五Dubbo服务引用源码分析--4网络处理-4.3consumer端接收响应
五Dubbo服务引用源码分析--4网络处理-4.3consumer端接收响应
5.3.4 consumer端接收响应
然后,consumer端返回到DubboInvoker.doInvoke过程中
DubboInvoker
@Override
protected Result doInvoke(final Invocation invocation) throws Throwable {
/** ………………………………………………………………向RpcInvocation中添加属性信息……………………………………………………*/
RpcInvocation inv = (RpcInvocation) invocation;
final String methodName = RpcUtils.getMethodName(invocation);
//getUrl()=dubbo://192.168.0.101:20880/com.alibaba.dubbo.demo.DemoService?anyhost=true&application=demotest-consumer&bean.name=com.alibaba.dubbo.demo.DemoService&check=false&dubbo=2.0.2&generic=false&interface=com.alibaba.dubbo.demo.DemoService&methods=getPermissions&organization=dubbox&owner=programmer&pid=42298&qos.enable=false®ister.ip=192.168.0.101&remote.timestamp=1672565419921&side=consumer×tamp=1672565435211-----服务提供者providerUrl
//设置RpcInvocation的path=RpcInvocation
inv.setAttachment(Constants.PATH_KEY, getUrl().getPath());
inv.setAttachment(Constants.VERSION_KEY, version);
/** ……………………………………获取客户端………………………………………………*/
ExchangeClient currentClient;
if (clients.length == 1) {
currentClient = clients[0];
} else {
currentClient = clients[index.getAndIncrement() % clients.length];//如果多个client,递增选择下一个
}
try {
boolean isAsync = RpcUtils.isAsync(getUrl(), invocation);//false,默认为非异步--同步
boolean isOneway = RpcUtils.isOneway(getUrl(), invocation);//false,默认非单向--双向(双向有返回值)
//默认1000ms延迟
int timeout = getUrl().getMethodParameter(methodName, Constants.TIMEOUT_KEY, Constants.DEFAULT_TIMEOUT);
/**…………………………………………………………………………………………同步、异步处理……………………………………………………………………………………………………………… */
//TAG2.1 请求服务同步、异步、是否需要返回值的处理
//不需要返回值的同步请求
if (isOneway) {
boolean isSent = getUrl().getMethodParameter(methodName, Constants.SENT_KEY, false);
//发起同步请求
currentClient.send(inv, isSent);
RpcContext.getContext().setFuture(null);//设置RpcContext.future为null;
return new RpcResult();
} else if (isAsync) {
//发起异步异步请求
ResponseFuture future = currentClient.request(inv, timeout);
//将future包装为FutureAdapter,并传入RpcContext.future
RpcContext.getContext().setFuture(new FutureAdapter<Object>(future));
return new RpcResult();
} else {
//需要返回值的同步请求
RpcContext.getContext().setFuture(null);///设置RpcContext.future为null
/** …………………………………………………………………………………………客户端exchangeClient.request远程调用……………………………………………………………………………………*/
//TAG2.2 ReferenceCountExchangeClient.request(inv,timeout)
//发送异步请求得到ResponseFuture,然后执行ResponseFuture.get(),阻塞consumer线程,获取执行结果
return (Result) currentClient.request(inv, timeout).get();
}
} catch (TimeoutException e) {
throw new RpcException(RpcException.TIMEOUT_EXCEPTION, "Invoke remote method timeout. method: " + invocation.getMethodName() + ", provider: " + getUrl() + ", cause: " + e.getMessage(), e);
} catch (RemotingException e) {
throw new RpcException(RpcException.NETWORK_EXCEPTION, "Failed to invoke remote method: " + invocation.getMethodName() + ", provider: " + getUrl() + ", cause: " + e.getMessage(), e);
