六Spring事务源码分析--8创建事务代理
六Spring事务源码分析--8创建事务代理
6.5.2 创建事务代理
在spring初始化过程中,会进行相关的初始化配置,包括构建拦截器链。
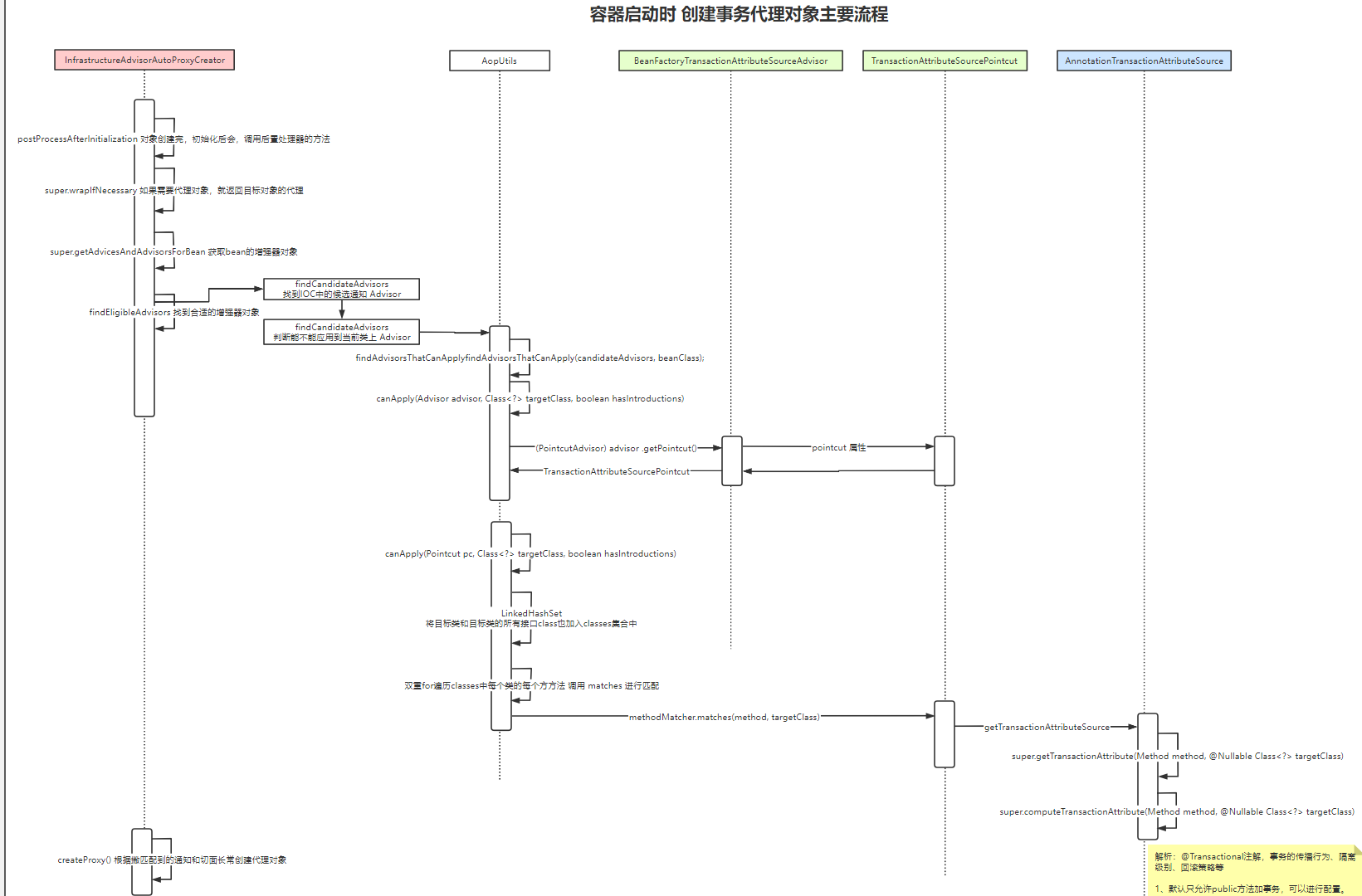
spring事务时基于AOP的around增强实现,因此初始化过程,同AOP有大致相同的流程。
Spring事务初始化流程:
TAG0.1 AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.initializeBean()
TAG0.2 applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization--调用所有后置处理器
TAG0.3 wrapIfNecessary
TAG1 getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean
TAG1.1 findEligibleAdvisors
//TAG1 findCandidateAdvisors
TAG1.1.1 findCandidateAdvisors---beanFactory中的Advisor---该方法中会获取beanFactory中的Advisor.class类型的所有类
//TAG1.2 isEligibleBean
TAG1.1.1.1 isEligibleBean---调用InfrastructureAdvisorAutoProxyCreator的isEligibleAdvisorBean方法
//TAG2 findAdvisorsThatCanApply---过滤出能作用于当前类的advisor,并且解析出transactionAttribute存入Source类
TAG1.1.2 findAdvisorsThatCanApply
TAG1.1.2.1 canApply(candidate, clazz)
TAG1.1.2.2 canApply(candidate, clazz, hasIntroductions)--调用advisor.pointcut的属性,分别进行classFilter、methodMatcher的匹配
//TAG3 createProxy
TAG2 createProxy
TAG2.1 new ProxyFactory
TAG2.2 evaluateProxyInterfaces--设置代理模式
TAG2.3 buildAdvisors--AOP核心(构建拦截器链)
TAG2.3.1 resolveInterceptorNames---@Aspect的advisor
TAG2.3.1.2 this.interceptorNames--??
