三TCC-transaction分布式事务关键组件--2事务拦截器
三 TCC-transaction分布式事务关键组件--2事务拦截器
2.2.3 事务拦截器
TCC有两个拦截器:
CompensableTransactionInterceptor:可补偿事务拦截器
用于tcc事务的流程执行begin(try)、commit(confirm)、rollback(cancel)
ResourceCoordinatorInterceptor:资源协调拦截器
用于记录tcc事务的Participant(参与方)
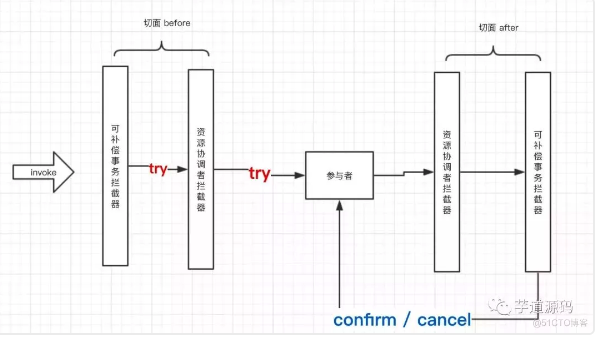
这两个拦截器,例如ResourceCoordinatorInterceptor,其基于@Compensable注解在try方法上、@Aspect注解在aspect类上作为切面类,能够拦截事务的try方法。在参与者的try方法前后是around切面逻辑,拦截器在try目标方法执行前后,分别调用两个拦截器内的方法,实现TCC事务的透明化执行过程。
@Aspect
public abstract class ResourceCoordinatorAspect {
private ResourceCoordinatorInterceptor resourceCoordinatorInterceptor = new ResourceCoordinatorInterceptor();
@Pointcut("@annotation(org.mengyun.tcctransaction.api.Compensable) || @annotation(org.mengyun.tcctransaction.api.EnableTcc)")
public void transactionResourcePointcut() {
}
@Around("transactionResourcePointcut()")
public Object interceptTransactionResourceMethodWithCompensableAnnotation(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable {
Method method = ((MethodSignature) pjp.getSignature()).getMethod();
Compensable compensable = method.getAnnotation(Compensable.class);
return interceptTransactionContextMethod(new AspectJTransactionMethodJoinPoint(pjp, compensable, ThreadLocalTransactionContextEditor.class));
}
0 @Compensable注解
该注解标注在参与者的try方法上,并指定cancel/confirm方法名、事务的传播级别
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target({ElementType.METHOD})
public @interface Compensable {
//指定事务传播级别
public Propagation propagation() default Propagation.REQUIRED;
//指定cc方法
public String confirmMethod() default "";
public String cancelMethod() default "";
//是否异步执行
public boolean asyncConfirm() default false;
public boolean asyncCancel() default false;
}
传播级别定义:
public enum Propagation {
/**
* 支持当前事务,如果当前没有事务,就新建一个事务。
*/
REQUIRED(0),
/**
* 支持当前事务,如果当前没有事务,就以非事务方式执行。
*/
SUPPORTS(1),
/**
* 支持当前事务,如果当前没有事务,就抛出异常。
*/
MANDATORY(2),
/**
* 新建事务,如果当前存在事务,把当前事务挂起。
*/
REQUIRES_NEW(3);
1 CompensableTransactionInterceptor可补偿事务拦截器
用于tcc事务的流程执行begin(try)、commit(confirm)、rollback(cancel)
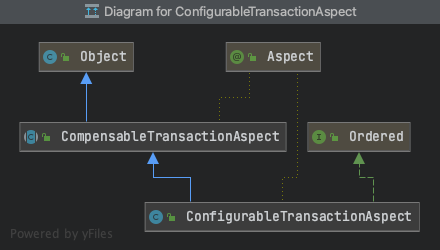
(1)CompensableTransactionAspect切面类
//配置当前类为aspect切面类(springAOP)
@Aspect
public abstract class CompensableTransactionAspect {
//切面类内对目标方法拦截,需要调用拦截器执行具体的TCC框架逻辑
private CompensableTransactionInterceptor compensableTransactionInterceptor = new CompensableTransactionInterceptor();
//设置拦截器内的TransactionManager
public void setTransactionManager(TransactionManager transactionManager) {
this.compensableTransactionInterceptor.setTransactionManager(transactionManager);
}
//配置@Compensable标注的方法为切点
@Pointcut("@annotation(org.mengyun.tcctransaction.api.Compensable)")
public void compensableTransactionPointcut() {
}
//在切点处,配置around环绕执行的逻辑
@Around("compensableTransactionPointcut()")
public Object interceptCompensableMethod(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable {
//获取@Compensable注解的方法对象
Method method = ((MethodSignature) pjp.getSignature()).getMethod();