}
}
TAG1 defaultFuture.get()---阻塞等待response响应(lock--condition)
在目前Dubbo2.6.5版本上,DubboInvoker.doInvoke方法中,currentClient.request(inv, timeout)获取到DefaultFuture对象。然后,对于需要返回值的同步请求,需要执行(Result) currentClient.request(inv, timeout).get(),这里defaultFuture.get()会阻塞等待response返回到consumer端的DefaultFuture上,然后将结果包装成rpcResult返回。
HeaderExchangeChannel
@Override
public ResponseFuture request(Object request, int timeout) throws RemotingException {
if (closed) {
throw new RemotingException(this.getLocalAddress(), null, "Failed to send request " + request + ", cause: The channel " + this + " is closed!");
}
/** …………………………………………………………………………创建请求request……………………………………………………*/
Request req = new Request();
req.setVersion(Version.getProtocolVersion());
req.setTwoWay(true);//设置需要返回值
req.setData(request);//设置请求的数据
/**………………………………………………………………………………………………………………同步转异步……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… */
//设置超时时间到defaultFuture中
DefaultFuture future = new DefaultFuture(channel, req, timeout);//创建默认future,实现异步访问功能
try {
//TAG2.2.1.1 NettyClient.send
//nettyClient.send
channel.send(req);
} catch (RemotingException e) {
future.cancel();//出现异常,取消调用
throw e;
}
return future;
}
在consumer端发送请求时,同步转异步所创建的DefaultFuture类,如下:
public class DefaultFuture implements ResponseFuture {
//request.id:channel,缓存通信通道 :key为 request Id 用于标识请求, Value 为这次请求会和提供者之间的Channel
private static final Map<Long, Channel> CHANNELS = new ConcurrentHashMap<Long, Channel>();
// 缓存future :key 为request Id, Value 为这次请求的 DefaultFuture
private static final Map<Long, DefaultFuture> FUTURES = new ConcurrentHashMap<Long, DefaultFuture>();
static {
Thread th = new Thread(new RemotingInvocationTimeoutScan(), "DubboResponseTimeoutScanTimer");
th.setDaemon(true);
th.start();
}
private final long id; //requestId
private final Channel channel;//当前请求的的通道
private final Request request;//当前请求
private final int timeout;//请求超时时间
private final Lock lock = new ReentrantLock(); //独占锁
private final Condition done = lock.newCondition(); //lock的条件变量
private final long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
private volatile long sent;
private volatile Response response;//请求的返回对象
private volatile ResponseCallback callback; //返回response后的回调函数对象
public DefaultFuture(Channel channel, Request request, int timeout) {
this.channel = channel;
this.request = request;
this.id = request.getId();
this.timeout = timeout > 0 ? timeout : channel.getUrl().getPositiveParameter(Constants.TIMEOUT_KEY, Constants.DEFAULT_TIMEOUT);
// put into waiting map. 将当前请求的信息,放入缓存
FUTURES.put(id, this);
CHANNELS.put(id, channel);
}
@Override
public Object get() throws RemotingException {
//阻塞timeout,等待response结果返回
return get(timeout);
}
@Override
public Object get(int timeout) throws RemotingException {
if (timeout <= 0) {
timeout = Constants.DEFAULT_TIMEOUT;
}
if (!isDone()) {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