TAG2.3.2 advisorAdapterRegistry.wrap
TAG2.4 proxyFactory.getProxy(classLoader)
TAG2.4.1 createAopProxy
TAG2.4.2 getProxy
TAG2.4.2.1 JdkDynamicAopProxy
TAG2.4.2.2 ObjenesisCglibAopProxy
在spring初始化执行到 TAG0.1 AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.initializeBean()时,会调用后置处理器执行初始化后置处理postProcessAfterInitialization。
InfrastructureAdvisorAutoProxyCreator执行后置处理流程:
TAG1 findCandidateAdvisors(AOP)
这个方法,获取beanFactory中所有的Advisor.class类型的所有类
然后,调用方法findCandidateAdvisors,找到自动代理需要用到的,所有候选的advisors。
AbstractAdvisorAutoProxyCreator
protected List<Advisor> findCandidateAdvisors() {
Assert.state(this.advisorRetrievalHelper != null, "No BeanFactoryAdvisorRetrievalHelper available");
return this.advisorRetrievalHelper.findAdvisorBeans();
}
BeanFactoryAdvisorRetrievalHelper
public List<Advisor> findAdvisorBeans() {
// Determine list of advisor bean names, if not cached already.
String[] advisorNames = this.cachedAdvisorBeanNames;
if (advisorNames == null) {
/**…………………………………………………………………………找到beanFactory中的Advisor类型的所有类、子类的名称(刨除FactoryBeans)…………………………………………………… */
advisorNames = BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(
this.beanFactory, Advisor.class, true, false);
this.cachedAdvisorBeanNames = advisorNames;
}
if (advisorNames.length == 0) {
return new ArrayList<>();
}
List<Advisor> advisors = new ArrayList<>();
for (String name : advisorNames) { //1
//判定给定名称的advisor是否是符合条件的---方法见下面
//TAG1.2 isEligibleBean
if (isEligibleBean(name)) { //2
//如果当前bean正在创建中,跳过正在创建过程中的advisor对象
if (this.beanFactory.isCurrentlyInCreation(name)) { //3
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Skipping currently created advisor '" + name + "'");
}
} //3
else { //3
try {
/**………………………………………………………………………………从beanFactory中找出所有的Advisor…………………………………………………………………… */
//从beanFactory中获取name的bean,作为advisor加入list中
advisors.add(this.beanFactory.getBean(name, Advisor.class));
}
catch (BeanCreationException ex) {
Throwable rootCause = ex.getMostSpecificCause();
if (rootCause instanceof BeanCurrentlyInCreationException) {
BeanCreationException bce = (BeanCreationException) rootCause;
String bceBeanName = bce.getBeanName();
if (bceBeanName != null && this.beanFactory.isCurrentlyInCreation(bceBeanName)) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Skipping advisor '" + name +
"' with dependency on currently created bean: " + ex.getMessage());
}
// Ignore: indicates a reference back to the bean we're trying to advise.
// We want to find advisors other than the currently created bean itself.