Compensable compensable = method.getAnnotation(Compensable.class);
return compensableTransactionInterceptor.interceptCompensableMethod(new AspectJTransactionMethodJoinPoint(pjp, compensable, ThreadLocalTransactionContextEditor.class));
}
//获取当前切面执行的优先级
public abstract int getOrder();
}
(2)ConfigurableTransactionAspect 切面配置类(执行优先级)
@Aspect
public class ConfigurableTransactionAspect extends CompensableTransactionAspect implements Ordered {
@Override
public int getOrder() {
return Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE; //指定当前切面的优先级
}
@Autowired
public void setTransactionManager(TransactionManagerFactory transactionManagerFactory) {
super.setTransactionManager(transactionManagerFactory.getTransactionManager());
}
}
当前切面配置类,主要是实现orderde接口,定义切面的优先级Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE(ResourceCoordinatorInterceptor配置的优先级为Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE+1,所以执行时,位于后面,先执行CompensableTransactionAspect)
(3)CompensableTransactionInterceptor拦截器
public class CompensableTransactionInterceptor {
//拦截器中持有transactionManager
private TransactionManager transactionManager;
public void setTransactionManager(TransactionManager transactionManager) {
this.transactionManager = transactionManager;
}
public Object interceptCompensableMethod(TransactionMethodJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable {
//获取当前transactionManager的本地线程变量上事务队列的首部transaction
Transaction transaction = transactionManager.getCurrentTransaction();
//创建可补偿方法执行上下文对象
CompensableMethodContext compensableMethodContext = new CompensableMethodContext(pjp, transaction);
//如果方法被@Compensable注解&transaction context为null&transaction对象为null,那么ParticipantRole为ROOT根角色
//如果方法被@Compensable注解&transaction context存在&transaction对象为null,那么表示已经创建transaction context事务上下文,此时ParticipantRole的为privider提供者角色
//TAG1 compensableMethodContext.getParticipantRole()
switch (compensableMethodContext.getParticipantRole()) {
case ROOT: //执行root根事务方法
//TAG2 rootMethodProceed
return rootMethodProceed(compensableMethodContext);
case PROVIDER: //执行provider提供者事务方法
//TAG3 providerMethodProceed
return providerMethodProceed(compensableMethodContext);
default: //默认不处理,继续目标方法try的执行
return compensableMethodContext.proceed();
}
}
这里,CompensableTransactionInterceptor拦截器,在被@Compensable标注的try方法执行时,通过切面类拦截,然后调用此处拦截器方法:
1 获取当前transactionManager的本地线程变量上事务队列的首部transaction;
2 创建CompensableMethodContext;
3 根据TCC方法上下文,判断当前参与者的角色,是ROOT(事务发起者)还是PROVIDER(分支事务的参与者)------根据不同参与者类型,执行不同的事务处理
TAG1 compensableMethodContext.getParticipantRole()
该方法,是通过transactionContext、compensable、transaction三个对象的存在情况,判断当前参与者的角色--是ROOT发起根事务的角色、还是PRIVIDER分支事务参与者的角色。
判断参与者角色是ROOT还是PROVIDER原则:
//如果方法被@Compensable注解&transaction context为null&transaction对象为null,那么ParticipantRole为ROOT根角色
//如果方法被@Compensable注解&transaction context存在&transaction对象为null,那么表示已经创建transaction context事务上下文,此时ParticipantRole的为privider提供者角色
public class CompensableMethodContext {
