五Netty源码分析--4Bootstrap.connect
五Netty源码分析--4Bootstrap.connect
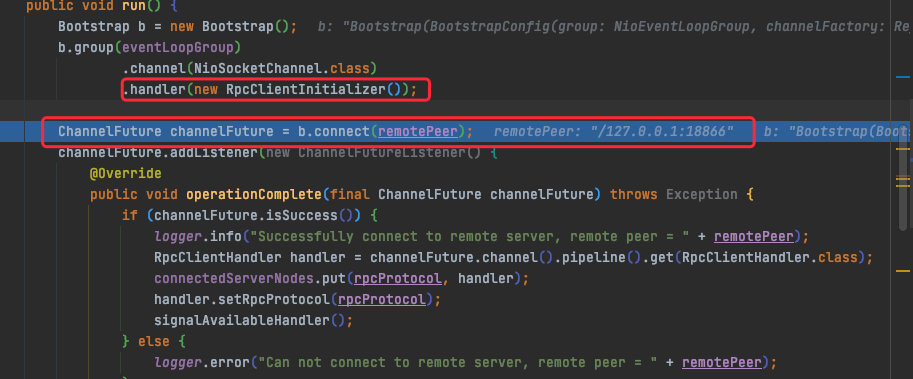
client端与server端bootstrap配置和启动流程大致相同,server端需要bind端口并监听,来对外提供连接服务;而client端,执行b.connect连接server端。
4.1 Bootstrap.connect()方法
Bootstrap
public ChannelFuture connect(SocketAddress remoteAddress) {
ObjectUtil.checkNotNull(remoteAddress, "remoteAddress");
validate();
return doResolveAndConnect(remoteAddress, config.localAddress());
}
private ChannelFuture doResolveAndConnect(final SocketAddress remoteAddress, final SocketAddress localAddress) {
//TAG1 initAndRegister 异步方法,创建、初始化并注册client端channel
final ChannelFuture regFuture = initAndRegister();
final Channel channel = regFuture.channel();
//判断异步执行结果
if (regFuture.isDone()) {
if (!regFuture.isSuccess()) {
return regFuture;
}
return doResolveAndConnect0(channel, remoteAddress, localAddress, channel.newPromise());
}
//channelFuture.addListener的异步监听,在channel创建、初始化、注册完成后operationComplete,继续执行对server端连接
else {
// Registration future is almost always fulfilled already, but just in case it's not.
final PendingRegistrationPromise promise = new PendingRegistrationPromise(channel);
regFuture.addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture future) throws Exception {
// Directly obtain the cause and do a null check so we only need one volatile read in case of a
// failure.
Throwable cause = future.cause();
if (cause != null) {
// Registration on the EventLoop failed so fail the ChannelPromise directly to not cause an
// IllegalStateException once we try to access the EventLoop of the Channel.
promise.setFailure(cause);
} else {
// Registration was successful, so set the correct executor to use.