continue;
}
}
throw ex;
}
} //3
} //2
} //1
return advisors;
}
TAG1.2 isEligibleBean(AOP)
判断当前beanName是否是有资格的advisorBean。
AbstractAdvisorAutoProxyCreator
//内部类
private class BeanFactoryAdvisorRetrievalHelperAdapter extends BeanFactoryAdvisorRetrievalHelper {
public BeanFactoryAdvisorRetrievalHelperAdapter(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
super(beanFactory);
}
@Override
protected boolean isEligibleBean(String beanName) {
//这里会调用InfrastructureAdvisorAutoProxyCreator的isEligibleAdvisorBean方法
//TAG1.2.1 isEligibleAdvisorBean
return AbstractAdvisorAutoProxyCreator.this.isEligibleAdvisorBean(beanName);
}
}
TAG1.2.1 isEligibleAdvisorBean--InfrastructureAdvisorAutoProxyCreator
public class InfrastructureAdvisorAutoProxyCreator extends AbstractAdvisorAutoProxyCreator {
@Override
protected boolean isEligibleAdvisorBean(String beanName) {
return (this.beanFactory != null && this.beanFactory.containsBeanDefinition(beanName) &&
this.beanFactory.getBeanDefinition(beanName).getRole() == BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE);
}
InfrastructureAdvisorAutoProxyCreator提供isEligibleAdvisorBean(String beanName)方法判断当前beanname是否是符合条件的AdvisorBean,而只有ProxyTransactionManagementConfiguration配置类创建的advisor、advice和AnnotationTransactionAttributeSource为BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE。
因此该类逻辑是筛选出spring事务的advisor类。
TAG2 findAdvisorsThatCanApply(AOP)
从给定的candidateAdvisors过滤出可以应用到当前bean的advisor(需要分别通过pointcut的classfilter和methodmatcher匹配过滤)
AbstractAdvisorAutoProxyCreator
protected List<Advisor> findAdvisorsThatCanApply(
List<Advisor> candidateAdvisors, Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) {
//ThreadLocal<String>保存的当前正在被代理的bean(该ThreadLocal仅仅在Advisor匹配时,保存当前被代理bean)
ProxyCreationContext.setCurrentProxiedBeanName(beanName);
try {
//匹配当前beanclass对应的advisors
return AopUtils.findAdvisorsThatCanApply(candidateAdvisors, beanClass);
}
finally {
ProxyCreationContext.setCurrentProxiedBeanName(null);
}
}
AopUtils
public static List<Advisor> findAdvisorsThatCanApply(List<Advisor> candidateAdvisors, Class<?> clazz) {
if (candidateAdvisors.isEmpty()) {
return candidateAdvisors;
}
List<Advisor> eligibleAdvisors = new ArrayList<>();
for (Advisor candidate : candidateAdvisors) { //1
//TAG2.1 canApply(candidate, clazz)
//即是引介类型的advisor,且能canApply
if (candidate instanceof IntroductionAdvisor && canApply(candidate, clazz)) { //2
eligibleAdvisors.add(candidate);
} //2
} //1
//判断当前是否有引介类型的IntroductionAdvisor
boolean hasIntroductions = !eligibleAdvisors.isEmpty();
for (Advisor candidate : candidateAdvisors) { //1
if (candidate instanceof IntroductionAdvisor) {
// already processed 已经处理过
continue;
}
/** ……………………………………………………………………………………针对PointcutAdvisor类型的,如果canApply……………………………………………………………………………………………………*/
//TAG2.2 canApply(candidate, clazz, hasIntroductions)
if (canApply(candidate, clazz, hasIntroductions)) {
eligibleAdvisors.add(candidate);
}
} //1
return eligibleAdvisors;
}
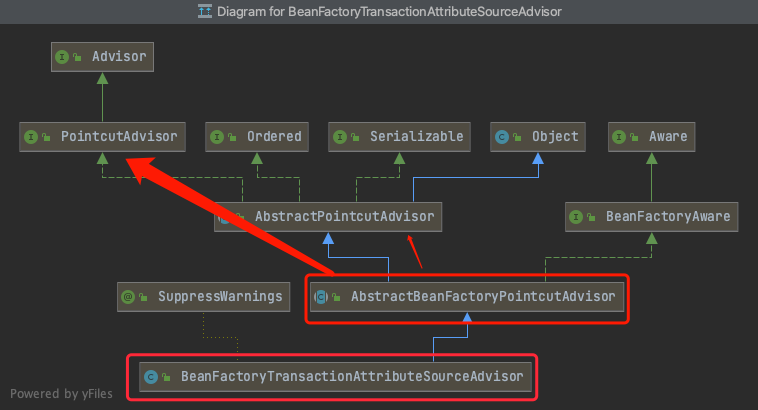
对于spring事务,advisor类是BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor。
TAG2.1 canApply(candidate, clazz)-(AOP)
public static boolean canApply(Advisor advisor, Class<?> targetClass) {
//第三个参数,hasIntroductions位false
return canApply(advisor, targetClass, false);
}
//第三个参数,表示当前target的advisor chain,是否包含引介类型的advisor
public static boolean canApply(Advisor advisor, Class<?> targetClass, boolean hasIntroductions) {
//advisor引介类型
if (advisor instanceof IntroductionAdvisor) {
//调用classfilter的match,匹配当前targetclass
return ((IntroductionAdvisor) advisor).getClassFilter().matches(targetClass);
}
//PointcutAdvisor类型
else if (advisor instanceof PointcutAdvisor) {
PointcutAdvisor pca = (PointcutAdvisor) advisor;
//调用封装方法匹配
return canApply(pca.getPointcut(), targetClass, hasIntroductions);
}
else {
// It doesn't have a pointcut so we assume it applies.