lock.lock();
try {
/** 判断当前defaultFuture是否得到response
public boolean isDone() {
return response != null;
}*/
while (!isDone()) {
/**…………………………………………………………………………………………DefaultFuture中对于结果的阻塞--通知模型……………………………………………………………………………………………… */
//private final Condition done = lock.newCondition(); lock与condition的用法
done.await(timeout, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
if (isDone() || System.currentTimeMillis() - start > timeout) {
break;
}
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
if (!isDone()) {
throw new TimeoutException(sent > 0, channel, getTimeoutMessage(false));
}
}
return returnFromResponse();
}
private Object returnFromResponse() throws RemotingException {
Response res = response;
if (res == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("response cannot be null");
}
if (res.getStatus() == Response.OK) {
return res.getResult();
}
if (res.getStatus() == Response.CLIENT_TIMEOUT || res.getStatus() == Response.SERVER_TIMEOUT) {
throw new TimeoutException(res.getStatus() == Response.SERVER_TIMEOUT, channel, res.getErrorMessage());
}
throw new RemotingException(channel, res.getErrorMessage());
}
在DefaultFuture.get()中,阻塞timeout时间,如果response尚未返回,那么使用lock.lock()------lock.newCondition().await(timeout, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)的阻塞--通知模型,在response返回到consumer端后,被唤醒。
TAG2 Consumer接收response流程
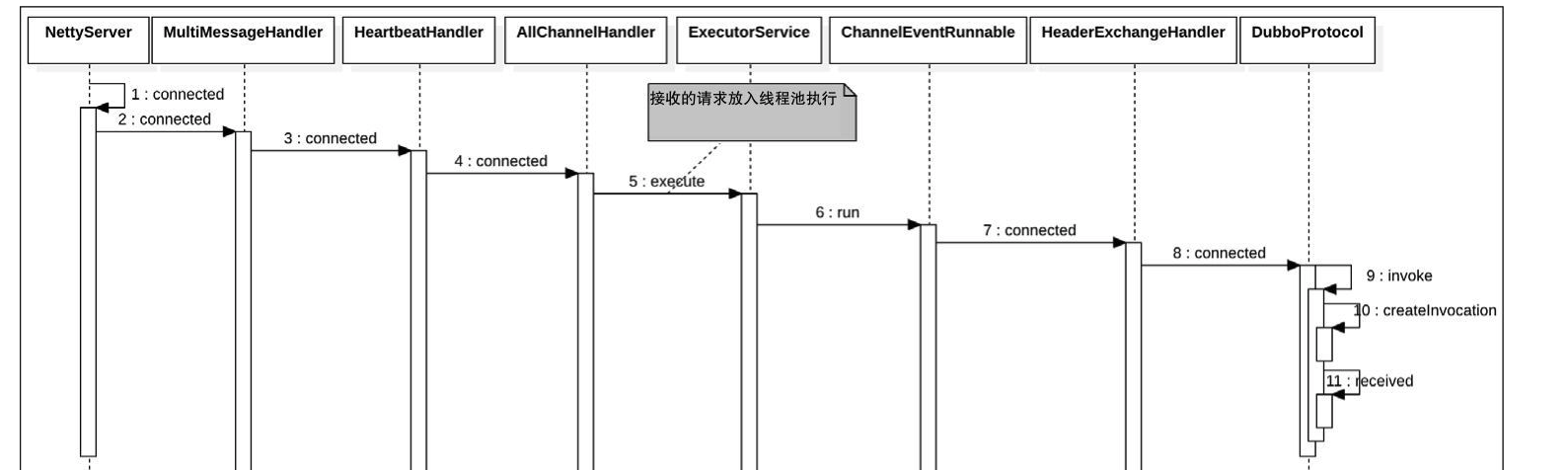
这里,consumer端接收response和provider接收request,NettyClient的处理流程相同,在consumer的网络连接客户端接收到响应消息时,会首先由dubbo的serialize框架反序列化、解码处理,然后由channelHandler对消息进行处理。
NettyHandler->NettyServer->MultiMessageHandler#received -> HeartbeatHandler#received -> Dubbo线程模型指定的 Handler#received -> DecodeHandler#received -> HeaderExchangeHandler#received -> DubboProtocol.requestHandler#received
由内到外的ChanelHandler处理链:
DubboProtocol.ExchangeHandlerAdapter
HeaderExchangeHandler主要还是管理连接等。
DecodeHandler主要是对请求进行解码。
AllChannelHandler是主要负责线程管理。
HeartbeatHandler主要负责心跳检测。
MultiMessageHandler主要负责将Dubbo内部定义的多条消息的聚合消息进行拆分处理。
NettyHandler
同样的,在AllChannelHandler处理器中,将任务包装成ChannelEventRunnable。交给consumer端的业务线程池异步处理:
public void received(Channel channel, Object message) throws RemotingException {
ExecutorService cexecutor = getExecutorService();
try {
cexecutor.execute(new ChannelEventRunnable(channel, handler, ChannelState.RECEIVED, message));
TAG2.1 HeaderExchangeHandler.received
然后执行到HeaderExchangeHandler.received根据消息类型,进行消息分发处理:
HeaderExchangeHandler.received
@Override
public void received(Channel channel, Object message) throws RemotingException {
channel.setAttribute(KEY_READ_TIMESTAMP, System.currentTimeMillis());
//获取HeaderExchangeChannel对象,其内包裹NettyChannel
ExchangeChannel exchangeChannel = HeaderExchangeChannel.getOrAddChannel(channel);
try {
/**………………………………………………………………………………………………………………处理request请求…………………………………………………………………………………… */
if (message instanceof Request) {
// handle request.
