五Dubbo服务引用源码分析--2创建远程调用的代理-2.4DubboProtocol.refer
五Dubbo服务引用源码分析--2创建远程调用的代理-2.4DubboProtocol.refer
继续上篇文章内容,向下分析DubboProtocol.refer的源码:
/**…………DubboProtocol.refer………………*/
INV InvokerDelegate(protocol.refer(serviceType, url), url, providerUrl)
public class Protocol$Adaptive implements com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.Protocol {
public com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.Invoker refer(java.lang.Class arg0, com.alibaba.dubbo.common.URL arg1) throws com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.RpcException {
if (arg1 == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("url == null");
com.alibaba.dubbo.common.URL url = arg1;
String extName = ( url.getProtocol() == null ? "dubbo" : url.getProtocol() ); //dubbo
if(extName == null) throw new IllegalStateException("Fail to get extension(com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.Protocol) name from url(" + url.toString() + ") use keys([protocol])");
com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.Protocol extension = (com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.Protocol)ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.Protocol.class).getExtension(extName);
//INV1 Qos/Filter/Listener/Dubbo.refer
return extension.refer(arg0, arg1);
}
这里extension为包裹过的protocol
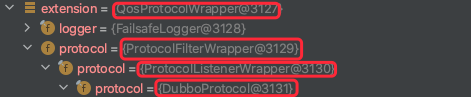
url参数=dubbo://192.168.0.100:20880/com.alibaba.dubbo.demo.DemoService?anyhost=true&application=demotest-consumer&bean.name=com.alibaba.dubbo.demo.DemoService&check=false&dubbo=2.0.2&generic=false&interface=com.alibaba.dubbo.demo.DemoService&methods=getPermissions&organization=dubbox&owner=programmer&pid=75508&qos.enable=false®ister.ip=192.168.0.100&remote.timestamp=1672381137107&side=consumer×tamp=1672387055607
INV1 Qos/Filter/Listener/Dubbo.refer
public <T> Invoker<T> refer(Class<T> type, URL url) throws RpcException {
if (Constants.REGISTRY_PROTOCOL.equals(url.getProtocol())) {
startQosServer(url);
return protocol.refer(type, url);
}
//对于dubbo://协议处理(传递到内层wrapper上)
return protocol.refer(type, url);
}
ProtocolFilterWrapper
public <T> Invoker<T> refer(Class<T> type, URL url) throws RpcException {
if (Constants.REGISTRY_PROTOCOL.equals(url.getProtocol())) {
return protocol.refer(type, url);
}
//INV1.1 buildInvokerChain
//这里,首先进行protocol.refer,然后,根据返回的invoker构造拦截器链
return buildInvokerChain(protocol.refer(type, url), Constants.REFERENCE_FILTER_KEY, Constants.CONSUMER);
}
ProtocolListenerWrapper