return true;
}
}
public static boolean canApply(Pointcut pc, Class<?> targetClass, boolean hasIntroductions) {
Assert.notNull(pc, "Pointcut must not be null");
//TAG2.1.1 pc.getClassFilter().matches
//首先,Pointcut.ClassFilter的matches(targetclass)方法,判断当前类是否能被pointcut拦截
if (!pc.getClassFilter().matches(targetClass)) {
//classfilter.match匹配失败
return false;
}
//获取Pointcut.methodMatcher
MethodMatcher methodMatcher = pc.getMethodMatcher();
if (methodMatcher == MethodMatcher.TRUE) {
// No need to iterate the methods if we're matching any method anyway...
return true;
}
IntroductionAwareMethodMatcher introductionAwareMethodMatcher = null;
if (methodMatcher instanceof IntroductionAwareMethodMatcher) {
introductionAwareMethodMatcher = (IntroductionAwareMethodMatcher) methodMatcher;
}
Set<Class<?>> classes = new LinkedHashSet<>();
if (!Proxy.isProxyClass(targetClass)) {
classes.add(ClassUtils.getUserClass(targetClass));
}
//获取targetclass的所有的接口,存入classes中
classes.addAll(ClassUtils.getAllInterfacesForClassAsSet(targetClass));
//遍历targetclass的所有父类(包括接口)
for (Class<?> clazz : classes) {
//获取每个父类中声明的方法
Method[] methods = ReflectionUtils.getAllDeclaredMethods(clazz);
//遍历method
for (Method method : methods) {
if (introductionAwareMethodMatcher != null ?
//引介类型的方法匹配
introductionAwareMethodMatcher.matches(method, targetClass, hasIntroductions) :
//TAG2.1.2 methodMatcher.matches
//pointcutadvisor内methodmatcher的匹配
methodMatcher.matches(method, targetClass)) {
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
canApply的执行逻辑:
1 从Pointcut.ClassFilter的matches(targetclass)方法,判断当前目标类,是否被切面拦截;
2 如果当前目标类被切面拦截,需要增强,然后判断targetclass的方法,是否被切面拦截
2.1 分别获取targetclass的所有classes,遍历classes,获取所有的声明的方法,并遍历;
2.2 对遍历的每个方法对象method,执行Pointcut.MethodMatcher的matches方法,进行匹配。
总的说:传入advisor.pointcut,只要能拦截住candidateClass的任意一个method,就返回true。
TAG2.1.0 BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor
public class BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor extends AbstractBeanFactoryPointcutAdvisor {
//持有事务属性源(负责解析事务属性--xml或@Transactional)
@Nullable
private TransactionAttributeSource transactionAttributeSource;
//pointcut为新建类TransactionAttributeSourcePointcut
private final TransactionAttributeSourcePointcut pointcut = new TransactionAttributeSourcePointcut() {
@Override
@Nullable
protected TransactionAttributeSource getTransactionAttributeSource() {
return transactionAttributeSource;
}
};
spring事务advisor的pointcut为TransactionAttributeSourcePointcut。
abstract class TransactionAttributeSourcePointcut extends StaticMethodMatcherPointcut implements Serializable {
//构造函数,自动设置过滤类为TransactionAttributeSourceClassFilter
protected TransactionAttributeSourcePointcut() {
setClassFilter(new TransactionAttributeSourceClassFilter());
}
//方法匹配
@Override
public boolean matches(Method method, Class<?> targetClass) {
TransactionAttributeSource tas = getTransactionAttributeSource();
return (tas == null || tas.getTransactionAttribute(method, targetClass) != null);
}
TAG2.1.1 pc.getClassFilter().matches
调用pointcut的类过滤器classfilter匹配:
TransactionAttributeSourcePointcut
//内部类
private class TransactionAttributeSourceClassFilter implements ClassFilter {
@Override
public boolean matches(Class<?> clazz) {
if (TransactionalProxy.class.isAssignableFrom(clazz) ||
TransactionManager.class.isAssignableFrom(clazz) ||
PersistenceExceptionTranslator.class.isAssignableFrom(clazz)) {
return false;
}
TransactionAttributeSource tas = getTransactionAttributeSource();
//TAG2.1.1.1 TransactionAttributeSource.isCandidateClass
return (tas == null || tas.isCandidateClass(clazz));
}
}
TAG2.1.1.1 TransactionAttributeSource.isCandidateClass
public interface TransactionAttributeSource {
//确定当前targetclass是否是TransactionAttributeSource元数据格式的事务属性的候选者
//false:表示该类在类或者方法级别没有事务属性。不会遍历给定类targetclass的方法来执行getTransactionAttribute
//true:表示该类在类或者方法级别有事务属性。要针对给定类targetclass的每个方法单独进行完全自省
default boolean isCandidateClass(Class<?> targetClass) {
return true;
}
由子类实现
public class AnnotationTransactionAttributeSource extends AbstractFallbackTransactionAttributeSource
implements Serializable {
//是否只支持public方法为事务方法