Request request = (Request) message;
//处理事件对象,如心跳事件
if (request.isEvent()) {
handlerEvent(channel, request);
} else {
//如果request需要有返回值,此时需要获取返回结果,并返回给consumer端
if (request.isTwoWay()) {
//TAG1.5 handleRequest(exchangeChannel, request)
Response response = handleRequest(exchangeChannel, request);
//TAG1.6 channel.send(response)
channel.send(response);
}
//如果不需要返回值的request,仅仅向后调用指定服务,不需要返回调用结果
else {
//TAG1.7 DubboProtocol#ExchangeHandlerAdapter dubboProtocol初始化创建的属性--也是一个ChannelHandler对象
handler.received(exchangeChannel, request.getData());
}
}
}
/**………………………………………………………………………………………………………………处理response响应…………………………………………………………………………………… */
else if (message instanceof Response) {
handleResponse(channel, (Response) message);
} else if (message instanceof String) {
//telnet相关、dubbo的qos相关请求信息
if (isClientSide(channel)) {
Exception e = new Exception("Dubbo client can not supported string message: " + message + " in channel: " + channel + ", url: " + channel.getUrl());
logger.error(e.getMessage(), e);
} else {
String echo = handler.telnet(channel, (String) message);
if (echo != null && echo.length() > 0) {
channel.send(echo);
}
}
} else {
handler.received(exchangeChannel, message);
}
} finally {
HeaderExchangeChannel.removeChannelIfDisconnected(channel);
}
}
对于响应消息,处理
static void handleResponse(Channel channel, Response response) throws RemotingException {
if (response != null && !response.isHeartbeat()) {
//调用DefaultFuture的static静态方法
DefaultFuture.received(channel, response);
}
}
这里,在consumer端的HeaderExchangeHandler这一channelHandler接收到response消息时,直接调用DefaultFuture的静态方法,并传入channel、response
TAG2.2 DefaultFuture.received(channel, response)(静态方法)