// See https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/2586
promise.registered();
//TAG2 doResolveAndConnect0 连接server端
doResolveAndConnect0(channel, remoteAddress, localAddress, promise);
}
}
});
return promise;
}
}
TAG1 initAndRegister
AbstractBootstrap
final ChannelFuture initAndRegister() {
Channel channel = null;
try {
//TAG1.1 hannelFactory.newChannel
channel = channelFactory.newChannel();
//TAG1.2 init(channel)
init(channel);
} catch (Throwable t) {
if (channel != null) {
// channel can be null if newChannel crashed (eg SocketException("too many open files"))
channel.unsafe().closeForcibly();
// as the Channel is not registered yet we need to force the usage of the GlobalEventExecutor
return new DefaultChannelPromise(channel, GlobalEventExecutor.INSTANCE).setFailure(t);
}
// as the Channel is not registered yet we need to force the usage of the GlobalEventExecutor
return new DefaultChannelPromise(new FailedChannel(), GlobalEventExecutor.INSTANCE).setFailure(t);
}
//TAG1.3 group().register(channel)
ChannelFuture regFuture = config().group().register(channel);
if (regFuture.cause() != null) {
if (channel.isRegistered()) {
channel.close();
} else {
channel.unsafe().closeForcibly();
}
}
return regFuture;
}
client端的initAndRegister()与server端相同
initAndRegister逻辑:
//TAG1.1 channelFactory.newChannel 创建channel;
//TAG1.2 init(channel) 初始化channel;
//TAG1.3 group().register(channel) 注册channel到NioEventLoop上的selector上;
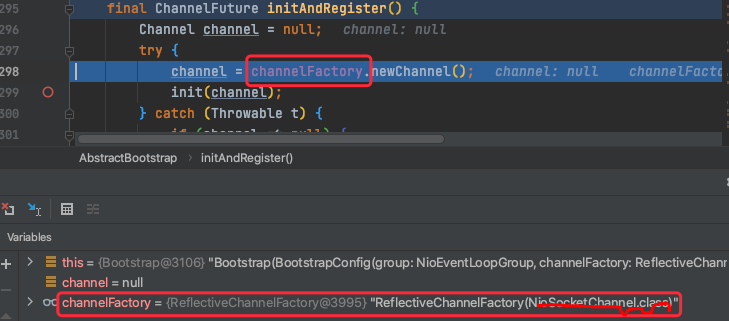
TAG1.1 channelFactory.newChannel
bootstrap的channel配置NioSocketChannel.class
public class ReflectiveChannelFactory<T extends Channel> implements ChannelFactory<T> {
@Override
public T newChannel() {
try {
//无参构造函数
return constructor.newInstance();
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw new ChannelException("Unable to create Channel from class " + constructor.getDeclaringClass(), t);
}
}
public class NioSocketChannel extends AbstractNioByteChannel implements io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel {
//创建SelectorProvider对象
private static final SelectorProvider DEFAULT_SELECTOR_PROVIDER = SelectorProvider.provider();
public NioSocketChannel() {
this(DEFAULT_SELECTOR_PROVIDER);
}
public NioSocketChannel(SelectorProvider provider) {
//TAG1.1.1 newSocket(provider)
//TAG1.1.2 NioSocketChannel(channel)
this(newSocket(provider));
}
TAG1.1.1 newSocket(provider)
private static SocketChannel newSocket(SelectorProvider provider) {
try {
//创建原生socketchannel
return provider.openSocketChannel();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new ChannelException("Failed to open a socket.", e);