private final boolean publicMethodsOnly;
//存储解析器集合---这个解析器负责解析@Transactional注释,创建TransactionAttribute
private final Set<TransactionAnnotationParser> annotationParsers;
//
@Override
public boolean isCandidateClass(Class<?> targetClass) {
//遍历当前缓存的所有注解解析器,看是否有支持当前类targetclass解析的parser
for (TransactionAnnotationParser parser : this.annotationParsers) {
//TAG2.1.1.1.1 TransactionAnnotationParser.isCandidateClass
//用特定的注释解析器parser,判断当前class是否是parser可以解析成TransactionAttribute
if (parser.isCandidateClass(targetClass)) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
TAG2.1.1.1.1 TransactionAnnotationParser.isCandidateClass
public interface TransactionAnnotationParser {
/**
决定当前类,是否是注解模式@transactional的候选类。
如果返回false,不再遍历targetclass上的method对象以及执行parseTransactionAnnotation解析;
如果返回true,表示当前类被事务增强,需要执行parseTransactionAnnotation,遍历每个method,获取事务属性
*/
default boolean isCandidateClass(Class<?> targetClass) {
return true;
}
public class SpringTransactionAnnotationParser implements TransactionAnnotationParser, Serializable {
//判断当前targetClass,是否被@Transactional注解
@Override
public boolean isCandidateClass(Class<?> targetClass) {
//这个方法,判断targetclass是否承载指定注释@Transactional的候选类(注解在类型、方法或字段的级别)
return AnnotationUtils.isCandidateClass(targetClass, Transactional.class);
}
这个方法,主要是判断当前类,在类上、或者方法上是否被@Transactonal注解过,如果有,则为true
TAG2.1.2 methodMatcher.matches
对于ransactionAttributeSourcePointcut 实现 StaticMethodMatcherPointcut,因此本身就是个静态的methodMatcher。
abstract class TransactionAttributeSourcePointcut extends StaticMethodMatcherPointcut implements Serializable {
@Override
public boolean matches(Method method, Class<?> targetClass) {
TransactionAttributeSource tas = getTransactionAttributeSource();
//TAG2.1.2.1 TransactionAttributeSource.getTransactionAttribute
return (tas == null || tas.getTransactionAttribute(method, targetClass) != null);
}
TAG2.1.2.1 TransactionAttributeSource.getTransactionAttribute
public interface TransactionAttributeSource {
//返回给定方法的事务属性(如果方法非事务方法,返回null)
@Nullable
TransactionAttribute getTransactionAttribute(Method method, @Nullable Class<?> targetClass);
}
public abstract class AbstractFallbackTransactionAttributeSource
implements TransactionAttributeSource, EmbeddedValueResolverAware {
//MethodClassKey(method, targetClass)为key,TransactionAttribute为value
private final Map<Object, TransactionAttribute> attributeCache = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(1024);
//返回给定方法的事务属性(如果方法非事务方法,返回null)
@Override
@Nullable
public TransactionAttribute getTransactionAttribute(Method method, @Nullable Class<?> targetClass) {
if (method.getDeclaringClass() == Object.class) {
return null;
}
// 首先,看是否有缓存
Object cacheKey = getCacheKey(method, targetClass);
TransactionAttribute cached = this.attributeCache.get(cacheKey);
if (cached != null) {
if (cached == NULL_TRANSACTION_ATTRIBUTE) {
return null;
}
else {
return cached;
}
}
//如果没有缓存
else {
//TAG2.1.2.1.0 computeTransactionAttribute
// 解决对应targetclass上method的事务属性---见下面代码
TransactionAttribute txAttr = computeTransactionAttribute(method, targetClass);
// Put it in the cache.
if (txAttr == null) {
this.attributeCache.put(cacheKey, NULL_TRANSACTION_ATTRIBUTE);
}
else {
//事务拦截点方法的字符串信息
String methodIdentification = ClassUtils.getQualifiedMethodName(method, targetClass);
if (txAttr instanceof DefaultTransactionAttribute) {
DefaultTransactionAttribute dta = (DefaultTransactionAttribute) txAttr;
//设置事务属性的拦截点描述信息--method的字符串信息
dta.setDescriptor(methodIdentification);
dta.resolveAttributeStrings(this.embeddedValueResolver);
}
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Adding transactional method '" + methodIdentification + "' with attribute: " + txAttr);
}
//TAG2.1.2.1.1 txArr存入source缓存
/**………………………………………解析出的事务属性txAttr缓存入source的本地缓存Map<Object, TransactionAttribute> attributeCache…………………………*/
//存入当前缓存
this.attributeCache.put(cacheKey, txAttr);
}
return txAttr;
}
}
TAG2.1.2.1.0 computeTransactionAttribute
//解析事务属性的模板方法(通用方法框架,具体实现交给子类实现)
protected TransactionAttribute computeTransactionAttribute(Method method, @Nullable Class<?> targetClass) {
// Don't allow non-public methods, as configured.