在DefaultFuture中通过 CHANNELS、FUTURES中缓存request.id或者respons.id对应的channel、defaultFuture对象。因此,这里可以使用静态方法,仅仅传入response,通过response.getId()就可以获取对应的future。
public static void received(Channel channel, Response response) {
try {
DefaultFuture future = FUTURES.remove(response.getId());
//如果response对应的id,在之前请求时,创建过defaultFuture,那么doReceived
if (future != null) {
//TAG2.2.1 future.doReceived(response)
future.doReceived(response);
} else {
logger.warn("The timeout response finally returned at "
+ (new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS").format(new Date()))
+ ", response " + response
+ (channel == null ? "" : ", channel: " + channel.getLocalAddress()
+ " -> " + channel.getRemoteAddress()));
}
} finally {
CHANNELS.remove(response.getId());
}
}
TAG2.2.1 future.doReceived(response)--condition.signal通知
private void doReceived(Response res) {
lock.lock();
try {
//获取响应消息
response = res;
/**…………………………………………………………………………………………condition通知…………………………………………………………………… */
if (done != null) {
//这里,调用condition.signal()唤醒,在defaultFuture.get()中阻塞等待的线程
done.signal();
}
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
if (callback != null) {
//如果在DefaultFuture中配置了response响应后的回调方法,这里执行回调方法
invokeCallback(callback);
}
}
当获取到response响应后,执行condition.signal()唤醒dafaultfuture.get()阻塞的线程。然后consumer端获取到结果。
(关于回调方法的部分,在5.4dubbo异步化部分详细讲到)。
此时,consumer端就获取了provider端服务调用结果。
5.3.5 connect/request在Exchange -> Transport -> Serialize 层流程总结
结合系统的架构图,总结下在consumer端connect连接、发送request请求两个过程中,consumer端和provider端Exchange -> Transport -> Serialize 层的流程:
5.3.5.1 connect连接及处理总结:
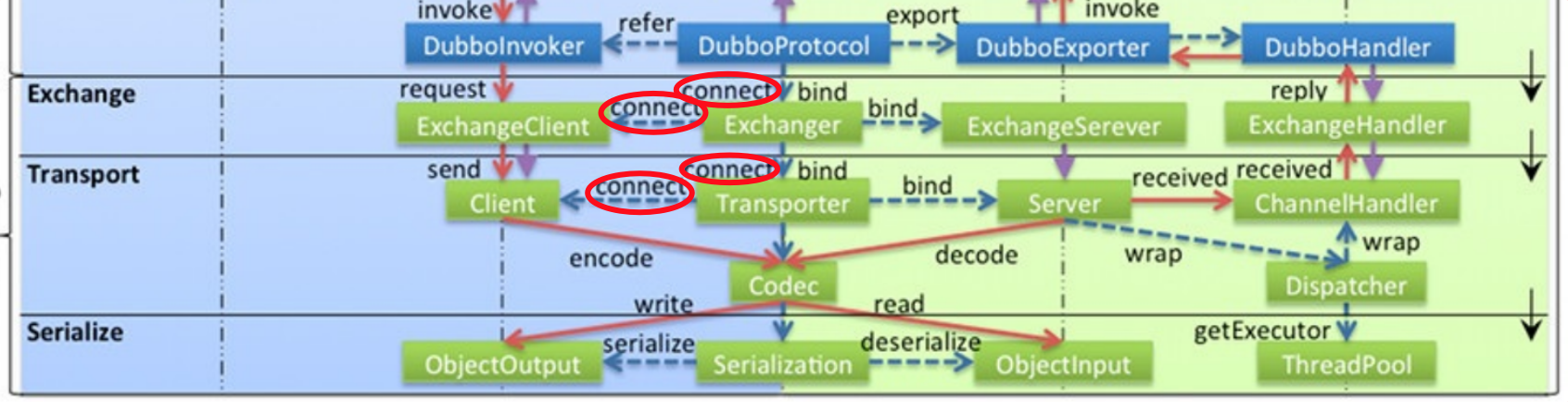
1 consumer端:
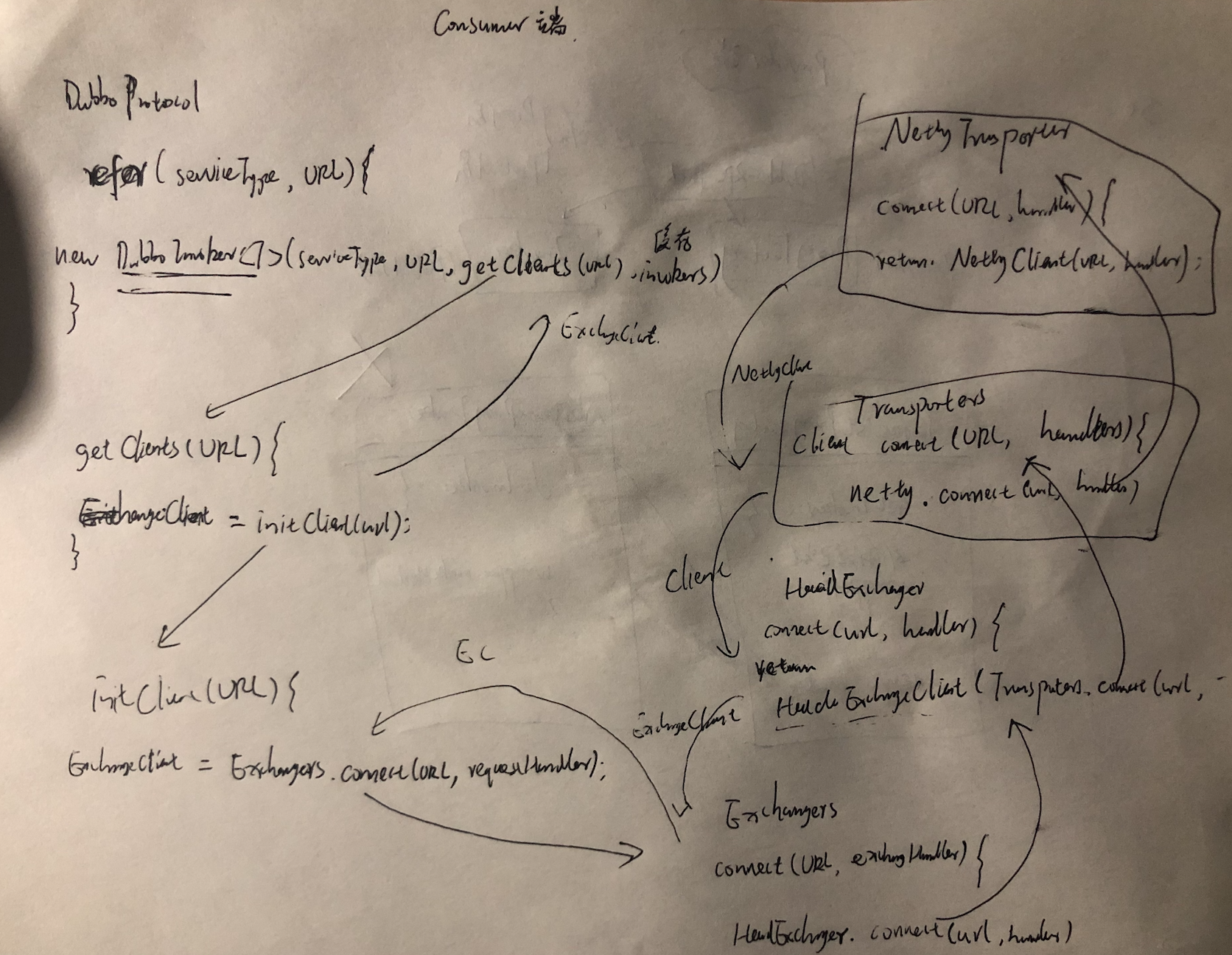