}
}
public abstract class SelectorProviderImpl extends SelectorProvider {
public SocketChannel openSocketChannel() throws IOException {
//创建NIO原生的socketchannel
return new SocketChannelImpl(this);
}
TAG1.1.2 NioSocketChannel(channel)
public NioSocketChannel(SocketChannel socket) {
this(null, socket);
}
public NioSocketChannel(Channel parent, SocketChannel socket) {
//TAG1.1.2.1 super
//parent为null,socket为原生SocketChannelImpl
super(parent, socket);
config = new NioSocketChannelConfig(this, socket.socket());
}
TAG1.1.2.1 super(设置nettychannel关注事件READ)
protected AbstractNioByteChannel(Channel parent, SelectableChannel ch) {
//设置关注事件为READ
super(parent, ch, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
}
protected AbstractNioChannel(Channel parent, SelectableChannel ch, int readInterestOp) {
super(parent);
this.ch = ch; //绑定原生SocketChannelImpl
this.readInterestOp = readInterestOp; //设置关注时间为READ
try {
ch.configureBlocking(false);
} catch (IOException e) {
try {
ch.close();
} catch (IOException e2) {
logger.warn(
"Failed to close a partially initialized socket.", e2);
}
throw new ChannelException("Failed to enter non-blocking mode.", e);
}
}
client端关注的事件为READ,当client连接server端connect成功后,server端会通知client端连接成功,此时已经注册的read,会直接监听server端返回的信息。
TAG1.2 init(channel)--对比ServerBootstrap.init
Bootstrap
void init(Channel channel) {
ChannelPipeline p = channel.pipeline();
//向pipeline中添加bootstrap中配置的handler处理器
p.addLast(config.handler());
//将bootstrap中配置的options、attrs等属性初始化到channel
setChannelOptions(channel, options0().entrySet().toArray(newOptionArray(0)), logger);
setAttributes(channel, attrs0().entrySet().toArray(newAttrArray(0)));
}
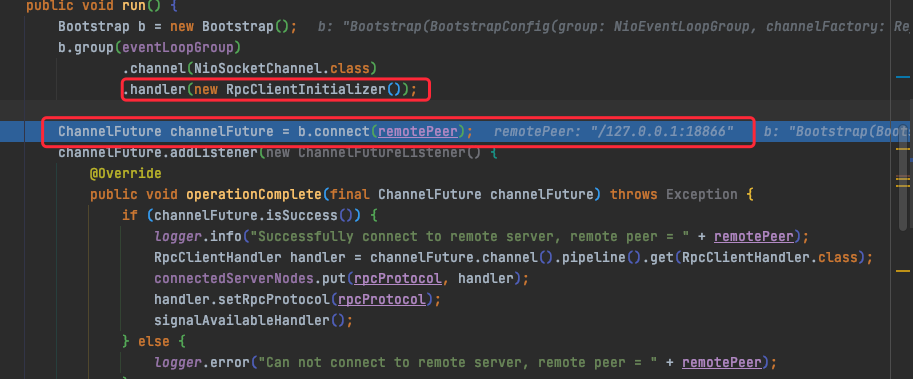
这里添加的是RpcClientInitializer。
对比ServerBootstrap.init(channel):
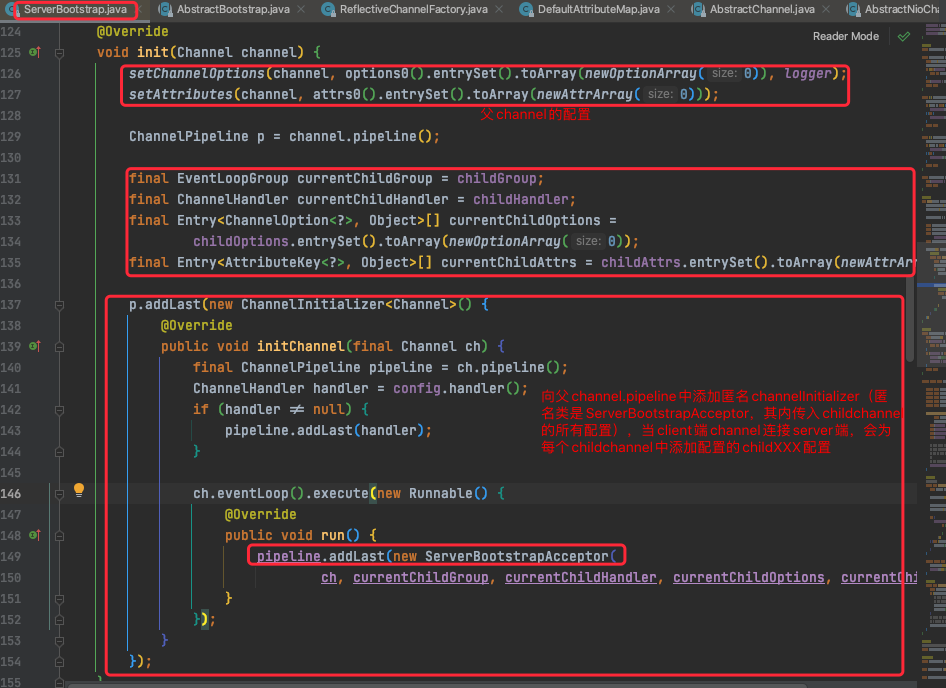
这里是Netty服务端的reactor线程池模型的实现。由bossgroup负责client端连接处理;对于客户端的handler处理,使用workergroup处理就绪事件,因此,需要为每个新连接的childchannel,添加对应的客户端channel的handler。
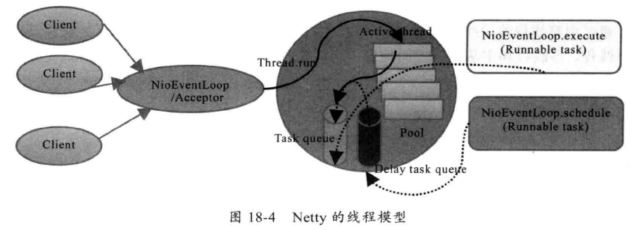
而client端只是reactor模型,只有一个线程池bossgroup,处理就绪事件,包括connect、read、write等。
TAG1.3 group().register(channel)--略,看server端
注册channel到nioeventloop。
AbstractBootstrap
final ChannelFuture initAndRegister() {
Channel channel = null;
try {
//TAG1.1 hannelFactory.newChannel
channel = channelFactory.newChannel();
//TAG1.2 init(channel)
init(channel);
//TAG1.3 group().register(channel)
ChannelFuture regFuture = config().group().register(channel);
MultithreadEventLoopGroup
@Override
public ChannelFuture register(Channel channel) {
//next()获取group中下一个nioeventloop,然后将channel注册到nioeventloop上的selector
return next().register(channel);
}