if (allowPublicMethodsOnly() && !Modifier.isPublic(method.getModifiers())) {
return null;
}
//给定的method,可能是interface的方法对象,而我们需要获取目标对象targetclass内的方法对象specificMethod
Method specificMethod = AopUtils.getMostSpecificMethod(method, targetClass);
/**…………………………………………………………………………1 method位于targetclass--specificMethod………………………………………………………… */
// 首先,尝试从specificMethod中获取(就是从targetclass的方法上)
TransactionAttribute txAttr = findTransactionAttribute(specificMethod);
if (txAttr != null) {
return txAttr;
}
// 其次,从specificMethod的声明类上(就是targetclass上获取)
txAttr = findTransactionAttribute(specificMethod.getDeclaringClass());
if (txAttr != null && ClassUtils.isUserLevelMethod(method)) {
return txAttr;
}
/**……………………………………………………………………………………2 method位于targetclass父类上…………………………………………………………………………………… */
//如果specificMethod != method,表示method不在targetclass上,而在父类上
if (specificMethod != method) {
// 从method的原始方法上获取事务属性.
txAttr = findTransactionAttribute(method);
if (txAttr != null) {
return txAttr;
}
// 从method所在的原本的类上,获取事务属性
txAttr = findTransactionAttribute(method.getDeclaringClass());
if (txAttr != null && ClassUtils.isUserLevelMethod(method)) {
return txAttr;
}
}
return null;
}
上述定义了根据给定的method和targetclass获取事务属性的通用逻辑。其中,在解析事务属性方法中computeTransactionAttribute,根据传入的参数method和targetclass,method可能是targetclass内的方法,也可能是targetclass父类的方法。根据这两种情况,分别来解析属性。
1 method位于targetclass--specificMethod
2 method位于targetclass父类上
具体的解析方法findTransactionAttribute,交给子类去解决。
public class AnnotationTransactionAttributeSource extends AbstractFallbackTransactionAttributeSource
implements Serializable {
//是否只支持public方法为事务方法
private final boolean publicMethodsOnly;
//存储解析器集合---这个解析器负责解析@Transactional注释,创建TransactionAttribute
private final Set<TransactionAnnotationParser> annotationParsers;
@Override
@Nullable
protected TransactionAttribute findTransactionAttribute(Class<?> clazz) {
return determineTransactionAttribute(clazz);
}
@Override
@Nullable
protected TransactionAttribute findTransactionAttribute(Method method) {
return determineTransactionAttribute(method);
}
//将注解的元素(被注解的类或者方法对象),转换为TransactionAttribute对象
@Nullable
protected TransactionAttribute determineTransactionAttribute(AnnotatedElement element) {
for (TransactionAnnotationParser parser : this.annotationParsers) {
//TAG2.1.2.1.1 TransactionAnnotationParser.parseTransactionAnnotation
//将element解析为TransactionAttribute
TransactionAttribute attr = parser.parseTransactionAnnotation(element);
if (attr != null) {
return attr;
}
}
return null;
}
TAG2.1.2.1.1 TransactionAnnotationParser.parseTransactionAnnotation
public interface TransactionAnnotationParser {
/**基于当前parser的注解类型,解析给定class、method的信息构建为TransactionAttribure对象*/
@Nullable
TransactionAttribute parseTransactionAnnotation(AnnotatedElement element);