1 消费端启动时,通过DubboProtocol.refer创建DubboInvoker,其构造函数需要传入ExchangeClient客户端,创建client客户端过程,需要发送connect连接请求。
DubboProtocol.refer->getClients->initClient(url)-->Exchangers.connect(url,requestHandler)-->HeaderExchanger.connect(url,handler)->HeaderExchangeClient(Transporters.connect(url,handler))-->nettyTransporter.connect-->reture NettyClient(url,handler)-->AbstractClient.connect-->NettyClient.doConnect-->bootstrap.connect(getConnectAddress())调用Netty启动类发送connect连接请求
2 Protocol->Exchange:
DubboProtocol.refer->getClients->initClient(url)-->Exchangers.connect(url,requestHandler)
3 Exchange->Transport:
Exchangers.connect(url,requestHandler)-->HeaderExchanger.connect(url,handler)->HeaderExchangeClient(Transporters.connect(url,handler))
4 Transport->Serialize:
HeaderExchangeClient(Transporters.connect(url,handler))-->nettyTransporter.connect-->reture NettyClient(url,handler)-->AbstractClient.connect-->NettyClient.doConnect-->bootstrap.connect(getConnectAddress())调用Netty启动类发送connect连接请求--->encode->Codec.write后续编解码的序列化处理、以及发送,省略
2 provider端:
consumer端发起TCP的连接connect请求后,provider端的NettyServer的connected方法激活调用,根据在拦截器链构造过程中,选择默认的线程模型AllDispatcher,其对应的处理器AllChannelHandler,在接受到请求时,会将request包装成ChannelEventRunnable任务,并投递到其业务线程池中处理(all中创建的fixed线程池,线程为200)
connect经过nettyServer端初始化时配置的编解码器、nettyHandler = new NettyHandler(getUrl(), NettyServer.this)。而nettyServer中包括provider暴露服务过程中创建的Netty的pipeline上的channelHandler。大致流程如下(没有实际操作的handler省略)
NettyHandler.connect->NettyServer.connect->略->HeaderExchangeHandler.connected->DubboProtocol.requestHandler(属性).connected
provider端在处理connect连接请求时,没有什么处理,不再具体跟进代码分析。
5.3.5.2 request请求及处理总结
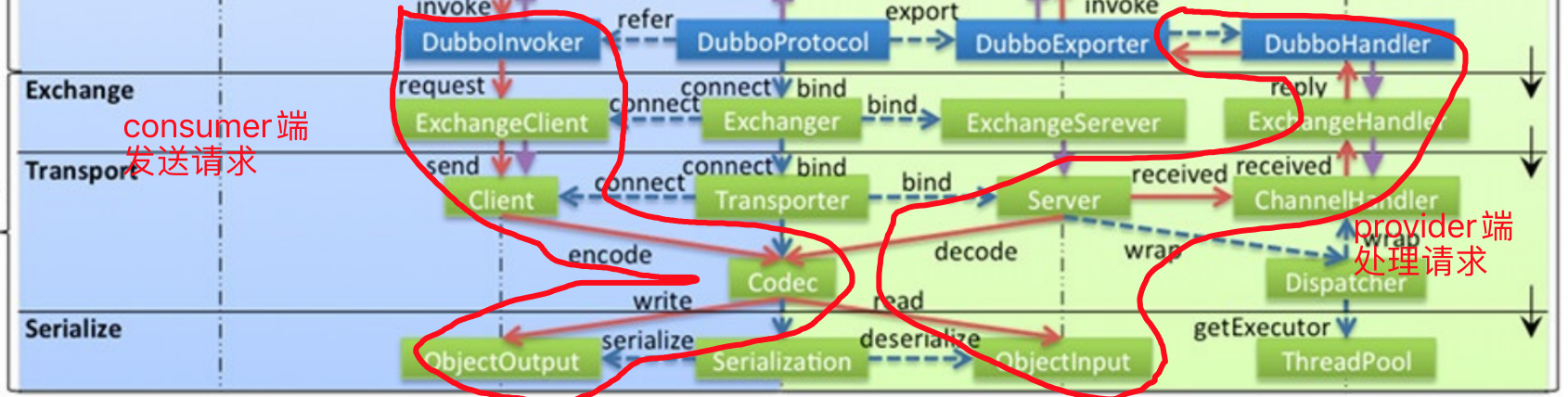