public <T> Invoker<T> refer(Class<T> type, URL url) throws RpcException {
if (Constants.REGISTRY_PROTOCOL.equals(url.getProtocol())) {
return protocol.refer(type, url);
}
//首先执行protocol.refer,然后,创建ListenerInvokerWrapper,其会在服务引用时,执行listener.referred的监听操作
return new ListenerInvokerWrapper<T>(protocol.refer(type, url),
Collections.unmodifiableList(
ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(InvokerListener.class)
.getActivateExtension(url, Constants.INVOKER_LISTENER_KEY)));
}
INV2 DubboProtocol.refer--创建RPC功能invoker
serviceType为调用服务的接口,URL以dubbo开头,后续跟了dubbo服务地址,以及服务名称DemoService,该url描述了一个dubbo协议的服务。因此,refer此处逻辑,是调用远程host处dubbo协议的demoService的服务。
DubboProtocol.refer
public <T> Invoker<T> refer(Class<T> serviceType, URL url) throws RpcException {
optimizeSerialization(url);
// 创建RPC功能的invoker
//INV2.1 getClients(url)
//INV2.2 DubboInvoker
DubboInvoker<T> invoker = new DubboInvoker<T>(serviceType, url, getClients(url), invokers);
//将创建好的invoker加入集合
invokers.add(invoker);
return invoker;
}
上述创建RPC功能的invoker。参数中,getClients(url)获取客户端实例,为ExchangeClient。
//INV2.1 getClients(url)--创建client客户端
getClients(URL)方法,根据url中参数,判定是否需要共享连接,获取客户端。
DubboProtocol
private ExchangeClient[] getClients(URL url) {
// 是否共享连接connection
boolean service_share_connect = false;
int connections = url.getParameter(Constants.CONNECTIONS_KEY, 0);
// if not configured, connection is shared, otherwise, one connection for one service
//如果url中没有配置connection连接的数量,表示共享;否则,一个连接对应一个service服务
if (connections == 0) {
service_share_connect = true;
connections = 1;
}
ExchangeClient[] clients = new ExchangeClient[connections];
for (int i = 0; i < clients.length; i++) {
if (service_share_connect) {
//INV2.1.1 getSharedClient(url)获取共享连接connection
clients[i] = getSharedClient(url);
} else {
clients[i] = initClient(url);
}
}
return clients;
}
//INV2.1.1 getSharedClient(url)获取共享连接connection
此处,跟入getSharedClient获取共享客户端方法
dubbo://192.168.0.100:20880/com.alibaba.dubbo.demo.DemoService?anyhost=true&application=demotest-consumer&bean.name=com.alibaba.dubbo.demo.DemoService&check=false&dubbo=2.0.2&generic=false&interface=com.alibaba.dubbo.demo.DemoService&methods=getPermissions&organization=dubbox&owner=programmer&pid=75508&qos.enable=false®ister.ip=192.168.0.100&remote.timestamp=1672381137107&side=consumer×tamp=1672387055607
url参数:
//DubboProtocol
private ExchangeClient getSharedClient(URL url) {
String key = url.getAddress(); //192.168.0.100:20880
//检查缓存
ReferenceCountExchangeClient client = referenceClientMap.get(key);