//事务方法连结点(具体详看spring部分)
TransactionMethodJoinPoint pjp = null;
TransactionContext transactionContext = null;
Compensable compensable = null;
private Transaction transaction = null;
public ParticipantRole getParticipantRole() {
// 1 如果方法是@Compensable注释的,则表示需要tcc事务,如果没有活动事务,则需要require new。
// 2 If方法没有@Compensable注解,但TransactionContext存在:
//2.1如果有活动事务,则表示需要参与者tcc事务。如果transactionContext为空,那么它将事务登记为CONSUMER角色;
// 2.2 如果没有活动事务activeTransaction,表示有另一个方法被调用,因为Consumer已经登记为了事务,这个方法不需要登记为参与者。
//如果方法被@Compensable注解&transaction context为null&transaction对象为null,那么ParticipantRole为ROOT根角色
if (compensable != null && transaction == null && transactionContext == null) {
return ParticipantRole.ROOT;
}
//如果方法被@Compensable注解&transaction context存在&transaction对象为null,那么表示已经创建transaction context事务上下文,此时ParticipantRole的为privider提供者角色
if (compensable != null && transaction == null && transactionContext != null) {
return ParticipantRole.PROVIDER;
}
//不进行事务处理
return ParticipantRole.NORMAL;
}
public Object proceed() throws Throwable {
return this.pjp.proceed();
}
TAG2 rootMethodProceed发起TCC流程
当ParticipantRole为ROOT时,发起根事务,开启TCC流程:
private Object rootMethodProceed(CompensableMethodContext compensableMethodContext) throws Throwable {
Object returnValue = null;
//事务对象
Transaction transaction = null;
//是否异步执行confirm/cancel
boolean asyncConfirm = compensableMethodContext.getAnnotation().asyncConfirm();
boolean asyncCancel = compensableMethodContext.getAnnotation().asyncCancel();
try {
//发起根root事务
transaction = transactionManager.begin(compensableMethodContext.getUniqueIdentity());
try {
//执行方法原逻辑,即try逻辑
returnValue = compensableMethodContext.proceed();
} catch (Throwable tryingException) {
try {
//当原逻辑执行失败时,即try阶段失败---回滚
transactionManager.rollback(asyncCancel);
} catch (Exception rollbackException) {
logger.warn("compensable transaction rollback failed, recovery job will try to rollback later", rollbackException);
}
throw tryingException;
}
//当原逻辑执行成功时,即try阶段成功,提交事务
transactionManager.commit(asyncConfirm);
} finally {
//将事物从当前线程事务队列移除
transactionManager.cleanAfterCompletion(transaction);
}
return returnValue;
}
主要逻辑:
1 transactionManager.begin发起根事务;
2 compensableMethodContext.proceed()执行try;
2.1 如果try失败抛异常,transactionManager.rollback(asyncCancel)回滚
3 transactionManager.commit(asyncConfirm) try执行成功,commit提交事务;
4 transactionManager.cleanAfterCompletion(transaction)将transaction从事务管理器transactionManager的本地线程变量的事务队列中移除;
5 返回结果;
TAG3 providerMethodProceed服务提供者参与TCC流程
当参与者角色为PROVIDER时,执行该方法:(ROOT是发起事务,在TCC三个阶段开始前,所以不需要通过compensableMethodContext.getTransactionContext().getStatus()判断当前所处的阶段;但是PROVIDER角色时,参与者参与事务,因此需要知道自己当前处于当前事务的哪个阶段执行过程TRYING、CONFIRMING、CANCELLING。
private Object providerMethodProceed(CompensableMethodContext compensableMethodContext) throws Throwable {
Transaction transaction = null;
//是否异步执行cc
boolean asyncConfirm = compensableMethodContext.getAnnotation().asyncConfirm();