}
public class SpringTransactionAnnotationParser implements TransactionAnnotationParser, Serializable {
@Override
@Nullable
public TransactionAttribute parseTransactionAnnotation(AnnotatedElement element) {
//从注解@Transactional上,获取注解的属性的信息
AnnotationAttributes attributes = AnnotatedElementUtils.findMergedAnnotationAttributes(
element, Transactional.class, false, false);
if (attributes != null) {
return parseTransactionAnnotation(attributes);
}
else {
return null;
}
}
public TransactionAttribute parseTransactionAnnotation(Transactional ann) {
return parseTransactionAnnotation(AnnotationUtils.getAnnotationAttributes(ann, false, false));
}
//解析注解的属性信息,并构建和转换为事务属性TransactionAttribute
protected TransactionAttribute parseTransactionAnnotation(AnnotationAttributes attributes) {
//创建RuleBasedTransactionAttribute事务属性,并在后续根据注解属性,设置入事务属性
RuleBasedTransactionAttribute rbta = new RuleBasedTransactionAttribute();
Propagation propagation = attributes.getEnum("propagation");
rbta.setPropagationBehavior(propagation.value());
Isolation isolation = attributes.getEnum("isolation");
rbta.setIsolationLevel(isolation.value());
rbta.setTimeout(attributes.getNumber("timeout").intValue());
String timeoutString = attributes.getString("timeoutString");
Assert.isTrue(!StringUtils.hasText(timeoutString) || rbta.getTimeout() < 0,
"Specify 'timeout' or 'timeoutString', not both");
rbta.setTimeoutString(timeoutString);
rbta.setReadOnly(attributes.getBoolean("readOnly"));
rbta.setQualifier(attributes.getString("value"));
rbta.setLabels(Arrays.asList(attributes.getStringArray("label")));
List<RollbackRuleAttribute> rollbackRules = new ArrayList<>();
for (Class<?> rbRule : attributes.getClassArray("rollbackFor")) {
rollbackRules.add(new RollbackRuleAttribute(rbRule));
}
for (String rbRule : attributes.getStringArray("rollbackForClassName")) {
rollbackRules.add(new RollbackRuleAttribute(rbRule));
}
for (Class<?> rbRule : attributes.getClassArray("noRollbackFor")) {
rollbackRules.add(new NoRollbackRuleAttribute(rbRule));
}
for (String rbRule : attributes.getStringArray("noRollbackForClassName")) {
rollbackRules.add(new NoRollbackRuleAttribute(rbRule));
}
rbta.setRollbackRules(rollbackRules);
return rbta;
}
TAG2.1.2.1.1 txArr存入source缓存
解析出的事务属性txAttr缓存入source的本地缓存Map<Object, TransactionAttribute> attributeCache。
TAG3 createProxy
上述过程,完成对可作用于当前targetclass的advisor的过滤,并且把事务属性transactionAttribute解析,并缓存到transactionAttributeSource上的缓存'Map<Object, TransactionAttribute> attributeCache'。
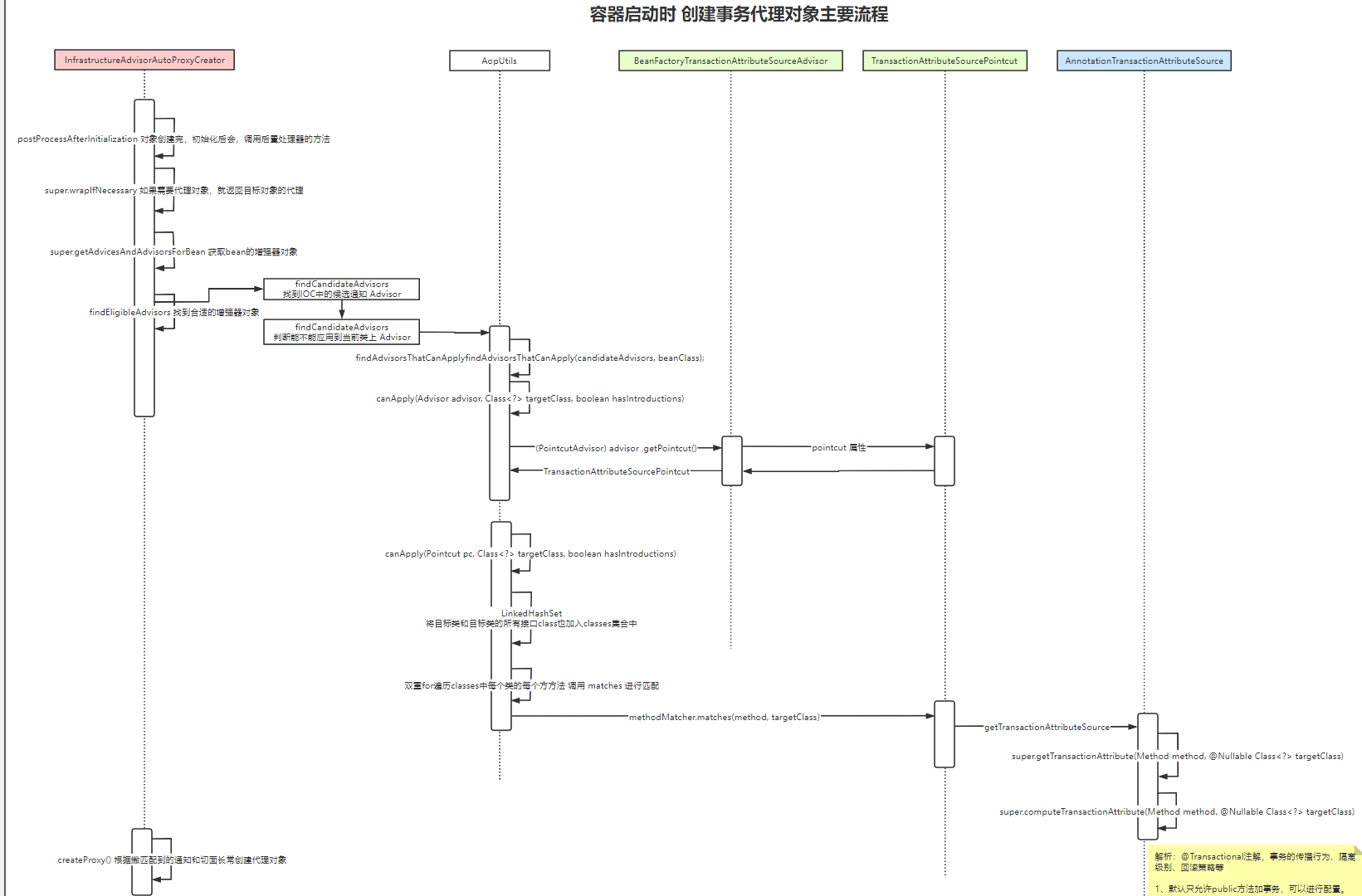
Spring事务初始化流程:
TAG0.1 AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.initializeBean()
TAG0.2 applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization--调用所有后置处理器