SingleThreadEventLoop
@Override
public ChannelFuture register(Channel channel) {
return register(new DefaultChannelPromise(channel, this));
}
@Override
public ChannelFuture register(final ChannelPromise promise) {
ObjectUtil.checkNotNull(promise, "promise");
//调用channel的内部类unsafe.register,注册channel到eventloop
promise.channel().unsafe().register(this, promise);
return promise;
}
AbstractChannel>>>>AbstractUnsafe
public final void register(EventLoop eventLoop, final ChannelPromise promise) {
if (eventLoop == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("eventLoop");
}
if (isRegistered()) {
promise.setFailure(new IllegalStateException("registered to an event loop already"));
return;
}
if (!isCompatible(eventLoop)) {
promise.setFailure(
new IllegalStateException("incompatible event loop type: " + eventLoop.getClass().getName()));
return;
}
AbstractChannel.this.eventLoop = eventLoop;
if (eventLoop.inEventLoop()) {
register0(promise);
} else {
try {
eventLoop.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
register0(promise);
}
});
} catch (Throwable t) {
logger.warn(
"Force-closing a channel whose registration task was not accepted by an event loop: {}",
AbstractChannel.this, t);
closeForcibly();
closeFuture.setClosed();
safeSetFailure(promise, t);
}
}
}
这里的注册register流程,和server端相同。详看server端。
TAG2 doResolveAndConnect0---连接操作
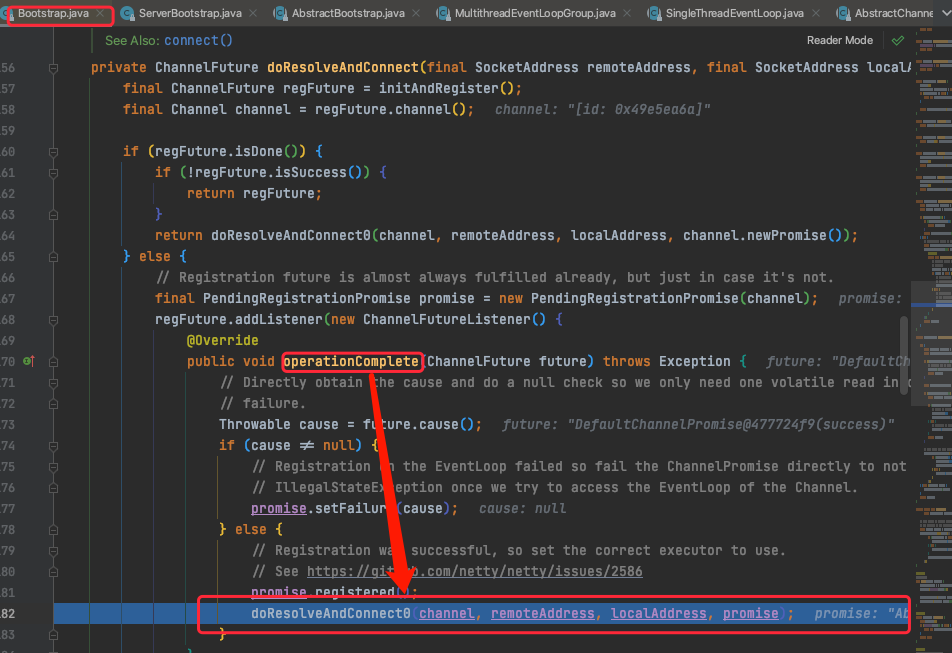
Bootstrap
private ChannelFuture doResolveAndConnect0(final Channel channel, SocketAddress remoteAddress,
final SocketAddress localAddress, final ChannelPromise promise) {
try {
final EventLoop eventLoop = channel.eventLoop();
//创建SocketAddress的地址解析器
final AddressResolver<SocketAddress> resolver = this.resolver.getResolver(eventLoop);
//如果地址解析器不支持remoteAddress,或者已经解析过,直接doConnect,进行连接server端
if (!resolver.isSupported(remoteAddress) || resolver.isResolved(remoteAddress)) {
doConnect(remoteAddress, localAddress, promise);
return promise;
}
//异步方式解析remoteAddress
final Future<SocketAddress> resolveFuture = resolver.resolve(remoteAddress);
/**…………………………………………………………………………………………future--listener模式……………………………………………………………………………………………………………… */
if (resolveFuture.isDone()) {
final Throwable resolveFailureCause = resolveFuture.cause();
//解析失败,关闭channel,并设置promise为failure
if (resolveFailureCause != null) {
// Failed to resolve immediately
channel.close();
promise.setFailure(resolveFailureCause);
}
//解析成功
else {
//TAG2.1 doConnect
doConnect(resolveFuture.getNow(), localAddress, promise);
}
return promise;
}
// Wait until the name resolution is finished.