boolean asyncCancel = compensableMethodContext.getAnnotation().asyncCancel();
try {
//获取TransactionContext().getStatus()中,当前TCC执行的阶段
switch (compensableMethodContext.getTransactionContext().getStatus()) {
/** ……………………………………………………………………………………………………TRYING………………………………………………………………………………………………………………*/
case TRYING:
//如果trying阶段,需要propagationNewBegin传播并发起分支事务(包括创建transaction、存储、注册)
transaction = transactionManager.propagationNewBegin(compensableMethodContext.getTransactionContext());
Object result = null;
try {
//执行原try逻辑
result = compensableMethodContext.proceed();
//设置transactionManager上事务队列首个事务状态TRY_SUCCESS,并在数据库中更新
transactionManager.changeStatus(TransactionStatus.TRY_SUCCESS);
} catch (Throwable e) {
try {
//如果try执行失败,设置transactionManager上事务队列首个事务状态为TRY_FAILED,并更新数据库中数据
transactionManager.changeStatus(TransactionStatus.TRY_FAILED);
} catch (Exception ignore) {
//ignore
}
throw e;
}
return result;
/** ……………………………………………………………………………………………………CONFIRMING………………………………………………………………………………………………………………*/
case CONFIRMING:
try {
//获取传播分支事务
transaction = transactionManager.propagationExistBegin(compensableMethodContext.getTransactionContext());
//执行提交
transactionManager.commit(asyncConfirm);
} catch (NoExistedTransactionException excepton) {
//the transaction has been commit,ignore it.
logger.warn("no existed transaction found at CONFIRMING stage, will ignore and confirm automatically. transaction xid:{}", compensableMethodContext.getTransactionContext().getXid());
}
break;
/** ……………………………………………………………………………………………………CANCELLING………………………………………………………………………………………………………………*/
case CANCELLING:
try {
//从消费者端传递过来的,分支事务branch的状态status
ParticipantStatus transactionStatusFromConsumer = compensableMethodContext.getTransactionContext().getParticipantStatus();
//获取传播分支事务
transaction = transactionManager.propagationExistBegin(compensableMethodContext.getTransactionContext());
// 1 只有transaction's status 处于TRY_SUCCESS、TRY_FAILED、CANCELLING stage,才能rollback(表示第一阶段的try执行结束,所以,单纯的trying状态,是不能够rollback的)
// 2 如果 transactionStatusFromConsumer 是TRY_SUCCESS,也表示第一阶段try执行结束, 无论当前transaction的状态是否是trying,都可以rollback
// (原因:transaction's status is TRYING while transactionStatusFromConsumer is TRY_SUCCESS 可能会发生的,就是当 transaction's changeStatus 是异步执行时.)
if (transaction.getStatus().equals(TransactionStatus.TRY_SUCCESS)
|| transaction.getStatus().equals(TransactionStatus.TRY_FAILED)
|| transaction.getStatus().equals(TransactionStatus.CANCELLING)
|| ParticipantStatus.TRY_SUCCESS.equals(transactionStatusFromConsumer)) {
transactionManager.rollback(asyncCancel);
} else {
//in this case, transaction's Status is TRYING and transactionStatusFromConsumer is TRY_FAILED
// this may happen if timeout exception throws during rpc call.
throw new IllegalTransactionStatusException("Branch transaction status is TRYING, cannot rollback directly, waiting for recovery job to rollback.");
}
} catch (NoExistedTransactionException exception) {
//the transaction has been rollback,ignore it.