TAG0.3 wrapIfNecessary
TAG1 getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean
TAG1.1 findEligibleAdvisors
//TAG1 findCandidateAdvisors
TAG1.1.1 findCandidateAdvisors---beanFactory中的Advisor---该方法中会获取beanFactory中的Advisor.class类型的所有类
//TAG1.2 isEligibleBean
TAG1.1.1.1 isEligibleBean---调用InfrastructureAdvisorAutoProxyCreator的isEligibleAdvisorBean方法
//TAG2 findAdvisorsThatCanApply---过滤出能作用于当前类的advisor,并且解析出transactionAttribute存入Source类
TAG1.1.2 findAdvisorsThatCanApply
TAG1.1.2.1 canApply(candidate, clazz)
TAG1.1.2.2 canApply(candidate, clazz, hasIntroductions)--调用advisor.pointcut的属性,分别进行classFilter、methodMatcher的匹配
//TAG3 createProxy
TAG2 createProxy
TAG2.1 new ProxyFactory
TAG2.2 evaluateProxyInterfaces--设置代理模式
TAG2.3 buildAdvisors--AOP核心(构建拦截器链)
TAG2.3.1 resolveInterceptorNames---@Aspect的advisor
TAG2.3.1.2 this.interceptorNames--??
TAG2.3.2 advisorAdapterRegistry.wrap
TAG2.4 proxyFactory.getProxy(classLoader)
TAG2.4.1 createAopProxy
TAG2.4.2 getProxy
TAG2.4.2.1 JdkDynamicAopProxy
TAG2.4.2.2 ObjenesisCglibAopProxy
后续过程,根据对当前targetclass上匹配到的advisor,然后创建代理类
wrapIfNecessary
AbstractAutoProxyCreator{
//记录Clazz对象是否需要增强的map,object为bean.getClass,boolean表示是否需要增强
private final Map<Object, Boolean> advisedBeans = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(256);
protected Object wrapIfNecessary(Object bean, String beanName, Object cacheKey) {
if (StringUtils.hasLength(beanName) && this.targetSourcedBeans.contains(beanName)) {
return bean;
}
//如果不需要增强,直接返回bean
if (Boolean.FALSE.equals(this.advisedBeans.get(cacheKey))) {
return bean;
}
//如果bean为AopInfrastructureBean实现类,不AOP增强,不产生AOP代理类
if (isInfrastructureClass(bean.getClass()) || shouldSkip(bean.getClass(), beanName)) {
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE);
return bean;
}
//TAG1 getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean
// Create proxy if we have advice.
//从beanFactory中找出所有的Advisor.class类型的类,并过滤出可以作用于当前bean的advisor集合
Object[] specificInterceptors = getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(bean.getClass(), beanName, null);
//当指定的拦截器不为DO_NOT_PROXY(null)时
if (specificInterceptors != DO_NOT_PROXY) {
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.TRUE);
//TAG3 createProxy
//根据拦截器specificInterceptors、目标类SingletonTargetSource,创建代理对象(AOP代理对象)
//SingletonTargetSource(bean)封装被代理对象
Object proxy = createProxy(
bean.getClass(), beanName, specificInterceptors, new SingletonTargetSource(bean));
this.proxyTypes.put(cacheKey, proxy.getClass());
return proxy;
}
//不需要创建aop代理类
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE);
return bean;
}
使用specificInterceptors等信息创建targetclass的代理对象。这个过程和AOP中过程重复,不做代码跟踪了。




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号