resolveFuture.addListener(new FutureListener<SocketAddress>() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(Future<SocketAddress> future) throws Exception {
if (future.cause() != null) {
channel.close();
promise.setFailure(future.cause());
} else {
doConnect(future.getNow(), localAddress, promise);
}
}
});
} catch (Throwable cause) {
promise.tryFailure(cause);
}
return promise;
}
上面doResolveAndConnect0逻辑:
1 先解析remoteAddress,异步执行返回resolver;
2 异步执行结果判断,并listener监听---doConnect
TAG2.1 doConnect
Bootstrap
private static void doConnect(
final SocketAddress remoteAddress, final SocketAddress localAddress, final ChannelPromise connectPromise) {
final Channel channel = connectPromise.channel();
//TAG2.1.1 channel.eventLoop().execute
//在channel绑定的eventloop上添加task任务(任务执行channel.connect)
channel.eventLoop().execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
if (localAddress == null) {
//TAG2.1.2 channel.connect
channel.connect(remoteAddress, connectPromise);
} else {
channel.connect(remoteAddress, localAddress, connectPromise);
}
//监听异步connect结果connectPromise,如果failure,关闭channel
connectPromise.addListener(ChannelFutureListener.CLOSE_ON_FAILURE);
}
});
}
TAG2.1.1 channel.eventLoop().execute(对比Server端)
SingleThreadEventExecutor(Server端源码解析)
@Override
public void execute(Runnable task) {
if (task == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("task");
}
boolean inEventLoop = inEventLoop();
TAG1.3.1.1.2.1 addTask
//如果当前线程是nioeventloop所绑定thread,直接添加task任务到任务队列(task任务为register0()操作的runnable)
addTask(task);
//当前线程不是nioeventloop绑定的thread,这里启动eventloop的线程
if (!inEventLoop) { //2
TAG1.3.1.1.2.2 startThread
//创建并启动一个线程
startThread();
if (isShutdown()) { //3
boolean reject = false;
try {
//如果线程关闭,移除task任务(register0)
if (removeTask(task)) {
reject = true;
}
} catch (UnsupportedOperationException e) {
}
if (reject) {
reject();
}
}//3
} //2
if (!addTaskWakesUp && wakesUpForTask(task)) {
wakeup(inEventLoop);
}
}
因为这里是channel.eventLoop().execute执行,是在eventloop绑定线程,因此会将此task直接加入任务队列中。
client端的启动和server端,TAG1.3 group().register(channel)流程相同,在步骤TAG1.3.1.1.2 eventLoop.execute--(NioEventLoop启动)中,nioeventloop的线程启动,nioeventloop.run()会轮询,轮询添加的task和检查就绪的事件,进行处理。
TAG2.1.2 channel.connect
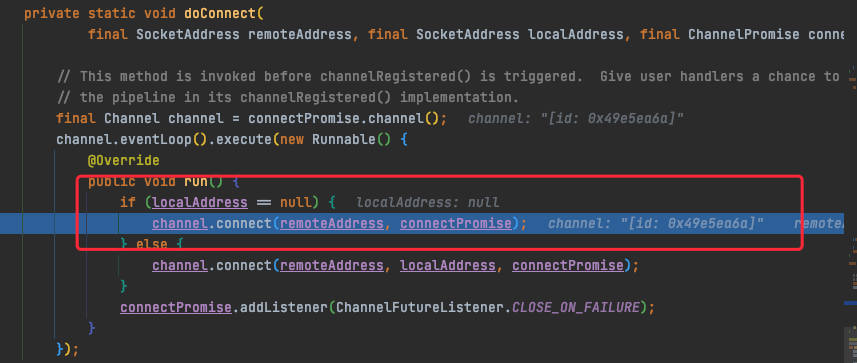
AbstractChannel
public ChannelFuture connect(SocketAddress remoteAddress, ChannelPromise promise) {
//TAG2.1.2.1 pipeline.connect
return pipeline.connect(remoteAddress, promise);
}
这里remoteAddress地址为18866端的服务。
//TAG2.1.2.1 pipeline.connect(pipeline上事件触发tail.connect)
DefaultChannelPipeline
@Override
public final ChannelFuture connect(SocketAddress remoteAddress, ChannelPromise promise) {
//outbound事件connect,因此从tail处执行