logger.info("no existed transaction found at CANCELLING stage, will ignore and cancel automatically. transaction xid:{}", compensableMethodContext.getTransactionContext().getXid());
}
break;
}
} finally {
//清理当前事务对象
transactionManager.cleanAfterCompletion(transaction);
}
Method method = compensableMethodContext.getMethod();
return ReflectionUtils.getNullValue(method.getReturnType());
}
对于服务提供者provider,在事务执行过程的逻辑如下:
switch (compensableMethodContext.getTransactionContext().getStatus()) {
TRYING:
1 propagationNewBegin传播并发起分支事务------该方法调用前提:TransactionStatus.TRYING&ParticipantRole.PROVIDER;
2 compensableMethodContext.proceed()执行try方法逻辑;
3 transactionManager.changeStatus(TransactionStatus.TRY_SUCCESS) try成功,修改transaction状态,并update持久存储内;
2.1 如果try失败,transactionManager.changeStatus(TransactionStatus.TRY_FAILED),修改transaction状态,并update;
4 return;
CONFIRMING:
1 propagationExistBegin传播并获取分支事务------该方法调用前提:TransactionStatus.CONFIRMING&ParticipantRole.PROVIDER;
2 transactionManager.commit(asyncConfirm)提交;
(confirm失败的逻辑,在transactionManager中,会update更新transaction)
CANCELLING:
1 propagationExistBegin传播并获取分支事务------该方法调用前提:TransactionStatus.CANCELLING&ParticipantRole.PROVIDER;
2 可以执行rollback的条件和情况如下:
// 1 只有transaction's status 处于TRY_SUCCESS、TRY_FAILED、CANCELLING stage,才能rollback(表示第一阶段的try执行结束,所以,单纯的trying状态,是不能够rollback的)
// 2 如果 transactionStatusFromConsumer 是TRY_SUCCESS,也表示第一阶段try执行结束, 无论当前transaction的状态是否是trying,都可以rollback
// (原因:transaction's status is TRYING while transactionStatusFromConsumer is TRY_SUCCESS 可能会发生的,就是当 transaction's changeStatus 是异步执行时.)
finally{
transactionManager.cleanAfterCompletion(transaction);清理事务
}
2 ResourceCoordinatorInterceptor资源协调拦截器
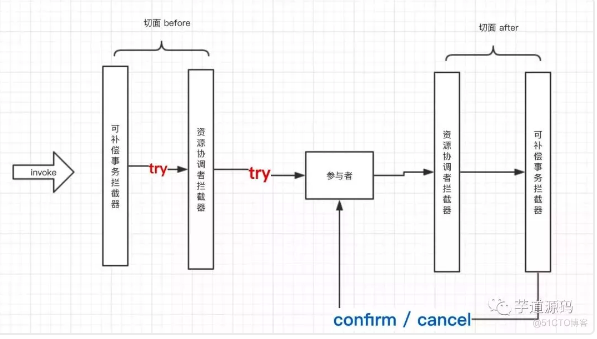
用于记录tcc事务的Participant(参与方),ResourceCoordinatorInterceptor只在try阶段使用,负责participant的创建、添加入transaction、pjp.proceed执行try方法、根据try执行是否成功设置participant的执行状态。负责参与者的管理。
(1)ResourceCoordinatorAspect 切面类
@Aspect
public abstract class ResourceCoordinatorAspect {
private ResourceCoordinatorInterceptor resourceCoordinatorInterceptor = new ResourceCoordinatorInterceptor();
@Pointcut("@annotation(org.mengyun.tcctransaction.api.Compensable) || @annotation(org.mengyun.tcctransaction.api.EnableTcc)")
public void transactionResourcePointcut() {
}
@Around("transactionResourcePointcut()")
public Object interceptTransactionResourceMethodWithCompensableAnnotation(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable {
Method method = ((MethodSignature) pjp.getSignature()).getMethod();
Compensable compensable = method.getAnnotation(Compensable.class);
return interceptTransactionContextMethod(new AspectJTransactionMethodJoinPoint(pjp, compensable, ThreadLocalTransactionContextEditor.class));
}
public Object interceptTransactionContextMethod(TransactionMethodJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable {
return resourceCoordinatorInterceptor.interceptTransactionContextMethod(pjp);
}
public void setTransactionManager(TransactionManager transactionManager) {
this.resourceCoordinatorInterceptor.setTransactionManager(transactionManager);
}
public abstract int getOrder();
}
具体分析和可补偿事务拦截器相同,省略。
(2)ConfigurableCoordinatorAspect切面配置类(执行优先级)
@Aspect
public class ConfigurableCoordinatorAspect extends ResourceCoordinatorAspect implements Ordered {
@Override
public int getOrder() {
return Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE + 1;
}
@Autowired
public void setTransactionManager(TransactionManagerFactory transactionManagerFactory) {
super.setTransactionManager(transactionManagerFactory.getTransactionManager());