//1 当本地缓存中有客户端,返回
if (client != null) {
if (!client.isClosed()) {
//如果dubboProtocol的exchangeClient缓存中有address对应的客户端,则返回客户端共享,并增加引用计数(“引用计数”功能的 ExchangeClient)
client.incrementAndGetCount();
return client;
} else {
//当client关闭,从缓存移除
referenceClientMap.remove(key);
}
}
//2 当缓存没有client,新建
locks.putIfAbsent(key, new Object());
//对当前address加锁,
synchronized (locks.get(key)) {
if (referenceClientMap.containsKey(key)) {
return referenceClientMap.get(key);
}
/**……………………………………………………………………………………………………创建客户端…………………………………………………………………………………………………… */
//INV2.1.2 initClient(url) 创建exchangeClient
// 创建 ExchangeClient 客户端
ExchangeClient exchangeClient = initClient(url);
// 将 ExchangeClient 实例传给 ReferenceCountExchangeClient,这里使用了装饰模式
client = new ReferenceCountExchangeClient(exchangeClient, ghostClientMap);
//加锁,将key-client入缓存
referenceClientMap.put(key, client);
ghostClientMap.remove(key);
locks.remove(key);
return client;
}
}
getSharedClient(URL url)方法获取共享客户端,首先会先从DubboProtocol本地缓存获取;如果没有,加锁创建新客户端initClient,并存入缓存。继续跟入创建新客户端代码:
//INV2.1.2 initClient(url) 创建exchangeClient
private ExchangeClient initClient(URL url) {
// 获取客户端client类型,默认为 netty
String str = url.getParameter(Constants.CLIENT_KEY, url.getParameter(Constants.SERVER_KEY, Constants.DEFAULT_REMOTING_CLIENT));
// 添加编解码和心跳包参数到 url 中
url = url.addParameter(Constants.CODEC_KEY, DubboCodec.NAME);
url = url.addParameterIfAbsent(Constants.HEARTBEAT_KEY, String.valueOf(Constants.DEFAULT_HEARTBEAT));
// 检测客户端类型,是否是Dubbo所支持的(transport为底层通信,目前支持Mina、Netty、Grizzly)
if (str != null && str.length() > 0 && !ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(Transporter.class).hasExtension(str)) {
throw new RpcException("Unsupported client type: ...");
}
ExchangeClient client;
try {
// 获取 lazy 配置
if (url.getParameter(Constants.LAZY_CONNECT_KEY, false)) {
// 创建懒加载 ExchangeClient 实例
client = new LazyConnectExchangeClient(url, requestHandler);
} else {
//INV2.1.3 Exchangers.connect(url, requestHandler)--CONN
// 创建普通 ExchangeClient 实例
client = Exchangers.connect(url, requestHandler);
}
} catch (RemotingException e) {
throw new RpcException("Fail to create remoting client for service...");
}
return client;
}
initClient(URL)中,通过向url中添加parm参数,添加心跳、编解码等处理器。然后通过Exchangers.connect(url, requestHandler)创建ExchangeClient。
//INV2.1.3 Exchangers.connect(url, requestHandler)--CONN
//INV2.1.3 Exchangers.connect(url, requestHandler)--CONN
// 创建普通 ExchangeClient 实例
client = Exchangers.connect(url, requestHandler);