1 consumer端(发送请求):
1 服务启动时,consumer端在connect连接过程通过Exchanger.connect(url,handler)连接服务,并获取到ExchangeClient客户端,后续的服务调用时通过client端发起的。
在调用服务时,invokerInvocationHandler.invoke拦截对服务的调用请求,最终调用protocol层的DubboInvoker.doInvoke
总流程如下:
DubboInvoker#doInvoke -> ReferenceCountExchangeClient#request -> HeaderExchangeClient#request -> HeaderExchangeChannel#request--->NettyClient#send->---(NettyClient初始化过程中,添加了编解码器、channelHandler)-->DubboCountCodec#encode -> DubboCodec#encode------->Serialization#serialize
2 Protocol->Exchange:consumer调用服务,通过DubboInvoker#doInvoke执行exchangeClient.request发起请求,从protocol进入Exchange层
DubboInvoker#doInvoke -> ReferenceCountExchangeClient#request -> HeaderExchangeClient#request -> HeaderExchangeChannel#request
3 Exchange->Transport: 在调用NettyClient#send发送请求时(nettyClient在初始化过程中,向netty的channelPipeline中添加了编解码器、channelHandler,在发送消息时,netty会对消息进行编码处理
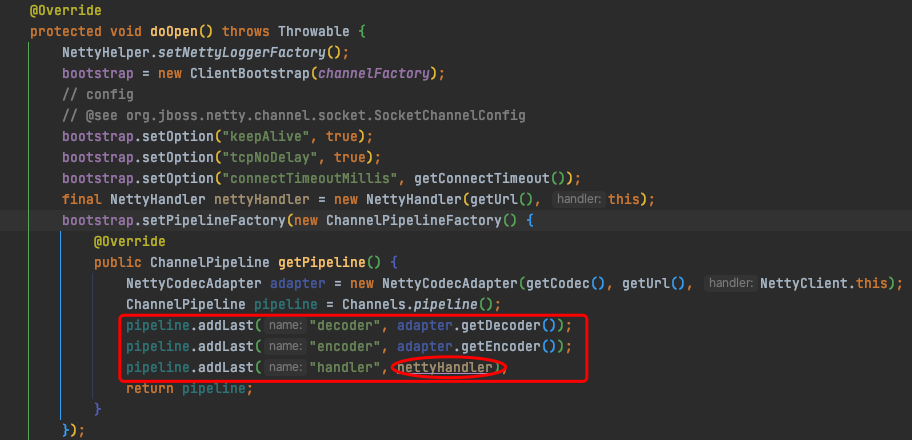
向NettyClient添加的consumer端的channelHandler链如下:
由内到外的ChanelHandler处理链:
DubboProtocol.ExchangeHandlerAdapter
HeaderExchangeHandler主要还是管理连接等。
DecodeHandler主要是对请求进行解码。
AllChannelHandler是主要负责线程管理。
HeartbeatHandler主要负责心跳检测。
MultiMessageHandler主要负责将Dubbo内部定义的多条消息的聚合消息进行拆分处理。
NettyServer---该类作为channelHandler保存上面的handler链
NettyHandler
调用链如下:
NettyClient#send->---(NettyClient初始化过程中,添加了编解码器、channelHandler)-->(channelHandler)InternalEncoder.encode->DubboCountCodec#encode -> DubboCodec#encode
4 Transport->Serialize: 在 DubboCodec#encode 中会调用 Serialization#serialize 获取到 ObjectOutput 对象,并通过 ObjectOutput#writer 来获取序列化后的内容
Serialization#serialize
2 provider端(处理请求):
1 provider服务启动时,通过Exchangers.bind绑定服务端口,并且获取到ExchangeServer,在provider端初始化时候,向netty的pipeline添加了编解码器、NettyHandler(url,NettyServer.this),NettyServer中包含ChannelHandler处理器链