}
}
切面优先级为Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE + 1,其在可补偿事务拦截器切面后执行。
(3)ResourceCoordinatorInterceptor资源协调拦截器
这个拦截器两个作用:
1 负责participant参与者对象的创建(条件:事务transaction对象不为null&&transaction.getStatus()事务状态为TRYING),然后将participant加入transaction的list中,并update入持久化存储;
2 并在try执行过程中,如果执行成功,设置ParticipantStatus.TRY_SUCCESS;如果失败,ParticipantStatus.TRY_FAILED。
总结:
ResourceCoordinatorInterceptor只在try阶段使用,负责participant的创建、添加入transaction、pjp.proceed执行try方法、根据try执行是否成功设置participant的执行状态。负责参与者的管理。
public class ResourceCoordinatorInterceptor {
private TransactionManager transactionManager;
public void setTransactionManager(TransactionManager transactionManager) {
this.transactionManager = transactionManager;
}
public Object interceptTransactionContextMethod(TransactionMethodJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable {
Transaction transaction = transactionManager.getCurrentTransaction();
if (transaction != null && transaction.getStatus().equals(TransactionStatus.TRYING)) { //1
//当事务状态为trying时,添加事务参与者
Participant participant = enlistParticipant(pjp);
Object result = null;
//创建TransactionStatus.TRYING, ParticipantStatus.TRYING两个状态的事务上下文TransactionContext
TransactionContext transactionContext = new TransactionContext(transaction.getRootDomain(), transaction.getRootXid(), participant.getXid(), TransactionStatus.TRYING, ParticipantStatus.TRYING);
FactoryBuilder.factoryOf(participant.getTransactionContextEditorClass()).getInstance().set(transactionContext, pjp.getTarget(), pjp.getMethod(), pjp.getArgs());
try {
//执行try方法原逻辑
result = pjp.proceed(pjp.getArgs());
//如果执行成功,设置参与者participantStatus为TRY_SUCCESS
participant.setStatus(ParticipantStatus.TRY_SUCCESS);
} catch (Throwable e) {
participant.setStatus(ParticipantStatus.TRY_FAILED);
//if root transaction, here no need persistent transaction
// because following stage is rollback, transaction's status is changed to CANCELING and save
// transactionManager.update(participant);
throw e;
} finally {
FactoryBuilder.factoryOf(participant.getTransactionContextEditorClass()).getInstance().clear(transactionContext, pjp.getTarget(), pjp.getMethod(), pjp.getArgs());
}
return result;
} //1
//如果不需要加入participant对象到transaction,那么执行方法原逻辑(即拦截器链,继续向下执行,try方法)
return pjp.proceed(pjp.getArgs());
}
private Participant enlistParticipant(TransactionMethodJoinPoint pjp) {
Transaction transaction = transactionManager.getCurrentTransaction();
CompensableMethodContext compensableMethodContext = new CompensableMethodContext(pjp, transaction);
String confirmMethodName = compensableMethodContext.getConfirmMethodName();
String cancelMethodName = compensableMethodContext.getCancelMethodName();
Class<? extends TransactionContextEditor> transactionContextEditorClass = compensableMethodContext.getTransactionContextEditorClass();
TransactionXid xid = TransactionXid.withUniqueIdentity(null);
Class targetClass = compensableMethodContext.getDeclaredClass();
InvocationContext invocationContext = new InvocationContext(targetClass,
confirmMethodName,
cancelMethodName,
compensableMethodContext.getMethod().getParameterTypes(), compensableMethodContext.getArgs());
//构造参与者Participant
Participant participant =
new Participant(
transaction.getRootDomain(),
transaction.getRootXid(),
xid,
invocationContext,
transactionContextEditorClass);
//将participant加入transactionManager的当前transaction的list<Participant>中,然后update
transactionManager.enlistParticipant(participant);
return participant;
}
}




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号