}
CONN1 ExchangeHandlerAdapter--处理providers请求

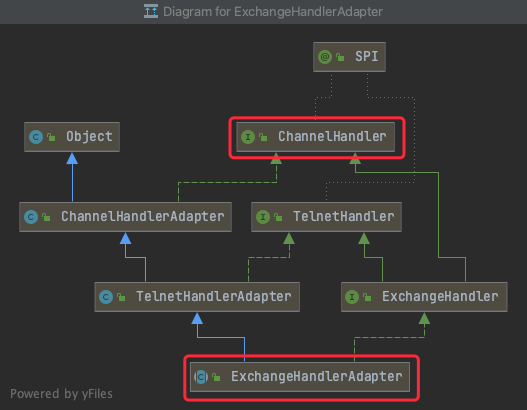
处理器为DubboProtocol内创建的属性。看出,该handler是Netty框架内存放在pipeline上的channelHandler,用于在消息传递中进行拦截、处理的类。
DubboProtocol
//provider端用于处理request的处理器
private ExchangeHandler requestHandler = new ExchangeHandlerAdapter() {
//处理调用请求
public Object reply(ExchangeChannel channel, Object message) throws RemotingException {
//handler只处理Invocation的信息
if (message instanceof Invocation) { //1
Invocation inv = (Invocation) message;
/**…………………………………………………………………………………………创建invoker……………………………………………………………………………………………… */
//从channel获取port,从invocation获取服务path,serviceKey=path:port,然后exporterMap.get(serviceKey).getInvoker获取服务的invoker
Invoker<?> invoker = getInvoker(channel, inv);
//如果是callback 需要处理高版本调用低版本的问题
if (Boolean.TRUE.toString().equals(inv.getAttachments().get(IS_CALLBACK_SERVICE_INVOKE))){ //2
String methodsStr = invoker.getUrl().getParameters().get("methods");
boolean hasMethod = false;
if (methodsStr == null || methodsStr.indexOf(",") == -1){//3
hasMethod = inv.getMethodName().equals(methodsStr);
} else {
String[] methods = methodsStr.split(",");
for (String method : methods){//4
if (inv.getMethodName().equals(method)){
hasMethod = true;
break;
}
} //4
}//3
if (!hasMethod){
logger.warn(new IllegalStateException("The methodName "+inv.getMethodName()+" not found in callback service interface ,invoke will be ignored. please update the api interface. url is:" + invoker.getUrl()) +" ,invocation is :"+inv );
return null;
}
} //2
/**……………………………………………… RpcContext.getContext()获取threadLocal线程变量,并将remote的客户端地址存入……………………………………………… */
RpcContext.getContext().setRemoteAddress(channel.getRemoteAddress());
/** ……………………………………………………………………………………………invoker.invoke(invocation)调用服务……………………………………………………………………………………*/
return invoker.invoke(inv);
} //1
throw new RemotingException(channel, "Unsupported request: " + message == null ? null : (message.getClass().getName() + ": " + message) + ", channel: consumer: " + channel.getRemoteAddress() + " --> provider: " + channel.getLocalAddress());
}
//接收信息
@Override
public void received(Channel channel, Object message) throws RemotingException {
if (message instanceof Invocation) {
reply((ExchangeChannel) channel, message);
} else {
super.received(channel, message);
}
}
@Override
public void connected(Channel channel) throws RemotingException {
//在connected连接时,调用invoker方法,其methodKey为onConnect
invoke(channel, Constants.ON_CONNECT_KEY);
}
