 accessDecisionManager 做acl
try {
this.accessDecisionManager.decide(authenticated, object, attributes);
}
catch (AccessDeniedException accessDeniedException) {
publishEvent(new AuthorizationFailureEvent(object, attributes, authenticated,
accessDeniedException));
throw accessDeniedException;
}
if (debug) {
logger.debug("Authorization successful");
}
if (publishAuthorizationSuccess) {
publishEvent(new AuthorizedEvent(object, attributes, authenticated));
}
// Attempt to run as a different user
Authentication runAs = this.runAsManager.buildRunAs(authenticated, object,
attributes);
if (runAs == null) {
if (debug) {
logger.debug("RunAsManager did not change Authentication object");
}
// no further work post-invocation
return new InterceptorStatusToken(SecurityContextHolder.getContext(), false,
attributes, object);
}
else {
if (debug) {
logger.debug("Switching to RunAs Authentication: " + runAs);
}
SecurityContext origCtx = SecurityContextHolder.getContext();
SecurityContextHolder.setContext(SecurityContextHolder.createEmptyContext());
SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(runAs);
// need to revert to token.Authenticated post-invocation
return new InterceptorStatusToken(origCtx, true, attributes, object);
}
}
3.9.1 AccessDecisionManager
/** this.accessDecisionManager.decide(authenticated, object, attributes);
authenticated为认证过的auth;
object为new FilterInvocation(request, response, chain);
attributes为this.obtainSecurityMetadataSource().getAttributes(object),即给认证授权对象添加配置属性(ConfigAttribute) */
@Override
public void decide(Authentication auth, Object o, Collection<ConfigAttribute> collection) throws AccessDeniedException, AuthenticationException {
//当前用户所具有的权限
Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> authorities = auth.getAuthorities();
//配置的属性
Iterator<ConfigAttribute> iterator = collection.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
ConfigAttribute ca = iterator.next();
//当前请求需要登录, “ROLE_LOGIN” 是 SecurityMetadataSource 填充的,表示需要登录!
String needRole = ca.getAttribute();
if ("ROLE_LOGIN".equals(needRole)) {
// 未登录
if (auth instanceof AnonymousAuthenticationToken) {
throw new BadCredentialsException("用户未登录");
} else {
// 已登录返回
return;
}
}
// admin权限也返回、当前用户权限匹配配置的权限也返回
for (GrantedAuthority authority : authorities) {
if (authority.getAuthority().equals(needRole) ||
Constant.ROLE_ADMIN.equals(authority.getAuthority())) {
return;
}
}
}
// 权限不足
throw new AccessDeniedException("权限不足!");
}
抛出的 BadCredentialsException 和 AccessDeniedException 会有上面的异常filter 处理。




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号