return tail.connect(remoteAddress, promise);
}
AbstractChannelHandlerContext
public ChannelFuture connect(SocketAddress remoteAddress, ChannelPromise promise) {
//localaddress为null
return connect(remoteAddress, null, promise);
}
@Override
public ChannelFuture connect(
final SocketAddress remoteAddress, final SocketAddress localAddress, final ChannelPromise promise) {
if (remoteAddress == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("remoteAddress");
}
if (isNotValidPromise(promise, false)) {
// cancelled
return promise;
}
//CONN1 findContextOutbound
//找到context中CONNECT处理的handlercontext
final AbstractChannelHandlerContext next = findContextOutbound(MASK_CONNECT);
EventExecutor executor = next.executor();
if (executor.inEventLoop()) {
//CONN2 next.invokeConnect
next.invokeConnect(remoteAddress, localAddress, promise);
} else {
safeExecute(executor, new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
next.invokeConnect(remoteAddress, localAddress, promise);
}
}, promise, null);
}
return promise;
}
CONN1 findContextOutbound
do-while,找到感兴趣的事件,这里实现pipeline上handlerContext链的遍历---略
CONN2 HandlerContext.invokeConnect
AbstractChannelHandlerContext
private void invokeConnect(SocketAddress remoteAddress, SocketAddress localAddress, ChannelPromise promise) {
//判断当前context是否执行handlerAdd操作--详细看server端,添加后,当前handler才可以处理时间
if (invokeHandler()) {
try {
//CONN2.1 handler().connect--(headcontext.connect)
((ChannelOutboundHandler) handler()).connect(this, remoteAddress, localAddress, promise);
} catch (Throwable t) {
notifyOutboundHandlerException(t, promise);
}
} else {
//重新调用//TAG2.1.2.1 pipeline.connect(pipeline上事件触发tail.connect),只传播事件,不处理
connect(remoteAddress, localAddress, promise);
}
}
逻辑:
1 invokeHandler:判断当前context是否执行过handleradd操作(如果执行过,可以处理事件)
1.1 如果执行过handleradd,处理事件---handler()).connect;
1.2 如果没有执行过handleradd,只传播事件,不处理。执行context.connect,然后再次执行CONN1 findContextOutbound,遍历下一个context。
CONN2.1 handler().connect--(headcontext.connect)
最终遍历到HeadContext,来执行client的实际connect。
DefaultChannelPipeline>>HeadContext
@Override
public void connect(
ChannelHandlerContext ctx,
SocketAddress remoteAddress, SocketAddress localAddress,
ChannelPromise promise) {
//连接
unsafe.connect(remoteAddress, localAddress, promise);
}
AbstractNioChannel>>AbstractNioUnsafe
@Override
public final void connect(
final SocketAddress remoteAddress, final SocketAddress localAddress, final ChannelPromise promise) {
if (!promise.setUncancellable() || !ensureOpen(promise)) {
return;
}
try {
if (connectPromise != null) {
// Already a connect in process.
throw new ConnectionPendingException();
}