@Override
public void disconnected(Channel channel) throws RemotingException {
if(logger.isInfoEnabled()){
logger.info("disconected from "+ channel.getRemoteAddress() + ",url:" + channel.getUrl());
}
//在disconnected断开连接时,调用invoker方法,其methodKey为onDisconnect
invoke(channel, Constants.ON_DISCONNECT_KEY);
}
//调用服务
private void invoke(Channel channel, String methodKey) {
Invocation invocation = createInvocation(channel, channel.getUrl(), methodKey);//构建invocation
if (invocation != null) {
try {
received(channel, invocation);
} catch (Throwable t) {
logger.warn("Failed to invoke event method " + invocation.getMethodName() + "(), cause: " + t.getMessage(), t);
}
}
}
//根据client端请求,创建调用的invocation信息
private Invocation createInvocation(Channel channel, URL url, String methodKey) {
String method = url.getParameter(methodKey);
if (method == null || method.length() == 0) {
return null;
}
RpcInvocation invocation = new RpcInvocation(method, new Class<?>[0], new Object[0]);
invocation.setAttachment(Constants.PATH_KEY, url.getPath());
invocation.setAttachment(Constants.GROUP_KEY, url.getParameter(Constants.GROUP_KEY));
invocation.setAttachment(Constants.INTERFACE_KEY, url.getParameter(Constants.INTERFACE_KEY));
invocation.setAttachment(Constants.VERSION_KEY, url.getParameter(Constants.VERSION_KEY));
if (url.getParameter(Constants.STUB_EVENT_KEY, false)){
invocation.setAttachment(Constants.STUB_EVENT_KEY, Boolean.TRUE.toString());
}
return invocation;
}
};
仔细看该ExchangeHandlerAdapter类,其内定义了在client端发来请求时,provider通过创建invoker,来实现调用服务的逻辑。
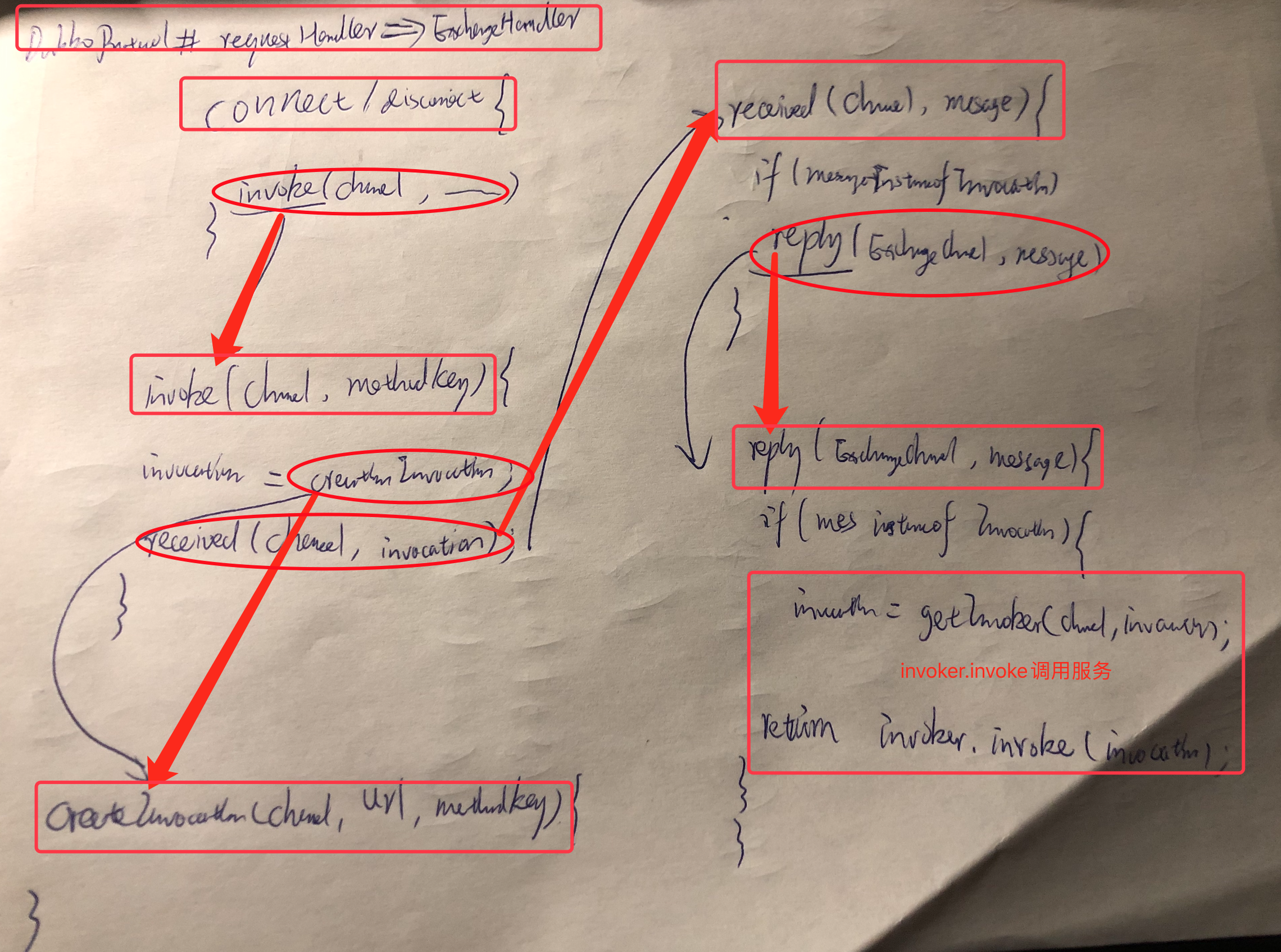
CONN2 Exchangers.connect(url, requestHandler)
Exchangers是exchange层门面类。跟入connect连接:
public class Exchangers {
public static ExchangeClient connect(URL url, ExchangeHandler handler) throws RemotingException {
if (url == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("url == null");
}
if (handler == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("handler == null");
}
//加入CODEC_KEY:exchange的url上的参数对
url = url.addParameterIfAbsent(Constants.CODEC_KEY, "exchange");
//CONN2.1 getExchanger(url)
//CONN2.2 HeaderExchanger.connect(url,handler)
// SPI加载,获取 Exchange 实例,默认为 HeaderExchanger
return getExchanger(url).connect(url, handler);
}
//CONN2.1 getExchanger(url)--HeadExchanger
public static Exchanger getExchanger(URL url) {
//Exchanger类型为header
String type = url.getParameter(Constants.EXCHANGER_KEY, Constants.DEFAULT_EXCHANGER);
return getExchanger(type);
}