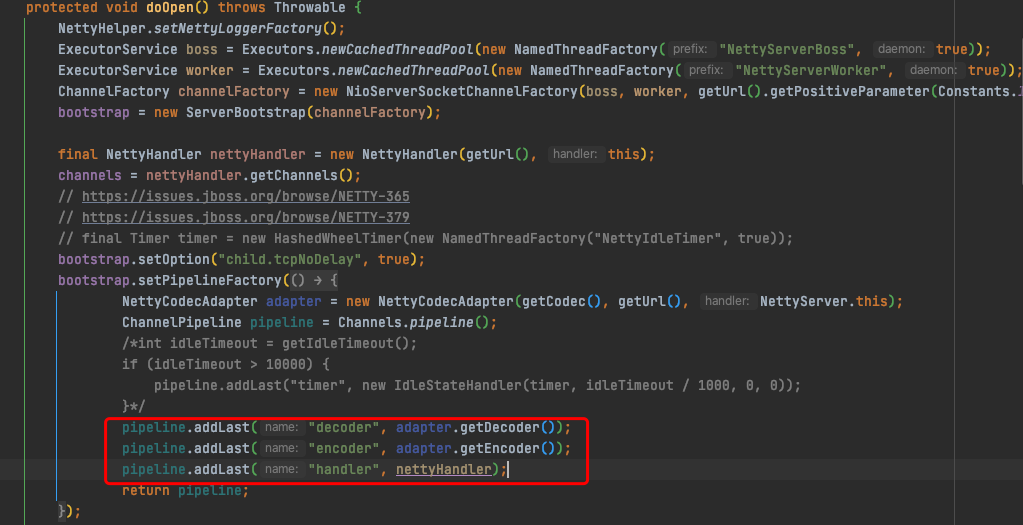
NettyHandler->NettyServer->MultiMessageHandler#received -> HeartbeatHandler#received -> Dubbo线程模型指定的 Handler#received -> DecodeHandler#received -> HeaderExchangeHandler#received -> DubboProtocol.requestHandler#received
由内到外的ChanelHandler处理链:
DubboProtocol.ExchangeHandlerAdapter
HeaderExchangeHandler主要还是管理连接等。
DecodeHandler主要是对请求进行解码。
AllChannelHandler是主要负责线程管理。
HeartbeatHandler主要负责心跳检测。
MultiMessageHandler主要负责将Dubbo内部定义的多条消息的聚合消息进行拆分处理。
NettyHandler
2 当consumer端发送请求后,provider端netty的channel接受到消息后,会调用InternalDecode.decode-->Codec.decode反序列化、解码
DubboCountCodec#decode -> DubboCodec#decode -> Serialization#deserialize
3 Serialize-->Transport: 反序列化后的内容,会按照如下的channelHandler调用链处理
NettyServerHandler#channelRead ->
NettyServer#received ->
MultiMessageHandler#received ->
HeartbeatHandler#received ->
AllChannelHandler#received (根据Dubbo 线程模型的不同会有不同的实现) ->
DecodeHandler#received ->
HeaderExchangeHandler#received -> 判断方法请求,是否需要返回值:
请求需要返回值 : ExchangeHandler#reply (DubboProtocol 内部的 requestHandler 属性)
请求不需返回值 : ExchangeHandler#received (DubboProtocol 内部的 requestHandler 属性) -> ExchangeHandler#received

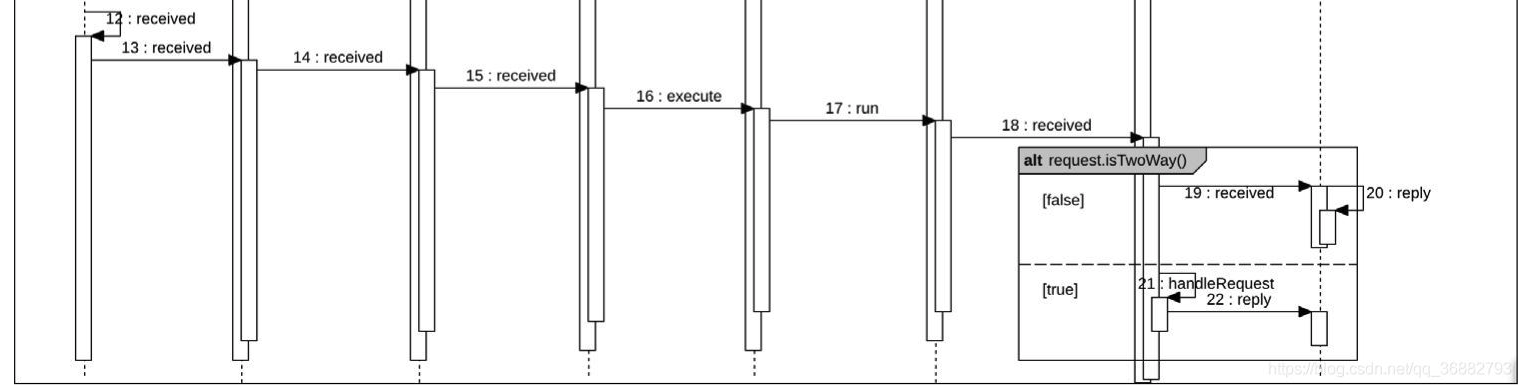
4 Transport-->Exchange:
如果不需要返回值:ExchangeHandler#received (DubboProtocol 内部的 requestHandler 属性) -> ExchangeHandler#received,进入Exchange层;
如果需要返回值:直接调用 ExchangeHandler#reply 进入 Protocol。
5 Exchange-->Protocol:
请求无论是否需要返回值,最终都会调用ExchangeHandler#reply (DubboProtocol 内部的 requestHandler 属性)。其getInvoker会获取DubboExporter并调用invoke完成调用。
3 consumer(接受响应)
略




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号