boolean wasActive = isActive();
//CONN2.1.1 doConnect
//实际connect操作
if (doConnect(remoteAddress, localAddress)) {
fulfillConnectPromise(promise, wasActive);
}
//doconnect失败处理
else {
connectPromise = promise;
requestedRemoteAddress = remoteAddress;
// Schedule connect timeout.
int connectTimeoutMillis = config().getConnectTimeoutMillis();
if (connectTimeoutMillis > 0) {
connectTimeoutFuture = eventLoop().schedule(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
ChannelPromise connectPromise = AbstractNioChannel.this.connectPromise;
ConnectTimeoutException cause =
new ConnectTimeoutException("connection timed out: " + remoteAddress);
if (connectPromise != null && connectPromise.tryFailure(cause)) {
close(voidPromise());
}
}
}, connectTimeoutMillis, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
promise.addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture future) throws Exception {
if (future.isCancelled()) {
if (connectTimeoutFuture != null) {
connectTimeoutFuture.cancel(false);
}
connectPromise = null;
close(voidPromise());
}
}
});
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
promise.tryFailure(annotateConnectException(t, remoteAddress));
closeIfClosed();
}
}
CONN2.1.1 doConnect(如fail,设置channel就绪关注CONN,由eventloop.run处理)
NioSocketChannel
@Override
protected boolean doConnect(SocketAddress remoteAddress, SocketAddress localAddress) throws Exception {
if (localAddress != null) {
//绑定localaddress到channel
doBind0(localAddress);
}
boolean success = false;
try {
//连接server
boolean connected = SocketUtils.connect(javaChannel(), remoteAddress);
//如果连接失败,设置当前channel就绪,且关注的事件为CONNECT
if (!connected) {
selectionKey().interestOps(SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT);
}
success = true;
return connected;
} finally {
if (!success) {
doClose();
}
}
}
NioSocketChannel.doConnect逻辑:
1 如果存在localAddress,那么绑定端口到channel;
2 SocketUtils.connect执行连接操作:
2.1 如果连接失败,设置channel就绪,并设置关注事件为CONNECT。(channel就绪后,会在client端nioeventloop.run()的for(;;)的无限循环中,轮询处理新添加task(ST5 runAllTasks)、处理就绪channel(processSelectedKey)

SocketUtils
public static boolean connect(final SocketChannel socketChannel, final SocketAddress remoteAddress)
throws IOException {
try {
return AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedExceptionAction<Boolean>() {
@Override
public Boolean run() throws IOException {
//原生channel连接server
return socketChannel.connect(remoteAddress);
}
});
} catch (PrivilegedActionException e) {
throw (IOException) e.getCause();
}
}
socketChannel.connect(remoteAddress),执行client端实际连接server端的操作。




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号