public static Exchanger getExchanger(String type) {
return ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(Exchanger.class).getExtension(type);
}
创建HeadExchanger。
//CONN2.2 HeaderExchanger.connect(url,handler)
public class HeaderExchanger implements Exchanger {
//connect创建客户端
public ExchangeClient connect(URL url, ExchangeHandler handler) throws RemotingException {
//CONN2.2.1 new DecodeHandler(new HeaderExchangeHandler(handler))
//CONN2.2.2 Transporters.connect(url,handler)
// 这里包含了多个调用,分别如下:
// 1. 创建 HeaderExchangeHandler 对象
// 2. 创建 DecodeHandler 对象
// 3. 通过 Transporters 构建 Client 实例
// 4. 创建 HeaderExchangeClient 对象
return new HeaderExchangeClient(Transporters.connect(url, new DecodeHandler(new HeaderExchangeHandler(handler))), true);}
//CONN2.2.1 new DecodeHandler(new HeaderExchangeHandler(handler))--handler处理链(同provider端)
这里构造netty上的channelHandler的处理链,过程和provider端的过程相同,略。
从上述过程,可知是对channelHandler的链式包装,构成handler处理链。

各个handler的作用:
HeaderExchangeHandler主要还是管理连接等。
DecodeHandler主要是对请求进行解码。
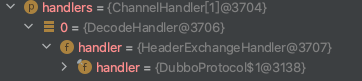
//CONN2.2.2 Transporters.connect(url,handler)-->创建NettyClient
public class Transporters {
//通过 Transporters 构建 Client 实例
public static Client connect(URL url, ChannelHandler... handlers) throws RemotingException {
if (url == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("url == null");
}
ChannelHandler handler;
if (handlers == null || handlers.length == 0) {
//handler为channel.pipeline上事件处理器,定义了一系列inbound和outbound事件触发方法
handler = new ChannelHandlerAdapter();
} else if (handlers.length == 1) {
handler = handlers[0];
} else {
// 如果 handler 数量大于1,则创建一个 ChannelHandler 分发器
handler = new ChannelHandlerDispatcher(handlers);
}
// 获取 Transporter 自适应拓展类Transporter@Adaptive,并调用 connect 方法生成 Client 实例
return getTransporter().connect(url, handler);
}
public static Transporter getTransporter() {
return ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(Transporter.class).getAdaptiveExtension();
}
public class NettyTransporter implements Transporter {
public Client connect(URL url, ChannelHandler listener) throws RemotingException {
// 创建 NettyClient 对象
return new NettyClient(url, listener);
}
总结:DubboProtocol.refer构建invoker流程
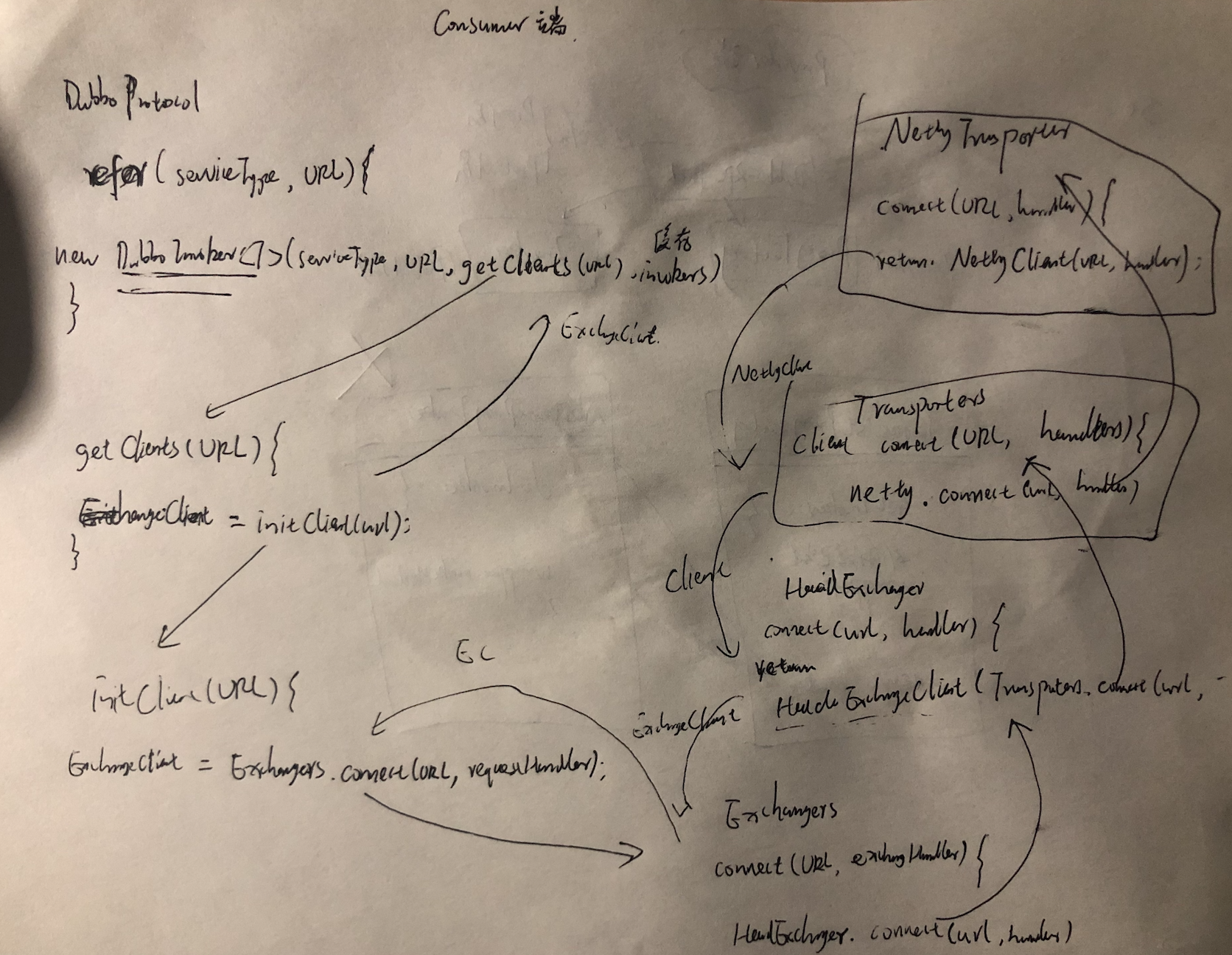
总结:
1 consumer端,DubboProtocol.refer创建的是DubboInvoker的实例,在init初始化构建后,底层有NettyClient的客户端,具备远程通信功能;
2 ExchangeClient没有通信能力,需要对底层NettyClient层层封装;
3 DubboProtocol中,refer方法创建一个DubboInvoker实例,每次创建实例加入invokers的集合中。




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号